11.9 : משוואת קלאוזיוס- קלפרון
The equilibrium between a liquid and its vapor depends on the temperature of the system; a rise in temperature causes a corresponding rise in the vapor pressure of its liquid. The Clausius-Clapeyron equation gives the quantitative relation between a substance’s vapor pressure (P) and its temperature (T); it predicts the rate at which vapor pressure increases per unit increase in temperature.
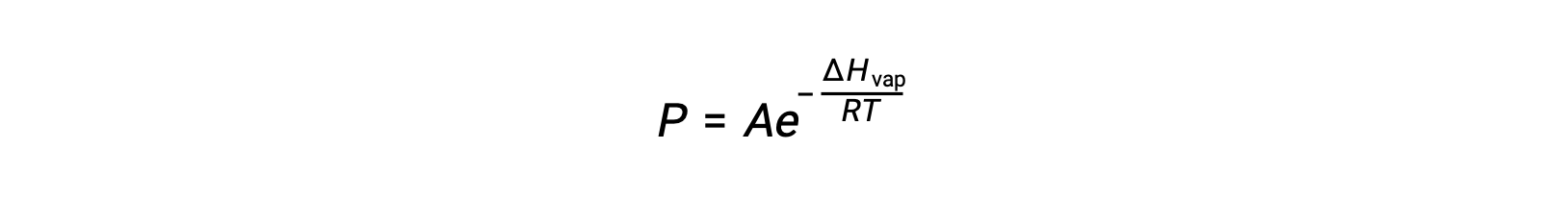
where ΔHvap is the enthalpy of vaporization for the liquid, R is the gas constant, and A is a constant whose value depends on the chemical identity of the substance. Temperature (T) must be in kelvin in this equation. However, since the relationship between vapor pressure and temperature is not linear, the equation is often rearranged into logarithmic form to yield the linear equation:
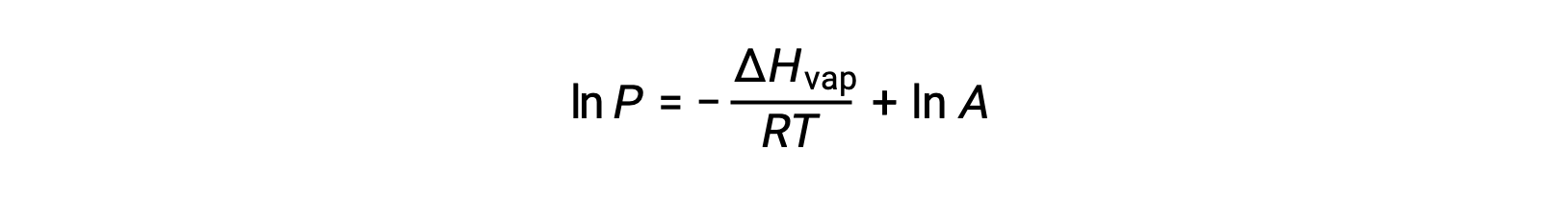
For any liquid, if the enthalpy of vaporization and vapor pressure at a particular temperature is known, the Clausius-Clapeyron equation allows to determine the liquid’s vapor pressure at a different temperature. To do this, the linear equation may be expressed in a two-point format. If at temperature T1, the vapor pressure is P1, and at temperature T2, the vapor pressure is P2, the corresponding linear equations are:
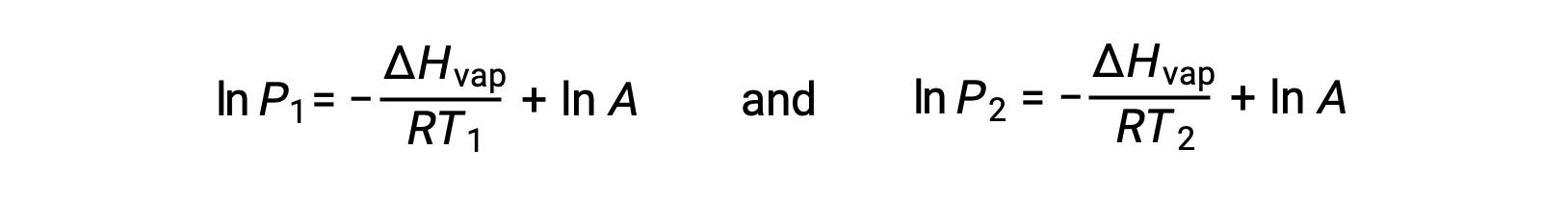
Since the constant, A, is the same, these two equations may be rearranged to isolate ln A and then set them equal to one another:
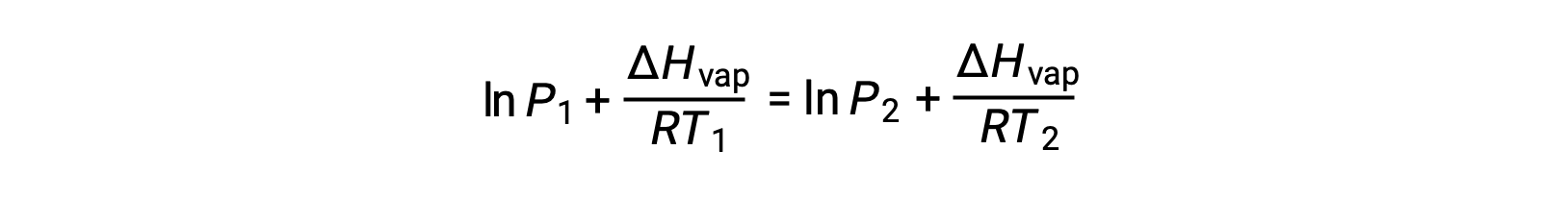
which can be combined into:
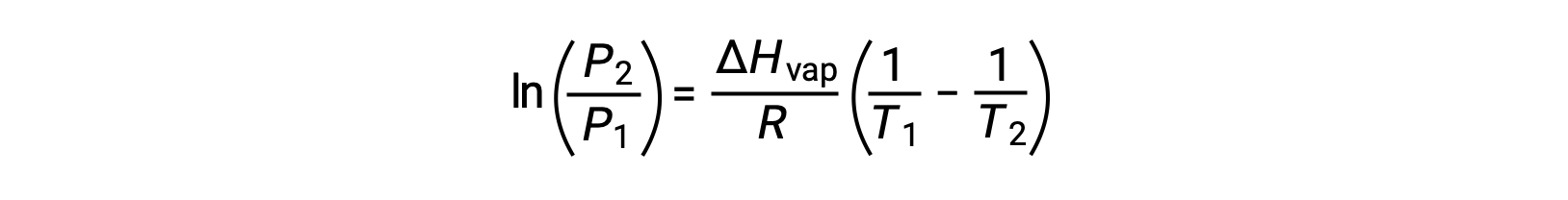
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 10.3: Phase Transitions.
From Chapter 11:

Now Playing
11.9 : משוואת קלאוזיוס- קלפרון
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
55.4K Views

11.1 : השוואה מולקולרית של גזים, נוזלים ומוצקים
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
40.3K Views

11.2 : כוחות בין מולקולריים לעומת תוך מולקולריים
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
85.4K Views

11.3 : כוחות בין מולקולריים
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
56.7K Views

11.4 : השוואת כוחות בין מולקולריים: נקודת התכה, נקודת רתיחה ומסיסות
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
43.6K Views

11.5 : מתח פנים, פעילות קפילרית וצמיגות
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
27.4K Views

11.6 : מעברי פאזה
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
18.7K Views

11.7 : מעברי פאזה: אידוי ועיביוי
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
17.1K Views

11.8 : לחץ אדים
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
34.1K Views

11.10 : מעברי פאזה: התכה וקיפאון
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
12.2K Views

11.11 : מעברי פאזה: המראה וריבוץ
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
16.6K Views

11.12 : עקומות חימום וקירור
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
22.3K Views

11.13 : דיאגרמת פאזות
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
39.2K Views

11.14 : מבנים של מוצקים
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
13.6K Views

11.15 : מוצקים מולקולריים ויוניים
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
16.6K Views
See More
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved