需要订阅 JoVE 才能查看此. 登录或开始免费试用。
Method Article
平面梯度扩散系统的调查趋化三维胶原基质
摘要
Cell migration is an important part of human development and life. In order to understand the mechanisms that can alter cell migration, we present a planar gradient diffusion system to investigate chemotaxis in a 3D collagen matrix, which allows one to overcome modern diffusion chamber limitations of existing assays.
摘要
The importance of cell migration can be seen through the development of human life. When cells migrate, they generate forces and transfer these forces to their surrounding area, leading to cell movement and migration. In order to understand the mechanisms that can alter and/or affect cell migration, one can study these forces. In theory, understanding the fundamental mechanisms and forces underlying cell migration holds the promise of effective approaches for treating diseases and promoting cellular transplantation. Unfortunately, modern chemotaxis chambers that have been developed are usually restricted to two dimensions (2D) and have complex diffusion gradients that make the experiment difficult to interpret. To this end, we have developed, and describe in this paper, a direct-viewing chamber for chemotaxis studies, which allows one to overcome modern chemotaxis chamber obstacles able to measure cell forces and specific concentration within the chamber in a 3D environment to study cell 3D migration. More compelling, this approach allows one to successfully model diffusion through 3D collagen matrices and calculate the coefficient of diffusion of a chemoattractant through multiple different concentrations of collagen, while keeping the system simple and user friendly for traction force microscopy (TFM) and digital volume correlation (DVC) analysis.
引言
细胞的优选运动朝向的浓度梯度,被称为趋化作用,起着在体内的病理和生理过程中起重要作用。这样的例子是皮肤和粘膜伤口愈合1,形态2,炎症3,和肿瘤生长4,5。还已经表明,癌细胞可通过个人和集体细胞迁移策略6迁移。此外,扩散不稳定机制可以诱导单或聚簇的细胞从肿瘤体/对象分离,然后可以移民朝营养素源,从而侵入更广泛的领域和组织7。
此外,已经表明,不同的迁移机制可以是主动的二维和三维中,由于粘附分子8的不同的作用。因此,此举是为了生理有关体外实验来研究细胞运动的measureable和简单的方法就是意义的理解细胞的运动现象9。不幸的是,在分析细胞迁移的困难,全面量化的趋化性试验通常需要很长的费力的方法,建立在公正的细胞运动和迁移现象模型测量。
过去的实验方法来研究细胞趋化包括在Boyden小室10和下琼脂糖测定11。然而,这些早期试验中,细胞迁移实验没有监测方面的运动时间。更重要的是,用于该实验的浓度梯度没有明确定义或完全地理解,而只维持信令为不超过几个小时以上。此外,早期的趋化室的尝试限制细胞迁移到两个维度,并没有允许一个监视迁移12的动力学。纵观Boyden小室,端点检测不会允许研究者以目视观察的迁移,无法直接区分化学激活(随机运动)的趋化(定向运动)。此外,几个变量-差异的孔径和厚度的膜制造的腔室非常难以轻易再现和隐蔽细胞对趋化因子13,14的流动反应。
随着微流体的新的认识,新的商会和微型设备进行了调查作为一种工具来调查间质性流动条件下的细胞运动和趋化性15,16。根据这些新的设备,新的小区的度量进行了介绍和研究,象剪切应力对细胞17,18的效果。不幸的是,过去和现在的微流控趋庭,因为许多生物过程,包括肿瘤细胞的侵袭和转移,IM限制细胞迁移的研究,以2D基板,一个重要挫折宗细胞迁移,涉及到3D的迁移。
直接观察室-其中趋化溶液与含有细胞三维凝胶接触也被也报道19,20。这些室具有两个隔室,一个包含一个趋化和一种含有细胞,旁彼此水平21或作为同心环22接合。这些系统指出了正确的方向,但不保持一个趋系统的长时间。
此外,研究人员还透析细胞,以及示踪分子通过胶原样品进行静水压力23-25 扩散检验扩散通过胶原膜。在胶原凝胶一些扩散实验依靠凝胶的使用磁场和化学掺入26物理和化学修饰。在建模科亚扩散性流行的方法genous组织依赖于连续漂白点的荧光成像。这种方法已经揭示各向异性大分子在面向胶原组织中的扩散系数。然而,光漂白已被用于在关节软骨和不胶原基质。虽然类似的,必要的模拟实验,必须通过具体理解胶原凝胶的扩散系数来进行。更重要的是,系统不使用用于测量细胞力产生的方法。
不幸的是,大多数系统似乎缺少了一个理想的系统中的一个或两个关键要素:细胞跟踪,通过矩阵,一个相对简单的设置了一个轻松的再现性,最小化的趋化因子的扩散梯度的理解使细胞-细胞相互作用,并且以测量的尺寸单位为量化( 即 ,速度,力,具体浓度)的能力。 Moghe 等。 27提出了一个系统,该系统满足大多数的这些要求,其中细胞在整个凝胶最初分散,而不是集中在过滤表面上,但是难以测量的力,所述细胞产生。
为此目的,我们提出了一个平面梯度扩散系统中的3D胶原基质,它允许一个克服现有测定法,它是基于时间推移显微镜,加上图像分析技术来测量细胞的现代扩散腔的限制,调查趋力在3D环境中。这个协议提供了创建一个简单的3D扩散室,其可用于研究3D趋于不同小区的一个简单但创新的方式。
研究方案
1. 3D模具设计和零件
- 模
- 之前的工作,得到的有机硅弹性体的试剂盒,一个活细胞成像室,一个22毫米的玻璃盖玻片,和一个加工铝金属立方体,尺寸为10.07毫米×3.95毫米×5.99毫米。通过将盖玻片在底部支架和所指示的厂商组装腔室的其余部分制备活细胞成像室,用于成型。
- 接着,使用镊子,将加工铝金属立方体中的活细胞成像室外壳的中间,并且在盖玻片的顶部,然后待用。
- 根据制造商的协议,使5毫升弹性体的混合硅氧烷弹性体的解决方案。
- 使用一次性实验室锅铲,倒入有机硅弹性体解决方案进入活细胞成像室的设置,并确保不移动放置加工铝金属立方体。将系统中的实验台上,在安全的位置O / N进行固化。
- 第二天早上,解构活细胞成像室,使用镊子所推荐的制造商,拔出的模具。使用镊子,仔细提取模具加工铝金属立方体。转到水槽和用去离子水冲洗模具。将模具在纸巾上干燥。
- 干燥后,用一个爱好美工刀,通过模具切缝,间隔2.34毫米相距纵向到底,硅胶模具内。保证了模具停留在一个安全干燥的地方,直到您准备构建系统的实验。
- 亲水性和疏水盖玻片准备
- 以允许胶原基质粘附到表面上,创建亲水盖玻片:
- 使用一次性吸液管,测量出150微升3-氨基丙基 - 三甲氧基硅烷和倒在50ml管溶液。加30毫升100%乙醇至50ml管中的与第二一次性吸,并盖上盖子。涡的解决方案,持续2分钟,以确保完全混合。 P我们在一玻璃培养皿溶液待用。
- 倒入将15ml 100%乙醇在第二培养皿中,并预留(请务必标注菜肴)。
- 使用新的一次性吸移管,量出30ml去离子水和倒溶液到50毫升管中。其次,采用了全新的一次性吸管量出1,875微升戊二醛,倒液进入同样的50毫升管,并盖上盖子。涡的解决方案,持续2分钟,以确保完全混合。将混合物倒入第三个培养皿中,并预留。
- 使用镊子,取出22之一毫米的圆形玻璃盖玻片并使用一次性吸冲洗两面用100%的乙醇的混合物。
- 放置漂洗玻璃盖玻片成3-氨基丙基 - 三甲氧基硅烷用30毫升100%乙醇溶液皿,并允许坐在溶液5分钟。
- 用钳子,取出玻璃盖玻片,并与一次性吸管100%乙醇溶液再次冲洗。
- 冲洗滴玻璃盖玻片到1,875微升戊二醛和30ml去离子水的混合物,并搁置30分钟。
- 30分钟后,取出玻璃盖玻片钳和用去离子水冲洗,并放置到干燥的组织O / N干在室温。
- 重复浸盖玻片,并根据需要使用相同的解决方案产生的移动尽可能多的盖玻片。
- 在给定的协议使疏水盖玻片。
- 加入500μl十三氟-1,1,2,2-四氢辛基,100微升乙酸和在50毫升的管中,涡旋2分钟19.4毫升己烷。倒入玻璃培养皿的解决方案,并预留。
- 用干净的镊子,取出一块玻璃盖玻片拖放到准备混合溶液2分钟。经过2分钟过去了,取出玻璃盖玻片钳和使用一次性吸管和地点盖玻片上干组织O / N干在室温用去离子水冲洗。商店盖玻片在塑料培养皿直至使用。
- 重复盖玻片DIPP荷兰国际集团,并根据需要使用相同的解决方案产生的移动尽可能多的盖玻片。
- 以允许胶原基质粘附到表面上,创建亲水盖玻片:
2.模具大会
- 在使用的模具,采用一次性吸管冲洗模具90%的乙醇在化学废物容器。接下来,放置在培养皿中装有去离子水的模具和允许坐O / N。
- 取模子里出来的使用镊子和地方的毛巾晾干解决方案开始在模具组装之前。
- 而模具是空气干燥,切正方形亲水盖玻片成两个矩形比3.95毫米×5.99毫米使用高精度金刚石刻划工具略大。将每个切矩形盖玻片到切入硅胶模具的插槽。
- 翻转模上下颠倒并应用真空润滑脂沿着使用一次性吸硅氧烷模具的底部。接下来,翻转模具靠背右侧朝上,然后按模具的底部到圆形亲水玻璃罩唇形成密封。
- 与一次性手套,拿起组装模具,并放置到一次性培养皿中,然后进入生物罩。打开紫外线生物罩灯1小时的实验发生之前进行消毒模具。
3.胶原蛋白混合物和3D矩阵
- 之前制备胶原混合物,染色剂和制备细胞用于根据标准方法28成像。
- 使用标准实验室技术和协议29,30,在一个生物罩,混合细胞培养基和趋化在15ml管所需的化学引诱物的浓度。吸移管加入5ml特定细胞媒体趋化浓度溶液到15毫升管和移动溶液到加热的水浴中。
- 使用移液管,提取5毫升只是细胞培养基到第二15ml试管并置于加热的水浴升温显微镜实验溶液。
- 在生物罩,吸管30微升10×磷酸盐缓冲编溶液(PBS)中成微离心管中。加入6微升1N氢氧化钠(氢氧化钠)到相同的微离心管中,涡旋15秒。
- 得到胶原I鼠尾溶液从冰箱,并使用标准实验室技术和协议29移动到生物罩。确保胶原蛋白是依然寒冷。吸取168.3微升胶原的成同一微离心管中。
- 接着,用移液管以相同的微离心管中添加18微升的黄绿色荧光羧化物修饰的微球。涡流的微离心管中进行30秒的所有解决方案。
- 添加77.7微升所需的细胞培养基细胞混合物(约2×10 6细胞/ ml的浓度)的入微量离心管中并混合使用的吸头20秒。必要时,由适于加入荧光珠和细胞活力表( 表1)的自定义胶原混合物以下改变基质密度。
- 吸管300#181;升胶原细胞混合物的进入中心孔(孔#2)制得的模具组件的。放置在模具上的一次性培养皿并将其移到一个标准培养箱20分钟,在37℃,5%的CO 2。
- 从孵化器中删除系统,并将放回生物罩。使用镊子,通过夹紧到每个盖玻片的顶部和拉起和远离模具中取出疏水盖玻片。
- 将整个系统所需的显微镜和图像,以确保胶原模具两侧仍然直,以允许一个平面扩散梯度。
- 与系统仍然在显微镜下,使用100微升单通道移液器,加入100微升细胞培养基到孔#1。接着,使用100微升单通道移液器加入100微升的细胞培养基具有所需的化学引诱物的浓度成孔#3。
- 马上加入到解决方案两口井后,开始成像。
4.成像和弥散造型
- 如果一个人想找到的扩散系数的具体胶原蛋白的密度来计算特定浓度,按照以下协议:
- 遵循给定的协议上述标题"胶原混合和3D矩阵",而不是产生细胞介质具有所需的化学引诱物的浓度,使在一个15毫升管5微米罗丹明使用标准计算和协议30。
- 图像的3D胶原基质共聚焦系统,安装在使用氩激光(488纳米)来捕捉荧光倒置显微镜。图像,每2或3秒长达7小时。
- 为扩散建模:使用以下所示的数学模型,写处理和分析的计算软件代码包含有这些一般步骤。
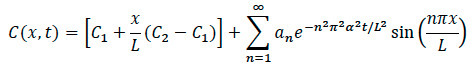
- 导入影像到了重新调整和规范计算软件由最大INTEN减到。图像转换为灰色颜色映射图像的选择的边缘。挑一轴线沿所述图像的中心,该中心的右侧,到中心的左边。
- 使用的计算软件代码,绘制归一化的强度,随着真实强度和这两者之间的区别。
- 接着,输入必要的用于装配(浓度,时间和长度)的参数。
- 绘制的归一化浓度对时间和整个x轴的浓度分布与多项式拟合到数据。
- 计算扩散使用的计算软件代码的系数。
5.实验测量
- 返回参照的扩散方程,重写方程找到特定浓度在系统内的任何位置,如图所示。
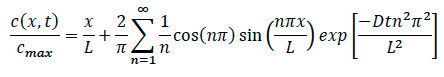
其中:
次的L =长度Ë胶原基质
在调查X =位置
D =系数扩散
T =经过时间 - 在实验中趋化,确保记录的那一刻趋化因子添加到系统的具体时间。一旦细胞迁移运动被发现,确保记录的共焦时间推移记录,并注意从边缘成像的地方发生的具体时间和地点。
- 在数据分析期间,插注意到经过时间,地点和扩散系数为特定的小区入方程找到在胶原为扩散和细胞实验中的任何点的归一特定的浓度。
6.跟踪细胞迁移利用TFM
- 要使用TFM / DVC技术遵循以下协议跟踪细胞迁移:
- 在加入所需的化学引诱物的浓度成孔#3之后,开始成像的3D胶原基质与安装在一个倒MICR共焦系统oscope需要找一个小区进行调查。
- 一旦移动单元找到,将细胞在视场的中间,并利用一压电马达(到图像中的z轴),图像每1或2分钟。
- 为了计算单元力产生变形,产生一个计算程序,找到下面的TFM / DVC协议31的荧光珠的位移。
结果
该测定的准确评估细胞迁移的能力依赖于该系统的一个良好的设置。因此,它是为要确保设计的扩散系统模具准确和非常谨慎地放置两个疏水和亲水盖玻片, 如图1关键的。如果系统设计正确,并且在扩散建模台确保找到一个很良好的线性起跑线,一个是能够实现很好的荧光图像,描绘在图2中 ,用于分析所述系统的扩散。
在成功的关键细胞趋化分析...
讨论
对于成功的扩散实验或不含有细胞的最重要的步骤是:正确设置的模具组件;开发必要的手巧,以防止提取疏水盖玻片的过程中损坏;确保找到一个很好的线性起跑线正确计算扩散系数;既纠正胶原蛋白和趋化实验计算;正确使用活细胞成像系统,以确保基质不干燥的;并保持无菌,健康培养。
当进行扩散实验,就必须确保扩散曲线匹配的线性扩散模型的传统形状( 图4)?...
披露声明
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
致谢
The authors would like to acknowledge Drs. Jonathan Reichner and Angle Byrd for cell experiment insight. The National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Program (GRFP) supported this work.
材料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Silicone elastomer kit | Dow Corning Corp | 182 SIL ELAST KIT .5KG | a two-part misture with a 10:1 mix |
| Live cell imaging chamber | Live Cell Instrument | CM-B18-1 | CMB for 18 mm round coverslips |
| 22 mm Glass Coverslip | Fisher Scientific | NC0180281 | Neuvitro Corp. cover slip 22 mm 1.5 |
| Machined aluminum metal cube | |||
| Hobby utility knife | X-Acto | X3201 | |
| 3-(aminopropyl) trimethoxysilane | Sigma-Aldrich | 281778-5ML | |
| Glutaraldehyde | Polysciences, Inc | 00216A-10 | Glutaraldehyde, EM Grade, 8% |
| 50 ml tube | Fisher Scientific | 14-432-22 | Standard floor model and tabletop centrifuges |
| Glass Petri dish | Fisher Scientific | 08-747A | Reusable Petri Dishes: Complete (60 x 15 mm) |
| Forceps | Fisher Scientific | 22-327-379 | Fine Point Forceps |
| Cover glasses | Fisher Scientific | 12-518-105A | Rectangle; 30 x 22 mm; Thickness No. 1 |
| Tridecafluoro-1,1,2,2-tetrahydrooctyl | Gelest | SIT8174.0 | |
| Acetic acid | Sigma-Aldrich | 320099 | Acetic acid ACS reagent, ≥99.7% |
| Hexane | Sigma-Aldrich | 296090 | anhydrous, 95% |
| Ethyl alcohol | Sigma-Aldrich | E7023 | 200 proof, for molecular biology |
| High-precision diamond scribing tool | Lunzer | PV-081-3 | Straight extended tip scribe, .020" (.50 mm) diameter by .200" (5.0 mm) tip length |
| Vacuum grease | Dow Corning | 14-635-5C | High-Vacuum Grease |
| 15 ml tube | Fisher Scientific | 14-959-49D | 15 ml conical centrifuge tubes with hydrophobic, biologically inert surface |
| 10x phosphate buffered solution | Fisher Scientific | BP399-500 | 1.37 M Sodium Chloride, 0.027 M Potassium Chloride, and 0.119 M Phosphate Buffer |
| 1 N sodium hydroxide | Sigma-Aldrich | 38215 | Sodium hydroxide concentrate |
| Collagen I, rat tail | BD Biosciences | 354236 | Rat tail |
| Micro centrifuge tube | Fisher Scientific | 02-681-332 | Volume: 2.0 ml; O.D. x L: 13 x 40 mm; sterile; single-wrapped |
| [header] | |||
| Carboxylate-modified microspheres | Invitrogen | F-8813 | Carboxylate-modified microspheres, 0.5 µm, yellow-green fluorescent (505/515), 2% solids |
| Rhodamine | Sigma-Aldrich | 83689 | Rhodamine B for fluorescence |
参考文献
- Adzick, N. S. The Molecular and Cellular Biology of Wound Repair. Ann Surg. 225 (2), 236 (1997).
- Reddi, A. H. Bone morphogenetic proteins: an unconventional approach to isolation of first mammalian morphogens. Cytokine Growth F. R. 8 (1), 11-20 (1997).
- Coussens, , Werb, Z, L. M., Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. 420 (6917), 860-867 (2002).
- Vital-Lopez, F. G., Armaou, A., Hutnik, M., Maranas, C. D. Modeling the effect of chemotaxis on glioblastoma tumor progression. AIChE J. 57 (3), 778-792 (2011).
- Hughes-Alford, S. K., Lauffenburger, D. A. Quantitative analysis of gradient sensing: towards building predictive models of chemotaxis in cancer. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 24 (2), 284-291 (2012).
- Friedl, P., Gilmour, D. Collective cell migration in morphogenesis, regeneration and cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol Cell Bio. 10 (7), 445-457 (2009).
- Cristini, V. Morphologic Instability and Cancer Invasion. Clin. Cancer Res. 11 (19), 6772-6779 (2005).
- Lammermann, T., et al. Rapid leukocyte migration by integrin-independent flowing and squeezing. Nature. 453 (7191), 51-55 (2008).
- Parent, C. A., Devreotes, P. N. A cell's sense of direction. Science. 284 (5415), 765-770 (1999).
- Boyden, S. The chemotactic effect of mixtures of antibody and antigen on polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J. Exp. Med. 115, 453-466 (1962).
- Nelson, R. D., Quie, P. G., Simmons, R. L. Chemotaxis under agarose: a new and simple method for measuring chemotaxis and spontaneous migration of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes. J. Immunol. 115 (6), 1650-1656 (1975).
- Rosoff, W. J., McAllister, R., Esrick, M. A., Goodhill, G. J., Urbach, J. S. Generating controlled molecular gradients in 3D gels. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 91 (6), 754-759 (2005).
- Wells, A., Kassis, J., Solava, J., Turner, T., Lauffenburger, D. A. Growth factor-induced cell motility in tumor invasion. Acta Oncol. 41 (2), 124-130 (2002).
- Wilkinson, P. C. Assays of leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. J. Immunol. Methods. 216 (1-2), 139-153 (1998).
- Bonvin, C., Overney, J., Shieh, A. C., Dixon, J. B., Swartz, M. A. A multichamber fluidic device for 3D cultures under interstitial flow with live imaging: development, characterization, and applications. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 105 (5), 982-991 (2010).
- Noo, L. J., et al. Neutrophil chemotaxis in linear and complex gradients of interleukin-8 formed in a microfabricated device. Nat. Biotechnol. 20 (8), 826-830 (2002).
- Shao, J., et al. Integrated microfluidic chip for endothelial cells culture and analysis exposed to a pulsatile and oscillatory shear stress. Lab Chip. 9 (21), 3118-3125 (2009).
- Haessler, U., Kalinin, Y., Swartz, M. A., Wu, M. An agarose-based microfluidic platform with a gradient buffer for 3D chemotaxis studies. Biomed. Microdevices. 11 (4), 827-835 (2009).
- Friedl, P., Wolf, K. Tumour-cell invasion and migration: diversity and escape mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 3 (5), 362-374 (2003).
- Sixt, M., Lammermann, T. In vitro analysis of chemotactic leukocyte migration in 3D environments. Methods Mol. Biol. 769, 149-165 (2011).
- Zigmond, S. H. Ability of polymorphonuclear leukocytes to orient in gradients of chemotactic factors. J. Cell Biol. 75 (2 Pt 1), 606-616 (1977).
- Zicha, D., Dunn, G. A., Brown, A. F. A new direct-viewing chemotaxis chamber. J. Cell. Sci. 99 (Pt 4), 769-775 (1991).
- Gilbert, D. L. Macromolecular diffusion through collagen membranes. Int. J. Pharm. 47 (1-3), 79-88 (1988).
- Ramanujan, S., et al. Diffusion and convection in collagen gels: implications for transport in the tumor interstitium. Biophys. J. 83 (3), 1650-1660 (2002).
- Weadock, K., Silver, F. H., Wolff, D. Diffusivity of 125I-calmodulin through collagen membranes: effect of source concentration and membrane swelling ratio. Biomaterials. 7 (4), 263-267 (1986).
- Erikson, A., Andersen, H. N., Naess, S. N., Sikorski, P., Davies, C. d. L. Physical and chemical modifications of collagen gels: impact on diffusion. Biopolymers. 89 (2), 135-143 (2008).
- Moghe, P. V., Nelson, R. D., Tranquillo, R. T. Cytokine-stimulated chemotaxis of human neutrophils in a 3-D conjoined fibrin gel assay. J. Immunol. Methods. 180 (2), 193-211 (1995).
- Sundd, P., et al. Live cell imaging of paxillin in rolling neutrophils by dual-color quantitative dynamic footprinting. Microcirculation. 18 (5), 361-372 (2011).
- Sanders, E. R. Aseptic Laboratory Techniques: Volume Transfers with Serological Pipettes and Micropipettors. J. Vis. Exp. (63), 2754 (2012).
- Stephenson, F. H. . Calculations for Molecular Biology and Biotechnology: A Guide to Mathematics in the Laboratory 2e. , (2010).
- Bar-Kochba, E., Toyjanova, J., Andrews, E., Kim, K., Franck, C. A Fast Iterative Digital Volume Correlation Algorithm for Large Deformations. Exp. Mech. In press, (2014).
- Shenoy, V., Rosenblatt, J. Diffusion of Macromolecules in Collagen and Hyaluronic Acid, Rigid-Rod-Flexible Polymer Composite Matrixes. Macromolecules. 28 (26), 8751-8758 (1995).
- Leddy, H., Guilak, F. Site-Specific Molecular Diffusion in Articular Cartilage Measured using Fluorescence Recovery after Photobleaching. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 31 (7), 753-760 (2003).
转载和许可
请求许可使用此 JoVE 文章的文本或图形
请求许可探索更多文章
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。