Method Article
染色质监管机构和各国的全基因组快照
摘要
如何染色质监管机构和染色质状态的问题会影响体内的基因组是关键,我们的细胞命运决定是如何在早期发育中的胚胎制成的认识。芯片起,最流行 的做法在全球范围内,在这里介绍的爪蟾胚胎研究染色质的功能。
摘要
The recruitment of chromatin regulators and the assignment of chromatin states to specific genomic loci are pivotal to cell fate decisions and tissue and organ formation during development. Determining the locations and levels of such chromatin features in vivo will provide valuable information about the spatio-temporal regulation of genomic elements, and will support aspirations to mimic embryonic tissue development in vitro. The most commonly used method for genome-wide and high-resolution profiling is chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by next-generation sequencing (ChIP-Seq). This protocol outlines how yolk-rich embryos such as those of the frog Xenopus can be processed for ChIP-Seq experiments, and it offers simple command lines for post-sequencing analysis. Because of the high efficiency with which the protocol extracts nuclei from formaldehyde-fixed tissue, the method allows easy upscaling to obtain enough ChIP material for genome-wide profiling. Our protocol has been used successfully to map various DNA-binding proteins such as transcription factors, signaling mediators, components of the transcription machinery, chromatin modifiers and post-translational histone modifications, and for this to be done at various stages of embryogenesis. Lastly, this protocol should be widely applicable to other model and non-model organisms as more and more genome assemblies become available.
引言
The first attempts to characterize protein-DNA interactions in vivo were reported about 30 years ago in an effort to understand RNA polymerase-mediated gene transcription in bacteria and in the fruit fly1,2. Since then, the use of immunoprecipitation to enrich distinct chromatin features (ChIP) has been widely adopted to capture binding events and chromatin states with high efficiency3. Subsequently, with the emergence of powerful microarray technologies, this method led to the characterization of genome-wide chromatin landscapes4. More recently, chromatin profiling has become even more comprehensive and high-resolution, because millions of co-immunoprecipitated DNA templates can now be sequenced in parallel and mapped to the genome (ChIP-Seq)5. As increasing numbers of genome assemblies are available, ChIP-Seq is an attractive approach to learn more about the genome regulation that underlies biological processes.
Here we provide a protocol to perform ChIP-Seq on yolk-rich embryos such as those of the frog Xenopus. Drafts of the genomes of both widely used Xenopus species—X. tropicalis and X. laevis—have now been released by the International Xenopus Genome Consortium6. The embryos of Xenopus species share many desirable features that facilitate and allow the interpretation of genome-wide chromatin studies, including the production of large numbers of high-quality embryos, the large size of the embryos themselves, and their external development. In addition, the embryos are amenable to classic and novel manipulations like cell lineage tracing, whole-mount in situ hybridisation, RNA overexpression, and TALEN/CRISPR-mediated knockout technology.
The following protocol builds on the work of Lee et al., Blythe et al. and Gentsch et al.7-9. Briefly, Xenopus embryos are formaldehyde-fixed at the developmental stage of interest to covalently bind (cross-link) proteins to their associated genomic DNA. After nuclear extraction, cross-linked chromatin is fragmented to focus subsequent sequencing on specific genomic binding or modification sites, and to minimize the contributions of flanking DNA sequences. Subsequently, the chromatin fragments are immunoprecipitated with a ChIP-grade antibody to enrich those containing the protein of interest. The co-immunoprecipitated DNA is stripped from the protein and purified before creating an indexed (paired-end) library for next-generation sequencing (NGS). At the end, simple command lines are offered for the post-sequencing analysis of ChIP-Seq data.
研究方案
注:所有非洲爪蟾的工作完全符合英国动物(科学程序)作为由MRC国家医学研究所的执行法案1986
1.准备
- 估计所需的ChIP实验(见讨论)胚胎的数目。
- 准备被存储在RT以下解决方案:无EDTA,pH值500毫升10×Marc的改性林格(MMR)调节至7.5,并通过高压灭菌(1 M氯化钠,的20mM氯化钾,20mM的氯化钙 ,10mM的硫酸镁 ,的50mM HEPES pH为7.5)10,1毫升的SDS洗脱缓冲液(50mM的Tris-HCl pH 8.0的,1毫摩尔EDTA,1%SDS)和1毫升5×DNA上样缓冲液(0.2%橙G,30%甘油,60毫摩尔EDTA pH8.0)中。
- 准备被存储在4℃以下的溶液:加入50ml HEG缓冲液(50mM HEPES-KOH pH为7.5,1mM EDTA中pH为8.0,20%甘油)500毫升提取缓冲液的E1液(50mM HEPES-KOH pH值7.5,150毫米氯化钠,1 mM的EDTA。 10%甘油,0.5%IGEPAL CA-630,0.25%的Triton X-100)中,E 2(10毫摩尔Tris - 盐酸pH值8.0,150mM的氯化钠,1mM EDTA中,0.5毫摩尔EGTA),和E3(10毫摩尔Tris盐酸pH为8.0,150 mM氯化钠,1mM的EDTA,1%IGEPAL CA-630,0.25%的Na-脱氧胆酸盐,0.1%SDS),500毫升的RIPA缓冲液(50mM HEPES-KOH pH值7.5,500mM的氯化锂,1mM EDTA中,1%IGEPAL CA-630,0.7%的Na-脱氧胆酸)和50ml的TEN缓冲液(10mM的Tris-HCl pH 8.0的,1毫摩尔EDTA,150 mM氯化钠)。
- 得分和剪辑一个15毫升的锥形聚苯乙烯管在7毫升大关。使用该管含有核提取物进行超声。
- 对于后测序分析,使用多核Unix风格的操作系统的计算机至少有8 GB的RAM和500 GB的可用磁盘空间。安装以下软件,本地大部分都用在命令行:FastQC,Illumina公司CASAVA-1.8质量过滤器,蝴蝶结11,SAMtools 12,HOMER 13,MACS2 14,IGV 15,16,Cluster3 17,Java的TreeView控件,BLAST + 18,和b2g4pipe 19。检查编译器和第三方软件的安装说明和要求。
- 建立一个蝴蝶结指数短期调整NGS读取到非洲爪蟾的基因组。一个例子是在这里显示为X.热带基因组V7.1(2011年11月),可以下载从Xenbase FTP服务器(/酒吧/基因组学/ JGI)一个FASTA文件(genome.fa)。移动FASTA文件,以蝴蝶结的指数子目录。
- (提示字符后的位置>)使用下面的命令行来生成xenTro7索引文件:
>领结建造/path/to/bowtie/index/genome.fa xenTro7
>出口BOWTIE_INDEXES = /路径/要/领结/指数/
- (提示字符后的位置>)使用下面的命令行来生成xenTro7索引文件:
- 请从UCSC基因组浏览器或镜像站点的NIMR服务器,可通过工具/表浏览器最新版本的基因组(genomes.nimr.mrc.ac.uk)上的基因注释文件(GTF)。使用基因组FASTA文件和GTF文件自定义ħOMER的爪蟾 ( 如X.热带基因组V7.1, - 名xenTro7)。
- 另外,使用预建的HOMER包一些旧版本的爪蟾基因组。
> loadGenome.pl -name xenTro7 -org空-fasta /path/to/genome.fa -gtf路径/到/ genes.gtf
- 另外,使用预建的HOMER包一些旧版本的爪蟾基因组。
- 通过上传索引FASTA文件(genome.fa与在同一文件夹genome.fa.fai文件)和注释文件(genes.gtf)创建基因组轨道(.genome文件 )的基因组浏览器IGV。创建基因组支架指数(genome.fa.fai)为非洲爪蟾基因组如下:
> samtools faidx /path/to/genome.fa - 利用BLAST +通过基因本体论(GO)术语的几种模式生物(人,小鼠,斑马鱼,果蝇和酵母)到非洲爪蟾的基因如下:
- 下载所有的编码序列(CDS)从UCSC基因组浏览器的工具,通过一个单一的FASTA文件(cds.fa)/表浏览器和更新BLAST +非冗余蛋白(NR)的预先格式化的BLAST数据库:
> update_blastdb.pl NR - 搜索人(txid9606),鼠标(txid10090),斑马鱼(txid7955),果蝇(txid7227)和酵母(txid4932)从通过其先进的搜索功能的网站NCBI蛋白质上(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih。 GOV /蛋白质/高级) ,并发送所得的GI(序列标识符)的列表(sequence.gi.txt)到计算机。
- 通过执行BLASTx比有一定的期望(E)值截止(这里10 -20)指派非洲爪蟾的基因从GI列表中选择最相似的蛋白质。确保输出格式为XML(-outfmt 5退房手续blastx_results.xml)。利用节省时间的螺纹(-num_threads),其与现有的计算机核的数量相关的。
> BLASTX -db /路径/要/ NR -gilist /path/to/sequence.gi.txt -query /路/吨O / cds.fa -evalue 1E-20
-outfmt 5退房手续/path/to/blastx_results.xml -num_threads [#线程] - 用文本编辑器打开文件夹b2g4pipe的b2gPipe.properties文件,并更新数据库属性Dbacces.dbname = b2go_sep13和Dbacces.dbhost = publicdb.blast2go.com。运行b2g4pipe从安装文件夹中。
> Java的Xmx1000m -cp *:EXT / *:es.blast2go.prog.B2GAnnotPipe -in /path/to/blastx_results.xml
退房手续结果/ xenTro7 -prop b2gPipe.properties -v -annot
注:此程序提取物GO条款每个爆击,并将其分配给相应的爪蟾基因(xenTro7.annot)。最新的数据库设置可以在工具上找到/常规设置/的Blast2GO Java Web Start应用的数据访问设置(见9.11.1)。
- 下载所有的编码序列(CDS)从UCSC基因组浏览器的工具,通过一个单一的FASTA文件(cds.fa)/表浏览器和更新BLAST +非冗余蛋白(NR)的预先格式化的BLAST数据库:
2.染色质交联
- 施肥爪蟾卵,去果冻和文化EMbryos根据标准方法20。
- 传送dejellied胚胎(最大2500 非洲爪蟾或10,000 十热带 )在感兴趣的发育阶段到8毫升玻璃样品小瓶帽并与0.01X MMR洗一次短暂它们。
- 固定用1%甲醛的胚胎在0.01X MMR( 例如 ,添加225微升36.5-38%甲醛8毫升0.01X,MMR)为15至40分钟,在RT(见讨论用于固定的时间和所需的胚胎数每个芯片实验)。
注:甲醛是腐蚀性和高毒性。这是危险的情况下眼睛和皮肤接触,消化不良,和吸入。添加甲醛的小瓶时,使用通风橱。 - 通过简单地洗胚胎三次冷0.01X MMR停止固定。不要让安莉芳操作系统做出与液面接触,因为表面张力,使它们破裂。
- 分装胚胎成在冰上2ml微量管与最多每管250的胚胎,它占据大约250微升( 十热带 )或孵化前600微升( 非洲爪蟾 )的体积。
- 吸走高达0.01X MMR越好。如果您立即继续第3跳过下面的步骤。
- 平衡在250微升冷HEG缓冲胚胎。一旦胚定居到管的底部除去尽可能多的液体尽可能和扣冷冻在液氮中。储存在-80℃。
3.染色质提取
注:交联的染色质的从爪蟾胚胎的以下提取工作最有效地用在步骤2.3和50至80 X所示的固定倍热带或25至40 X.蟾每毫升提取缓冲液E1,E2和E3的胚胎。每次萃取步骤被重复,从而需要缓冲器的计算量的两倍。对于升频,使用多个2毫升microcentri华夫格管或50毫升离心管中。染色质提取期间保持在冰上的样品和缓冲液。
- 补充缓冲器的E1,E2和E3用1mM DTT和蛋白酶抑制剂片剂的适当的卷。如果执行芯片与磷酸特异性抗体,进一步补充缓冲器用5mM NaF和2mM的钠3 VO 4。
- 通过上下吹打均质固定胚胎的E1。离心机匀浆在冷冻离心机(4℃),在1000×g离心2分钟(或5分钟的情况下使用50ml试管中)。吸出上清液,并附着在壁的任何脂质。
- 在E1悬浮颗粒。保持样品在冰上10分钟。离心机和丢弃上清液如在步骤3.2。
- 在E2悬浮颗粒。离心机和丢弃上清液如在步骤3.2。
- 重复步骤3.4,但保持样品冰上,然后离心10分钟。
- 在E3悬浮颗粒。保持样品在冰上至少10分钟。离心机并丢弃苏pernatants如在步骤3.2。
注:在此阶段,再悬浮应该成为相当透明。在E3的阴离子洗涤剂通过使大部分剩余的蛋黄血小板可溶的提取物交联的核。 - 交联核的重悬和游泳池的颗粒(通常棕色从不溶颜料颗粒)在1毫升的E3的总体积。稀释样品E3为2或3毫升如果它出现非常粘稠并且难以吸移管。保持在冰上或在4℃下继续在相同或第二天步骤4。卡扣冷冻在液氮中,并储存在-80℃以备后用。
4.染色质碎片
注:超声处理既用于溶解和剪切交联的染色质。下面是运行Misonix超声仪3000配备了1/16英寸锥形微尖和声音外壳参数。如果使用其他sonicators,按照制造商的建议进行剪切交联的染色质或使用6至12瓦为4至8分钟,共。
- 从步骤3.7转移核样品放入一个定制管超声处理(步骤1.4)。保持超声处理过程中冷却样品通过具有连接到一个800毫升塑料烧杯经由短温度计钳充满冰水的管中。
- 放置在一个实验室千斤顶的烧杯中。调节千斤顶使超声波仪微尖浸没在样品中大约三分之二的体积深度和中心不接触管壁。
- 超声处理的样品共7分,每中断30秒,1分钟的暂停。将电源设置为1.0。启动超声处理,并立即增加功率设置(通常为2至4),以达到9至12中的读取W.立即暂停,如果样品开始发泡。重新定位管,然后重新启动时,泡沫完全消失。
- 转移剪切染色质成预冷的1.5 ml离心管和旋转全速(> 15,000 XG)中5分钟,在4℃。
- 将上清液转移到预冷的1.5 ml离心管中。收集50微升的上清液(含理想的约40万或更多核染色质)的可视化染色质碎片(第5)的程度。使用上清液的其余部分为芯片(第6节)。
- 店内样品在4℃至一天。卡扣冻结的样品作为等分(每码片的实验1)在液氮中用于长期贮存在-80℃。
5.成像染色质碎片
- 加入50微升的SDS洗脱缓冲液,4μl的5M NaCl和1微升蛋白酶K(20微克/微升),以50微升的上清液从步骤4.6。
- 孵育6至15小时(O / N)在杂交烘箱中于65℃。
- 使用市售PCR纯化试剂盒纯化DNA。如果需要的话,可以使用的乙酸钠(pH 5.2)的3M如制造商推荐,以调节pH。洗脱的DNA两次用11微升洗脱缓冲液(10mM的Tris-HCl pH值8.5)。
- 跑沿着一个100bp的整个样品和通过电泳1.4%琼脂糖凝胶1 kb的DNA梯前添加0.4微升RNA酶A(20微克/微升)和5微升5×加载的DNA缓冲液中。为了达到最佳效果,防污凝胶电泳后安全核酸染色溶液。
6.染色质免疫沉淀
注:在这一部分中,使用低保留1.5ml微量管中,至少有1每管指示缓冲液在4℃下洗磁珠5分钟。之前从珠除去缓冲,离开管中的磁性架中进行20至30秒,每一次,或直到溶液澄清。
- 转移10到30μl来自步骤4.6的上清液(剪切染色质)到一个新的试管将在后面用作输入样品,其对应于用于芯片总染色质的约1%。商店在4°C,直到沉淀的样品准备用于逆转交联。
- 剩余的染色质转移到新管中。对于芯片的qPCR实验需要的抗体控制,染色质分布等体积两个管。
- 加在芯片级抗体(或相应的抗体对照)染色质。作为一个粗略的指导,使用约1微克每百万细胞表达所关注的表位的抗体。
- 以更准确地估计每块芯片的实验所需要的抗体的量,运行在同一芯片与不同量的抗体( 例如 ,0.25微克,1微克和2.5微克),并通过芯片的qPCR比较收率在阴性和阳性对照的位点(见第10条)。作为抗体的控制,使用相同的同种型和宿主动物物种的抗体的正常血清。
- 孵育在肩(10转)O / N在4℃。
- 与E3 5分钟一洗一次抗体 - 兼容磁珠足够量吨4℃。检查 制造商的规范为珠的抗体结合能力(通常为5〜20微升磁珠结合1微克IgG抗体)。
- 加入洗涤过的珠与抗体预温育的染色质。进一步孵育在旋转器上(10转)4小时。
- 洗涤珠四次(芯片的qPCR)或10倍(芯片起)与预冷的RIPA缓冲液中,然后一旦用预冷的TEN缓冲液中。
- 只有进行这一步,如果执行芯片起实验。
- 重悬在50μl每管TEN缓冲液洗涤珠。池从单个芯片实验中所有的珠子被他们转移到一个新的管。使用磁性齿条和冷藏(4℃)离心分离在1000×g离心收集珠子在管的底部。丢弃尽可能多的液体尽可能不中断的珠粒料。
- 带材的ChIP重新悬浮珠子在50至100微升的SDS洗脱缓冲液和vort材料落珠连续exing它们与恒温(1000 rpm)离心15分钟,在65℃下。该离心机全速(> 15000 XG)30秒后。上清液(芯片洗脱液)转移到新的管中。
- 重复上一步,并结合该芯片洗脱液。
7.染色质反向交联和DNA纯化
- 添加足够的SDS洗脱缓冲液,以输入采样(步骤6.1),以达到在芯片样品,这是100至200微升(步骤6.10)的容积。补充既芯片和输入样本与1/20体积的5M NaCl洗涤。在65℃孵育样品6至15小时(O / N)在杂交烘箱。
- 加入1体积的TE缓冲液和RNA酶A在200微克/毫升。孵育1小时,在37℃。
- 添加蛋白酶K,在200微克/毫升。孵育2至4小时,在55℃。
- 通过苯酚纯化DNA:氯仿:异戊醇提取,随后用乙醇沉淀如先前所概述9。对于芯片起,加32微升洗脱缓冲液(10mM的Tris-HCl,pH值8.5),以溶解DNA沉淀。留在冰上的样品30分钟,以确保所述DNA被完全溶解。
注:商用PCR纯化试剂盒具有较低的DNA的恢复,但都比较方便,并可以用于芯片的qPCR样品。 - 对于芯片起,使用荧光为基础的方法测定的1微升芯片和输入的DNA的浓度。遵循制造商的说明,并确保的DNA的浓度落在荧光计的可靠的检测范围内。
8.芯片起文库构建和验证
注:目前的方法进行DNA文库制备允许建造高复杂库NGS从1到2纳克。在一些复杂性为代价,库可以从少至50皮克的DNA(见表具体材料/设备的)来制成。使用的DNA的相同量为芯片和输入库。简单地说,到麦Ë索引(配对末端)的ChIP-SEQ库,芯片和输入的DNA必须是最终修复,连接到特殊适配器(见表具体材料/设备),大小选择和PCR扩增。
- 按照制造商的指引,使芯片序列库。看到进一步的建议进行讨论。
- 洗脱每个库在12微升的洗脱缓冲液,并确定1微升每个芯片和输入库中使用荧光浓度。预计5至25纳克/微升的浓度。考虑减少PCR循环(少于18个周期)的数量,如果浓度高于25纳克/微升。
注:准确的定量是关键,以达到最佳效果NGS。用浓度低至1毫微克/微升后18个PCR循环库可以进行测序,但常常是较低的复杂度。 - 使用1微升库,确定片段大小分布,来检查任何适配器二聚体污染(带约120个基点)为c嘻哈基于毛细管电泳。 1:1的珠到样品比重复的固相可逆固定化纯化(而不是1.6:1)如果该库包含适配器二聚体。
- 在确认阳性和阴性对照位点(见第10部分)进行定量PCR检查是否类似DNA富集趋势前,文库制备后观察。提交质量控制批准库测序。
9.后测序分析和数据可视化
注:目前,NGS往往是进行内部或商业测序设施(见一些NGS准则的讨论)。标准输出是单个或多个gzip压缩FASTQ文件(* .fastq.gz)储存数以百万计的测序读数。通常情况下,多路读取已经分离根据自己的索引,每个读包含每个BAS序列标识符和质量控制分数(PHRED + 33 Illumina公司1.8+)Ë电话。这种方法在这里是唯一一个出很多方法如何分析NGS数据。鼓励读者以检查是否有下面的命令行需要改变,因为这领域正在快速推进和更新定期发生。
- 串联gzip压缩FASTQ文件,并检查使用FastQC脚本测序数据的质量。执行此,大部分为芯片和输入序列数据如下命令 (显示芯片的例子)从终端:
>猫/path/to/*.fastq.gz> ChIP.fastq.gz
> fastqc ChIP.fastq.gz
注:从高复杂度的ChIP-SEQ库成功测序原始数据应该通过绝大多数测试。故障主要源于穷人测序运行和实验文物,如偏PCR扩增或适配器污染。一定程度的重叠(冗余)预计为冗余读取能代表真正的 DNA富集 21。然而,人们可以购买限制读取标签-的5'端或读取-一个每碱基对,以消除任何多余的读出,而不会影响峰的检测灵敏度(步骤9.4)21。 - 预处理测序数据删除适配器污染(homerTools修剪-3 <接头序列>)允许一个错配(-mis 1)。使用第一个20个碱基的(索引)适配器(5'至3')邻近的后结扎感兴趣的DNA片段(示出为适配器的具体材料/设备的表中列出)。
>的gzip -cd ChIP.fastq.gz | fastq_illumina_filter -VN> ChIP.fastq
> homerTools修剪-3 GATCGGAAGAGCACACGTCT -mis 1 -min 36 ChIP.fastq
注:过滤去除读取(-N)时,才需要在默认情况下通过Illumina的1.8生成的FASTQ文件。省略fastq_illumina_filter命令( 即 '| fastq_illumina_filter -VN")如果比1.8的旧版本生成的序列标识符。 - 对齐处理前读出使用的蝴蝶结的参照基因组(xenTro7)。只保留唯一映射读取(-m 1)使用在第28基地和SAM格式的每最大70.报告对准读取所有不匹配的总PHRED + 33的质量得分默认设置,即最大两个错配(-S) 。增加兆字节每个线程(--chunkmbs)的数量,如果该块内存耗尽:
>领结-m 1 -S -p [#线程] --chunkmbs [如200] xenTro7 ChIP.fastq.trimmed> ChIP.sam
注:蝴蝶结预计PHRED + 33质量评分默认。包括选项- phred64-quals如果与PHRED + 64的质量得分由Illumina公司超过1.8生成的FASTQ文件。 - 使用两个HOMER命令变换对齐(SAM)文件转换成一个大人物文件(.bw):
> makeTagDirectory芯片/微单-tbp 1 ChIP.sam
> makeUCSCfile芯片/-bigWig /路径/要/ genome.fa.fai -fsize 1E20范数1E7 -o ChIP.bw
注:转换需要的参考基因组(步骤1.8)的支架指数(genome.fa.fai)。在此配置文件限制为每个碱基对(-tbp 1)和归一个标签10万读( 范数1E7)。大人物是首选格式动态可视化与基因组浏览器质型材等IGV(步骤9.12)中的一个。 - 确定的标记在基因组标志的分布(-d芯片/)(例如 ,+/- 10kb的25 bp的垃圾箱,-si 泽20000 -hist 25)如转录起始(TSS,例如此处示出)和终止( TTS)的网站。运行的HOMER perl脚本annotatePeaks.pl与非洲爪蟾注释xenTro7(步骤1.7):
> annotatePeaks.pl TSS xenTro7 -size 20000 -hist 25 -d芯片/> ChIP_tagDensity.tss - 发现芯片之间的DNA富集显著峰(-t ChIP.sam)和输入(-c Input.sam)中的X.热带基因组使用MACS2为200基点(--bw = 200)为模型建立1%FDR截止(-q 0.01)和DNA片段(超声后)。旗--broad添加到该命令行,如果希望感兴趣的染色质功能的广泛分布,如组蛋白标记或RNA聚合酶。
> macs2 callpeak -t ChIP.sam -c Input.sam -f SAM -n沉淀-g 1.4376e9 -q 0.01 --bw = 200
注:X的有效尺寸热带基因组装配V7.1约为1.4376十亿基点(-g 1.4376e9)。 MACS2生成一个BED文件(ChIP_peaks.bed)争取与他们的基因组位置的峰值。 - 比较集群热图的形式几个染色质的配置文件:
- 创建一个从兴趣标签密度目录标签分配矩阵(-d芯片/ other_ChIP /)在MACS2峰( 如 +/- 1 kb的25基点箱,-size 2000 -hist 25 -ghist):
> annotatePeaks.pl ChIP_peaks.bed xenTro7 -size 2000 -hist 25 -ghist -d芯片/ other_ChIP /> ChIP.matrix - 使用Cluster3的图形用户界面上载ChIP.matrix文件和分层群集根据到最近的质心的最小欧几里得距离这些标记密度。打开Java中的TreeView生成的CTD文件,以可视化的集群。
- 创建一个从兴趣标签密度目录标签分配矩阵(-d芯片/ other_ChIP /)在MACS2峰( 如 +/- 1 kb的25基点箱,-size 2000 -hist 25 -ghist):
- 寻找新的和以前已知的具有约束力的图案,这是丰富高峰峰会+/- 100基点(-size 200)。使用annotatePeaks.pl映射图案事件和绘制图案密度:
> findMotifsGenome.pl ChIP_peaks.bed xenTro7 ChIP_motifs / -size 200 -p [#线程]
> annotatePeaks.pl ChIP_peaks.bed xenTro7 -m motif1.motif> ChIP_peaks.motif1
> annotatePeaks.pl ChIP_peaks.bed xenTro7 -m motif1.motif -size 800 -hist 25> motif1.density
注:findMotifsGenome.pl脚本INFERS从比较富集到随机选择的基因为中心的背景序列。最丰富新颖的主题是在一个位置权重矩阵的形式下motif1.motif保存。鼓励读者以证实这些结果与其他从头主题的查找方法,如cisFinder 22和23 MEME。 - 通过计算其到最近的基因的距离和由确定内400bp的窗口(-size 400)他们的规格化读出计数注解峰:
> annotatePeaks.pl ChIP_peaks.bed xenTro7 -size 400 -d芯片/输入/> ChIP_peaks.genes - 使用以下AWK命令列出的数目(N),位置和个人的(R)读出归一化数和每最接近(目标)基因的所有(LR)的峰汇总输出。
>的awk'BEGIN {FS =" t"} $ 7> = -5000 &&7美元<= 1000
{N [$ 8] + = 1; ř[$ 8] + = $ 9; LR [$ 8] = LR [$ 8',&#39; $ 7'('$ 9')'} {END为(i在N)
{打印我' t'N [I]' t'R [I]" t"SUBSTR(LR [I],2)}}'ChIP_peaks.genes> ChIP_peaks.summary
注:在$的数 字指的是列数,这可能需要修改,以适应在上一步中创建的ChIP_peaks.genes文件。这个脚本典范过滤掉超过5 kb的上游和TSS下游1 kb的峰值。$ 7,8美元9美元指到TSS,分别基因标识和每峰的归读计数的距离。 - 如下执行的靶基因中丰富GO方面进行分析:
- 从通过Java Web Start(javaws的)19从命令行启动Blast2GO的图形用户界面。
> javaws的http://blast2go.com/webstart/blast2go1000.jnlp - 按照上传标注的开发者说明文件的爪蟾基因(xenTro7.annot)在1.9.4中产生和识别靶基因的平面文件。确保同一基因标识在这两个文件中使用。
- 从通过Java Web Start(javaws的)19从命令行启动Blast2GO的图形用户界面。
- 加入大人物(ChIP.bw,Input.bw)和BED文件(ChIP_peaks.bed)为IGV为可视化的轨道型材的染色质。与RNA-SEQ补充数据跟踪,如果可供开发的同台演出。结果保存为一个会话。
- 使用的编程平台- [R (www.r-project.org)或MATLAB如上产生进一步处理和数据可视化。另外,情节与Excel的小数据集。
10.芯片定量PCR试验芯片和确认芯片起
- 使用在线平台引物3设计周围约100bp的DNA引物,在60℃(Tm值)为正(峰-特异性)和阴性对照的位点。确认使用引物特异性的,在硅片 PCR搜索落实到UCSC基因组浏览器。
- 创建的从约1%的输入开始3倍稀释液的8点的标准曲线或者使用2 - ΔΔC(T)的方法8,24用于DNA富集的定量。
- 在一式三份的技术对所有样本, 即芯片,控制执行实时PCR,如果需要的话,标准曲线样品。
- 情节的DNA富集作为输入的DNA的百分比或芯片的相对于对照样品,在正和负对照的位点的比例。
结果
相同的结果的那些这里提出预计如果是公执行的协议和所使用的抗体是芯片级质量(见讨论)。该协议允许核的甲醛固定爪蟾胚胎提取和染色质的通过超声处理的效率的剪切( 图1A-C)。剪切染色示出的DNA片段,主要范围为100至1000碱基对和300至500碱基对( 图1C)峰值的不对称分布。一个最小的50皮克免疫沉淀的DNA是必需的成功做出与同样大小的DNA插入( 图2A)的索引配对末端芯片序列库。该库应该基本上不含适配器二聚体,其可以在电泳可以看出在大约120碱基对。
在测序边合成,处理前读被映射到基因组中( 图2B,C)。在一个成功的实验 X。热带胚胎,通常为50%至70%的单端的40 bp的读取可以唯一地映射到V7.1的基因组装配与最多两个错配。而输入读取对准相当均匀分布在基因组芯片的排列读取结果链特有的富集侧翼感兴趣的染色功能。这是因为所有的片段是从5'端( 图2C)25测序。扩展排列在阅读方向的平均片段大小产生单质特性准确的配置文件,如转录因子结合事件。当IGV或任何其它相容的基因组浏览器可视化这些DNA占有率显示为峰。峰呼叫者像磁珠被用来确定这些峰( 图3A)的位置。这样的结合位点数万一直在X.确定热带基因组的T-box转录因子如VegT 26。芯片的qPCR experiments应确认通过的ChIP-SEQ( 图3B)发现的局部富集。
芯片起实验允许探索的染色质的功能的全基因组的特性。例如,在计算过的基因组的元素的读取分配如转录起始和终止位点可能突出围绕的基因的任何空间结合偏好( 图3C)。同样地,读出分布在峰值位置的热图被用于在全基因组规模( 图3D)来比较不同的染色质的功能。某些转录因子结合的基因组DNA的基本峰DNA序列特异性。 从头主题的分析可以获取此类信息,包括潜在的共同因素( 图3E)共同丰富图案。绝大多数的靶基因的表现在一个较低的DNA占用,而不是更高的水平( 图3F)。此无尺度的功能似乎是潮流当中相当普遍anscription因素和表明靶基因的仅一小部分直接与生物相关27,28调节。的富集的GO术语或其它的属性,如靶基因的差异表达可以进一步揭示见解在爪蟾胚胎( 图3G)的染色质功能的生物功能的分析。
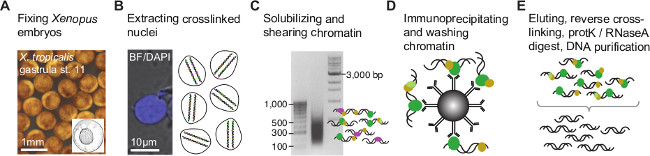
数字爪蟾胚胎1.染色质免疫沉淀的过程。 (A)的胚胎是甲醛固定在感兴趣的共价结合(交联)与基因组DNA相关联的任何蛋白质的发育阶段。在核提取(B)中 ,交联的染色质片段化来缩小的基因组DNA结合或染色质修饰位点通过最小化侧翼的DN序列(C)。随后,将染色质片段免疫沉淀与芯片级抗体充实那些含有目的(D)中的表位。共免疫沉淀DNA被剥离的蛋白质和创建芯片片段库NGS( 图2)之前纯化(E)。 请点击此处查看该图的放大版本。

图2.芯片起文库制备,测序边合成,映射和峰呼叫。 (A)中的电泳显示具有250〜450碱基对的DNA模板的好芯片起库。这些模板带来的由通用(58基点)两侧感兴趣的DNA插入和索引(63基点)的适配器。(B) 百万簇,每个含有相同的模板簇,是测序碱通过碱在所有四种核苷酸具有可逆的,鲜明的荧光团和相同的终止性质的存在。荧光图像的实时处理,以调用相应的碱,这最终组装成的读取。(℃)仅读取地图唯一到爪蟾基因组被保留。因为所有的片段是从5'末端测序,芯片的映射读取结果中链特异峰侧翼感兴趣的染色质功能。因此,峰值检测呼叫者源自免疫沉淀和延长读取到平均片段长度精确定位功能的染色质丰富。 请点击此处查看该图的放大版本。

图3.后测序分析和数据的可视化的由合子的T-box转录因子VegT(zVegT),所有读这里显示计数归一千万唯一映射和非冗余的读取。(A)的摘录的装置的一个例子的zVegT的全基因组信息X中的结合热带原肠胚(阶段11至12.5新科普和麦嘉华29后)。每个峰,一个堆积的扩展读出,表示一个结合位点。这些峰被称为由MACS2具有小于1%的错误发现率(FDR)。每个MESP基因显示出非常近端和上游zVegT结合,但只有mespa和mespb由该阶段(RNA测序数据30)来表示。(B)的 zVegT由芯片的qPCR在几个位点所确定的DNA的占用水平(包括非-被结合区0.5 kb的β 肌动蛋白的上游)的配RM通过芯片序列中发现的具体富集。比较结果mespa峰值称为(红色条)中(A)。该DNA占用等级被可视作为输入的两个百分比,与VegT抗体(IgG同种型的兔多克隆)和与抗体对照(正常兔IgG)的芯片中的芯片上。误差棒反映两个生物学重复的标准偏差。(C)的基因表达谱分析显示优先zVegT结合(标记分级超过25碱基对)相对于周围的任何其他基因组区域和基因机构内的启动子。(D)的热图显示了K均值集群(K = 5)DNA入住率(分级标签超过25个基点)的zVegT和的Smad2 / Smad3蛋白(芯片序列数据31),相对于全部zVegT结合的地区,在原肠期。热图是记录2基础,集中在每个碱基5标签。(E) 从头主题分析,发现了典型的T-box转录因子结合基序zVegT- 38%如果底层基序得分标准化为5%的发现率在背景序列结合的区域。该密度图表示最高富集在zVegT结合位点中心的T型盒基序,而典型的Smad2 / Smad3蛋白结合基序是难以富集。(F)的直方图显示zVegT DNA的占用程度,这是计算每个靶基因从5 kb的上游之间的所有峰(+/- 200基点)[ - ]。相应的转录起始位点和1 kb的下游[+](G)300强的基因与内-5 kb的DNA最高的入住率和1 kb的是富集的早期胚胎发育的生物过程。这些GO条款与zVegT的假定的功能线。罗斯福是基于双尾Fisher精确检验和多重检验校正。 请点击此处查看该图的放大版本。
讨论
我们的协议概括了如何制备和分析来自非洲爪蟾胚胎的全基因组染色质分布。它涵盖了每一个步骤,从交联蛋白的内源性基因位点在体内处理数以百万计的读取较丰富的基因组位点在硅片中。由于可用的基因组草案越来越多,该协议应适用于其他模型和非模式生物。最重要的实验部分,它设置该协议除了以前的工作8,31,33,34,是后定影过程以提取交联核。它有利于有效的染色质溶解和剪切,易倍增。连同文库制备的改进的效率这个协议允许的高复杂的ChIP-SEQ文库的构建从半两百万个细胞中表达感兴趣的染色质相关的表位。对于芯片的qPCR实验中,几10000这些细胞通常是足够检查DNA富集也许在六个不同的基因位点。这些数字是保守的估计,但可以根据蛋白质表达水平,抗体质量而变化,交联效率,以及表位可访问性。作为指导,单个爪蟾胚胎中含有大约4,000个细胞,在中期囊胚期(8.5新科普和费伯29之后),40,000个细胞的晚期原肠胚阶段(12)和100,000个细胞在早期tailbud阶段(20)。
需要精确固定的时间进行有效免疫凭经验由芯片定量PCR(第10条)确定。在一般情况下,较长的固定时间,如果实验涉及十需要蟾胚胎早期发育阶段,弱(或间接)DNA绑定属性。然而,不推荐固定爪蟾胚胎长于40分钟,或处理比表示(第3节)的更多的胚胎,如染色质剪切变得效率较低。重要的是不固定后使用任何甘氨酸作为淬火甲醛可使核提取蛋黄丰富的胚胎非常困难这个共同的一步。目前,这样做的原因是不知道。可以想到的是甲醛-甘氨酸加合物进一步反应与N-末端氨基的基团或精氨酸残基35。
抗体是关键的任何沉淀实验和足够的控制需要被进行,以显示它的特异性针对感兴趣的表位(参见由LANDT 等人 36的准则)。如果没有沉淀同类抗体是可用的,引入相应的表位标记的融合蛋白的可能是一个合法的替代,因为这些蛋白质可以占据内源性结合位点37。在这种情况下,未注射的胚胎是最好的作为阴性对照,而不是与非特异性血清芯片使用。如果感兴趣的蛋白被表达以低水平产生ENRI的差恢复这种策略也可应用高等教育委员会DNA。
作为用于制造芯片起库,因为在使用中的DNA的量低,则建议选择减少的清洗步骤的次数,并结合反应保持的DNA的任何损失在最小的程序。适配器和引物需要与多重测序和NGS平台兼容(见表具体材料/设备)。如果使用Y型适配器(含长单链臂),关键是要用三到五轮的PCR的大小选择的DNA插入之前预扩增文库( 例如 ,100至300碱基对)用凝胶电泳。单链末端引起DNA片段迁移不均匀。试运行用不同量的输入的DNA( 例如 ,0.1,0.5,1,2,第5,10和20毫微克)的建议,以确定PCR循环的总数(小于或等于18个循环),以使一个尺寸需要100至200毫微克 - 请选择库。减少的PCR周期数使得热镀的测序ndant读取的可能性较小。固相可逆固定化珠是良好清理试剂有效地回收感兴趣的DNA和可靠地从结扎和PCR反应除去任何游离的适配器和二聚体。
在的数量,类型和长度方面的读取,约20至3000万单端读出的36 bp的是足以满足大多数芯片起实验来覆盖整个基因组的爪蟾具有足够的深度。最普遍的NGS机器经常能够满足这些标准。然而,它可能是有益的,以增加数目的读出,如果读出的一个广泛分布的预期,与组蛋白修饰观察到的,而不是尖锐的峰。对于许多芯片起实验,4至5不同的索引库可以汇集并使用高性能NGS机测序在一个流动细胞车道。有时也建议使读扩展长度和序列的DNA模板的两端(配对末端),以增加mappability瓦特母鸡分析重复的基因组区域内染色质。
此协议已被成功地应用到各种各样的染色质的功能,如转录因子,信令介质和翻译后蛋白修饰。但是,胚胎细胞获得的异质性程度日益加深,因为他们发展和染色质分布变得难以解释。希望的步骤已在拟南芥和果蝇到组织特异性轮廓染色质景观通过提取细胞类型特异性核38,39。我们的协议包括核提取步骤,这可能铺平道路组织特异性的ChIP-SEQ其他胚胎。
披露声明
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
致谢
We thank Chris Benner for implementing the X. tropicalis genome (xenTro2, xenTro2r) into HOMER and the Gilchrist lab for discussions on post-sequencing analysis. I.P. assisted the GO term analysis. G.E.G and J.C.S. were supported by the Wellcome Trust and are now supported by the Medical Research Council (program number U117597140).
材料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 1/16 inch tapered microtip | Qsonica | 4417 | This microtip is compatible with Sonicator 3000 from Misonix and Q500/700 from Qsonica. |
| 8 ml glass sample vial with cap | Wheaton | 224884 | 8 ml clear glass sample vials for aqueous samples with 15-425 size phenolic rubber-lined screw caps. |
| Adaptor | e.g., IDT or Sigma | NA | TruSeq universal adaptor,
AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAG ATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACAC GACGCTCTTCCGATC*T. TruSeq indexed adaptor, P-GATCGGAAGAGCACACGTC TGAACTCCAGTCAC ‐NNNNNN‐ ATCTCGTATGCCGTCT TCTGCTT*G. *, phosphorothioate bondphosphate group at 5' end. NNNNNN, index (see TruSeq ChIP Sample Preparation Guide for DNA sequence). Order adaptors HPLC purified. Adaptors can be prepared by combining equimolar amounts (each 100 µM) of the universal and the indexed adaptor and cooling them down slowly from 95 °C to room temperature. Use 1.5 pmol per ng of input DNA. Store at -20 °C. |
| b2g4pipe (software) | Blast2GO | non-commercial | http://www.blast2go.com/data/blast2go/b2g4pipe_v2.5.zip |
| BLAST+ (software) | Camacho et al. | non-commercial | http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PAGE_TYPE=BlastDocs& DOC_TYPE=Download |
| Bowtie (software) | Langmead et al. | non-commercial | http://bowtie-bio.sourceforge.net/index.shtml |
| cisFinder (software) | Sharov et al. | non-commercial | http://lgsun.grc.nia.nih.gov/CisFinder/ |
| Chip for capillary electrophoresis | Agilent Technologies | 5067-1504 | Load this chip with 1 µl DNA for library quality control. Store at 4 °C. |
| Chip-based capillary electrophoresis system | Agilent Technologies | G2940CA | The Agilent 2100 BioAnalyzer is used to check the quality of ChIP-Seq libraries. Keep reagents at 4 °C. |
| ChIP-Seq library preparation kit (KAPA Hyper Prep Kit) | Kapa Biosystems | KK8504 | Kit contains KAPA end repair and A-tailing enzyme mix, end Repair and A-tailing buffer, DNA ligase, ligation buffer, KAPA HiFi HotStart ReadyMix (2X), and KAPA library amplification primer mix (10X) (see also PCR primers). Adaptors are not included. Store at -20 °C. |
| ChIP-Seq library preparation kit (alternative, ThruPLEX-FD Prep Kit) | Rubicon Genomics | R40048 | Kit uses their own stem-loop adaptors and primers. This kit eliminates intermediate purification steps and is as sensitive as the KAPA Hyper Prep Kit. Store at -20 °C. |
| Cluster3 (software) | de Hoon et al. | non-commercial | http://bonsai.hgc.jp/~mdehoon/software/cluster |
| FastQC (software) | Simon Andrews | non-commercial | http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc |
| Fluorometer | life technologies | Q32866 | Qubit 2.0 Fluorometer |
| Fluorometer reagents | life technologies | Q32851 | The kit provides concentrated assay reagent, dilution buffer, and pre-diluted DNA standards for the Qubit fluorometer. Store DNA standards at 4 °C, buffer and dye at room temperature. |
| Formaldehyde | Sigma | F8775-4X25ML | Formaldehyde solution, for molecular biology, 36.5-38% in H2O, stabilised with 10-15% methanol. Store at room temperature. CAUTION: Formaldehyde is corrosive and highly toxic. |
| Gel (E-Gel EX agarose , 2%) | life technologies | G4010 | Pre-cast gel with 11 wells, openable format. Leave one lane between ladder and library empty to avoid cross-contamination. Store gels at room temperature. |
| Gel electrophoresis system | life technologies | G6465 | E-Gel iBase and E-Gel Safe Imager combo kit for size-selecting ChIP-Seq libraries. |
| Gel extraction kit | Qiagen | 28706 | Store all reagents at room temperature. Use 500 µl of QG buffer per 100 mg of 2% agarose gel slice to extract DNA. Use MinElute columns (from MinElute PCR purification kit) to elute DNA twice. |
| HOMER (software) | Chris Benner | non-commercial | http://homer.salk.edu/homer/index.html |
| Hybridization oven | Techne | FHB1D | Hybridizer HB-1D |
| IGV (software) | Robinson et al. | non-commercial | http://www.broadinstitute.org/igv/home |
| Illumina CASAVA-1.8 quality filter (software) | Assaf Gordon | non-commercial | http://cancan.cshl.edu/labmembers/gordon/fastq_illumina_filter |
| Java TreeView (software) | Alok Saldanha | non-commercial | http://jtreeview.sourceforge.net |
| Laboratory jack | Edu-Lab | CH0642 | This jack is used to elevate sample in sound enclosure for sonication. |
| Ladder, 100 bp | New England BioLabs | N3231 | Keep 1x solution at room temperature. Store stock at -20 °C. |
| Ladder, 1 kb | New England BioLabs | N3232 | Keep 1x solution at room temperature. Store stock at -20 °C. |
| Low-retention 1.5-ml microcentrifuge tubes | life technologies | AM12450 | nonstick, RNase-free microfuge tubes, 1.5 ml |
| MACS2 (software) | Tao Liu | non-commercial | https://github.com/taoliu/MACS |
| Magnetic beads | life technologies | 11201D | These Dynabeads are superparamagnetic beads with affinity purified polyclonal sheep anti-mouse IgG covalently bound to the bead surface. Store at 4 °C. |
| Magnetic beads | life technologies | 11203D | These Dynabeads are superparamagnetic beads with affinity purified polyclonal sheep anti-rabbit IgG covalently bound to the bead surface. Store at 4 °C. |
| Magnetic beads | life technologies | 10001D | These Dynabeads are superparamagnetic beads with recombinant protein A covalently bound to the bead surface. Store at 4 °C. |
| Magnetic beads | life technologies | 10003D | These Dynabeads are superparamagnetic beads with recombinant protein G covalently bound to the bead surface. Store at 4 °C. |
| Magnetic rack | life technologies | 12321D | DynaMag-2 magnet |
| MEME | Bailey et al. | non-commercial | http://meme.nbcr.net/meme/ |
| Na3VO4 | New England BioLabs | P0758 | Sodium orthovanadate (100 mM) is a commonly used general inhibitor for protein phosphotyrosyl phosphatases. Store at -20 °C. |
| NaF | New England BioLabs | P0759 | Sodium fluoride (500 mM) is commonly used as general inhibitor of phosphoseryl and phosphothreonyl phosphatases. Store at -20 °C. |
| NGS machine | Illumina | SY-301-1301 | Genome Analyzer IIx |
| NGS machine (high performance) | Illumina | SY-401-2501 | HiSeq |
| Normal serum (antibody control) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-2028 | Use as control for goat polyclonal IgG antibodies in ChIP-qPCR experiments. Store at 4 °C. |
| Normal serum (antibody control) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-2025 | Use as control for mouse polyclonal IgG antibodies in ChIP-qPCR experiments. Store at 4 °C. |
| Normal serum (antibody control) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-2027 | Use as control for rabbit polyclonal IgG antibodies in ChIP-qPCR experiments. Store at 4 °C. |
| Nucleic acid staining solution | iNtRON | 21141 | Use RedSafe nucleic acid staining solution at 1:50,000. Store at room temperature. |
| Orange G | Sigma | O3756-25G | 1-Phenylazo-2-naphthol-6,8-disulfonic acid disodium salt. Store at 4 °C. |
| PCR primers | e.g., IDT or Sigma | Primers to enrich adaptor-ligated DNA fragments by PCR: AATGATACGGCGACCACCGA*G and CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGA*G, phosphorothioate bond. Primers designed by Ethan Ford. Combine primers at 5 µM each. Use 5 µl in a 50 µl PCR reaction. Store at -20 °C. | |
| MinElute PCR purification kit | Qiagen | 28006 | for purification of ChIP-qPCR and shearing test samples. Store MinElute spin columns at 4 °C, all other buffers and collection tubes at room temperature. |
| Phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1, pH 7.9) | life technologies | AM9730 | Phenol:Chloroform:IAA (25:24:1) is premixed and supplied at pH 6.6. Use provided Tris alkaline buffer to raise pH to 7.9. Store at 4 °C. CAUTION: phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol is corrosive, highly toxic and combustible. |
| Primer3 (software) | Steve Rozen & Helen Skaletsky | non-commercial | http://biotools.umassmed.edu/bioapps/primer3_www.cgi |
| Protease inhibitor tablets | Roche | 11836170001 | cOmplete, Mini, EDTA-free. Use 1 tablet per 10 ml. Store at 4 °C. |
| Protease inhibitor tablets | Roche | 11873580001 | cOmplete, EDTA-free. Use 1 tablet per 50 ml. Store at 4 °C. |
| Proteinase K | life technologies | AM2548 | proteinase K solution (20 µg/µl). Store at -20 °C. |
| RNase A | life technologies | 12091-039 | RNase A (20 µg/µl). Store at room temperature. |
| Rotator | Stuart | SB3 | Rotator SB3 |
| SAMtools (software) | Li et al. | non-commercial | http://samtools.sourceforge.neta |
| Solid phase reversible immobilisation beads | Beckman Coulter | A63882 | The Agencourt AMPure XP beads are used to minimise adaptor dimer contamination in ChIP-Seq libraries. Store at 4 °C. |
| Sonicator 3000 | Misonix/Qsonica | Newer models are now available. Q125, Q500 or Q700 are all suitable for shearing crosslinked chromatin. | |
| Sound enclosure | Misonix/Qsonica | optional: follow the manufacturer's recommendation to obtain the correct sound enclosure. | |
| Thermomixer | eppendorf | 22670000 | Thermomixer for 24 x 1.5 mL tubes. Precise temperature control from 4 °C above room temperature to 99 °C. |
参考文献
- Gilmour, D. S., Lis, J. T. Detecting protein-DNA interactions in vivo: distribution of RNA polymerase on specific bacterial genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 81 (14), 4275-4279 (1984).
- Gilmour, D. S., Lis, J. T. In vivo interactions of RNA polymerase II with genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 5 (8), 2009-2018 (1985).
- Solomon, M. J., Larsen, P. L., Varshavsky, A. Mapping protein-DNA interactions in vivo with formaldehyde: evidence that histone H4 is retained on a highly transcribed gene. Cell. 53 (6), 937-947 (1988).
- Ren, B., et al. Genome-wide location and function of DNA binding proteins. Science. 290 (5500), 2306-2309 (2000).
- Johnson, D., Mortazavi, A., Myers, R., Wold, B. Genome-wide mapping of in vivo protein-DNA interactions. Science. 316 (5830), 1497-1502 (2007).
- Hellsten, U., et al. The genome of the Western clawed frog Xenopus tropicalis. Science. 328 (5978), 633-636 (2010).
- Lee, T. I., Johnstone, S. E., Young, R. A. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and microarray-based analysis of protein location. Nature Protocols. 1 (2), 729-748 (2006).
- Blythe, S. A., Reid, C. D., Kessler, D. S., Klein, P. S. Chromatin immunoprecipitation in early Xenopus laevis embryos. Dev Dyn. 238 (6), 1422-1432 (2009).
- Gentsch, G. E., Smith, J. C. Investigating physical chromatin associations across the Xenopus genome by chromatin immunoprecipitation. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2014 (5), (2014).
- Ubbels, G. A., Hara, K., Koster, C. H., Kirschner, M. W. Evidence for a functional role of the cytoskeleton in determination of the dorsoventral axis in Xenopus laevis eggs. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 77, 15-37 (1983).
- Langmead, B., Trapnell, C., Pop, M., Salzberg, S. L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 10 (3), R25 (2009).
- Li, H., et al. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 25 (16), 2078-2079 (2009).
- Heinz, S., et al. Simple combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime cis-regulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell identities. Mol Cell. 38 (4), 576-589 (2010).
- Zhang, Y., et al. Model-based analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol. 9 (9), R137 (2008).
- Robinson, J. T., et al. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat Biotechnol. 29 (1), 24-26 (2011).
- Thorvaldsdottir, H., Robinson, J. T., Mesirov, J. P. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief Bioinform. 14 (2), 178-192 (2013).
- Imoto, S., Nolan, J., Bioinformatics Miyano, S. . 20 (9), 1453-1454 (2004).
- Camacho, C., et al. BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinformatics. 10, 421 (2009).
- Conesa, A., et al. Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics. 21 (18), 3674-3676 (2005).
- Sive, H., Grainger, R., Harland, R. . Early development of Xenopus laevis: A laboratory manual. , (2000).
- Chen, Y., et al. Systematic evaluation of factors influencing ChIP-seq fidelity. Nat Methods. 9 (6), 609-614 (2012).
- Sharov, A. A., Ko, M. S. H. Exhaustive search for over-represented DNA sequence motifs with CisFinder. DNA Res. 16 (5), 261-273 (2009).
- Bailey, T. L., et al. MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucl Acids Res. 37 (2), W202-W208 (2009).
- Livak, K. J., Schmittgen, T. D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25 (4), 402-408 (2001).
- Park, P. J. ChIP-seq: advantages and challenges of a maturing technology. Nat Rev Genet. 10 (10), 669-680 (2009).
- Gentsch, G. E., et al. In vivo T-box transcription factor profiling reveals joint regulation of embryonic neuromesodermal bipotency. Cell Rep. 4 (6), 1185-1196 (2013).
- Barabasi, A. L., Oltvai, Z. N. Network biology: understanding the cell's functional organization. Nat Rev Genet. 5 (2), 101-113 (2004).
- Biggin, M. D. Animal transcription networks as highly connected, quantitative continua. Dev Cell. 21 (4), 611-626 (2011).
- Nieuwkoop, P. D., Faber, J. . Normal table of Xenopus laevis (Daudin): a systematical and chronological survey of the development from the fertilized egg till the end of metamorphosis. , (1994).
- Akkers, R. C., et al. A hierarchy of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 acquisition in spatial gene regulation in Xenopus embryos. Dev Cell. 17 (3), 425-434 (2009).
- Yoon, S. J., Wills, A. E., Chuong, E., Gupta, R., Baker, J. C. . HEB and E2A function as SMAD/FOXH1 cofactors. Genes Dev. 25 (15), 1654-1661 (2011).
- Jallow, Z., Jacobi, U. G., Weeks, D. L., Dawid, I. B., Veenstra, G. J. Specialized and redundant roles of TBP and a vertebrate-specific TBP paralog in embryonic gene regulation in Xenopus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 101 (37), 13525 (2004).
- Buchholz, D. R., Paul, B. D., Shi, Y. -. B. Gene-specific changes in promoter occupancy by thyroid hormone receptor during frog metamorphosis. Implications for developmental gene regulation. J Biol Chem. 280 (50), 41222-41228 (2005).
- Wills, A. E., Guptaa, R., Chuonga, E., Baker, J. C. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and deep sequencing in Xenopus tropicalis and Xenopus laevis. Methods. 66 (3), 410-421 (2014).
- Metz, B., et al. Identification of formaldehyde-induced modifications in proteins: reactions with model peptides. J Biol Chem. 279 (8), 6235-6243 (2004).
- Landt, S. G., et al. ChIP-seq guidelines and practices of the ENCODE and modENCODE consortia. Genome Res. 22 (9), 1813-1831 (2012).
- Mazzoni, E. O., et al. Embryonic stem cell-based mapping of developmental transcriptional programs. Nat Methods. 8 (12), 1056-1058 (2011).
- Deal, R. B., Henikoff, S. A simple method for gene expression and chromatin profiling of individual cell types within a tissue. Dev Cell. 18 (6), 1030-1040 (2010).
- Bonn, S., et al. Tissue-specific analysis of chromatin state identifies temporal signatures of enhancer activity during embryonic development. Nat Genet. 44 (2), 148-156 (2012).
转载和许可
请求许可使用此 JoVE 文章的文本或图形
请求许可探索更多文章
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。