需要订阅 JoVE 才能查看此. 登录或开始免费试用。
用于基于抗体的治疗分子质量数计算的开源框架
摘要
本文介绍了如何使用软件应用程序mAbScale来计算基于单克隆抗体的蛋白质疗法的质量数。
摘要
生物治疗肿块是验证身份和结构完整性的一种手段。完整蛋白质或蛋白质亚基的质谱 (MS) 为生物制药开发的不同阶段提供了一种简单的分析工具。当MS的实验质量数在理论质量数的预定义质量数误差范围内时,蛋白质的身份得到确认。虽然有几种计算工具可用于计算蛋白质和肽分子量,但它们要么不是为直接应用于生物治疗实体而设计的,要么由于付费许可证而存在访问限制,要么需要将蛋白质序列上传到主机服务器。
我们开发了一种模块化质量数计算程序,可以轻松测定治疗性糖蛋白(包括单克隆抗体 (mAb)、双特异性抗体 (bsAb) 和抗体-药物偶联物 (ADC))的平均或单同位素质量数和元素组成。这个基于 Python 的计算框架的模块化特性将允许该平台在未来扩展到其他模式,例如疫苗、融合蛋白和寡核苷酸,并且该框架也可用于自上而下的质谱数据查询。通过创建具有图形用户界面 (GUI) 的开源独立桌面应用程序,我们希望克服在无法将专有信息上传到基于 Web 的工具的环境中使用的限制。本文介绍了mAbScale工具在不同基于抗体的治疗方式中的算法和应用。
引言
在过去的二十年里,生物治疗药物已经发展成为现代制药工业的中流砥柱。SARS-CoV2 大流行和其他危及生命的疾病进一步增加了对更快、更广泛地开发生物制药分子的需求 1,2,3。
生物治疗药物分子量与其他分析检测相结合,对于分子的鉴定至关重要。完整和减少的亚基质量数用于整个发现和开发生命周期,作为旨在保持质量的控制策略的一部分,如QTPP(质量目标产品简介)4中所述。
生物制药行业的分析开发在很大程度上依赖于质量测量,以使用肽图分析或多属性方法(MAM)监测进行完整质量分析和深度表征。利用现代质谱 (MS) 平台的这些技术的核心是能够提供高分辨率的精确质量 (HR/AM) 测量。大多数HR/AM仪器的质量精度在0.5-5 ppm范围内,与质量范围成正比。准确测量完整大分子质量数的能力能够快速、可靠地鉴定大分子治疗药物。由于使用大分子(>10 kDa)的典型实验条件无法获得同位素分辨率,因此必须计算平均质量数以进行比较和鉴定5,6。<....
研究方案
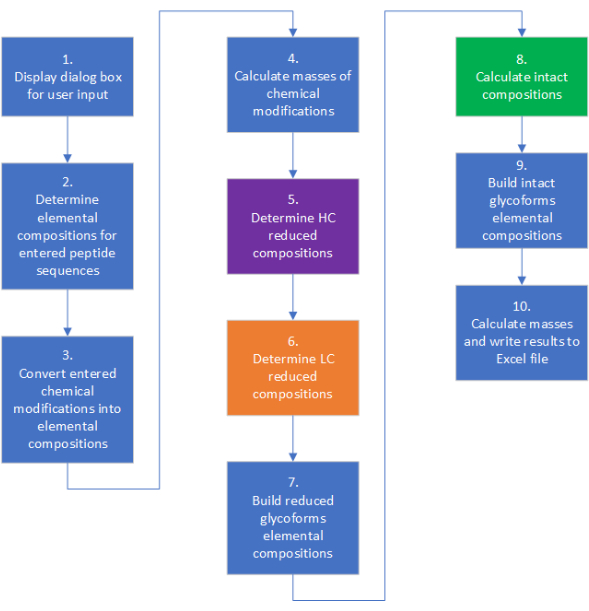
mAbScale 的高级工作流程 如图 2 所示。每个步骤都有更复杂的内部决策分支、循环和组合函数。描述计算过程的详细算法工作流程见 补充图 1。应用程序输出以电子表格格式保存在用户选择的文件夹中。输出文件由多个单独的工作表组成,这些工作表可以归类为用户输入、分子量计算和平均同位素质量数推导的参考(补充表中提供了示例输出)。用户输入的工作表包括用户输入的蛋白质氨基酸序列和其他信息、平均元素质量和聚糖质量,用于计算元素组成和不同分子量。分子量计算表包括各种形式的化学组成、有和没有糖基化和化学修饰的还原质量数,以及有和没有糖基化和化学修饰的完整质量数。如果用户在用户输入页面中输入两种不同的 HC 和/或两种不同的 LC,则将自动生成含有半抗体质量的纸,因为半抗体是需要相对于所需异二聚体进行鉴定和定量的主要杂质。mAbScale 的源代码可通过以下存储库访问:https://github.com/kkhatri99/mAbScale。
结果
选择多种单克隆抗体来代表不同类型的单克隆抗体。选择市售的mAb标准品来表示在Fc区域具有相同重链、相同轻链和一个N-连接糖基化位点的常规mAb。此外,还选择了具有额外轻链 N-连接糖基化的单克隆抗体、双特异性单克隆抗体和抗体-药物偶联物 (ADC) 单克隆抗体,以扩大应用范围。 表1总结了这些示例mAb的化学成分、计算质量数、测量质量和质量数误差。mAbScale报告的蛋白质化学.......
讨论
mAbScale提供了一个直观的用户界面,可以灵活地改变质量数和元素计算的构建模块。用户应对目标分子有基本的了解,以便使用该应用程序,得出正确的质量数,并解释结果。例如,由于完整或减少质量数的行数众多,完整或减少的质量输出表可能会让人不知所措,因为默认的聚糖数据库包含88种N-连接聚糖,这些聚糖通常存在于治疗性抗体的Fc部分,并且该应用程序计算了数据库18
披露声明
该软件在 Apache 2.0 许可下发布。葛兰素史克研究与发展有限公司版权所有 (2022)。保留所有权利。根据 Apache 许可证 2.0 版(以下简称“许可证”)获得许可;除非遵守许可,否则您不得使用此文件。您可以在 http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 获取许可证的副本。除非适用法律要求或书面同意,否则根据许可分发的软件按“原样”分发,不附带任何明示或暗示的保证或条件。请参阅许可证,了解许可证下管理权限和限制的特定语言。L.C.是葛兰素史克(GSK)的员工。T.H. 和 K.K. 作为 GSK 的员工开发了该软件,现在分别是 Merck 和 Moderna 的合作伙伴。
致谢
作者感谢罗伯特·舒斯特(Robert Schuster)在数据验证方面的帮助。
....材料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Acquity UPLC system | Waters Corp., Milford, MA | N/A | Modular system |
| Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) | GlaxoSmithKline | N/A | Proprietory molecule |
| BEH 200 SEC column | Waters Corp., Milford, MA | 176003904 | |
| Bispecific mAb | GlaxoSmithKline | N/A | Proprietory molecule |
| Byos | Protein Metrics, Cupertino, CA | https://proteinmetrics.com/byos/ Version 4.5 | |
| GPMAW | GPMAW | http://www.gpmaw.com/ | |
| LC-MS grade water | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA | W6-1 | |
| mAb standard | Waters Corp., Milford, MA | 186009125 | Waters Humanized mAb Mass Check Standard |
| mAbScale | GlaxoSmithKline | Apache License, Version 2.0 | |
| Xevo G2 Q-TOF mass spectrometer | Waters Corp., Milford, MA | N/A | Modular system |
参考文献
- Reichert, J. M., Valge-Archer, V. E. Development trends for monoclonal antibody cancer therapeutics. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 6 (5), 349-356 (2007).
- Kintzing, J. R., Filsinger Interrante, M. V., Cochran, J. R.
转载和许可
请求许可使用此 JoVE 文章的文本或图形
请求许可探索更多文章
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。