需要订阅 JoVE 才能查看此. 登录或开始免费试用。
Method Article
跨体内迟发型变态反应检测方法的抗原特异性调节
摘要
我们描述了一个有价值的诊断方法,有可能被用来决定撤出未经移植排斥反应的风险升高,移植后的免疫抑制。该法采用迟发型超敏反应的原则,并提供准确的评估,既供者特异性效应和调节免疫应答安装收件人。
摘要
体内 T细胞依赖的免疫应答,宿主的免疫系统在最近的过去经历了一个外来抗原(Ag)的表现形式是一种快速的迟发型超敏反应(DTH)。 DTH反应通常分为致敏阶段,指的是最初的抗原经验,挑战阶段,通常如下致敏后数天。往往被视为无能的证据缺乏的迟发型超敏反应皮肤测试证明召回银。传统的DTH试验已有效地用于诊断许多微生物感染。
尽管共享相似的免疫功能,如淋巴细胞浸润,水肿,组织坏死,直接DTH直喷导致致敏供者抗原与移植物丢失的可能性,因为不是一个可行的诊断技术在移植患者。为了避免这个问题,哼哼开发一个鼠标“体内反”DTH检测1,2。此测试本质上是一个传输的DTH试验,人外周血单核细胞(PBMCs)和特异性抗原皮下注射到羽片或一个天真的的鼠标和DTH像肿胀足垫3 18-24小时后测量。人类抗原提呈细胞如巨噬细胞或区议会高度血管小鼠组织中的T细胞的抗原提呈触发炎症级联反应,并吸引了小鼠的免疫细胞,导致肿胀反应。该反应是抗原特异性的,并需要事先致敏抗原。一个积极的捐助者反应在电视DTH检测反映的DTH反应,移植的病人已经发展向移植同种抗原的亲炎症免疫处置。
在此检测中最重要的特征是,它也可以被用于检测调节性T细胞,从而引起旁观者抑制。一个旁观者抑制供体抗原的存在是的DTH召回响应特征与接受同种异体移植受者2,4-14。同种异体反应性和监管的TV-DTH移植术后监测可能确定谁可以受益于减少免疫抑制的患者没有拒绝或肾功能恶化的风险升高的一个子集。
一个有前途的领域是电视DTH检测监测自身免疫15,16和17在肿瘤免疫学的应用。
研究方案
1。淋巴细胞的制备
- 收集血液进入ACD(酸性柠檬酸葡萄糖)管。
- 按照标准方法,用淋巴细胞分离液从新鲜人外周血的PBMC隔离。
- 外周血单个核细胞用PBS三次洗净,去除污染的血小板。血小板被发现干扰反式被检体内的DTH试验。最大允许PBMC制备血小板污染是≤1×10 7 /注塑。
- 如果有明显的红血细胞污染,执行第一次洗涤后,使用ACK裂解缓冲液裂解红细胞。将ACK缓冲液,用PBS洗涤2次。
2。制备特异性抗原
- 使用上面所示的过程从供体外周血的PBMC隔离。
- 于PBS中的浓度为120x10 6细胞/ ml(4×10 6个细胞/ 30微升)重悬供体的PBMC。
- 加入1μM的苯甲基磺酰氟的混合物,以防止蛋白质退化。
- 超声处理的细胞悬浮液,用2毫米的探头超声波破碎仪使用7个1秒的脉冲。 (注意:保持材料的冷,并避免过多的气泡,如果出现泡沫,让细胞悬液,坐冰2-3分钟)。
- 验证使用血球细胞> 90%的中断。
- 在14,000 rpm离心该混合物在4℃下冷藏20分钟的离心。
- 上清转移到一个新的2.0毫升安全锁管,并确定蛋白浓度。
3。细胞制备的注射
- 为每次注射等分7×10 6到2.0毫升安全锁管PBMC。
- 离心一分钟6000转离心,去除上清。
- 带或不带抗原在PBS中重悬细胞。调整进样体积为35微升,用PBS。下面的计划是用于注射:
阴性对照:外周血单个核细胞+ PBS
阳性对照:PBMC + TT / DT(25亩克/注射液)
实验抗原特异性反应:外周血单个核细胞+测试AG(4-8微克/注塑)
实验抗原特异性调节:PBMC +测试的Ag + TT / DT
4。测量前,注射,测量后
- 异氟醚麻醉CB17 SCID小鼠。使用弹簧式卡尺测量后脚掌厚度。认厚度足垫的中心,一个边缘上行走的脚的焊垫接触,以提供一个基准,以保持测量部位一致。脚垫的厚度记录时,压力表读数稳定。
- 慢慢细胞悬液注入皮下的小鼠使用半CC胰岛素注射器,28号针头的脚垫。针指向脚趾,斜面朝上,执行注入。 (注意:确保没有任何泄漏)。
- 注射后18-24小时,麻醉鼠标垫肿胀与异氟醚和重复测量。
- Subtr行事每个足垫的厚度,在注射之前,从后喷射值取得足垫的膨胀值,在10 -4英寸为单位表示的数据。计算的抗原特异性的净肿胀:控制垫肿胀(外周血单个核细胞+的PBS)中减去从足垫肿胀的处理获得的值(外周血单个核细胞+供体同种抗原,TT / DT,或供体同种抗原+ TT / DT)。阳性对照响应召回抗原TT / DT≥25×10 -4英寸以上背景响应PBS所需的测试被认为是有效的。
- 确定供者抗原的存在下进行比较,使用下列公式计算各喷射净肿胀抑制召回响应:
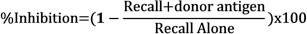
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
结果
1。评估肾移植供体抗原特异性反应使用电视DTH检测
为了测试我们的捐助者反应在肾移植术后细胞免疫注射PBMC从这些患者与供者抗原单独或与召回抗原破伤风类毒素(TT)。仅与TT作为阳性对照细胞注射。我们观察到三个主要模式的迟发型超敏反应移植受者( 图1)。所有患者反应强烈,召回AG(TT)。患者#62所示的调节柄,其特征在于由一个弱响应于供体抗原和一?...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
讨论
跨体内的DTH检测是一种新型的诊断测试与评估细胞介导的反应,移植,癌症和自身免疫性病人中的一个潜在的临床应用。它是有价值的,因为它不仅是有用的监测召回T效应反应,而且还可以检测调节性T反应。一种可靠的方法来检测人类DTH调控可能预测免疫抑制戒断安全的患者中单药治疗或耐受性试验的候选人是谁。
DTH电视的间接通路的MHC allorecognition的检测是非常敏感?...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
披露声明
这份手稿的作者有没有利益冲突的披露。
致谢
笔者想承认的贡献AM万巴斯柯克我们的理解的发展DTH反应,移植受者的监管。这项工作是支持的NIH拨款PO1AI084853和R01AI066219-06,由欧盟资助的一个研究。
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
材料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| ACD tube for blood collection | BD | 02-684-26 | |
| Lymphocyte Separation Medium | Cellgro | 25-072-CV | |
| Dulbecco's Phosphate-Buffered Saline | Cellgro | 21-031-CM | Without calcium & magnesium |
| ACK Lysis Buffer | BioWhittaker | 10-548E | |
| TT/DT or EBV | Sanofi Pasteur Inc./ Meridian Life Science, Inc. | TT/DT 25 μg/injection EBV 8 μg/injection | |
| Protease inhibitor PMSF | Sigma-Aldrich | 78830 | |
| Eosine for cell count | Sigma-Aldrich | E-6003 | |
| Alloantigen | Purified HLA antigens, synthetic allopeptides can be used instead of donor cell-free lysates | ||
| 50 ml sterile centrifuge tubes | Fisher Scientific | 06-443-18 | |
| 10 ml pipettes and pipettor | BD Falcon | 13-675-20 | |
| 2 ml safe-lock tubes | Costar | 3213 | |
| 1000 μl, 100 μl , 10 μl pipettes with sterile tips | |||
| Hemocytometer | Fisher | 02-671-10 | |
| Full size centrifuge and microfuge | Beckman Coulter/Eppendorf | ||
| 1/2cc or 1cc insulin syringes | Becton Dickinson | 14-826-79 | 28 gauge |
| Vibracell sonicator | Divtech Equipment Co. Sonocs Materials Inc | 2 mm probe | |
| Dial thickness gauge | Mitutoyo, Japan | ||
| SCID mice | Harlan | ||
| Isoflurane | Piramal Healthcare | Inhalant anesthesia |
参考文献
- Carrodeguas, L., et al. Trans vivo analysis of human delayed-type hypersensitivity reactivity. Hum. Immunol. 60, 640-651 (1999).
- VanBuskirk, A. M., et al. Human allograft acceptance is associated with immune regulation. J. Clin. Invest. 106, 145-155 (2000).
- Burlingham, W. J., Jankowska-Gan, E. Mouse strain and injection site are crucial for detecting linked suppression in transplant recipients by trans-vivo DTH assay. Am. J. Transplant. 7, 466-470 (2007).
- Burlingham, W. J., et al. Loss of tolerance to a maternal kidney transplant is selective for HLA class II: Evidence from trans-vivo DTH and alloantibody analysis. Human Immunology. 61, 1395-1402 (2000).
- Geissler, F., et al. Human liver allograft acceptance and the 'tolerance assay': In vitro anti-donor T cell assays show hyporeactivity to donor cells but, unlike DTH, fail to detect linked suppression. Transplantation. 72, 571-580 (2001).
- Jankowska-Gan, E., et al. Human liver allograft acceptance and the 'tolerance assay'. II. donor HLA-A, -B but not DR antigens are able to trigger regulation of DTH. Hum. Immunol. 63, 862(2002).
- Minor H Antigen HA-1-specific Regulator and Effector CD8+ T Cells, and HA-1 Microchimerism, in Allograft Tolerance. J. Exp. Med. Cai, J., et al. 199, 1017-1023 (2004).
- Rodriguez, D. S., et al. Immune regulation and graft survival in kidney transplant recipients are both enhanced by human leukocyte antigen matching. Am. J. Transplant. 4, 537-543 (2004).
- Xu, Q., et al. Human CD4+CD25low adaptive T regulatory cells suppress delayed-type hypersensitivity during transplant tolerance. J. Immunol. 178, 3983-3995 (2007).
- Derks, R. A., Jankowska-Gan, E., Xu, Q., Burlingham, W. J. Dendritic cell type determines the mechanism of bystander suppression by adaptive T regulatory cells specific for the minor antigen HA-1. J. Immunol. 179, 3443-3451 (2007).
- Jankowska-Gan, E., et al. Successful reduction of immunosuppression in older renal transplant recipients who exhibit donor-specific regulation. Transplantation. 88, 533-541 (2009).
- Jankowska-Gan, E., et al. Pretransplant immune regulation predicts allograft outcome: bidirectional regulation correlates with excellent renal transplant function in living-related donor-recipient pairs. Transplantation. 93, 283-290 (2012).
- Knechtle, S. J., et al. Early and limited use of tacrolimus to avoid rejection in an alemtuzumab and sirolimus regimen for kidney transplantation: clinical results and immune monitoring. Am. J. Transplant. 9, 1087-1098 (2009).
- Haynes, L. D., et al. Donor-specific indirect pathway analysis reveals a B-cell-independent signature which reflects outcomes in kidney transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 12, 640-648 (2012).
- Burlingham, W. J., et al. IL-17-dependent cellular immunity to collagen type V predisposes to obliterative bronchiolitis in human lung transplants. J. Clin. Invest. 117, 3498-3506 (2007).
- Bobadilla, J. L., et al. TH-17, Monokines, Collagen Type V, and Primary Graft Dysfunction in Lung Transplantation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 177 (6), (2008).
- Olson, B. M., et al. Human prostate tumor antigen-specific CD8+ regulatory T cells are inhibited by CTLA-4 or IL-35 blockade. J. Immunol. 189, 5590-5601 (2012).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
转载和许可
请求许可使用此 JoVE 文章的文本或图形
请求许可探索更多文章
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。