Method Article
דגם רקמות 3D ריאות אדם ללימודים פונקציונליים ב
In This Article
Summary
Human tuberculosis infection is a complex process, which is difficult to model in vitro. Here we describe a novel 3D human lung tissue model that recapitulates the dynamics that occur during infection, including the migration of immune cells and early granuloma formation in a physiological environment.
Abstract
שחפת (TB) עדיין מחזיק איום חמור על בריאותם של אנשים ברחבי העולם, ויש צורך במודלים יעילים וחסכוניים אבל אמין כדי לעזור לנו להבין את מנגנוני המחלה ולקדם את התגליות של אפשרויות טיפול חדשות. בתרביות תאים במבחנה של monolayers או שיתוף תרבויות חסרות הסביבה תלת-ממדית (3D) ותגובות רקמה. בזאת, אנו מתארים חדשניים במודל חוץ גופית של רקמת ריאה אנושית, שטומנת בחובו הבטחה להיות כלי יעיל ללימוד האירועים המורכבים המתרחשים במהלך זיהום בשחפת Mycobacterium (שחפת). מודל רקמת 3D מורכב מתאי רקמות ספציפיות אפיתל fibroblasts, אשר בתרבית במטריצה של קולגן על גבי קרום נקבובי. עם חשיפה לאוויר, תאי האפיתל רבד ולהפריש ריר בצד הפסגה. על ידי החדרת מקרופאגים העיקריים האנושיים נגוע במ ' שחפת למצב הרקמותl, שהראינו כי תאים חיסוניים לנדוד לתוך הרקמות הנגועים וצורת granuloma TB שלבים מוקדמים. מבנים אלה לשחזר את התכונה הייחודית של שחפת אדם, granuloma, שהוא שונה או לא נפוץ שנצפה במודלים של בעלי חיים ניסיוניים בשימוש נרחב במהותו. שיטה זו מאפשרת תרבות organotypic הדמיית 3D וניתוח כמותי חזק המספק מידע מרכזי על תכונות מרחב ובזמן של אינטראקציות תא-פתוגן מארח. יחדיו, מודל רקמת הריאה מספק רקמות מיקרו-סביבה רלוונטית מבחינה פיזיולוגית ללימודים שבחפת. לפיכך, יש מודל רקמת הריאה השלכות פוטנציאליות לשני מחקרים מכניסטית ומיושמים בסיסיים. חשוב לציין, המודל מאפשר תוספת או מניפולציה של סוגי תאים בודדים, שבכך מרחיב את השימוש בו לדוגמנות מגוון של מחלות זיהומיות המשפיעות על הריאות.
Introduction
בבני אדם, תגובות לזיהום, דלקת רקמה, גיוס סלולארי, שיפוץ רקמות והרגולציה של הומאוסטזיס רקמה הן אירועים מורכבים של תאים מסוגים שונים. לפיכך, תהליכים אלה למדו הטובים ביותר בסביבת הרקמות המקומית. בעבר, זה היה אפשרי בעיקר באמצעות מודלים של בעלי חיים ניסיוניים. עם זאת, חיות ניסוי בשימוש נרחב להחזיק מגבלות רבות כפי שהם לעתים קרובות מגיבים לפתוגנים באופן שונה מבני האדם וגם להציג במהלך המחלה 1 שונה. אדם במודל רקמת הריאה מבחנה מחזיק אפשרויות ללמוד תגובות חיסוני ספציפיות בריאות האנושיות.
זיהום שחפת אדם (TB) הוא מחלה הפוגעת בעיקר הריאות. שחפת Mycobacterium (שחפת), הסוכן סיבתי של שחפת, מגיעה לריאות באמצעות טיפות תרסיס שמועברים למרחב מכתשי, שבו החיידקים נבלעים על ידי dendri ריאהתאי טיק ומקרופאגים מכתשיים כחלק מהתגובה החיסונית המולדת לזיהום 2,3. Phagocytosis של הפתוגן מוביל למידור של באג בתוך phagosome ובאופן אידיאלי תוצאות בנטרול וההרג של הפתוגן ידי תָא בַּלעָן. עד 50% מאנשים שנחשפו למ ' הם האמינו שחפת להיות מסוגל לנקות את הזיהום באמצעות התגובה החיסונית המולדת 4. תוצאות אחרות של זיהום הן אישור על ידי המערכת החיסונית אדפטיבית בשלב מאוחר יותר, זיהום סמוי או במקרים הגרועים ביותר מחלה כרונית פעילה 5.
בעבר לא היו דגמי רקמה במבחנה ללימודים של שחפת אדם. תרביות תאים בודדות של מקרופאגים אדם או תאי דם היקפיים אחרים שימשו לעתים קרובות 6,7. החסרון של גישה זו הוא שהם לא יכולים לשקף את הדינמיקה של סוגי תאים שונים הפועלת יחד ברקמת ריאה נחשפה למ ' שחפת . לפיכך, יש צורך במודל במבחנה כדי להיות מסוגל לבצע מחקרים פונקציונליים ומכאניים בשחפת. במודל רקמת ריאה מבחנה אנושית המתואר כאן מבוסס התא הוקם במקור על ידי הקבוצה שלנו ללימודים בפונקציות תאים דנדריטים 8. יש לנו שיטה זו מותאמת למחקר של שחפת.
מודל רקמת ריאה האנושי מוצג כאן מורכב מתאי האפיתל רקמות ספציפיות ופיברובלסטים 8. תאים אלה בתרבית במטריצה של קולגן על גבי קרום נקבובי בכנס transwell ומבני צורה דומה רקמה נורמלית אנושית ריאות (איור 1). כאשר נחשפו לאוויר התאים מתחילים להפריש ריר בצד הפסגה 8. על ידי השתלת מקרופאגים העיקריים האנושיים נגוע במ ' שחפת למודל, שראינו כיצד תאי המערכת החיסונית להעביר ברקמה וליצור של גרנולומות TB 9 שלבים מוקדמים. זהו מודל descr רקמה האנושי הראשוןibed לשחפת והוא מציב כלי מבטיח ללימוד תגובות חיסון מולדים לשחפת ומחלות אחרות של הריאות. עד כה, יש לנו להשתמש רק מונוציטים ומקרופאגים כתאי מערכת חיסון במודל אבל רמת המורכבות יכולה להיות מוגברת על ידי הכללה של סוגי תאים רלוונטיים נוספים.
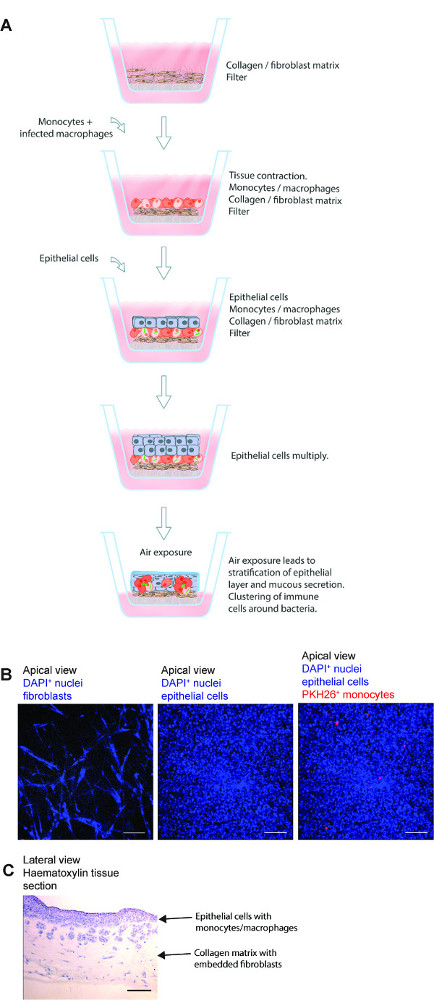
איור 1. מתווה סכמטי של מודל רקמת ריאה. (א) המודל מורכב מתאי האפיתל ריאות ספציפיות אנושיים, מ ' שחפת -infected מקרופאגים הראשוניים ומונוציטים שכותרתו צבע אדום זורעים על fibroblasts קולגן המוטבע הוכן על מסנן transwell. חשיפה של מודל הרקמה לאוויר יוזמת ייצור של חלבוני מטריצת חוץ-תאיים, הפרשת ריר וריבוד על ידי אפיתל. מודל רקמת 3D וכך פיתח הוא כלי שימושי ללמוד מ ' זיהום שחפת בסביבה שCLOsely דומה ריאות אנושיות. (ב) תמונות מיקרוסקופיות נציג של השלבים השונים בהכנת מודל הרקמות. מבנה מלא של סעיף רקמות מודל ריאות (C). קנה מידה -. 100 מיקרומטר אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
Protocol
הערה: דם היקפי אדם מתורמי דם בריאים אנונימי רכשו בבנק של Linköping בית החולים של אוניברסיטת הדם, שוודיה שימשה כמקור לתאי מערכת חיסון למחקר זה. פרוטוקול זה מיועד למוסיף 24 מ"מ צלחת 6 היטב. הסתגלות ישירה לפורמטים אחרים גם אינה מומלצת שכן חוזי מודל רקמה אנכי ואופקי בפיתוח.
1. הכנת חומרים, מדיה והתרבות של חיידקים / קווים סלולריים
- תרבות של חיידקים:
- לגדול מתח mycobacterial מ ' שחפת H37Rv נושא את הפלסמיד pFPV2 לבטא חלבון פלואורסצנטי ירוק (GFP) constitutively, במדיום מידלברוק 7H9 מכיל 0.05% Tween-80, גליצרול 0.5%, kanamycin (20 מיקרוגרם / מיליליטר), והשלים עם אלבומין מידלברוק, דקסטרוז והעשרת catalase ( מידלברוק ADC העשרה), במעלות צלזיוס 37 עם 5% CO 2 למשך 7-10 ימים.
הערה: כל הצעד הניסיוניים מעורב מ 'ארסי חי יש לבצע זני שחפת במתקן BSL-3.
- לגדול מתח mycobacterial מ ' שחפת H37Rv נושא את הפלסמיד pFPV2 לבטא חלבון פלואורסצנטי ירוק (GFP) constitutively, במדיום מידלברוק 7H9 מכיל 0.05% Tween-80, גליצרול 0.5%, kanamycin (20 מיקרוגרם / מיליליטר), והשלים עם אלבומין מידלברוק, דקסטרוז והעשרת catalase ( מידלברוק ADC העשרה), במעלות צלזיוס 37 עם 5% CO 2 למשך 7-10 ימים.
- הכן בינוני בינוני של הנשר (DMEM) השלם השתנה של 1x Dulbecco (בתוספת פירובט 1 מ"מ נתרן, L-גלוטמין 2 מ"מ, 100 U / פניצילין מיליליטר, 100 מיקרוגרם / מיליליטר סטרפטומיצין, 10 מ"מ HEPES, 0.1 חומצות אמינו לא חיוניים מ"מ ו -10 % חום מומת בסרום שור עוברי (FBS)). הכן גם בינוני מלאה DMEM ללא אנטיביוטיקה.
- הכינו בינוני בינוני 1x מינימום הכרחי (ממ) שלמה (פירובט נתרן 1 מ"מ, L-גלוטמין 2 מ"מ, 100 U / פניצילין מיליליטר, 100 מיקרוגרם / מיליליטר סטרפטומיצין, בידוד חום 10 מ"מ HEPES, 0.1 חומצות אמינו לא חיוניות מ"מ ושל 10% סרום מומת שור עוברי (FBS)).
- הכנה של פיברונקטין / צלוחיות מצופים קולגן (סה"כ 10 מיליליטר):
- מלוח פיפטה פוספט 1x 8.8 מיליליטר סטרילי שנאגרו (PBS) לתוך צינור נקי. הוסף 1 מיליליטר אלבומין בסרום השור (1 מ"ג / מיליליטר), 100 סוג μl אני שור קולגן (3 מ"ג / מיליליטר) ו -100 μl רקומביננטי huפיברונקטין אדם (1 מ"ג / מיליליטר).
- מערבבים את הפתרון על ידי סיבוב הצינור הפוך 5 פעמים. צלוחיות מצופות בפתרון פיברונקטין / קולגן (1 מיליליטר לT-25 ו -2 מיליליטר לבקבוק T-75). תשאיר את זה O / N על 37 מעלות צלזיוס. לאחר דגירה, להסיר את הפתרון ולאחסן את צלוחיות המצופים בRT.
הערה: הפתרון שנאסף יכול להיות מאוחסן על 4 מעלות צלזיוס ושימוש חוזר לשלוש פעמים. אחסון ליותר מ -2 שבועות עלול לגרום לנוזל להשחים (היווצרות של גבישים), שבו עליה חייב להיות מושלכת.
- תרבות של fibroblasts:
- לגדול ולשמור על MRC-5, (קו אנושי פיברובלסטים ריאות מסוג תאים שמקורם ברקמת ריאה נורמלית של עובר גבר בן 14 שבועות), בDMEM המלא ב 5% CO 2 על 37 מעלות צלזיוס. השתמש בפיברובלסטים בקטעים 24-26 ולגדול עד מחוברות 70-80%.
הערה: קו תא MRC-5 בקטע> 30 נוטה לאבד את המורפולוגיה ואינו מומלץ לשימוש במודל הרקמות.
- לגדול ולשמור על MRC-5, (קו אנושי פיברובלסטים ריאות מסוג תאים שמקורם ברקמת ריאה נורמלית של עובר גבר בן 14 שבועות), בDMEM המלא ב 5% CO 2 על 37 מעלות צלזיוס. השתמש בפיברובלסטים בקטעים 24-26 ולגדול עד מחוברות 70-80%.
- תרבות של תאי האפיתל:
- להשיג 16HBE14o- (16HBE), קו הנציח אדם הסימפונות אפיתל תאים ששומר על המורפולוגיה ותפקוד המובחנים של epithelia דרכי הנשימה אנושית הרגיל, (זה היה מתנה מד"ר דיטר Gruenert, הר ציון מרכז הסרטן, אוניברסיטת קליפורניה, סן פרנסיסקו , ארה"ב 10.). תאי 16HBE התרבות בפיברונקטין / צלוחיות מצופים קולגן ולשמור על התאים בממ המלאה ב 5% CO 2 על 37 מעלות צלזיוס.
- הכנת 5x DMEM
- הכן DMEM 5x ידי המסת 13.4 גרם של אבקת DMEM ו -3.7 גרם של סודה לשתייה ב150 מיליליטר של מים מזוקקים סטריליים. התאם את ה- pH של המדיום 7.3, מרכיבים את נפח 200 מיליליטר ולסנן אותו באמצעות 0.22 מיקרומטר סינון קרום. לאסוף בינוני המסוננים במכל סטרילי ומאוחסן עד לשימוש ב RT.
2. הכנת פיברובלסטים משובץ-קולגן
- aliquots הפשרה הקפוא של FBS וL- גלוטמין באמבט מים 37 מעלות צלזיוס.לאחר ההפשרה לשמור על דגימות קרח. הנח סודיום ביקרבונט (71.2 מ"ג / מיליליטר) וגנטמיצין (50 מ"ג / מיליליטר) ב 4 ° C. טרום מגניב 50 מיליליטר צינורות צנטריפוגה 10 מיליליטר וטפטפות סטרילי ל- C ° 4.
הערה: כל החומרים המשמשים (למעט DMEM 5x) הם מצוננים על קרח לפני שימוש וכל השלבים מבוצעים על קרח. הקלד אני שור קולגן (1.1 מ"ג / מיליליטר) חייב להישמר קר, כמו זה מונע מיצוק של קולגן. - הכן את תאי פיברובלסטים:
- טריפסין החם באמבט מים 37 מעלות צלזיוס ודגירת כמות מספקת עם fibroblasts ריאות (MRC-5) תאים במשך 10 דקות ב 5% CO 2 על 37 מעלות צלזיוס. לנטרל את טריפסין על ידי הוספת 1x DMEM מלא. לשאוב את ההשעיה התא וצנטריפוגות ב XG 300 במשך 5 דקות. לשאוב supernatant ו resuspend התאים על 2.3 x 10 5 תאים / מיליליטר בDMEM מלא. מניחים את התאים על קרח עד מוכן לשימוש.
- הכן מראש תערובת:
- להוסיף את הדברים הבאים לצינור שכותרתו "טרום-תערובת"; 395μl של 5x DMEM, 40 μl L-גלוטמין, 120 μl NaHCO3 (71.2 מ"ג / מיליליטר), 440 FBS μl, 5 μl גנטמיצין (50 מ"ג / מיליליטר), μl נפח 1,000 סה"כ, אז מערבולת מראש לערבב היטב ולשים על קרח.
הערה: הכרכים נתון להוספת תרבות אחת 24 מ"מ 6 היטב. לחשב את הסכומים הספציפיים הנדרשים למספר הכולל של מוסיף אך להוסיף אחד נוסף כדי להיות בטוח, מספיק מראש תערובת מוכנה.
- להוסיף את הדברים הבאים לצינור שכותרתו "טרום-תערובת"; 395μl של 5x DMEM, 40 μl L-גלוטמין, 120 μl NaHCO3 (71.2 מ"ג / מיליליטר), 440 FBS μl, 5 μl גנטמיצין (50 מ"ג / מיליליטר), μl נפח 1,000 סה"כ, אז מערבולת מראש לערבב היטב ולשים על קרח.
- מכין את תערובת קולגן acellular:
- לכל תרבות להוסיף 1 מיליליטר של תערובת קולגן acellular. להוסיף את הדברים הבאים לצינור חרוטי 50 מ"ל על קרח בהוראה שניתנה; 686 μl של 1.1 מ"ג / מיליליטר קולגן, 250 μl טרום תערובת ו -64 1x μl DMEM המלא להיקף כולל של 1,000 μl. מערבבים את הפתרון גם הבטחה אין בועות אוויר. לעבוד מהר ולהוסיף קולגן על הקיר של הצינור כדי למנוע בועות אוויר.
- הוסף 1 מיליליטר של תערובת שכבת acellular להוספה להציב בצלחת 6 היטב. אל תוסיף כל מדיום ולמחוץ להוספה. בcubate למשך 30 דקות בחממה 37 ° C. ודא את תערובת acellular מכסה את כל ההוספה ללא כל בועות אוויר.
- מכין את תערובת קולגן הסלולרית:
- מערבבים את המרכיבים של השכבה הסלולרית בצינור חרוטי 50 מיליליטר כל הזמן על קרח בצו הבא; 2 מיליליטר קולגן, 615 μl טרום תערובת, 58 μl של DMEM המלא 1x ופיברובלסטים 327 השעיה תא μl ריאות (MRC-5) כדי להפוך את הנפח הכולל עד 3,000 μl. כל תרבות דורשת 3 מיליליטר של תערובת קולגן סלולרית.
שלב קריטי: הקפד לערבב קולגן וpremix זהירות לפני התוספת של ההשעיה התא. זה יהיה לנטרל את ה- pH של קולגן כדי למנוע השפעות רעילות על fibroblasts. - מוסיף את השכבה הסלולרית (3 מיליליטר) על גבי שכבת הקולגן acellular דגירה עבור שעה 2 באינקובטור 37 ° C. לעבוד מהר ולהוסיף קולגן על הקיר של הצינור כדי למנוע בועות אוויר.
- בעקבות פילמור, להוסיף 2 מיליליטר של DMEM מלא לtהוא החלק התחתון של צלחת 6 גם (תחת ההוספה) ודגירה של 24 שעות.
הערה: אם פילמור לא התרחש, לבטל את מוסיף צלחת המכילה את מטריצת פיברובלסטים-קולגן ולהתחיל-שוב. הסיבה הסבירה ביותר היא שגיאה בתוספת או נפח שגוי של אחד ממגיבים המפורטים לעיל.
- מערבבים את המרכיבים של השכבה הסלולרית בצינור חרוטי 50 מיליליטר כל הזמן על קרח בצו הבא; 2 מיליליטר קולגן, 615 μl טרום תערובת, 58 μl של DMEM המלא 1x ופיברובלסטים 327 השעיה תא μl ריאות (MRC-5) כדי להפוך את הנפח הכולל עד 3,000 μl. כל תרבות דורשת 3 מיליליטר של תערובת קולגן סלולרית.
3. תרבות רציפה של מטריקס פיברובלסטים-קולגן
- רם בזהירות את התוסף באמצעות מלקחיים נקיים ולשאוב תקשורת והתרבות מתחתית הבאר. להוסיף 2 מיליליטר DMEM המלא לתחתית אחרי היטב על ידי DMEM מלא 2 מיליליטר בכנס. הימנע החדרת בועות אוויר תחת הכנס, כמו זה יהיה למנוע דיפוזיה של חומרים מזינים בין התאים החיצוניים ופנימיים. הסר בועות אוויר עם טיפ micropipette.
- לשנות את התקשורת והתרבות (בתוך ומתחת להוספה) בכל יום שני ותרבות לכ 5-7 ימים. דואג בהסרת התקשורת מהכנס. כדי להימנע מcontaCT עם מטריצת פיברובלסטים-קולגן, מעט להטות את הכנס באמצעות מלקחיים נקיים ולשאוב תקשורת מהקירות להוסיף.
שלב קריטי: fibroblasts במטריצת קולגן צריך לקבל פנוטיפ מוארך, ולשפץ קולגן, אשר לאחר מכן חוזים. בכ-5-7 ימים, המטריצה התקשרה כדי ליצור פלטפורמה (10-14 מ"מ קוטר) במרכז הכנס. המטריצה נדבקה מוכנה לשימוש בשלב הבא. כדי להשיג כיווץ אחיד של המטריצה זה קריטי, כי fibroblasts הם גם מעורב עם קולגן לפני זריעה (שלב 2.6.1).
4. זריעה של תאי מערכת חיסון (אינפקטד תערובת נגוע מונוציטים-מקרופאג /)
הערה: שלבי הניסוי הבאים כרוכים mycobacteria הארסית ולכן יש לבצע במתקן BSL-3.
- הכנת מונוציטים ומקרופאגים עיקריים:
- לבודד מונוציטים בדם היקפיים מתורם דם באמצעות establiלשפוך פרוטוקול. לבודד מונוציטים באותו היום כהגדרת המודל ותרבית הרקמה ולבדל אותם למקרופאגים לכ 7 ימים לפני זיהום עם מ ' שחפת.
הערה: הפעולה זו תבטיח שני מקרופאגים ומטריצת פיברובלסטים-קולגן נדבקה זמינים לאחר 7 ימים. גם לבודד מונוציטים טריים שיתווספו יחד עם מקרופאגים הנגועים.
- לבודד מונוציטים בדם היקפיים מתורם דם באמצעות establiלשפוך פרוטוקול. לבודד מונוציטים באותו היום כהגדרת המודל ותרבית הרקמה ולבדל אותם למקרופאגים לכ 7 ימים לפני זיהום עם מ ' שחפת.
- הכנתו של מ ' מקרופאגים שחפת -infected
- לקצור את החיידקים בתרבית, לשטוף עם 1x PBS המכיל 0.05% Tween-80, גלול בDMEM המלא ללא אנטיביוטיקה, עובר דרך 27 סטרילי מחט G קטוע לפזר גושי חיידקים ולמדוד את הצפיפות האופטית.
הערה: טרום לקבוע מ ' מושבה שחפת להרכיב שווה יחידה של צפיפות אופטית במעבדה. זה ייתן לי אומדן מספרם של חיידקים שישמש לזיהום. - דגירה מקרופאגים לשעה 4 ב M. שחפת בריבוי של זיהום (משרד הפנים) 10). לאחר הדבקה, לשטוף 3x עם 1x PBS להסיר חיידקים תאיים. השתמש מקרופאגים נגוע בתרבית באותו אופן, אבל בלי מ ' שחפת, כקבוצת ביקורת.
- לנתק את מקרופאגים מצלחת התרבות על ידי טיפול עם 2 מ"מ EDTA במשך 10 דקות על 37 מעלות צלזיוס וresuspended תאי DMEM מלא ללא אנטיביוטיקה.
- לקצור את החיידקים בתרבית, לשטוף עם 1x PBS המכיל 0.05% Tween-80, גלול בDMEM המלא ללא אנטיביוטיקה, עובר דרך 27 סטרילי מחט G קטוע לפזר גושי חיידקים ולמדוד את הצפיפות האופטית.
- תוויות של מונוציטים
הערה: בידוד ותיוג של מונוציטים יכולים להתבצע בספסל BSL-2 ולאחר מכן נלקחו לBSL-3 מתקן לעיבוד נוסף.- כתם מונוציטים מוכנים טרי (2 x 10 7 תאים) עם ריכוז סופי של צבע אדום PKH26 2 מיקרומטר במשך 5 דקות, על פי הוראות היצרן. 3x לשטוף ו resuspend התאים עם DMEM מלא אנטיביוטיקה ללא בצפיפות של 1 x 10 7 תאים / מיליליטר.
- תוספת של תאי מערכת חיסון לפיברובלסטים-קולגן מטריצה
- חרה 5-7 ימים של התרבות של מטריצת פיברובלסטים-קולגן, לשאוב תקשורת והתרבות מהתאים החיצוניים ופנימיים ולהוסיף 1.5 מיליליטר של DMEM ללא אנטיביוטיקה הטרי השלם לתא החיצוני.
- הכן מונוציטים-מקרופאג שכותרת תערובת (נגוע / נגועה) עם יחס של MO: MQ (5: 1) ב -50 DMEM μl מלא. 50,000 מקרופאגים, לקחת 250,000 מונוציטים שכותרת.
- להוסיף MO 50 μl: תערובת MQ למטריצת פיברובלסטים-קולגן ודגירה עבור שעה 1 ב 5% CO 2 על 37 מעלות צלזיוס. לאחר דגירה, בעדינות להוסיף 2 מיליליטר של תקשורת בתרבות להוספה ודגירה של 24 שעות נוספות ב 5% CO 2 על 37 מעלות צלזיוס.
הערה: ככל שתאים הוסיפו מחוברים באופן רופף, תוספת של תקשורת צריכה להיות איטית בעדינות על ידי הוספה על הקירות של הכנס.
5. זריעה של תאי הריאה אפיתל (16HBE)
הערה: השלבים הבאים יש לבצע במתקן BSL-3.
- דואר ריאות זרעתאי pithelial (16HBE) על גבי MO: MQ-פיברובלסטים-קולגן שכבה. כדי לבצע את זה, לנתק ראשון 16HBE תאים מהבקבוק על ידי טיפול עם טריפסין (כמו ב2.2.1.) וגלול ב 4 x 10 6 תאים / מיליליטר בDMEM ללא אנטיביוטיקה.
- לשאוב התקשורת והתרבות בתוך ומחוץ להוספה. לאחר מכן להוסיף 1.5 מיליליטר ללא DMEM אנטיביוטי מלא בתחתית הבאר מחוץ להוספה.
- הוסף 50 μl של 16HBE על גבי מטריצת קולגן תא-פיברובלסטים החיסונית. השאר למשך 2 דקות במכסת המנוע ודגירה עבור שעה 1 באינקובטור 37 מעלות צלזיוס עם 5% CO 2. לאחר דגירה, להוסיף בעדינות 2 מיליליטר של האנטיביוטיקה ללא DMEM המלא בכנס והתרבות על 37 מעלות צלזיוס במשך 3 ימים. צעד התרבות מאפשר התפשטות של תאי האפיתל במודל הרקמות.
הערה: ככל שתאים הוסיפו מחוברים באופן רופף, תוספת של תקשורת צריכה להיות איטית ועדינה על ידי הזזה דרך הקירות של הכנס.
6. מיזוג-חשיפה של ריאות 3Dדגם
הערה: יום 5 לאחר תוספת של מקרופאגים נגועים לאחר, דגמי הרקמה הם חשוף אוויר ואת השלבים הבאים יש לבצע במתקן BSL-3.
- לשאוב התקשורת והתרבות בתוך ומחוץ להוספה.
הערה: בשלב זה ניתן לאסוף supernatants לזיהוי של גורמים מופרשים. צנטריפוגה, סטרילי-מסנן והחנות supernatants ב -70 ° C. - להוסיף 1.8 מיליליטר DMEM ללא אנטיביוטיקה מלאה בתא החיצוני ודגירה ב 5% CO 2 ב 37 חממת מעלות צלזיוס למשך 2 ימים. אל תוסיף תקשורת ותרבות בכנס.
הערה: מיזוג הרמת של מודל הרקמות מאפשרת ההיווצרות של epithelia מרובדת והפרשת ריר, המספק את הכוח לרקמות ודמיון פיסיולוגי לרקמת ריאה אנושית.
7. קציר והרכבת דגם רקמות 3D ריאות
הערה: השלבים הבאים יש לבצע במתקן BSL-3.
- יום 7 לאחר השתלה של מקרופאגים הנגועים ב, דגמי הרקמה מוכנים לקציר. הסר את המדיה התרבות לחלוטין ממודל הרקמות. תקן את מודל הרקמה עם paraformaldehyde 4% למשך 30 דקות בחושך ב RT. צעד זה הורג את החיידקים ומתקן את מורפולוגיה רקמות / תאים לעיבוד נוסף.
- באמצעות אזמל, להפריד את הקרום מלהוסיף גם. העבר את הקרום המכיל את הרקמה ל1x PBS המכיל גם.
- לחתוך ולהסיר את הצדדים של מודל הרקמות באמצעות אזמל נקי. אז פורס את מודל הרקמה ל -4 חתיכות מרובעות שווים בערך. העבר את פיסת הרקמה על גבי זכוכית Superfrost. אחסן את חתיכות הרקמה ב1x PBS על 4 מעלות צלזיוס.
- ייבש את הרקמה למשך 5 דקות ולעלות באמצעות antifade להאריך זהב עם DAPI וcoverslip. השאר את השקופיות ללא הפרעה בחושך ב RT עד יבש.
הערה: עובי הרקמה עשוי להשתנות בין המרכז לפריפריה, גורם tilti הקלng של coverslip. כדי להימנע מכך, spacer (לparafilm למשל) עשוי להיות ממוקם בפינת להחליק את המכסה. - החל לק לקצוות של coverslip ולאפשר לו להתייבש. לטבול את השקופיות באתנול 70% כדי להפוך אותם בטוחים להביא מחוץ למתקן BSL-3.
8. ויזואליזציה, רכישה וניתוח כמותי 3D
- דמיינו את שקופיות רקמות באמצעות מערכת מיקרוסקופ confocal עם לייזרים הפולטים ב 488 ננומטר לעירור של ה- GFP (ערוץ ירוק), 420 ננומטר עבור DAPI (כחול) ו555 ננומטר למונוציטים שכותרת PKH26 (אדום) בהתאמה.
- לרכוש תמונות 3D ברזולוציה 512x512 עם Z- ערימות כיסוי במינימום של עובי 20 מיקרומטר ושיש 1-1.5 מיקרומטר הפרדה בין ערימות. לרכוש 5-10 תחומים שונים המכסים את כל פיסת הרקמה.
הערה: השתמש בתצורה כגון Nyqvist להגדרות אופטימליות של רזולוציה אופטית (אורך גל, כוח / חשיפת לייזר, גודל פיקסל וזום). הימנע האו"םדער או על הרוויה של פיקסלים. - לנתח את תמונות confocal עם תוכנת עיבוד תמונת 3D. לכימות 3D של צבירי תאים, הצעדים הבאים מומלצים לניתוח אופטימלי.
- פתח את תוכנת עיבוד תמונת 3D ולטעון את התמונה. מדוד את הממדים של אובייקטים להיות מנותחות בתמונה, לדוגמא, בגודל של גרעין, מונוציטים פרט וחיידקים בודדים. תצפיות אלה שימושיות להגדרה או סינון האובייקטים.
- שימוש בכלי התאמת תצוגה, לייעל נפח טיוח על ידי התאמת כל ערוץ לניגוד תמונה, בהירות ולמזג אטימות. צעד זה הוא למזער את ההפרעה של רעש בנפח טיוח.
הערה: תיקון גמא עלול להוביל למניפולציה של תמונות ולכן יש להימנע. - צור משטחים על-ידי בחירה במסלול האדום (מונוציטים) ולהגדיר את הסף (בחירה אוטומטית או ידנית). במידת הצורך, להשתמש במסננים כדי להגביל את הבחירה של מונוציטים אדומים או שלא לכלול בackground. באופן דומה, ליצור משטחים לירוקים (שחפת) וערוצים כחולים (גרעינים) כפי שתואר לעיל.
- לייצא את הנתונים לקבצי MS-Excel. ניתן לייצא פרמטר מסוים או את כל הנתונים. הפרמטרים רלוונטיים לניתוח של אשכולות תא הם נפח, עוצמה, מספר האובייקטים, מספר voxels והכדוריות.
- לשמור ולייצא את התמונות בפורמט תמונה מתאימה רצוי TIFF.
הערה: אנימציות גם יכולות להתבצע באמצעות תפריט האנימציה ונשמרה כקובץ מדיה. - שמור את הגדרות הניתוח של כל ערוץ באמצעות אפשרות הפרמטרים הוספה ויכול להאסף מאוחר יותר באמצעות פונקציה לבנות מחדש. במקביל לנתח יותר קבצים באמצעות כלי העיבוד אצווה.
הערה: כל התמונות שיש בהשוואה חייב להיות רכש, מעובד ומנותח באותו אופן. לדוגמא תמונה 8 סיביות (256 שלם) לא צריך להיות בהשוואה לתמונה 12 ביט (4096 מספר שלם).
תוצאות
מודל רקמת הריאה 3D לשחפת אנושית ניתן להשתמש ביעילות כדי ללמוד את אינטראקציות מארח הפתוגן במ ' זיהום שחפת. השלבים הבסיסיים של שיטה זו, תמונות מיקרוסקופיות נציג של צעדים שונים ומבנה מיקרוסקופי כולל של סעיף רקמות מתוארות באיור 1. יש המודל מספר מרכיבים של רקמת ריאה אנושית, כולל fibroblasts ריאות, תאי האפיתל הסימפונות ומונוציטים עיקריים / מקרופאגים משובץ בסביבת רקמות 3D. מלבד שילוב מרכיבים של רקמת ריאה אנושית, המודל דומה תנאים פיסיולוגיים כלומר ריבוד של epithelia והפרשת ריר.
דוגמא לשימוש במודל רקמת הריאה בניטור זיהום שחפת מוצגת באיור 2. להמחשה מ ' הגירת שחפת -immune תא ואינטראקציה, הצגנו מקרופאגים נגועים במ ' שחפת שמבטאת GFP(ירוק) יחד עם מונוציטים המבודדים הטרי שכותרת PKH26 (האדומה) למודל הרקמות (כחול, DAPI מוכתם לגרעינים). יום 7 לאחר תוספת של מ 'ב תאי -infected שחפת למודל הרקמות, מיקרוסקופיה confocal מגלה אשכולות של מונוציטים אדומים באתר של זיהום (ירוק) (איור 2), אשר מחקה את נגעי סימן ההיכר של שחפת אדם 9.
סדרה של תמונות נציג להדמיה 3D של מ ' שחפת -infected מודל וכימות של צבירי תאי רקמה מוצג באיור 3. הדמיית 3D נותנת גמישות למשתמש אינטראקציה, לבחון ולכמת כמה תכונות בתמונת 3D. הסידור המרחבי של חיידקים ירוקים ואשכולות מונוציטים אדומים ניתן לראות ממבט הפסגה, סיבוב ורוחב כפי שמודגם באיור 3, אשר חושפים אשכולות של מונוציטים באתר של מ ' שחפת. האשכולות לא אובשירת ברקמות נגוע (איור 3 א). אנחנו לכמת את הגודל ומספר אשכולות תא מונוציטים ומצאנו שהגודל (נפח) של אשכולות תא מוגבר (p <0.001), בעוד שמספר מונוציטים בודדים ירד (p <0.01) במ ' שחפת נגועה רקמות בהשוואה לדגמים נגוע רקמה (איור 3 ג ו3D). נתונים אלה מאמת הממצא הקודם שלנו של היווצרות granuloma המוקדמת במ ' זיהום שחפת שנצפה בדגמי רקמת ריאה מנותחים בסעיפים רקמות 2D 9.
הנתונים שלנו מצביעים על כך שמודל הרקמה מספק בית גידול טבעי 3D לחקור את המארח המורכב תאי ד'מ ' רשת תקשורת שחפת. מצאנו גם כי הדמיית 3D וניתוח כמותי כלים טובים יותר ללימוד התכונות במודל הרקמה (איור 3). כימות של אשכול תא (granuloma למשל) לעתים קרובות סטרץ הס לכמה שכבות תאים ויכולים להיות שנתפס לחלוטין על ידי ניתוח כמו 3D. יתר על כן, להדמיה של תכונות מרחב ובזמן מדויקות של תאים או חיידקים במודל פרט לאפשר לימודים בשידור חי-הדמיה, הגירה ומעקב במעבדה ייעודית.
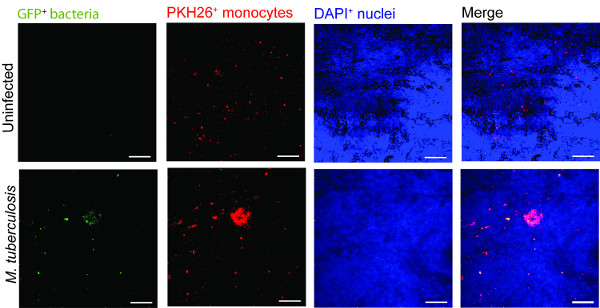
איור מונוציטים 2. באשכול מודל רקמות סביב מ 'ארסי שחפת. תמונות confocal נציג נגוע ומ ' מודל רקמות נגועות בשחפת מוצג. פנלים מירוקים (מ 'tuberculosis- GFP), (מונוציטים שכותרת PKH26) אדומים, (גרעינים צבעוניים DAPI) כחולים וערוצים התמזגו להראות הגיוס של מונוציטים ברקמה נגועה בהשוואה לרקמות נגוע. קנה מידה - 100 מיקרומטר.large.jpg "style =" font-size: 14px; קו-גובה: 28px; "target =" _ blank "> לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
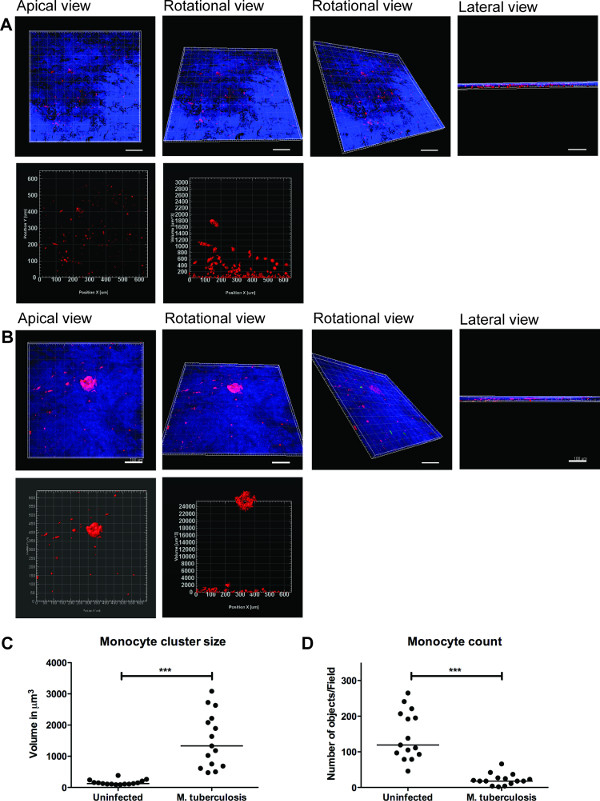
איור 3. הדמיה 3D וניתוח כמותי של מודל רקמה לספק מידע שימושי. נציג תמונות של הדמיית 3D של המודל כולו הרקמה () רקמה נגוע, (ב) נגוע במ ' שחפת, דרך חתך אופטי באמצעות מיקרוסקופ confocal Zeiss LSM700 וניתוח כמותי על ידי תוכנת Imaris עיבוד תמונה (גרסה 7.6.8). תמונות אלה נרכשו בהגדלה 20X, 14 Z- ערימות כיסוי עובי רקמה של 19.5 מיקרומטר עם 1.5 מיקרומטר מרווח, המאפשר הדמיה מהפסגה אופקית, סיבוב, מבט סיבובי אנכי ורוחבי (A ו- B). (ג) קואהגודל ניתוח ntitative של צבירי תאי מונוציטים חושפים משופר (p <0.0001) של אשכולות granuloma מוקדם לאחר מ ' זיהום שחפת בהשוואה להיעדרות של זיהום. (ד) כימות מספר מונוציטים הראו ירידה (p <0.01) ברקמות נגועות בהשוואה לרקמה נגוע, חוזר יותר אשכולות ברקמה נגועה. ירוק - מ ' -GFP שחפת, אדום - מונוציטים PKH26 כותרת, כחול - גרעין תא, בקנה מידה -. 100 מיקרומטר אנא לחץ כאן כדי לצפות בגרסה גדולה יותר של דמות זו.
Discussion
The ability to recruit and form organized cell clusters at the site of infection is the hallmark of human TB 11. These dynamic structures known as tubercle granulomas primarily consist of immune cells (macrophages, monocytes, T-cells and B-cells) and multi-nucleated giant cells surrounding M. tuberculosis. The role of the granuloma has long been considered to wall off the infection, preventing local spread of bacteria. However, more recent studies show that granuloma formation is critical for early bacterial survival, growth and dissemination 12. A strategy of new studies is to identify molecules or pathways that could efficiently be targeted to inhibit the cellular migration in granuloma formation and/or TB dissemination.
A caveat for novel studies on TB is the lack of models that recapitulate human TB. The most widely used experimental animals do not form true granuloma upon M. tuberculosis infection, and are therefore not appropriate choices for studies of TB 13-16. Non-human primates have the closest resemblance to human TB 17, but are not the preferred choice owing to high operational costs and ethical issues. Human TB is a complex immunological process and is difficult to model in vitro. Cell cultures of monolayers or co-cultures lack the 3D environment and tissue responses. Therefore, we have developed an innovative lung tissue model based on human primary immune cells and human lung-specific cell lines 8,9. The model displays characteristic features of human lung tissue, including epithelia with evenly integrated macrophages, formation of extracellular matrix, stratified epithelia and mucus secretion 9.
The 3D human lung tissue model has several benefits over the in vitro single or co-cultures seeded on tissue culture plates or transwell inserts. First, the human lung-specific cells (fibroblasts and epithelial cells) are not commonly included in the in vitro single or co-cultures. Second, the immune cells and lung-specific cells are embedded in a 3D physiological context (collagen rich extra-cellular matrix products). The response of cells to a stimulus/infection and the migratory behaviour of cells, for instance formation of a granuloma, differ significantly between a 2D and 3D environment. Furthermore, the described method enables the 3D visualization and robust 3D quantitative analysis that provides pivotal information on spatial distribution and intricate cellular interactions.
Experimental infection in the model tissue with M. tuberculosis resulted in clustering of macrophages at the site of infection, reminiscent of early TB granuloma (Figure 2 and 3). We have recently demonstrated that mutant strains defective in the ability to secrete the virulence factor ESAT-6 or Mycobacterium bovis BCG that lacks ESAT-6 did not induce the clustering of monocytes (no early granuloma), in contrast to the virulent M. tuberculosis 9. These data are consistent with the observations made from Mycobacterium marinum-infected zebrafish embryos, whose transparency allows for elegant live imaging of granuloma formation 12. As there is no gold-standard model for TB, we took advantage of the surgically resected tissue biopsies from TB patients for validation of the method 9. Our in vitro tissue model shares several characteristics with the lung and lymph node biopsies from TB patients, including the aggregation of macrophages in granuloma, the presence of both intra- and extracellular bacteria 18 and induction of necrosis 11.
Although the described model has physiological relevance to human TB and has several advantages over other in vitro models, it has some limitations. For instance, out of more than 20 collagen proteins identified in humans, only type I is included to the model to mimic the extra-cellular matrix. However, type I collagen is a complex mixture of extra-cellular matrix products and is the most abundant collagen in the human body. Further, we have demonstrated the presence of collagen IV and several extra-cellular matrix proteins such as tropoelastin, vimentin and laminin, which are produced by the epithelial cells and fibroblasts in the tissue model, indicating the synthesis of new collagen 8. Presently, the lung tissue model only has monocytes and macrophages, besides lung-specific cells. It lacks neutrophils and lymphocytes that are also known to be present in the granuloma. Remarkably the model is not limited to the introduction of additional immune cells and is of interest to explore how they contribute to the complex cellular interactions in human TB. Implantation of primary alveolar macrophages, skin-specific cells and lung carcinoma cells has already been tested in the model. Since our objective was to use a model that closely resembles human TB, introduction of mouse cells have not been attempted.
In summary, the lung tissue model has implications for both basic mechanistic and applied studies. Potential applications of the lung model include the study of innate immunity, investigating mechanistic aspects of host defences such as phagosomal maturation, autophagy, production of cytokines, chemokines and anti-microbial peptides, and functional characterization of individual cell types. Strikingly, the in vitro tissue model allows manipulation of one or more cells types and provides a relevant tissue micro-environment, not only for studies on TB, but for a variety of infectious and non-infectious diseases that affect the lungs.
Disclosures
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Microscopy core facility at the Faculty of Health Sciences, Linköping University for providing access to advanced imaging systems; Karl-Eric Magnusson (Emeritus Scientist) at the Dept. of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Linköping University for providing access to Imaris 3D/4D image processing software (Bitplane, Switzerland); and S. Braian for his help with the lung model cartoon. This work was supported by funds from the Swedish Research Council (Alternatives to animal research, 2012-1951) and Swedish Research Council (2012-3349) to M.L. and Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research to S.B. S.B. receive grants from the Karolinska Institutet, Swedish Research Council, the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency (Sida) and the Swedish Civil Contingencies Agency (MSB), and the Swedish Heart and Lung Foundation (HLF). M.S. received grants from the Karolinska Institutet and Stockholm County Council.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Cell culture inserts | BD Falcon | 353092 | |
| 6-well culture plates | BD Falcon | 353046 | |
| MRC-5 cells, lung fibroblasts | ATCC#CCL-171 | ||
| 16HBE cells, lung epithelial cells | Gift from Dr. Dieter Gruenert, Mt. Zion Cancer Center, University of California, San Fransisco, USA | ||
| 5 x Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (5 x DMEM) | Gibco | 12800-082 | Made from powder but add 5 times less water. Adjust pH to 7.3 and filter it using a 0.2 µm filter. |
| Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium with glucose (DMEM) 1x | Gibco | 41965-039 | |
| Minimum Essential Medium (MEM) 1x with Earle’s salts | Sigma | M4655 | |
| Non-Essential Amino Acids Solution, 100x | Life Technologies | 11140-035 | |
| L-glutamine 200 mM (100x) | Gibco | 25030-024 | |
| Sodium Pyruvate | Life Technologies | 11360-039 | |
| NaHCO3 (71.2 mg/ml) | Prepared in house | ||
| Heat inactivated Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) | Gibco | 10270-106 | Heat inactivated for 30 min, 56 °C |
| Gentamicin (50 mg/ml) | Gibco | 15750-060 | |
| Hepes buffer solution 1M | Gibco | 15630-056 | |
| Penicillin Streptomycin (Pen Strep) | Gibco | 15140-122 | |
| Lymphoprep | Axis-Shield | 7801 | |
| Ultrapure 0.5 M EDTA | Gibco | 15575 | |
| Bovine Collagen PA treated (500 ml) | Organogenesis | 200-055 | |
| Pure col purified Bovine Collagen solution (100 ml) | Advanced biomatrix | 5005-B | |
| Extracellular matrix protein, Fibronectin (1 mg) | BD | 354008 | |
| Primary human monocytes/macrophages | Isolated from human whole blood or buffy coats. | ||
| PKH26 Red fluorescent cell linker | Sigma | MINI26 | |
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv expressing green fluorescent protein | M. tuberculosis H37Rv wild type was transformed with the pFPV2 plasmid constitutively expressing GFP. | ||
| Middlebrook 7H9 medium | Difco | 271310 | |
| BBL Middlebrook ADC Enrichment | BBL | 211887 | |
| Tween-80 | |||
| Glycerol | |||
| Kanamycin B sulfate (20 µg/ml) | Sigma | B5264 | |
| Prolong Gold anti=-fade reagent with DAPI | Invitrogen | P36935 | |
| Trypsin -EDTA | |||
| Bovine serum albumin | |||
| Paraformaldehyde | |||
| DAPI | |||
| LSM700 Confocal microscope | Zeiss | ||
| iMaris Scientific 3D/4D image processing software, version 7.6.8 | Bitplane AG |
References
- Sakamoto, K. The pathology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Veterinary pathology. 49, 423-439 (2012).
- Saunders, B. M., Britton, W. J. Life and death in the granuloma: immunopathology of tuberculosis. Immunol Cell Biol. 85, 103-111 (2007).
- Kaufmann, S. H. New issues in tuberculosis. Ann Rheum Dis. Ann Rheum Dis. 63, ii50-ii56 (2004).
- Morrison, J., Pai, M., Hopewell, P. C. Tuberculosis and latent tuberculosis infection in close contacts of people with pulmonary tuberculosis in low-income and middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 8, 359-368 (2008).
- Barry 3rd, C. E., et al. The spectrum of latent tuberculosis: rethinking the biology and intervention strategies. Nat Rev Microbiol. 7, 845-855 (2009).
- Puissegur, M. P., et al. An in vitro dual model of mycobacterial granulomas to investigate the molecular interactions between mycobacteria and human host cells. Cell Microbiol. 6, 423-433 (2004).
- Kapoor, N., et al. Human Granuloma In Vitro Model, for TB Dormancy and Resuscitation. PLoS One. 8, e53657 (2013).
- Nguyen Hoang, ., T, A., et al. Dendritic cell functional properties in a three-dimensional tissue model of human lung mucosa. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 302, L226-L237 (2012).
- Parasa, V. R., et al. Modeling Mycobacterium tuberculosis early granuloma formation in experimental human lung tissue. Dis Model Mech. 7, 281-288 (2014).
- Cozens, A. L., et al. CFTR expression and chloride secretion in polarized immortal human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 10, 38-47 (1994).
- Brighenti, S., Andersson, J. Local immune responses in human tuberculosis: learning from the site of infection. J Infect Dis. 205, S316-S324 (2012).
- Davis, J. M., Ramakrishnan, L. The role of the granuloma in expansion and dissemination of early tuberculous infection. Cell. 136, 37-49 (2009).
- Gupta, U. D., Katoch, V. M. Animal models of tuberculosis. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 85, 277-293 (2005).
- Kashino, S. S., Napolitano, D. R., Skobe, Z., Campos-Neto, A. Guinea pig model of Mycobacterium tuberculosis latent/dormant infection. Microbes Infect. 10, 1469-1476 (2008).
- Singhal, A., et al. Experimental tuberculosis in the Wistar rat: a model for protective immunity and control of infection. PLoS One. 6, e18632 (2011).
- Subbian, S., et al. Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibition alters gene expression and improves isoniazid-mediated clearance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in rabbit lungs. PLoS Pathog. 7, e1002262 (2011).
- Lin, P. L., et al. Tumor necrosis factor neutralization results in disseminated disease in acute and latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection with normal granuloma structure in a cynomolgus macaque model. Arthritis Rheum. 62, 340-350 (2010).
- Rahman, S., et al. Compartmentalization of immune responses in human tuberculosis: few CD8+ effector T cells but elevated levels of FoxP3+ regulatory t cells in the granulomatous lesions. Am J Pathol. 174, 2211-2224 (2009).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved