Se requiere una suscripción a JoVE para ver este contenido. Inicie sesión o comience su prueba gratuita.
Aislamiento y cultivo de macrófagos sinoviales primarios y fibroblastos a partir de tejido murino de artritis
En este artículo
Resumen
El presente estudio proporciona un protocolo modificado para aislar macrófagos sinoviales y fibroblastos del tejido de artritis inflamatoria murina.
Resumen
La artritis reumatoide es una enfermedad autoinmune que provoca una inflamación crónica de las articulaciones. Los macrófagos sinoviales y los fibroblastos sinoviales tienen un papel central en la patogénesis de la artritis reumatoide. Es importante comprender las funciones de ambas poblaciones celulares para revelar los mecanismos subyacentes a la progresión patológica y la remisión en la artritis inflamatoria. En general, las condiciones experimentales in vitro deben imitar el entorno in vivo tanto como sea posible. Las células derivadas de tejidos primarios se han utilizado en experimentos que caracterizan los fibroblastos sinoviales en la artritis. Por el contrario, en experimentos que investigan las funciones biológicas de los macrófagos en la artritis inflamatoria, se han utilizado líneas celulares, macrófagos derivados de la médula ósea y macrófagos derivados de monocitos sanguíneos. Sin embargo, no está claro si estos macrófagos reflejan realmente las funciones de los macrófagos residentes en los tejidos. Para obtener macrófagos residentes, se modificaron los protocolos anteriores para aislar y expandir tanto los macrófagos primarios como los fibroblastos del tejido sinovial en un modelo de ratón con artritis inflamatoria. Estas células sinoviales primarias pueden ser útiles para el análisis in vitro de la artritis inflamatoria.
Introducción
La artritis reumatoide (AR) es una enfermedad autoinmune caracterizada por hiperplasia de la membrana sinovial, que conduce a la destrucción articular 1,2. Los macrófagos y fibroblastos residentes en los tejidos están presentes en la membrana sinovial sana para mantener la homeostasis articular. En los pacientes con AR, los fibroblastos sinoviales (SF) proliferan y las células inmunitarias, incluidos los monocitos, se infiltran en la membrana sinovial y en el líquido articular, procesos asociados a la inflamación 1,3,4. Los macrófagos sinoviales (SM), que incluyen los macrófagos residentes y los macrófagos derivados de monocitos de sangre periférica, y los SF se activan de forma aberrante y tienen un papel importante en la patogénesis de la AR. Estudios recientes han sugerido que las interacciones célula-célula entre los SM y los SF contribuyen tanto a la exacerbación como a la remisión de la AR 5,6.
Para comprender la patogénesis de la AR, se han utilizado varios modelos de artritis inflamatoria en roedores, incluida la artritis por transferencia sérica K/BxN, la artritis inducida por colágeno y la artritis inducida por anticuerpos de colágeno. Por lo general, se requieren ensayos basados en células para aclarar las funciones moleculares en la artritis. Por lo tanto, se han aislado células primarias de modelos animales de artritis. El método para aislar los SF del tejido murino de la artritis está bien establecido, y estas células han contribuido a la elucidación de los mecanismos moleculares en la patogénesis de la artritis 7,8. Por otro lado, los macrófagos derivados de la médula ósea, los macrófagos derivados de monocitos sanguíneos y las líneas celulares de macrófagos se han utilizado a menudo como recursos de macrófagos para estudios de artritis 9,10. Dado que los macrófagos pueden adquirir funciones asociadas con su microambiente, las fuentes generales de macrófagos pueden carecer de respuestas específicas para el tejido de la artritis. Además, es difícil obtener suficientes células sinoviales mediante la clasificación, ya que la membrana sinovial murina es un tejido muy pequeño incluso en modelos de artritis. La falta de uso de macrófagos sinoviales para estudios in vitro ha sido una limitación en los estudios de artritis. El establecimiento de un protocolo para aislar y expandir los macrófagos sinoviales sería una ventaja para la elucidación de los mecanismos patológicos en la AR.
En el método anterior para aislar SFs, los SMs fueron descartados7. Además de eso, se reportó un método para aislar y expandir macrófagos residentes de algunos órganos11. Por lo tanto, los protocolos existentes se modificaron en combinación. La modificación tiene como objetivo lograr el cultivo primario tanto de SM como de SF con alta pureza. El objetivo general de este método es aislar y expandir tanto los SM como los SF del tejido de la artritis murina.
Protocolo
Los experimentos con animales fueron aprobados por el Comité de Experimentos con Animales de la Universidad de Ehime y se realizaron de acuerdo con las Directrices de la Universidad de Ehime para Experimentos con Animales (37A1-1*16).
1. Preparación de instrumentos, reactivos y medios de cultivo
- Prepare el medio de cultivo de la siguiente manera: complemente el Medio Eagle Modificado de Dulbecco (DMEM) con un 10% de suero fetal bovino (FBS) y una solución antibiótica-antimicótica al 1% (anti-anti).
- Preparar el medio de digestión de la siguiente manera: complementar el medio de cultivo con 1 mg/ml de colagenasa tipo IV. Ajuste la concentración de colagenasa justo antes de usar.
- Diluir el colágeno tipo I-C a una concentración de 0,15 mg/ml con una solución de HCl de 1 mM. Inunde placas de cultivo (diámetro de 40 o 60 mm) con la solución de colágeno diluido. Después de 6-12 h a temperatura ambiente, retire la solución de colágeno de los platos y seque a temperatura ambiente. Los platos recubiertos de colágeno se pueden mantener a temperatura ambiente durante al menos 1 semana. Lave los platos prerrecubiertos con solución salina tamponada con fosfato (PBS) o medio antes de usarlos.
- Prepare instrumentos quirúrgicos estériles, como tijeras, pinzas con puntas dentadas y pinzas de punta fina. Remojar en etanol al 70% antes de usar.
2. Preparación del tejido de la sinovitis en ratones ( Figura 1A)
- Prepara un ratón con artritis inflamatoria en las patas traseras.
NOTA: Paraeste protocolo se utilizaron ratones hembra C57BL/6 (18-20 g), 7-8 semanas después del parto, con artritis inducida por anticuerpos de colágeno (CAIA) o artritis por transferencia sérica (STA) K/BxN 8. Aislar los SM del tejido no inflamado (es decir, sano) puede ser difícil, ya que el número de células es insuficiente. - Anestesiar a los ratones mediante una inyección intraperitoneal de 80 mg/kg de ketamina y 16 mg/kg de xilacina. Limpie los ratones con etanol al 70%.
- Corta la región pectoral con unas tijeras para exponer el corazón. Cortar la aurícula derecha del corazón con unas tijeras y luego introducir una aguja de mariposa de 23 G en el ventrículo izquierdo a través del ápice del corazón, seguido de un reflujo de 15-20 ml de PBS estéril con una jeringa para extraer manualmente la sangre periférica (aproximadamente 1 ml/2 s).
- Descorteza las patas traseras cortando la piel con unas tijeras y tirando de la piel con unas pinzas con puntas dentadas.
NOTA: Después de este paso, se recomienda el uso de pinzas para la manipulación de muestras. No toque el tejido descortezado con los dedos, para evitar la adhesión del pelo murino. - Disloque las articulaciones metatarsofalángicas tirando, seguido de un corte de los ligamentos de las articulaciones con unas tijeras para extraer los dedos de los pies.
- Corta los tendones de los músculos de la parte inferior de la pierna cerca del tobillo con unas tijeras. Agarre el tendón con pinzas y pele los músculos proximalmente en la parte inferior de la pierna para exponer la tibia. Retira el peroné.
- Disloque la articulación de la rodilla tirando, seguido de cortar los ligamentos de las articulaciones con unas tijeras para separar la tibia con la pata trasera hinchada. Mantener las muestras en un medio de cultivo helado (0,3 ml/cm2) hasta el paso 3.1.
3. Digestión del tejido de la sinovitis ( Figura 1B)
- Aspirar el medio de cultivo, evitando la muestra, y luego añadir medio de cultivo fresco (0,3 mL/cm2). Repite el proceso de lavado tres o cuatro veces.
NOTA: A partir de este paso, la manipulación de las muestras debe realizarse de forma aséptica en un banco limpio o en un armario de seguridad. - Disloque todas las uniones de las muestras tirando con pinzas de punta fina en el medio de cultivo bajo un microscopio estereoscópico (con un aumento de 10x-20x). Las pinzas de punta fina son convenientes en este paso. Extirpe la tibia y tantos vasos, tendones y ligamentos como sea posible. Tenga cuidado de no romper los huesos al dislocarse.
- Prepare dos tubos de 15 ml por muestra. Transfiera los huesos dislocados con tejidos blandos al primer tubo de 15 ml con pinzas. Añadir 4 mL de medio digestivo por muestra, obtenido de ambas patas traseras, en el tubo.
- Para recolectar células residuales y fragmentos de tejido, transfiera el medio en el que estaba contenida la muestra al segundo tubo de 15 ml. Centrifugar el medio a 500 x g durante 5 min a temperatura ambiente. Después de retirar el sobrenadante, vuelva a suspender el gránulo con 1 ml de medio de digestión y transfiera la solución de células y fragmentos de tejido al primer tubo de 15 ml que contiene casi todo el tejido (total de 5 ml de medio de digestión/patas traseras).
- Digirir la muestra durante 60-120 min a 37 °C agitando en un horno de hibridación.
NOTA: Se debe decidir el momento óptimo para digerir las muestras. El tiempo depende del grado de hinchazón en los tobillos y las colagenasas. En la mayoría de los casos, 60-120 minutos son suficientes. Después de 60 minutos de incubación, recoja una parte de la muestra digerida mediante pipeteo y observe bajo un microscopio. Si la digestión es insuficiente, la incubación debe continuar y la digestión debe controlarse cada 30 minutos. - Pipetear bien la solución. Filtre la solución celular a través de un filtro celular (tamaño de poro de 40 μm) hasta un tubo de 50 ml.
- Agregue 10 ml de medio de cultivo al tubo de 50 ml a través del filtro celular. Centrifugar a 300 x g durante 5 min a temperatura ambiente.
- Después de retirar el sobrenadante, vuelva a suspender con 10 mL de medio de cultivo. Repita la centrifugación. Después de retirar el sobrenadante, vuelva a suspender con 2 mL de medio de cultivo.
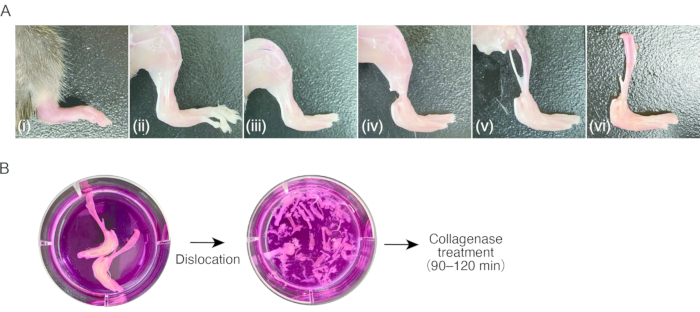
Figura 1: Procedimiento de muestreo del tejido de la artritis murina y digestión de la colagenasa . (A) (i) Pata trasera murina con artritis inflamatoria. ii) Extracción de la piel de la pata trasera. (iii) Luxación de las articulaciones metatarsofalángicas y extirpación de los dedos de los pies. (iv) Corte de los tendones del tobillo. (v) Extirpación de los músculos de la parte inferior de las piernas. (vi) Luxación de la articulación de la rodilla. b) Izquierda; patas extirpadas en medio de cultivo. Derecha; Tarso y metatarso dislocados en medio de cultivo. Haga clic aquí para ver una versión más grande de esta figura.
4. Aislamiento de fibroblastos sinoviales ( Figura 2A)
- Siembre todas las suspensiones celulares obtenidas de ambos tobillos en la placa recubierta de colágeno.
NOTA: Si se utilizan tobillos con hinchazón débil o moderada para obtener las células, se aplica un plato de 40 mm de diámetro. El tamaño de la placa recubierta de colágeno se puede cambiar a una placa de 60 mm de diámetro si ambos tobillos tienen una hinchazón severa. - Añadir medio de cultivo (aproximadamente 222 μL/cm2). Incubar durante 1 h a 37 °C en atmósfera humidificada con 5% de CO2.
- Recoja las células no adherentes con una pipeta (utilícelas en el paso 5.1). Lave el plato recubierto de colágeno con medio de cultivo y recoja el medio. Cultive las células adherentes en medio fresco (Figura 2B, i). La mayoría de las células que se adhieren rápidamente a la placa recubierta de colágeno exhiben una morfología fibroblastoide (en forma de huso).
- Eliminación de células subconfluentes mediante tratamiento con tripsina al 0,05% en solución salina equilibrada de Hanks (HBSS). En este método, la contaminación de otras células es limitada, aunque sea en la expansión inicial. Si se requieren más células purificadas similares a los fibroblastos, realice pases repetidos para permitir la mejora de la pureza; sin embargo, también se observa la expansión del citoplasma de las células en adhesión (Figura 2B, ii). Dado que los pasajes excesivos afectan la pérdida de características ingenuas en las células, utilice celdas con menos de 5 pasajes.
5. Aislamiento de macrófagos sinoviales ( Figura 2A)
- Siembre todas las células no adherentes del paso 4.4 en placas (diámetro de 40 o 60 mm) que no hayan sido recubiertas con colágeno.
NOTA: Las células no adherentes incluyen macrófagos, otros linfocitos y fibroblastos residuales del tejido de la sinovitis. - Cultivar las células a granel durante 1 día a 37 °C en una atmósfera humidificada con 5% de CO2.
- Para eliminar los linfocitos no adherentes, aspire el medio cultivado y, a continuación, agregue un medio de cultivo nuevo. Repita este proceso dos o tres veces (Figura 2B, iii).
- Cultive las células adherentes a granel durante 1-2 semanas en medio de cultivo, con cambios de medio cada 2 días mientras se mantiene la confluencia (Figura 2B, iv).
NOTA: El número de SM aumenta lentamente en condiciones de cocultivo con SF. Por lo tanto, el período de cocultivo debe ajustarse según sea necesario. - Lavar con PBS o HBSS dos veces. Tratar con tripsina al 0,05% en HBSS (aproximadamente 55 μL/cm2) durante 3 min a 37 °C en atmósfera humidificada con 5% de CO2. Los fibroblastos se desprenden fácilmente de la placa de cultivo mediante el tratamiento con tripsina, y los macrófagos exhiben resistencia al tratamiento con tripsina. Utilice esta propiedad para la selección de macrófagos sinoviales.
- Añadir medio de cultivo (aproximadamente 222 μL/cm2) suavemente a tripsina al 0,05% en HBSS. Después de este paso, no vierta el medio directamente sobre las células.
- Para eliminar las células desprendidas, aspire el medio cultivado y, a continuación, agregue suavemente el medio de cultivo fresco. Repite este proceso dos o tres veces. Mantenga las células restantes en la placa en medio de cultivo fresco hasta su uso (Figura 2B, v).
NOTA: Después del tratamiento con tripsina, las células adherentes exhiben características morfológicas similares a las de los macrófagos.

Figura 2: Separación de las fracciones ricas en macrófagos y fibroblastos del tejido inflamatorio de la artritis. (A) Esquema del procedimiento para separar las células ricas en macrófagos y fibroblastos del tejido de la artritis. (B) Imágenes representativas de contraste de fase de las etapas del procedimiento, (i) a (v) en la Figura 2A. La barra de escala representa 100 μm. Haga clic aquí para ver una versión más grande de esta figura.
Resultados
Los ratones hembra C57BL/6 a las 7-8 semanas de edad sufrieron artritis inducida por anticuerpos de colágeno. Las células similares a macrófagos y las células similares a fibroblastos se aislaron de forma independiente del tejido inflamatorio de la artritis de acuerdo con el procedimiento descrito anteriormente (Figura 2A, B). Las células similares a los macrófagos se utilizaron inmediatamente después del paso 5.7. Las células similares a los fibroblastos se cultivar...
Discusión
Este método desarrollado aquí mejora las técnicas anteriores para aislar tanto los SF de la artritis murina como los macrófagos residentes de varios órganos 7,11. El método modificado puede aislar tanto macrófagos como fibroblastos de la membrana sinovial inflamatoria con alta pureza, y es simple y reproducible. Dado que el método no requiere instrumentos complejos como un clasificador de células, cualquiera puede realizarlo. Además, la presente técnic...
Divulgaciones
Los autores declaran que no tienen intereses contrapuestos.
Agradecimientos
Los autores agradecen al personal de la División de Apoyo a la Investigación Médica, el Centro de Apoyo a la Investigación Avanzada (ADRES) y a los miembros de la División de Fisiopatología Integrativa del Centro de Proteociencia (PROS) de la Universidad de Ehime, por su asistencia técnica y apoyo útil. Este estudio fue financiado en parte por las subvenciones KAKENHI de la Sociedad Japonesa para la Promoción de la Ciencia (JSPS) JP17K17929, JP19K16015, JP21K05974 (a NS) y JP23689066, JP15H04961, JP15K15552, JP17K19728, JP19H03786 (a YI); subvenciones de la Fundación de Investigación Médica de Osaka para Enfermedades Intratables, la Fundación Nakatomi, la Beca Rising Stars de la Sociedad Japonesa para la Investigación Ósea y Mineral (JSBMR), la Fundación Sumitomo, la Fundación de Investigación Médica SENSHIN, la Fundación Mochida Memorial (a NS); y una beca de investigación médica de la Fundación Takeda de Ciencias, una beca de proyecto UCB Japón (UCBJ) y la beca JSBMR Frontier Scientist 2019 (a YI).
Materiales
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 5.0 g/L Trypsin/5.3 mmol/L EDTA solution | nacalai tesque | 35556-44 | Diluted with HBSS |
| Antibiotic–antimycotic (anti/anti) | Gibco | 15240-062 | |
| Butterfly needle | TERUMO | SV-23DLK | 23G |
| Cell strainer | Falcon | 352340 | 40 µm pore, Nylon |
| Cellmatrix Type I-C | Nitta gelatin | 637-00773 | Type I-C collagen |
| Centriguge tube 15 | TPP | 91014 | 15 mL tube |
| Centriguge tube 50 | TPP | 91050 | 50 mL tube |
| Collagenase from C. Histolyticum | Sigma | C5138 | Type IV collagenase |
| Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium GlutaMax (DMEM) | Gibco | 10569-010 | |
| Fetal bovine serum (FBS) | SIGAM | 173012 | Heat inactivation was performed |
| Hanks' balanced salt solution (HBSS) | Wako | 085-09355 | |
| Scissors | Bio Research Center | PRI28-1525A | |
| Tissue culture dish 40 | TPP | 93040 | For cell culture |
| Tissue culture dish 60 | TPP | 92006 | For cell culture |
| Tweezers | KFI | 1-9749-31 | Fine-point |
| Tweezers | Bio Research Center | PRI28-1522 | Serrated tip |
| ZEISS Stemi 305 | ZEISS | STEMI305-EDU | Stereomicroscope |
Referencias
- Smolen, J. S., Aletaha, D., McInnes, I. B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 388 (10055), 2023-2038 (2016).
- McInnes, I. B., Schett, G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. The New England Journal of Medicine. 365 (23), 2205-2219 (2011).
- Kurowska-Stolarska, M., Alivernini, S. Synovial tissue macrophages: friend or foe. RMD Open. 3 (2), (2017).
- Hannemann, N., Apparailly, F., Courties, G. Synovial macrophages: from ordinary eaters to extraordinary multitaskers. Trends in Immunology. 42 (5), 368-371 (2021).
- Alivernini, S., et al. Distinct synovial tissue macrophage subsets regulate inflammation and remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Medicine. 26 (8), 1295-1306 (2020).
- Saeki, N., Imai, Y. Reprogramming of synovial macrophage metabolism by synovial fibroblasts under inflammatory conditions. Cell Communication and Signaling. 18 (1), 188 (2020).
- Armaka, M., Gkretsi, V., Kontoyiannis, D., Kollias, G. A standardized protocol for the isolation and culture of normal and arthritogenic murine synovial fibroblasts. Protocol Exchange. , (2009).
- Saeki, N., et al. Epigenetic regulator UHRF1 orchestrates proinflammatory gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis in a suppressive manner. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 132 (11), (2022).
- Midwood, K., et al. Tenascin-C is an endogenous activator of Toll-like receptor 4 that is essential for maintaining inflammation in arthritic joint disease. Nature Medicine. 15 (7), 774-780 (2009).
- You, D. G., et al. Metabolically engineered stem cell-derived exosomes to regulate macrophage heterogeneity in rheumatoid arthritis. Science Advances. 7 (23), 0083 (2021).
- Ogawa, K., Tsurutani, M., Hashimoto, A., Soeda, M. Simple propagation method for resident macrophages by co-culture and subculture, and their isolation from various organs. BMC Immunology. 20 (1), 34 (2019).
- Andrä, I., et al. An evaluation of T-cell functionality after flow cytometry sorting revealed p38 MAPK activation. Cytometry Part A. 97 (2), 171-183 (2020).
- Ryan, K., Rose, R. E., Jones, D. R., Lopez, P. A. Sheath fluid impacts the depletion of cellular metabolites in cells afflicted by sorting induced cellular stress (SICS). Cytometry Part A. 99 (9), 921-929 (2021).
- Llorente, I., García-Castañeda, N., Valero, C., González-Álvaro, I., Castañeda, S. Osteoporosis in rheumatoid arthritis: dangerous liaisons. Frontiers in Medicine. 7, 601618 (2020).
- Croft, A. P., et al. Distinct fibroblast subsets drive inflammation and damage in arthritis. Nature. 570 (7760), 246-251 (2019).
- Wei, K., et al. Notch signalling drives synovial fibroblast identity and arthritis pathology. Nature. 582 (7811), 259-264 (2020).
Reimpresiones y Permisos
Solicitar permiso para reutilizar el texto o las figuras de este JoVE artículos
Solicitar permisoExplorar más artículos
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ACERCA DE JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos los derechos reservados