需要订阅 JoVE 才能查看此. 登录或开始免费试用。
Method Article
利用 体内 出生后电穿孔研究小脑颗粒神经元形态和突触发育
Erratum Notice
摘要
在这里,我们描述了一种方法,当这些细胞细化其突触结构并形成突触以整合到整个脑回路中时,在出生后大脑发育的时间过程中可视化小鼠小脑中颗粒神经元的突触发生。
摘要
神经元在大脑发育过程中经历其结构和功能的动态变化,以与其他细胞形成适当的连接。啮齿动物小脑是跟踪单细胞类型小脑颗粒神经元(CGN)随时间变化的发育和形态发生的理想系统。在这里,发育中的小鼠小脑中颗粒神经元祖细胞的 体内 电穿孔用于稀疏标记细胞以进行随后的形态学分析。该技术的功效体现在它能够展示CGN成熟的关键发育阶段,特别关注树突爪的形成,树突爪是这些细胞接收大部分突触输入的特殊结构。除了在整个小脑发育过程中提供CGN突触结构的快照外,该技术还可以适应以细胞自主的方式对颗粒神经元进行遗传操作,以研究任何感兴趣的基因的作用及其对CGN形态,爪发育和突触发生的影响。
引言
大脑发育是一个从胚胎发生到出生后生命的漫长过程。在此期间,大脑整合了内在和外在刺激的组合,这些刺激塑造了树突和轴突之间的突触连接,最终指导行为。啮齿动物小脑是研究突触如何发展的理想模型系统,因为单个神经元类型的小脑颗粒神经元(CGN)的发育可以在从祖细胞过渡到成熟神经元时进行跟踪。这部分是由于大多数小脑皮层在出生后发育,这使得出生后易于遗传操作和细胞标记1。
在哺乳动物中,CGN分化始于胚胎发育结束时,当时后脑中的增殖细胞子集迁移到菱形唇上,在小脑表面形成次级生发区2,3,4。尽管它们完全致力于颗粒神经元祖细胞(GNP)身份,但这些细胞继续在外部颗粒层(EGL)的外部增殖,直到出生后第14天(P14)。这一层的增殖导致小脑的大规模扩张,因为这些细胞只产生CGNs5。一旦新生的CGN退出EGL中的细胞周期,它们就会向内迁移到内部颗粒层(IGL),留下一个轴突,该轴突将在小脑的分子层中分叉并行进,形成平行纤维,突触到浦肯野细胞上6。这些纤维在分子层中的位置取决于细胞周期退出的时间。
首先分化的CGN将其平行纤维留向分子层的底部,而分化的CGN的轴突聚集在顶部7,8。一旦CGN细胞体到达IGL,它们就开始细化树突并与附近的抑制性和兴奋性神经元形成突触。CGN的成熟树枝状树表现出具有四个主要过程的刻板结构。在CGN成熟过程中,这些树突末端的结构形成一个爪子,该爪子富含突触后蛋白9,10。这些称为树突爪的特殊结构包含颗粒神经元上的大部分突触,对于接收来自脑桥的苔藓纤维神经支配的兴奋性输入以及来自局部高尔基体细胞的抑制性输入非常重要。一旦完全配置,CGN的突触连接允许这些细胞将输入从小脑前核中继到浦肯野细胞,浦肯野细胞从小脑皮层投射到小脑深部核。
GNPs的出生后体内电穿孔优于其他基于标记的方法,例如病毒感染和转基因小鼠系的产生,因为可以在快速的时间轴上实现所需构建体的表达,并且该方法针对少量细胞群,可用于研究细胞自主效应。该方法已在先前的研究中用于研究CGN的形态发育;然而,这些研究集中在单个时间点或短时间窗口9,10,11,12,13。该标记方法与图像分析相结合,以记录出生后前三周CGN分化的整个时间过程中发生的CGN形态变化。这些数据揭示了中广核树突发育的动态,这是小脑回路构建的基础。
研究方案
注意:所有程序均根据杜克大学机构动物护理和使用委员会(IACUC)批准的协议进行。
1. 体内电穿孔或 IVE 的 DNA 制备(术前 1 天)
- 收集以下材料:纯化的DNA(每只动物0.5-25μg),3M乙酸钠,乙醇,固绿染料,超纯蒸馏水,磷酸盐缓冲溶液(PBS)(见材料表)。
注意:对于DNA,从Addgene(FUGW,https://www.addgene.org/14883/)获得在人泛素启动子下表达绿色荧光蛋白(GFP)的构建体。在无处不在的启动子的控制下表达GFP或其他荧光蛋白的任何构建体都应该起作用。使用这种技术进行CGN特异性标记不依赖于构建体,而是取决于电穿孔。 - 通过混合所需量的DNA,10%体积的3M乙酸钠和250%体积的100%冰冷乙醇来制备用于电穿孔的DNA。请注意,DNA会立即从溶液中沉淀出来。
- 继续在-20°C下沉淀DNA混合物过夜或在-80°C下沉淀一小时。
- 沉淀在台式离心机中以>16,000 × g 沉淀DNA,并用70%乙醇洗涤两次。
- 让DNA沉淀完全干燥,并在1x PBS + 0.02%快速绿色溶液中复溶。

图 1:使用垫片将注射深度限制为 1.5 mm。 (A) 使用剃须刀片将 11.2 mm 段从装载移液器上切断。(B)垫片安装在汉密尔顿注射器的尖端(总长度为1.27厘米或0.5英寸),并用粘合剂或封口膜固定。暴露的尖端长度应为 1.5 毫米。请点击此处查看此图的大图。
2.出生后7日龄小鼠颗粒神经元祖细胞的 体内 电穿孔
注意:所有电穿孔手术均在无菌和高度通风的手术室中进行,所有人员都穿着完整的个人防护设备,包括手套、口罩、发帽、长袍和鞋套。或者,手术可以在通风和无菌罩中进行。
- 收集以下材料:用于电穿孔的DNA,小型手术剪刀,小型手术镊子,定制的汉密尔顿注射器,棉尖涂抹器,加热垫,betadine,70%乙醇,1x PBS,封口膜,组织粘合剂(氰基丙烯酸正丁酯),异氟醚,电穿孔器和镊子型电极(见 材料表)。
- 从无菌装载尖端切下垫片以适合汉密尔顿注射器,以将注射深度限制在 1.5 毫米(图 1A,B)。用粘合剂或封口膜固定垫片。
- 在异氟醚室中以0.8L / min的输送速率麻醉P7幼崽。通过监测动物呼吸减少和缺乏脚趾或尾巴捏反应来确认完全麻醉(图2A)。
- 一旦动物完全麻醉,将幼崽放在装有鼻锥的基座上,以 0.8 L/min 的递送速率提供恒定的 4% 异氟醚。用βdine的无菌拭子清洁幼犬的头顶3次,然后用70%乙醇,在两者之间交替,以准备该部位。让溶液干燥后再继续。
- 使用一把无菌剪刀,用一个切口做一个小切口,跨越从顶部到耳朵底部的距离,露出后脑(图2B)。
- 找到小脑(图2C),将汉密尔顿注射器的暴露尖端插入颅骨,垂直于大脑,并通过缓慢推动注射器的后柱塞将1.5μLDNA混合物注入小脑实质。输送DNA混合物后,缓慢地将针头拉回以防止回溢出,并使DNA溶液扩散30秒。
- 关闭异氟醚,并将幼犬放在37°C的加热垫上。通过将两端浸入无菌的 1x PBS 中来准备用于电穿孔的镊子型电极。
注意:润湿镊子型电极将防止在电脉冲给药期间幼犬皮肤上的接触灼伤。 - 将镊子电极定向到注射部位上方,正端朝下,负端在动物头部上方(图2D)。使用以下设置从电穿孔器施用五个电脉冲:50 ms、130 V 和 950 ms 脉冲间间隔。
注意:如果需要,请进行测试注射以确保注射部位位于小脑蚓部(图2E)。 - 捏住切口,并用无毒的正丁酯氰基丙烯酸酯组织粘合剂密封伤口。用70%乙醇清洁伤口,因为任何微量的血液都会增加父母杀婴和同类相食的可能性。
- 让动物在37°C的加热垫上恢复,然后再将幼崽送回大坝。手术后每30分钟监测幼犬至少2小时,以确保完全康复。
注意:父母任何一方杀婴都很常见。为防止同类相食,在开始电穿孔之前,将公猪放在不同的笼子里,并始终将清洁和回收的幼崽(即 没有血迹,完全移动)放回原始床上用品上的原始笼子中。幼崽也可以用原始笼子里的粪便擦拭,以尽量减少血腥味。如果原始大坝继续蚕食她的幼崽,则可能需要使用代孕坝。
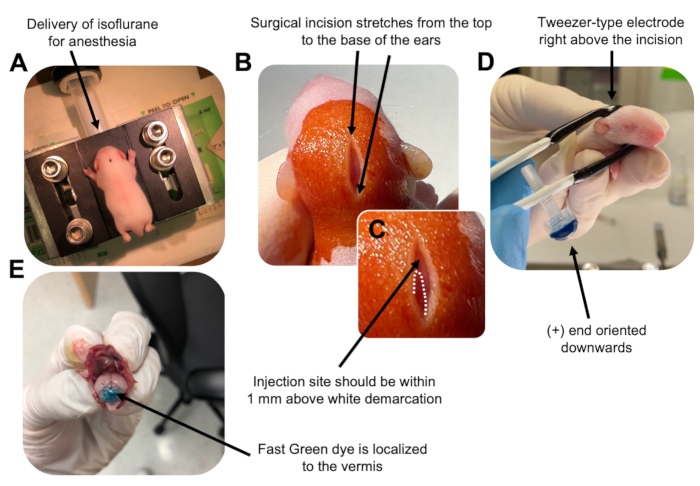
图 2: P7 野生型小鼠幼崽中颗粒神经元祖细胞的体内小脑电穿孔。 (A)幼崽用4%异氟醚以0.8L / min的速度输送麻醉,以确保在整个DNA溶液注射过程中麻醉。异氟醚以0.8L / min的速率输送。 (B)用甜菜碱和70%乙醇对小鼠灭菌3次后,做一个跨越耳朵距离的切口,露出后脑。(C)颅骨上白色分界线的放大图像,这是注射部位的标志。DNA构建体应在标记上方1毫米内注射;虚线勾勒出分界线,黑色箭头表示注射部位。小脑蚓部的脊可能是可见的,可用于寻找注射部位。(D) 镊子型电极取向,可实现高效电穿孔。加号(+)端必须向下定向,以便在给予电脉冲之前将带负电荷的DNA拉入小脑实质。(E) 测试注射 1 μL 的 0.02% Fast Green 染料,显示注射位于小叶 5-7 之间的小脑蚓部中部。请点击此处查看此图的大图。
3. 电穿孔CGN的免疫组化
- 收集以下材料:异氟醚,1x PBS,4%多聚甲醛(PFA),30%蔗糖,普通山羊血清,非离子洗涤剂,载玻片,玻璃盖玻片,指甲油,封片剂,Hoechst核染料以及适当的一抗和二抗(见材料表)。
- 用异氟醚麻醉实验动物,并用脚趾和尾巴捏确认完全麻醉。
- 通过将 1x PBS 和 4% PFA 缓慢注射到动物心脏的左心室来进行经心灌注。通过切割腔静脉让血液从动物身上排出。
- 通过将大脑浸入4°C的4%PFA中来固定大脑过夜。 第二天,用1x PBS快速冲洗大脑,并将大脑转移到1x PBS中的30%蔗糖中进行冷冻保护至少24小时。
- 如有必要,沿口尾轴将大脑切成两半,并使用正置荧光解剖显微镜确认转染报告构建体的表达。
注意:将大脑浸没在小盘中的 1x PBS 中,以防止其变干。 - 将大脑安装在冷冻切片机上,切片25μm矢状切片,并让切片在1x PBS和甘油的1:1混合物中展开。
注意:切片可以储存在-20°C的冷冻保护剂溶液中,以便长期储存。 - 在1x PBS中洗涤切片三次,每次10分钟以除去冷冻保护剂,并在室温下在轨道振荡器上用1x PBS + 10%正常山羊血清+ 0.2%非离子洗涤剂封闭组织1小时。
- 制备一抗溶液:1x PBS,10%山羊血清,0.2%非离子洗涤剂和抗GFP抗体,并以>16,000× g离心溶液5分钟。将抗体溶液中的切片在4°C的轨道振荡器上孵育48小时。
- 用1x PBS + 0.2%非离子洗涤剂洗掉一抗溶液15分钟五次。
- 制备二抗溶液:1x PBS、10% 山羊血清、0.2% 非离子去垢剂和适当的二抗检测 GFP;以 >16,000 × g 离心溶液。在室温下在轨道振荡器上孵育抗体溶液中的切片2-3小时。保护切片免受光照,以防止漂白。
- 用1x PBS + 0.2%非离子洗涤剂洗掉二抗溶液三次,每次15分钟。在 1x PBS + Hoechst 中孵育切片 5 分钟以染色细胞核。
- 用 1x PBS + 0.2% 非离子洗涤剂洗掉 Hoechst 溶液,然后安装到载玻片上。用安装介质覆盖切片,盖上载玻片,并用指甲油密封载玻片以防止蒸发。
4. CGN的形态学分析-三维(3D)重建和表面积和细胞体积
- 在共聚焦显微镜上以63倍物镜和2倍变焦对单个电穿孔CGN进行成像,以每叠0.5μm的速度拍摄z-stack图像。每个图像窗口对一个单元格进行成像,以便于图像分析和重建。
- 使用以下链接(https://imagej.net/Simple_Neurite_Tracer:_Basic_Instructions)安装斐济的简单神经突示踪器插件,以轻松有效地在三维(3D)空间中追踪电穿孔CGN的结构。
注意:有插件 (https://imagej.net/SNT) 的更新版本。 - 使用简单的神经突示踪剂以盲方式分析神经突长度和树枝状爪的形成。将电穿孔CGN的单通道z-stack图像上传到斐济,然后单击 插件|细分 |简单的神经突示踪剂 (图3D)。
- 访问下拉菜单,然后选择 创建新的 3D 查看器 (图 3D)。
- 滚动到树突的底部,在那里它连接到细胞体,并通过单击连接开始路径。通过单击单元格填充信号最亮的部分来手动跟踪路径,按 [y] 保留跟踪。如果树突不包含爪子,则跟踪直到枝晶的末端或直到爪子的底部,然后按[f]确认路径(图4D)。
- 接下来,通过在结构底部开始一条路径并追踪直到最长神经突的末端来追踪爪子。通过在 Windows 上按住 [ctrl] 或在 Mac OS 上按住 [alt] 并单击路径来跟踪二级和三级分支。按 [f] 确认路径。
- 观察迹线的测量值在单独的窗口中可见;将爪分支(初级、次级、三级)的所有测量值相加,得出每个爪子的总长度。
- 要分析电穿孔CGN的表面积和细胞体积,请下载Imaris细胞分析软件(https://imaris.oxinst.com/)。
注意:斐济还可用于使用现成的免费插件从 z 堆栈图像重建 3D 单元格。此外,Simple Neurite Tracer中还有一个体积渲染功能,但出于以下原因使用了Imaris。 - 将电穿孔CGN的z堆栈图像上传到Imaris上。通过按 Beyondpass 访问 3D 重建工具包。
- 要重建 CGN,请按 "曲面",然后选择包含图像窗口中整个单元格的感兴趣区域。完成后,按 "创建"下右下角的蓝色向前箭头。
- 如果图像包含不同信号的多个通道,请选择包含电穿孔 CGN 的通道,然后按蓝色向前箭头。
- 使用滑动条,设置最准确地拟合电穿孔细胞信号的所需阈值。放大靠近像元表面的位置以准确确定阈值。完成后,按双绿色箭头重建单元格并从元数据中获取表面积和体积大小。
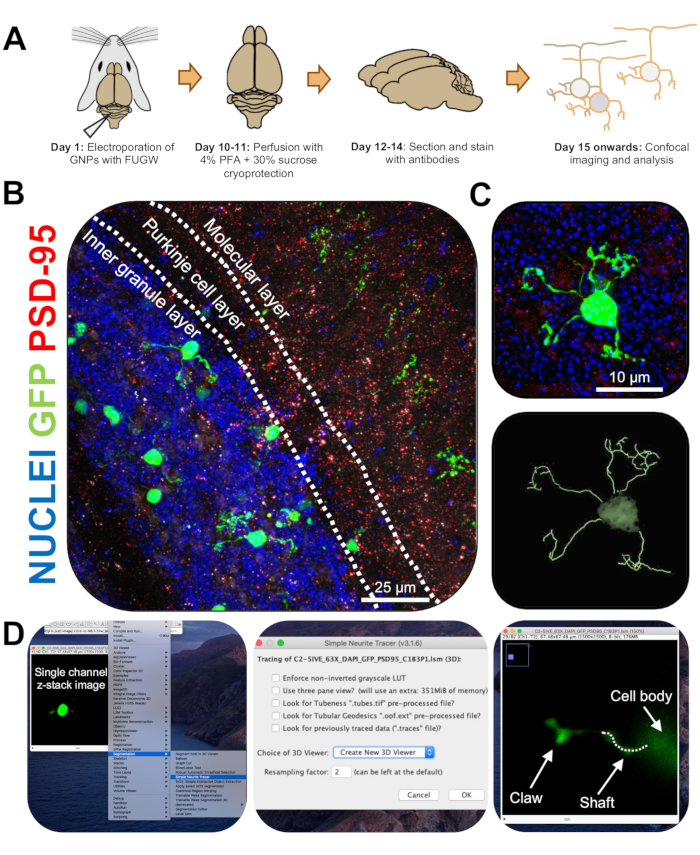
图3:电穿孔颗粒神经元的免疫组织化学分析和三维重建。 用表达GFP的构建体对P7 CD-1小鼠进行电穿孔。收集大脑并进行免疫组织化学,共聚焦显微镜和3D重建以进行形态学分析。(A) 从电穿孔到 10-DPI 鼠标图像处理的时间线。(B)电穿孔小脑10-DPI矢状横截面的最大投影图像;白线划定小脑层,比例尺为25μm。 (C)单个电穿孔颗粒神经元10-DPI的最大投影图像和相应的3D迹线,比例尺为10μm。 (D)使用FIJI插件Simple Neurite Tracer生成3D重建。所有测量都通过z堆栈跟踪,遵循细胞填充信号。分别追踪每个树突的轴和爪测量值;虚线表示当前平面内枝晶的一部分。缩写:3D = 三维;GFP = 绿色荧光蛋白;DPI = 注射后天数;PSD-95 = 突触后密度蛋白 95;GNPs = 颗粒神经元祖细胞;PFA = 多聚甲醛。 请点击此处查看此图的大图。
结果
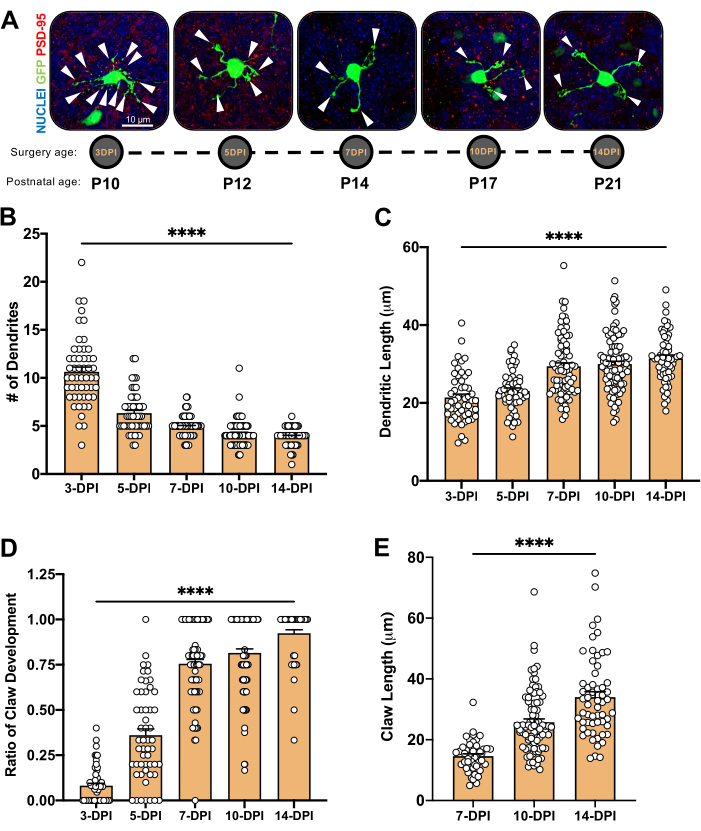
图4:小脑发育过程中颗粒神经元形态分析。 (A) 从3DPI到14DPI(出生后年龄P10至P21)、细胞核(蓝色)和GFP(绿色)的电穿孔CGN的最大投影图像;箭头表示单个树突,比例尺为10μm。 (B)树突的平均数量。(C)从体细胞基部到枝晶尖端测量的平均枝晶长度。(
讨论
小脑颗粒神经元是哺乳动物大脑中最丰富的神经元,几乎占啮齿动物大脑中神经元总数的60-70%1,14。小脑已被广泛用于阐明细胞增殖、迁移、树突形成和突触发育的机制6,9,10,11,15,16,17,18,
披露声明
作者声明不存在利益冲突。
致谢
这项工作得到了NIH资助R01NS098804(A.E.W.),F31NS113394(U.C.)和杜克大学夏季神经科学项目(D.G.)的支持。
材料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Betadine | Purdue Production | 67618-150-17 | |
| Cemented 10 µL needle | Hamilton | 1701SN (80008) | 33 gauge, 1.27 cm (0.5 in), 4 point style |
| Chicken anti-GFP | Millipore Sigma | AB16901 | Our lab uses this antibody at a 1:1000 concentration |
| Cotton-tip applicator | |||
| Donkey anti-chicken Cy2 | Jackson ImmunoResearch | 703-225-155 | Our lab uses this antibody at a 1:500 concentration |
| Ethanol (200 proof) | Koptec | V1016 | |
| Electroporator ECM 830 | BTX Harvard Apparatus | 45-0052 | |
| Fast Green FCF | Sigma | F7252-5G | |
| FUGW plasmid | Addgene | 14883 | |
| Glass slides | VWR | 48311-703 | Superfrost plus |
| Glycerol | Sigma-Aldrich | G5516 | |
| Heating pad | Softheat | ||
| Hoescht 33342 fluorescent dye | Invitrogen | 62249 | |
| Imaris | Bitplane | ||
| Isoflurane | Patterson Veterinary | 07-893-1389 | |
| Micro cover glass | VWR | 48382-138 | |
| Nail polish | Sally Hansen | Color 109 | |
| Normal goat serum | Gibco | 16210064 | |
| O.C.T. embedding compound | Tissue-Tek | 4583 | |
| Olympus MVX10 Dissecting Scope | Olympus | MVX10 | |
| P200 pipette reach tip | Fisherbrand | 02-707-138 | Used for needle spacer |
| Parafilm | Bemis | PM-996 | |
| PBS pH 7.4 (10x) | Gibco | 70011-044 | |
| Simple Neurite Tracer | FIJI | https://imagej.net/Simple_Neurite_Tracer:_Basic_ Instructions | |
| Sucrose | Sigma | S0389 | |
| Surgical tools | RWD Life Science | Small scissors and tweezers | |
| Triton X-100 | Roche | 11332481001 | non-ionic detergent |
| Tweezertrodes | BTX Harvard Apparatus | 45-0489 | 5 mm, platinum plated tweezer-type electrodes |
| Ultrapure distilled water | Invitrogen | 10977-015 | |
| Vectashield mounting media | Vectashield | H1000 | |
| Vetbond tissue adhesive | 3M | 1469SB | |
| Zeiss 780 Upright Confocal | Zeiss | 780 |
参考文献
- Altman, J., Bayer, S. A. . Development of the cerebellar system : in relation to its evolution, structure, and functions. , (1997).
- Rahimi-Balaei, M., Bergen, H., Kong, J., Marzban, H. Neuronal migration during development of the cerebellum. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 12, 484 (2018).
- Alder, J., Cho, N. K., Hatten, M. E. Embryonic precursor cells from the rhombic lip are specified to a cerebellar granule neuron identity. Neuron. 17 (3), 389-399 (1996).
- Hatten, M. E., Heintz, N. Mechanisms of neural patterning and specification in the developing cerebellum. Annual Review of Neuroscience. 18, 385-408 (1995).
- Ben-Arie, N., et al. Math1 is essential for genesis of cerebellar granule neurons. Nature. 390 (6656), 169-172 (1997).
- Borghesani, P. R., et al. BDNF stimulates migration of cerebellar granule cells. Development. 129 (6), 1435-1442 (2002).
- Espinosa, J. S., Luo, L. Timing neurogenesis and differentiation: insights from quantitative clonal analyses of cerebellar granule cells. Journal of Neuroscience. 28 (10), 2301-2312 (2008).
- Markwalter, K. H., Yang, Y., Holy, T. E., Bonni, A. Sensorimotor coding of vermal granule neurons in the developing mammalian cerebellum. Journal of Neuroscience. 39 (34), 6626-6643 (2019).
- Shalizi, A., et al. PIASx is a MEF2 SUMO E3 ligase that promotes postsynaptic dendritic morphogenesis. Journal of Neuroscience. 27 (37), 10037-10046 (2007).
- Shalizi, A., et al. A Calcium-regulated MEF2 sumoylation switch controls poststynaptic differentiation. Science. 311 (5763), 1012-1017 (2006).
- Konishi, Y., Stegmuller, J., Matsuda, T., Bonni, S., Bonni, A. Cdh1-APC controls axonal growth and patterning in the mammalian brain. Science. 303 (5660), 1026-1030 (2004).
- Holubowska, A., Mukherjee, C., Vadhvani, M., Stegmuller, J. Genetic manipulation of cerebellar granule neurons in vitro and in vivo to study neuronal morphology and migration. Journal of Visualized Experiments: JoVE. (85), e51070 (2014).
- Yang, Y., et al. Chromatin remodeling inactivates activity genes and regulates neural coding. Science. 353 (6296), 300-305 (2016).
- Herculano-Houzel, S. Coordinated scaling of cortical and cerebellar numbers of neurons. Frontiers in Neuroanatomy. 4, 12 (2010).
- Wilson, P. M., Fryer, R. H., Fang, Y., Hatten, M. E. Astn2, a novel member of the astrotactin gene family, regulates the trafficking of ASTN1 during glial-guided neuronal migration. Journal of Neuroscience. 30 (25), 8529-8540 (2010).
- Kokubo, M., et al. BDNF-mediated cerebellar granule cell development is impaired in mice null for CaMKK2 or CaMKIV. Journal of Neuroscience. 29 (28), 8901-8913 (2009).
- Schwartz, P. M., Borghesani, P. R., Levy, R. L., Pomeroy, S. L., Segal, R. A. Abnormal cerebellar development and foliation in BDNF-/- mice reveals a role for neurotrophins in CNS patterning. Neuron. 19 (2), 269-281 (1997).
- Segal, R. A., Pomeroy, S. L., Stiles, C. D. Axonal growth and fasciculation linked to differential expression of BDNF and NT3 receptors in developing cerebellar granule cells. Journal of Neuroscience. 15 (7), 4970-4981 (1995).
- Zhou, P., et al. Polarized signaling endosomes coordinate BDNF-induced chemotaxis of cerebellar precursors. Neuron. 55 (1), 53-68 (2007).
- Dhar, M., Hantman, A. W., Nishiyama, H. Developmental pattern and structural factors of dendritic survival in cerebellar granule cells in vivo. Scientific Reports. 8 (1), 17561 (2018).
- Ito, M. Synaptic plasticity in the cerebellar cortex and its role in motor learning. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences. 20, 70-74 (1993).
- Jorntell, H., Hansel, C. Synaptic memories upside down: bidirectional plasticity at cerebellar parallel fiber-Purkinje cell synapses. Neuron. 52 (2), 227-238 (2006).
- Nakanishi, S. Genetic manipulation study of information processing in the cerebellum. Neuroscience. 162 (3), 723-731 (2009).
- Chang, C. H., et al. Atoh1 controls primary cilia formation to allow for SHH-triggered granule neuron progenitor proliferation. Developmental Cell. 48 (2), 184-199 (2019).
Erratum
Formal Correction: Erratum: Utilizing In Vivo Postnatal Electroporation to Study Cerebellar Granule Neuron Morphology and Synapse Development
Posted by JoVE Editors on 4/06/2023. Citeable Link.
An erratum was issued for: Utilizing In Vivo Postnatal Electroporation to Study Cerebellar Granule Neuron Morphology and Synapse Development. A figure was updated.
Figure 2 was updated from:
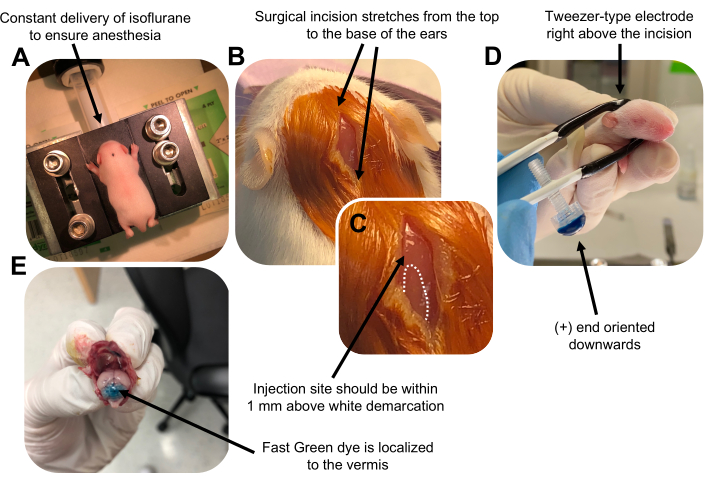
Figure 2: In vivo cerebellar electroporation of granule neuron progenitors in P7 wildtype mouse pups. (A) Pups are anesthetized with 4% isoflurane delivered at a rate of 0.8L/min to ensure anesthesia throughout the injection of the DNA solution. Isoflurane is delivered at a rate of 0.8 L/min. (B) After sterilizing the mouse 3 times with betadine and 70% ethanol, an incision is made that spans the distance of the ears, revealing the hindbrain. (C) A magnified image of a white demarcation on the cranium, a landmark for the injection site. DNA construct should be injected within 1 mm above the mark; dotted lines outline the demarcation, and black arrow denotes the injection site. The ridges of the cerebellar vermis may be visible and can be useful for finding the injection site. (D) Tweezer-type electrode orientation for efficient electroporation. Plus (+) end must be oriented downwards to pull negatively charged DNA into the cerebellar parenchyma prior to administration of electrical pulses. (E) Test injection of 1 µL of a 0.02% Fast Green dye shows injection is localized to the middle of the cerebellar vermis between lobules 5-7. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
to:

Figure 2: In vivo cerebellar electroporation of granule neuron progenitors in P7 wildtype mouse pups. (A) Pups are anesthetized with 4% isoflurane delivered at a rate of 0.8L/min to ensure anesthesia throughout the injection of the DNA solution. Isoflurane is delivered at a rate of 0.8 L/min. (B) After sterilizing the mouse 3 times with betadine and 70% ethanol, an incision is made that spans the distance of the ears, revealing the hindbrain. (C) A magnified image of a white demarcation on the cranium, a landmark for the injection site. DNA construct should be injected within 1 mm above the mark; dotted lines outline the demarcation, and black arrow denotes the injection site. The ridges of the cerebellar vermis may be visible and can be useful for finding the injection site. (D) Tweezer-type electrode orientation for efficient electroporation. Plus (+) end must be oriented downwards to pull negatively charged DNA into the cerebellar parenchyma prior to administration of electrical pulses. (E) Test injection of 1 µL of a 0.02% Fast Green dye shows injection is localized to the middle of the cerebellar vermis between lobules 5-7. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
转载和许可
请求许可使用此 JoVE 文章的文本或图形
请求许可探索更多文章
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。