A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
في الجسم الحي الأدنى الإسفار التصوير بالأشعة تحت الحمراء داخل الأوعية (NIRF) الجزيئية من البلاك التهابية ، وهو النهج المتعدد الوسائط إلى التصوير من تصلب الشرايين
In This Article
Summary
نحن التفصيل جديد بالقرب من الأشعة تحت الحمراء مضان (NIRF) قسطرة للتصوير 2 الأبعاد الجزيئية داخل الأوعية البيولوجيا البلاك في الجسم الحي. يمكن للقسطرة NIRF تصور العمليات البيولوجية الرئيسية مثل الالتهاب من خلال الإبلاغ عن وجود لوحة ، متعطشا fluorochromes NIR activatable وهادفة. القسطرة يستخدم السريرية الهندسية ومتطلبات السلطة ، واستهداف للتطبيق في الشرايين التاجية البشرية. الدراسة البحثية التالية توضح استراتيجية التصوير المتعدد الوسائط التي تستخدم رواية في الجسم الحي قسطرة NIRF داخل الأوعية الدموية لتحديد الصورة واللوحة التهاب نشط في proteolytically atheromata الأرنب الملتهبة.
Abstract
The vascular response to injury is a well-orchestrated inflammatory response triggered by the accumulation of macrophages within the vessel wall leading to an accumulation of lipid-laden intra-luminal plaque, smooth muscle cell proliferation and progressive narrowing of the vessel lumen. The formation of such vulnerable plaques prone to rupture underlies the majority of cases of acute myocardial infarction. The complex molecular and cellular inflammatory cascade is orchestrated by the recruitment of T lymphocytes and macrophages and their paracrine effects on endothelial and smooth muscle cells.1
Molecular imaging in atherosclerosis has evolved into an important clinical and research tool that allows in vivo visualization of inflammation and other biological processes. Several recent examples demonstrate the ability to detect high-risk plaques in patients, and assess the effects of pharmacotherapeutics in atherosclerosis.4 While a number of molecular imaging approaches (in particular MRI and PET) can image biological aspects of large vessels such as the carotid arteries, scant options exist for imaging of coronary arteries.2 The advent of high-resolution optical imaging strategies, in particular near-infrared fluorescence (NIRF), coupled with activatable fluorescent probes, have enhanced sensitivity and led to the development of new intravascular strategies to improve biological imaging of human coronary atherosclerosis.
Near infrared fluorescence (NIRF) molecular imaging utilizes excitation light with a defined band width (650-900 nm) as a source of photons that, when delivered to an optical contrast agent or fluorescent probe, emits fluorescence in the NIR window that can be detected using an appropriate emission filter and a high sensitivity charge-coupled camera. As opposed to visible light, NIR light penetrates deeply into tissue, is markedly less attenuated by endogenous photon absorbers such as hemoglobin, lipid and water, and enables high target-to-background ratios due to reduced autofluorescence in the NIR window. Imaging within the NIR 'window' can substantially improve the potential for in vivo imaging.2,5
Inflammatory cysteine proteases have been well studied using activatable NIRF probes10, and play important roles in atherogenesis. Via degradation of the extracellular matrix, cysteine proteases contribute importantly to the progression and complications of atherosclerosis8. In particular, the cysteine protease, cathepsin B, is highly expressed and colocalizes with macrophages in experimental murine, rabbit, and human atheromata.3,6,7 In addition, cathepsin B activity in plaques can be sensed in vivo utilizing a previously described 1-D intravascular near-infrared fluorescence technology6, in conjunction with an injectable nanosensor agent that consists of a poly-lysine polymer backbone derivatized with multiple NIR fluorochromes (VM110/Prosense750, ex/em 750/780nm, VisEn Medical, Woburn, MA) that results in strong intramolecular quenching at baseline.10 Following targeted enzymatic cleavage by cysteine proteases such as cathepsin B (known to colocalize with plaque macrophages), the fluorochromes separate, resulting in substantial amplification of the NIRF signal. Intravascular detection of NIR fluorescence signal by the utilized novel 2D intravascular NIRF catheter now enables high-resolution, geometrically accurate in vivo detection of cathepsin B activity in inflamed plaque.
In vivo molecular imaging of atherosclerosis using catheter-based 2D NIRF imaging, as opposed to a prior 1-D spectroscopic approach,6 is a novel and promising tool that utilizes augmented protease activity in macrophage-rich plaque to detect vascular inflammation.11,12 The following research protocol describes the use of an intravascular 2-dimensional NIRF catheter to image and characterize plaque structure utilizing key aspects of plaque biology. It is a translatable platform that when integrated with existing clinical imaging technologies including angiography and intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), offers a unique and novel integrated multimodal molecular imaging technique that distinguishes inflammatory atheromata, and allows detection of intravascular NIRF signals in human-sized coronary arteries.
Protocol
في نموذج حيواني فيفو : الجيل من تصلب الشرايين التجريبى الأبهرية الحرقفية
1) الأساس تصوير الأوعية الدموية والتعرية بالون
- قبل الحصول على خط الأساس تصوير الأوعية وتعرية البالون ، ويتم تغذية الأرانب البيضاء في نيوزيلندا ارتفاع الكولسترول (1 ٪) نظام غذائي لمدة 1 أسبوع. ويستخدم هذا الحيوان لأهميتها متعدية ك 1) في الأوعية aorto - iliacs في الارانب هي نفس العيار الشرايين التاجية البشرية (2.5 - 3.5mm) و 2) وhyperlipidemic ، البالون الاصابة بتصلب الشرايين ملتهبة نموذج يولد تحمل خلايا التهابية مماثلة (الضامة ) والجزيئات (cathepsins) كما في تصلب الشرايين الإنسان.
- التالية تغذية الكولسترول ، وهذا الحيوان هو تخدير مع البروبوفول والكيتامين. يتم إجراء واحد بوصة الرقبة خط الوسط شق بطني به باستخدام حجم 15 مشرط النصل. باستخدام تقنيات تشريح حادة ، تتعرض عضلات أسفل اللفافة على الجانب الأيمن من القصبة الهوائية. يتم فصل العضلات sternocephalicus اليسار على طول تقاطع في النسيج الضام ، ويتعرض حق الشريان السباتي المشترك. يتم فصل الشريان من العصب المبهم. توضع حلقات خياطة القريبة والبعيدة على الشريان للسماح للتراجع وانسداد. ويرصد 1 إلى 2mm ومشطوف بضع الشريان من خلالها 5 الفرنسية (القطر الخارجي 1.67mm) يتم إدراج غمد الأوعية الدموية والهيبارين (1000μ/mL ، ~ 150units/kg) يدار داخل arterially عبر غمد.
- ثم يتم حقن صبغة تباين (Ultravist) (1 إلى 2mL) على مدى فترة 2 ثانية للحصول على صورة وعائية السيطرة على الأورطى البعيدة على حد سواء والشرايين الحرقفية.
- ثم يصاب في الشرايين الحرقفي الفخذي والشريان الأورطي عن طريق تعرية البطانية. باستخدام أساليب الكشف الفلوري القياسية ، يتم وضع استئصال الصمة فوغارتي 3Fr قسطرة الشريان الحرقفي الفخذي في القاصي وتضخمت مع 0،3-0،5 سم على النقيض من (50 ٪ contrast/50 المالحة ٪) أو الهواء. ثم يتم سحب القسطرة قريب في حالته مضخمة على مسافة طول الحرقفي الأيمن والشريان الأورطي وحشي حتى يحصل على الخروج من الشريان الكلوي الأيسر. بعد تعرية البالون ، يتم تكرار القسطرة للوثيقة سالكية السفينة. بعد القسطرة ، تتم إزالة كافة القسطرة والأغماد وligated والداني الحق الشريان السباتي المشتركة ، وتتم خياطة العضلات واللفافة مع خياطة 4 / 0 للامتصاص ، وشق الجلد مغلقة مع خياطة غير قابل للامتصاص 4 / 0.
- ثم يسمح للحيوان لاسترداد مع ادارة جرعة من المضادات الحيوية واحد (Cephazolin ، 0.5 غرام IM). ألم الأدوية بما في ذلك 0.01 IM البوبرينورفين ملغ / كلغ (مرتين يوميا حسب الحاجة). ثم واصل والحيوانات على الكوليسترول بنسبة 1 ٪ لمدة 4 تعرية بعد بالون أسابيع. في الأسبوع 5 ، وانتقلت الحيوانات لحمية الكولسترول بنسبة 0.3 ٪.
متكامل متعدد الوسائط تصوير Atheromata أرنب
2) بطاقات المواد الملتهبة لوحة النشطة proteolytically باستخدام حقن nanosensor ؛ تصوير الأوعية الدموية والموجات فوق الصوتية داخل الأوعية (IVUS) ، والتصوير في فيفو NIRF داخل الأوعية عصيدة من أرنب
- ثمانية أسابيع بعد اصابة في بالون و 24 ساعة قبل التصوير ، ويتم حقن في الوريد مع الأرنب Prosense/VM110 nmol / كغ 500 (PerkinElmer) عن طريق الوريد الأذن.
- أربع وعشرين ساعة بعد الحقن ، وتخدير الحيوانات والتي تم الحصول عليها عن طريق الوصول الشرايين السباتية الشريان اليسار الموحد (انظر الخطوة 1.2). يدار داخل الشرايين الهيبارين (150 وحدة / كلغ). يتم الحصول على خط الأساس القسطرة على النحو الوارد أعلاه.
- يتم تحميل لقسطرة IVUS على سريري سلك الشريان التاجي 0.014 بوصة وقادرة على إدراجها في غمد. التوجيه باستخدام جهاز أشعة ، يتم وضع الطرف ظليل للأشعة السلك بشكل أقصى في الشريان الحرقفي الأيمن. متقدمة ثم IVUS القسطرة في الشريان الحرقفي القريبة باستخدام معيار تقنية المونوريل السريرية.
- وبدأ التراجع 100 ملم ، وتسجل الصور. يتم الحصول على إعادة الإعمار الطولي للسفينة ويتم تحديد لوحة اللمعية.
- يتم تحميل القسطرة NIRF 11،12 على السلك 0.014 بوصة (المونوريل النظام) ، ويتم إدخال قسطرة بعناية في غمد ورئيس التصوير المتمركزة في الشريان الحرقفي بشكل أقصى اليمين.
- يتم تنفيذ الانسحاب الآلي متعددة (1 ملم / ثانية انسحاب طولية ، و 30 طلقة في الدقيقة الواحدة) ، وأشار إشارات مضان داخل مناطق من تصلب الشرايين. وتسجل الصور وتحقيق مزيد من المعالجة مع زيادة مناسبة والنوافذ على أساس مجموعة من الإشارات.
3) القتل الرحيم والعزل من الأنسجة السابقين aorto - الحرقفي فيفو
- ويتم إنجاز مع 1cc القتل الرحيم وكيل القتل الرحيم (حل 390mg الصوديوم الصوديوم والفينيتوئين بنتوباربيتال 50mg) ، في الوريد ، حقنة واحدة.
- هو perfused شجرة الشرايين طبيعية مع المالحة 0.9 ٪ حتى الوريد الأجوف السفلي واضح من الدم. يتم تحديد تصلب الشريان الأورطي والشرايين الحرقفية وخالية من تشريح الأنسجة المحيطة بها. بالإضافة إلى ذلك ، صغيرة 2 × 2 سم من القطع لىكما يتم الحصول على النسخة والكلى والطحال والقلب.
- ويمكن أن يتم خارج الحي NIRF التصوير مع قسطرة الأوعية الدموية التصوير NIRF في هذه المرحلة. غير ممدود السفينة والقسطرة NIRF إعادة إدراجها في الشريان الأورطي القريبة حتى يتم وضعه على رأس التصوير في الشريان الحرقفي الأيمن أو التشعب. يتم تنفيذ الانسحاب الآلي متعددة على النحو الوارد أعلاه (انظر 2.6).
4) خارج الحي الإسفار الانعكاس التصوير (جمعة) من الشريان الأورطي والشرايين الحرقفية تشريح
- تشريح الأنسجة وضعت في 10-20 سم مكعب من المياه المالحة العادية ونقلها لتحاليل جمعة (صورة محطة 4000MM كوداك برو ، يعد أول الصحة ، وشركة).
- وممدود الأوعية الحرقفية الشريان الأورطي ، وأطوال الوقت الحقيقي التقريبي ويتم الحصول على الصور في موجات متعددة [الضوء الأبيض ، قناة الفلورية الخضراء (495 نانومتر السابقين ، م 515 نانومتر) ، Cy5 (سابقا 565 نانومتر ، م 670 نانومتر) وCy7 (السابقين 650 نانومتر ، م ن م 760)] قنوات. وتستخدم سلسلة من المرات التعرض لكل طول موجي (0.1 30sec) ويتم تصدير الصور المكتسبة في DICOM أو 16 بت ملفات TIFF unscaled لمزيد من التحليلات. والضوابط الإيجابية والسلبية ، وأجهزة تصوير (الكبد والطحال والكليتين والقلب) في قنوات مماثلة ، ومرات التعرض.
- ويلاحظ زيادة مجالات إشارة في القناة القريبة من الأشعة تحت الحمراء (780nm +) في الشرايين تصلب الشرايين.
5) تضمين الأنسجة لتحليلها وSectioning المناعى
- مناطق طبيعية (غير المصابين الأنسجة ، أي الشريان الحرقفي الأيسر) ويتم تحديد مجالات البلاك وحلقات صغيرة هي جزء لا يتجزأ من النسيج 50-10 ملم في وسائل الإعلام (درجة الحرارة المثلى للقطع) أكتوبر يتم تخزين في كتل -80 C حتى sectioning.
- يتم تنفيذ تقنيات قياسية للتحاليل وsectioning المناعى. وصمة عار الهيماتوكسيلين يوزين ، يتم تنفيذ الرام 11 و تلطيخ كاتيبسين باء.
تحليلات والتكامل المتعدد الوسائط صور (تصوير الأوعية الدموية ، IVUS ، NIRF وجمعة)
6) تجهيز الصور وNIRF جمعة
- DICOM الملفات التي تحتوي على بيانات من التصوير NIRF وجمعة (الذي اتخذ في الأشعة تحت الحمراء القريبة قناة نانومتر 780) يتم معالجتها باستخدام MATLAB الانسحاب والبرمجيات Osirix ، على التوالي. ويتحقق النوافذ المناسبة لعرض مجموعة كاملة من كثافة الإشارة. ويتم تصدير الصور على هيئة ملفات TIFF النهائي.
- يتم استيراد الملفات إلى مستوى برامج لتجهيز الصور (يمكن استخدامها الرئيسي). يتم محاذاة الصور على أساس نقاط مرجعية (أي فقرات على عائية ، التشعب الحرقفي ، والشريان الكلوي). ويتم تحديد مجالات السفينة العادية والبلاك.
- وتتبع يدويا المناطق ذات الاهتمام (ROI) (للالأنسجة الطبيعية ومجالات البلاك) ويتم الحصول على كثافات يعني إشارة باستخدام Osirix وMATLAB ، على التوالي لكل من جمعة والصور NIRF. لتوجيه تتبع المناسبة ، يتم استخدام صورة طولية IVUS السفينة ويتم التعرف عليها بسهولة تحديد الوعاء الطبيعي والبلاك.
- يتم احتساب الهدف إلى الخلفية (تي بي آر) نسب للمناطق البلاك.
ممثل النتائج :
عند الانتهاء من بروتوكول أعلاه ، يمكننا تحديد وتوصيف مجالات النشاط في زيادة كاتيبسين البروتيني وحة التهابات داخل الشريان الأورطي والأوعية الحرقفية. حقن لnanosensor activatable (Prosense/VM110) يتيح لنا التعرف على لوحة proteolytically نشطة. تظهر هذه زاهية أو إشارة مناطق شديدة عندما التقط به جمعة في قناة تحت الحمراء بالقرب من (750 نانومتر). وربط الانسحاب NIRF مع كثافة إشارة بنسبة جمعة والتحالفات مع IVUS التي تسمح بتسجيل الإشارات NIRF التشريحية. حسبت لوحة TBR تم الحصول عليها من جمعة وNIRF مماثلة (انظر الشكل 3 : يعني NIRF TBR 4.2 ، يعني جمعة TBR 2.9). التحليل المناعى لوحة مشرقة يؤكد وجود مكثف للRAM - 11 B كاتيبسين والنشاط في مجالات وحة (لا تظهر البيانات).
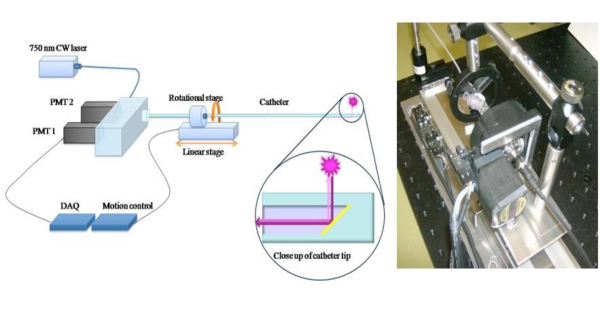
الشكل 1. التخطيطي لقسطرة NIRF 2D تمديد السريرية المحتملة لنهج 1D الاستشعار NIRF 6 ، ونحن بناء رواية 2 - D - NIRF القسطرة لتصوير الأوعية الدموية. 11،12 القسطرة ومبنية خصيصا يتكون من الألياف البصرية (125 قطرها ميكرون إيواء أنابيب البولي ايثيلين في : 2.9F) الذي ينير باستخدام الليزر 750 نانومتر مصدر الإثارة. ينبعث ضوء الليزر بزاوية 90 درجة بالنسبة لمحور الألياف. ويستخدم النظام اثنين من المحركات الآلية (التناوب ومتعدية) لتمكين يصاحب التصوير ب 360 درجة وانسحاب الطولي للحصول على التصوير 2D صحيحا. الصور المستخدمة بإذن من المرجع 11.
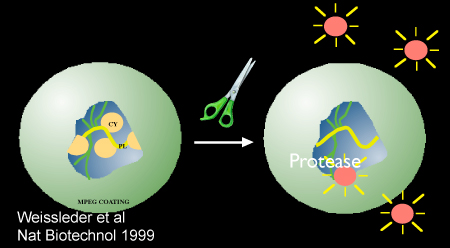
الشكل 2. التخطيطي يتظاهرون البروتيني بوساطة تفعيل nanosensor ، Prosense/VM110. الصورة المستخدمة بإذن من المرجع 10.
الشكل 3. في الجسم الحي والبلاك TBRs السابقين فيفو (الهدف ، إلى نسب الخلفية)
Discussion
ملتهبة لويحات ذات المخاطر العالية أو الضعيفة هي المسؤولة المحتمل لغالبية احتشاء عضلة القلب. تحديد مثل هذه اللوحات قبل ظهور الأعراض السريرية له آثار مهمة على حد سواء في توقع نتائج وتوجيه العلاج الطبي. التاجية التقليدية طرائق التصوير الشرياني مثل الأشعة السينية تصوي?...
Disclosures
FAJ -- مستشار السابقة ، VisEn الطبية ؛ الأتعاب ، وبوسطن العلمية
Acknowledgements
وقدم الدعم لهذا العمل من قبل المعاهد الوطنية للصحة منح # 108229 R01 HL ، جمعية القلب الأميركية للتنمية منح العلماء # 0830352N ، هوارد هيوز الطبي شهادة معهد جائزة التنمية والمشاريع بروادفيف ، وبرنامج الجماعة الأوروبية الإطاري السابع (FP7/2007-2013 بموجب منحة # 235689 الاتفاق) ، ويليام MGH زمالة شراير.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Prosense 750 | Visen Medical | VM110 | 500 nmol/kg IV injection |
| Heparin Sodium | APP Pharmaceuticals | 401586D | |
| Cephazolin | NovaPlus | 46015683 | |
| Lidocaine HCL 2% | Hospira Inc. | NDC 0409-4277-01 | |
| Buprenorphine | Bedford Laboratories | NDC 55390-100-10 | |
| Ketamine | Hospira Inc. | NDC 0409-2051-05 | |
| High Cholesterol Diet 1% | Research Diets | C30293 | |
| HIgh Cholesterol Diet 0.3% | Research Diets | C30255 |
References
- Andersson, J., Libby, P. Adaptive immunity and atherosclerosis. Clin Immunol. 134, 33-46 (2010).
- Calfon, M. A., Vinegoni, C. Intravascular near-infrared fluorescence molecular imaging of atherosclerosis: toward coronary arterial visualization of biologically high-risk plaques. Journal of Biomedical Optics. 15, 011107-011107 (2010).
- Chen, J., Tung, C. -. H. In Vivo Imaging of Proteolytic Activity in Atherosclerosis. Circulation. 105, 2766-2771 (2002).
- Jaffer, F. A., Libby, P. Molecular Imaging of Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation. 116, 1052-1061 (2007).
- Jaffer, F. A., Libby, P. Optical and Multimodality Molecular Imaging: Insights Into Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29, 1017-1024 (2009).
- Jaffer, F. A., Vinegoni, C. Real-Time Catheter Molecular Sensing of Inflammation in Proteolytically Active Atherosclerosis. Circulation. 118, 1802-1809 (2008).
- Kim, D. -. E., Kim, J. -. Y. Protease Imaging of Human Atheromata Captures Molecular Information of Atherosclerosis, Complementing Anatomic Imaging. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 30, 449-456 (2010).
- Libby, P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 420, 868-874 (2002).
- Naghavi, M., Libby, P. From Vulnerable Plaque to Vulnerable Patient: A Call for New Definitions and Risk Assessment Strategies: Part I. Circulation. 108, 1664-1672 (2003).
- Weissleder, R., Tung, C. -. H. In vivo imaging of tumors with protease-activated near-infrared fluorescent probes. Nat Biotech. 17, 375-375 (1999).
- Razansky, R. N., Rosenthal, A. Near-infrared fluorescence catheter system for two-dimensional intravascular imaging in vivo. Optics Express. 18, 11372-11381 (2010).
- Jaffer, F. A., Calfon, M. A. Two-Dimensional Intravascular Near-Infrared Fluorescence Molecular Imaging of Inflammation in Atherosclerosis and Stent-Induced Vascular Injury. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 57, 2516-2526 (2011).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved