A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
בשנת vivo קרוב אינפרא אדום דימות פלואורסצנטי intravascular (NIRF) מולקולרית של רובד דלקתיות, גישה multimodal כדי הדמיה של טרשת עורקים
In This Article
Summary
אנו פרט חדש קרוב אינפרא אדום (NIRF) קטטר פלואורסצנציה הדמיה 2 מימדי intravascular מולקולרית של ביולוגיה פלאק In vivo. קטטר NIRF יכול לדמיין תהליכים ביולוגיים מרכזיים כגון דלקת על ידי דיווח על נוכחות של פלאק נלהב fluorochromes activatable ממוקד ניר. קטטר מנצל קליניים דרישות הנדסת חשמל מיועד ליישום בעורקים הכליליים האדם. מחקר הבאה מתארת אסטרטגיה הדמיה multimodal אשר מנצל רומן In vivo Intravascular NIRF קטטר לתמונה ולכמת פלאק דלקתי פעיל atheromata proteolytically ארנב מודלק.
Abstract
The vascular response to injury is a well-orchestrated inflammatory response triggered by the accumulation of macrophages within the vessel wall leading to an accumulation of lipid-laden intra-luminal plaque, smooth muscle cell proliferation and progressive narrowing of the vessel lumen. The formation of such vulnerable plaques prone to rupture underlies the majority of cases of acute myocardial infarction. The complex molecular and cellular inflammatory cascade is orchestrated by the recruitment of T lymphocytes and macrophages and their paracrine effects on endothelial and smooth muscle cells.1
Molecular imaging in atherosclerosis has evolved into an important clinical and research tool that allows in vivo visualization of inflammation and other biological processes. Several recent examples demonstrate the ability to detect high-risk plaques in patients, and assess the effects of pharmacotherapeutics in atherosclerosis.4 While a number of molecular imaging approaches (in particular MRI and PET) can image biological aspects of large vessels such as the carotid arteries, scant options exist for imaging of coronary arteries.2 The advent of high-resolution optical imaging strategies, in particular near-infrared fluorescence (NIRF), coupled with activatable fluorescent probes, have enhanced sensitivity and led to the development of new intravascular strategies to improve biological imaging of human coronary atherosclerosis.
Near infrared fluorescence (NIRF) molecular imaging utilizes excitation light with a defined band width (650-900 nm) as a source of photons that, when delivered to an optical contrast agent or fluorescent probe, emits fluorescence in the NIR window that can be detected using an appropriate emission filter and a high sensitivity charge-coupled camera. As opposed to visible light, NIR light penetrates deeply into tissue, is markedly less attenuated by endogenous photon absorbers such as hemoglobin, lipid and water, and enables high target-to-background ratios due to reduced autofluorescence in the NIR window. Imaging within the NIR 'window' can substantially improve the potential for in vivo imaging.2,5
Inflammatory cysteine proteases have been well studied using activatable NIRF probes10, and play important roles in atherogenesis. Via degradation of the extracellular matrix, cysteine proteases contribute importantly to the progression and complications of atherosclerosis8. In particular, the cysteine protease, cathepsin B, is highly expressed and colocalizes with macrophages in experimental murine, rabbit, and human atheromata.3,6,7 In addition, cathepsin B activity in plaques can be sensed in vivo utilizing a previously described 1-D intravascular near-infrared fluorescence technology6, in conjunction with an injectable nanosensor agent that consists of a poly-lysine polymer backbone derivatized with multiple NIR fluorochromes (VM110/Prosense750, ex/em 750/780nm, VisEn Medical, Woburn, MA) that results in strong intramolecular quenching at baseline.10 Following targeted enzymatic cleavage by cysteine proteases such as cathepsin B (known to colocalize with plaque macrophages), the fluorochromes separate, resulting in substantial amplification of the NIRF signal. Intravascular detection of NIR fluorescence signal by the utilized novel 2D intravascular NIRF catheter now enables high-resolution, geometrically accurate in vivo detection of cathepsin B activity in inflamed plaque.
In vivo molecular imaging of atherosclerosis using catheter-based 2D NIRF imaging, as opposed to a prior 1-D spectroscopic approach,6 is a novel and promising tool that utilizes augmented protease activity in macrophage-rich plaque to detect vascular inflammation.11,12 The following research protocol describes the use of an intravascular 2-dimensional NIRF catheter to image and characterize plaque structure utilizing key aspects of plaque biology. It is a translatable platform that when integrated with existing clinical imaging technologies including angiography and intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), offers a unique and novel integrated multimodal molecular imaging technique that distinguishes inflammatory atheromata, and allows detection of intravascular NIRF signals in human-sized coronary arteries.
Protocol
במודל בעלי חיים vivo: הדור של טרשת עורקים AortoIliac ניסויית
1) Baseline אנגיוגרפיה ו Denudation בלון
- לפני קבלת הבסיס אנגיוגרפיה ו denudation בלון, ארנב לבן ניו זילנד מוזן כולסטרול גבוה (1%) דיאטה במשך שבוע 1. בעל חיים זה מנוצל הרלוונטיות כפי translational 1) aorto-iliacs כלי בארנבונים הם בקוטר זהה העורקים הכליליים האנושי (2.5-3.5 מ"מ) ו - 2), hyperlipidemic בלון פציעה מודל יוצרת טרשת עורקים דלקת נושאות תאים דלקתיים דומים (מקרופאגים ) ומולקולות (cathepsins) כמו טרשת עורקים אנושיים.
- בעקבות האכלה כולסטרול, החיה הרדים עם propofol ו קטמין. אינץ' אחד חתך הגחון הצוואר קו האמצע נעשית באמצעות שימוש בגודל 15-אזמל להב. באמצעות שימוש בטכניקות דיסקציה קהה, השרירים מתחת fascia בצד הימני של קנה הנשימה חשוף. השריר sternocephalicus שמאל מופרד לאורך צומת רקמת החיבור שלה, עורק התרדמה המשותף הימני נחשף. עורק מופרד העצב התועה. לולאות תפר הפרוקסימלית ומ דיסטלי ממוקמות על העורק כדי לאפשר את נסיגת ו חסימה. 1 עד 2 מ"מ משופעים arteriotomy מורכב שבאמצעותו 5 (קוטר חיצוני 1.67mm) צרפתית נדן וסקולרית מוכנס הפרין (1000μ/mL, ~ 150units/kg) מנוהל תוך arterially דרך המעטה.
- צבע ניגודיות (Ultravist) מוזרק אז (1 עד 2ml) על פני תקופה 2 שנייה לקבל הצנתר השליטה של האאורטה דיסטלי ושניהם העורקים הכסל.
- העורקים iliofemoral ואבי העורקים נפצעים אז denudation האנדותל. שימוש בשיטות fluoroscopy סטנדרטי, קטטר 3Fr embolectomy פוגארטי ממוקם בעורק iliofemoral דיסטלי ו מנופח עם סמ"ק 0.3-0.5 הניגוד (50% contrast/50% מלח) או אוויר. קטטר היא נסוגה אז proximally במצב מנופח שלה מרחק לאורך הכסל הימני אבי העורקים דיסטלי עד ההמראה של עורק הכליה השמאלית. בעקבות denudation את הבלון, אנגיוגרפיה חוזרת במסמך patency כלי שיט. בעקבות אנגיוגרפיה, כל צנתרים נדני יוסרו עורק התרדמה הימני פרוקסימלי נפוצה היא ligated, השריר fascia הם sutured עם תפר 4 / 0 נספגים, ואת החתך בעור נסגר עם תפר שאינם נספגים 4 / 0.
- החיה מותר אז להתאושש עם הממשל של אחד אנטיביוטיקה במינון (Cephazolin, 0.5 גרם IM). תרופות נגד כאבים, כולל 0.01 מ"ג / ק"ג עצירות IM (פעמיים ביום, לפי הצורך). בעלי חיים הם המשיכו לאחר מכן על כולסטרול 1% עבור denudation 4 שלאחר בלון שבועות. באותו שבוע 5, בעלי חיים המעבר לתזונה כולסטרול 0.3%.
דימות משולב Multi-מודאלית של הארנב Atheromata
2) תיוג של פלאק דלקתי פעיל proteolytically באמצעות nanosensor להזרקה, אנגיוגרפיה, אולטרסאונד intravascular (IVUS), ו - in vivo intravascular NIRF הדמיה של הארנב atheroma
- שמונה שבועות בעקבות פציעה בלון ו - 24 שעות לפני הדמיה, הארנב מוזרק לווריד עם 500 nmol / ק"ג Prosense/VM110 (PerkinElmer) דרך וריד באוזן.
- עשרים וארבע שעות לאחר ההזרקה, בעלי חיים מורדמים וגישה עורקי מתקבל דרך עורק התרדמה השמאלי משותף (ראה שלב 1.2). תוך עורקי הפרין מנוהל (150 יחידות / ק"ג). Baseline אנגיוגרפיה מתקבל כאמור לעיל.
- קטטר IVUS נטען על חוט קליני מסוגל 0.014 עורק כלילי אינץ ונוסף המעטה. באמצעות הדרכה fluoroscopic, קצה של חוט radiopaque ממוקם distally לתוך העורק הכסל הימני. קטטר IVUS מתקדמת מכן לתוך העורק הכסל הפרוקסימלי בטכניקה תקן קליניים מונוריל.
- נסיגה 100 מ"מ הוא יזם תמונות נרשמות. השיקום אורך של כלי השיט מתקבל ורובד luminal מזוהה.
- קטטר NIRF 11,12 נטען על חוט 0.014 אינץ' (מונוריל המערכת), ואת הקטטר מוחדר בזהירות לתוך נדן וראש הדמיה ממוקם distally לתוך עורק הכסל הימני.
- Pullbacks אוטומטיות מרובות (1 מ"מ / sec נסיגה אורך, 30 סיבובים לדקה) מבוצעים אותות הקרינה בתוך אזורי של טרשת עורקים מצוינים. תמונות מוקלטים עיבוד נוסף עם דרוג חלונאית המתאים בהתבסס על מגוון של אותות מושגת.
3) המתת חסד ובידוד של רקמת לשעבר aorto-vivo הכסל
- המתת חסד נעשה עם 1cc של סוכן המתת חסד (פתרון של 390mg נתרן 50 מ"ג נתרן ו pentobarbital פניטואין), הזרקה תוך ורידית, יחיד.
- העץ העורקי הוא perfused עם מלח רגיל 0.9% עד נחות הווריד הנבוב ברור של דם. טרשת עורקים באבי העורקים הכסל מזוהים גזור ללא הרקמות הסובבות. בנוסף, קטן 2 x 2 ס"מ חתיכות של liver, הכליות, הטחול והלב מתקבלים גם.
- Ex vivo NIRF הדמיה עם צנתר ההדמיה intravascular NIRF ניתן לעשות זאת בשלב זה. הכלי הוא מוארך את הקטטר NIRF מחדש מוכנס לתוך אבי העורקים הפרוקסימלי עד ראש הדמיה ממוקמת בעורק הכסל הסתעפות ימינה או. Pullbacks אוטומטיות מרובות מבוצעות כאמור לעיל (ראו 2.6).
4) Ex vivo Fluorescence ההחזרה דימות (יום שישי) של האאורטה והעורקים גזור הכסל
- רקמה גזור ממוקם 10-20 סמ"ק של תמיסת מלח רגיל מועבר עבור ניתוחים יום שישי (Kodak Image תחנת 4000MM Pro, Carestream Health, Inc).
- , אבי העורקים הם כלי הכסל מוארך זמן אמת אורכי משוער ותמונות מתקבלים באורכי גל מרובים [אור לבן, ערוץ פלואורסצנטי ירוק (495 ננומטר לשעבר, אותם 515 ננומטר), Cy5 (לשעבר 565 ננומטר, אותם 670 ננומטר) Cy7 (לשעבר 650 ננומטר, אותם 760 ננומטר)] ערוצים. סדרה של פעמים חשיפה מנוצלים עבור כל אורך גל (0.1-30sec) ותמונות רכשה מיוצאים כמו DICOM או 16-bit קבצים unscaled TIFF עבור ניתוחים נוספים. כפי שולטת חיוביות ושליליות, איברים (כבד, טחול, כליות, לב) הם צילמו את ערוצי דומה זמני חשיפה.
- תחומי אות מוגבר בערוץ קרוב אינפרא אדום (780nm +) הם ציינו עורקים טרשת עורקים.
5) רקמה והטבעה לניתוח חתך ו immunohistochemical
- תחומי נורמלי (לא נפגע רקמות, כלומר עורק הכסל משמאל) בתחומים של פלאק מזוהים קטן טבעות 5-10 מ"מ של רקמה המוטבעים אוקטובר (טמפרטורה אופטימלית חיתוך) אמצעי התקשורת. חוסמת מאוחסנים C -80 עד חתך.
- טכניקות סטנדרטיות עבור ניתוחים חתך ו immunohistochemical מבוצעות. Hematoxylin ו eosin כתם, רם-11 ו מכתים Cathepsin B מבוצעות.
ניתוח ואינטגרציה של רב מודאלית תמונות (אנגיוגרפיה, IVUS, NIRF ואת יום שישי)
6) עיבוד של תמונות NIRF ואת יום שישי
- קובצי DICOM המכיל נתונים הדמיה מ NIRF ואת יום שישי (ערוץ נלקחה ב 780 ליד אינפרא אדום ננומטר) pullbacks מעובדים באמצעות MATLAB ותוכנות Osirix, בהתאמה. חלונאית פרופר להציג מגוון רחב של עוצמת האות מושגת. תמונות הסופי מיוצא כקובצי TIFF.
- קבצים מיובאים לתוך תוכנת עיבוד תמונה רגילה (Keynote יכול לשמש). תמונות מיושרים מבוסס על נקודות התייחסות (כלומר החוליות על הצנתר, הסתעפות הכסל, ו עורק הכליה). תחומי כלי שלט נורמלי מזוהים.
- אזורים של עניין (ROI) הם לייחס באופן ידני (על רקמות באזורים הרגיל של פלאק) ו מתכוון לעוצמות אות נרכשים באמצעות Osirix ו MATLAB, בהתאמה עבור שני יום שישי ותמונות NIRF. כדי להנחות מעקב מתאים, התמונה IVUS האורך של הכלי משמש וזיהוי של כלי שלט נורמלי מזוהים בקלות.
- היעד ל (TBR) יחס רקע מחושבים אזורי פלאק.
נציג תוצאות:
עם השלמת בפרוטוקול לעיל, אנו יכולים לזהות ולאפיין תחומי פעילות הפרוטאז cathepsin מוגבר ב פלאק דלקתי בתוך אבי העורקים וכלי הכסל. הזרקת nanosensor activatable (Prosense/VM110) מאפשרת לנו לזהות פלאק פעיל proteolytically. אלה מופיעים בהיר או כמו האות אזורי אינטנסיבי כאשר צילמו באמצעות יום שישי בערוץ אינפרא אדום הקרוב (750 ננומטר). Pullbacks NIRF לתאם עם עוצמת אות מוגברת על ידי ו 'מערכים עם IVUS אשר מאפשרים רישום אנטומי של אותות NIRF. TBR פלאק מחושב של המתקבל שישי NIRF היו דומים (ראה איור 3: ממוצע NIRF TBR 4.2, כלומר יום שישי TBR 2.9). ניתוח immunohistochemical של פלאק בהיר מאשרת נוכחות אינטנסיבית של זיכרון RAM ו-11-B Cathepsin פעילות בתחומים של פלאק (מידע לא מוצג).
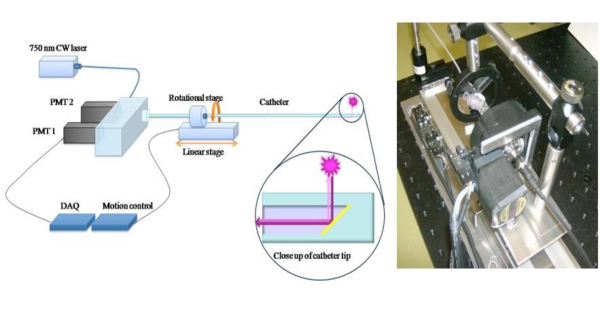
באיור 1. סכמטי של צנתר NIRF 2D כדי להרחיב את הפוטנציאל הקליני של גישה 1D חישה NIRF 6, בנינו רומן 2-D-NIRF צנתר הדמיה intravascular. 11,12 קטטר שהותקן מורכב סיב אופטי (125 בקוטר מיקרון שוכנו בתוך צינורות פוליאתילן: 2.9F) שמאיר באמצעות לייזר 750 ננומטר מקור עירור. אור הלייזר נפלט בזווית של 90 מעלות ביחס לציר הסיב. המערכת מנצלת שני מנועים אוטומטיים (הסיבוב ו translational) כדי לאפשר תואר במקביל הדמיה 360 ו הנסיגה האורך להשיג הדמיה 2D נכון. תמונות בשימוש באישורו מהפניה 11.
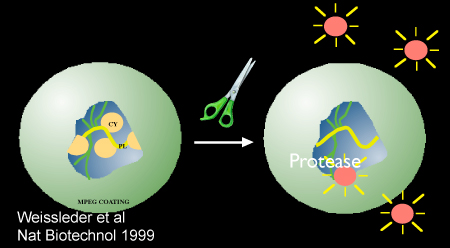
איור 2. הוכחת סכמטי פרוטאז בתיווך הפעלת nanosensor, Prosense/VM110. תמונה השתמשו באישור התייחסות 10.

איור 3. In vivo ו רובד לשעבר vivo TBRs (היעד ל יחסי ברקע)
Discussion
הפלאק בסיכון גבוה או פגיעה דלקתית אחראים סביר עבור רוב אוטם שריר הלב. הזיהוי של הפלאק כאמור לפני הופעת התסמינים הקליניים יש השלכות חשובות הן בניבוי התוצאות המנחה טיפול רפואי. קונבנציונלי שיטות דימות העורקים הכליליים כגון רנטגן אנגיוגרפיה בדרך כלל מתמקדים ואפיון של ...
Disclosures
FAJ - יועץ לשעבר, VisEn רפואי; Honoraria, בוסטון סיינטיפיק
Acknowledgements
תמיכה עבור עבודה זה סופק על ידי המכונים הלאומיים לבריאות מענק R01 HL # 108229, American Heart Association המדען פיתוח גרנט # 0830352N, הווארד יוז רפואי פיתוח קריירה מכון פרס, Broadview ונצ'רס, תוכנית המסגרת השביעית של הקהילה האירופית (FP7/2007-2013 תחת מענק הסכם # 235689), ואת ויליאם MGH Schreyer המלגה.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Prosense 750 | Visen Medical | VM110 | 500 nmol/kg IV injection |
| Heparin Sodium | APP Pharmaceuticals | 401586D | |
| Cephazolin | NovaPlus | 46015683 | |
| Lidocaine HCL 2% | Hospira Inc. | NDC 0409-4277-01 | |
| Buprenorphine | Bedford Laboratories | NDC 55390-100-10 | |
| Ketamine | Hospira Inc. | NDC 0409-2051-05 | |
| High Cholesterol Diet 1% | Research Diets | C30293 | |
| HIgh Cholesterol Diet 0.3% | Research Diets | C30255 |
References
- Andersson, J., Libby, P. Adaptive immunity and atherosclerosis. Clin Immunol. 134, 33-46 (2010).
- Calfon, M. A., Vinegoni, C. Intravascular near-infrared fluorescence molecular imaging of atherosclerosis: toward coronary arterial visualization of biologically high-risk plaques. Journal of Biomedical Optics. 15, 011107-011107 (2010).
- Chen, J., Tung, C. -. H. In Vivo Imaging of Proteolytic Activity in Atherosclerosis. Circulation. 105, 2766-2771 (2002).
- Jaffer, F. A., Libby, P. Molecular Imaging of Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation. 116, 1052-1061 (2007).
- Jaffer, F. A., Libby, P. Optical and Multimodality Molecular Imaging: Insights Into Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29, 1017-1024 (2009).
- Jaffer, F. A., Vinegoni, C. Real-Time Catheter Molecular Sensing of Inflammation in Proteolytically Active Atherosclerosis. Circulation. 118, 1802-1809 (2008).
- Kim, D. -. E., Kim, J. -. Y. Protease Imaging of Human Atheromata Captures Molecular Information of Atherosclerosis, Complementing Anatomic Imaging. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 30, 449-456 (2010).
- Libby, P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 420, 868-874 (2002).
- Naghavi, M., Libby, P. From Vulnerable Plaque to Vulnerable Patient: A Call for New Definitions and Risk Assessment Strategies: Part I. Circulation. 108, 1664-1672 (2003).
- Weissleder, R., Tung, C. -. H. In vivo imaging of tumors with protease-activated near-infrared fluorescent probes. Nat Biotech. 17, 375-375 (1999).
- Razansky, R. N., Rosenthal, A. Near-infrared fluorescence catheter system for two-dimensional intravascular imaging in vivo. Optics Express. 18, 11372-11381 (2010).
- Jaffer, F. A., Calfon, M. A. Two-Dimensional Intravascular Near-Infrared Fluorescence Molecular Imaging of Inflammation in Atherosclerosis and Stent-Induced Vascular Injury. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 57, 2516-2526 (2011).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved