A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Quantitative Assessment of Macropinocytosis in mTORC1-Hyperactive Cells using Flow Cytometry
In This Article
Summary
This protocol provides experimental tools to evaluate macropinocytic uptake of nutrients (carbohydrate and protein) by mTORC1-hyperactive cells. Detailed steps to quantify the uptake of fluorescently labeled dextran and bovine serum albumin (BSA) are described.
Abstract
Macropinocytosis is a highly conserved, actin-dependent endocytic process that allows the uptake of extracellular material, including proteins and lipids. In proliferating cells, macropinocytosis can deliver extracellular nutrients to the lysosome, processed into critical macromolecule building blocks. Recent studies have highlighted the dependence of multiple cancers on macropinocytosis, including breast, colorectal and pancreatic cancer. Ras mutations are thought to be the driver events behind macropinocytosis initiation, leading to the activation of cellular anabolic processes via the mTORC1 signaling pathway. Interestingly, mTORC1 can also be activated by macropinocytosis independently of Ras. Therefore, macropinocytosis represents a metabolic vulnerability that can be leveraged to target macropinocytic tumors by limiting their access to nutrients therapeutically.
In Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC) and Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM), mTORC1-hyperactivation leads to enhanced macropinocytosis and metabolic reprogramming. Here, we describe a flow cytometry-based protocol to assess macropinocytosis in mammalian cells quantitatively. TSC2-deficient MEFs are employed, which exhibit aberrant activation of mTORC1 and have been shown to have increased macropinocytosis compared to TSC2-expressing cells. Cells treated with pharmacologic inhibitors of macropinocytosis are incubated with fluorescently labeled, lysine-fixable, 70 kDa dextran, or fluorescently labeled bovine serum albumin (BSA) assayed by flow cytometry. To date, robust image-based techniques have been developed to quantitatively assess macropinocytosis in tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. This analysis provides a quantitative assessment of macropinocytosis in multiple experimental conditions and complements existing image-based techniques.
Introduction
Macropinocytosis is an endocytic process dedicated to the bulk uptake of extracellular material followed by the formation of macropinosomes, either recycled to the plasma membrane or fusing with lysosomes to degrade the internalized cargo1,2. Although cargo uptake is non-selective, macropinocytosis is a multi-step process, tightly regulated by Rab GTPases and membrane phospholipids3,4. Notably, cancer cells employ macropinocytosis to internalize extracellular nutrients, including proteins, polysaccharides and lipids. Macropinocytosis in cancer cells is activated by oncogenes downstream of Ras or v-Src as a mechanism to support their proliferation, especially under nutrient stress conditions5,6. Therefore, macropinocytosis represents a new therapeutic approach for targeting cancer cells by disrupting nutrient uptake pathways7,8.
In Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC) and Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM), loss of function mutations in TSC1 or TSC2 leads to hyperactivation of the mammalian/mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1)9. Aberrant mTORC1 activation is known to drive extensive metabolic reprogramming, including glucose and glutamine uptake and utilization, enhanced nucleic acid synthesis, lipid synthesis and autophagy10,11. To compensate for these increased anabolic demands, mTORC1-hyperactive cells increase the uptake of exogenous nutrients via macropinocytosis and enhance lysosomal degradation of internalized cargo12. In recent work, we identified ritanserin, an inhibitor of diacylglycerol kinase alpha (DGKA) as an agent that selectively inhibits the proliferation of TSC2-deficient cells13. DGKA is a lipid kinase that metabolizes diacylglycerol to phosphatidic acid (PA)14. PA is a crucial second messenger molecule that also plays a vital role in maintaining cell membrane homeostasis. Surprisingly, ritanserin strongly inhibits macropinocytosis by reprogramming phospholipid metabolism in TSC2-deficient cells. Therefore, targeting the nutrient uptake pathway of macropinocytosis in TSC2-deficient cells may provide novel therapeutic approaches in TSC and LAM.
Quantification of macropinocytic uptake in vitro and in vivo can provide crucial insights into macropinosome formation regulation and accelerate discovery of molecular mechanisms while identifying novel therapeutic approaches2,6. To date, multiple methodologies have been developed that adequately quantify macropinocytic uptake of fluorescent dextran both in vitro and in vivo2,15. Here we describe a flow cytometry-based approach to directly assess the amount of internalized dextran and albumin in mTORC1-hyperactive cells (Figure 1). This method can be utilized to analyze multiple experimental conditions in parallel and complements existing image-based approaches.
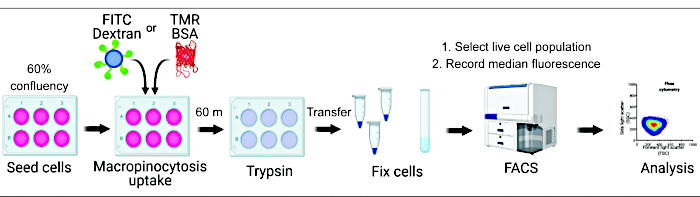
Figure 1. Workflow for the assessment of macropinocytosis in mammalian cells. Cells are seeded in six-well plates and subsequently treated with compounds of interest. Fluorescent dextran or BSA are added for 60 min, and the uptake is inhibited by washing with ice-cold PBS. Cells are fixed using paraformaldehyde, and fluorescence intensity is quantified by flow cytometry. Cells are gated, and data are analyzed with the appropriate software. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Protocol
1. Cell treatment
Day 1
- Seed TSC2-deficient and TSC2-expressing mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) in triplicate, in each well of a six-well tissue culture plate using DMEM, supplemented with 10% FBS. Cells should be 60-70% confluent by day 3.
- Seed additional control wells for each drug condition that will not be stained with FITC-Dextran or TMR-BSA.
Day 2
- Carefully aspirate media and rinse cells twice with PBS at room temperature.
- Treat cells with vehicle (DMSO), 100 µM of phosphatidic acid (PA), 25 µM of EIPA, 10 µM of ritanserin, or a combination of PA and ritanserin. Use DMEM supplemented with 1% FBS.
NOTE: DMSO volume should equal the maximal volume of solvent used in treating conditions. For example, if 10 µL of EIPA is used, the volume of DMSO in the vehicle conditions should also be 10 µL.
- Treat cells with vehicle (DMSO), 100 µM of phosphatidic acid (PA), 25 µM of EIPA, 10 µM of ritanserin, or a combination of PA and ritanserin. Use DMEM supplemented with 1% FBS.
Day 3
- Replace media with serum-free DMEM containing the abovementioned drugs and 0.5 mg/mL of FITC-Dextran or 0.5 mg/mL of TMR-BSA 16 h post-treatment. Incubate the cells in a 37 °C/5% CO2 cell culture incubator for 60 min.
NOTE: To minimize photobleaching of the fluorophores, FITC-Dextran and TMR-BSA tubes should be wrapped in aluminum foil and the experiment should be performed in a cell culture cabinet with the lights turned off. - Aspirate media and wash twice with ice-cold PBS.
- Detach cells using 500 µL of trypsin. Place cells in 37 °C/5% CO2 cell culture incubator for 2-3 min.
NOTE: Ensure all cells are detached by observing them under a brightfield microscope. - Using a clean pipette tip every time, collect cells in 1.5 mL tubes using 1% FBS supplemented DMEM on ice.
- Pellet cells by centrifugation at 425 x g for 2 min at 4 °C.
- Aspirate the supernatant.
- Detach cells using 500 µL of trypsin. Place cells in 37 °C/5% CO2 cell culture incubator for 2-3 min.
- Resuspend the cell pellet using 50 µL of 2% paraformaldehyde.
CAUTION: Paraformaldehyde is highly toxic and should be handled under an appropriate fume hood. Formaldehyde-containing waste should be disposed of according to institutional guidelines.- Incubate cells at room temperature for 10 min.
- Add 1 mL of ice-cold PBS to each tube and resuspend the cell pellet gently. Place the tubes on ice.
- Centrifuge cells at 425 x g for 2 min at 4 °C.
- Aspirate the supernatant.
- Resuspend cell pellet in 300 µL of ice-cold PBS.
- Transfer cells to the appropriate FACS tubes on ice.
- Proceed with flow cytometry.
2. Flow cytometry
- Briefly vortex the cells before inserting them into the FACS sample holder.
- Using low-speed flow, gate live cells from each unstained sample (negative control) using appropriate laser power as seen in Figure 2A. This step differs between instruments and will need to be optimized for each experiment. Adjust the power for both forward scatter (FSC) and side scatter (SSC) so that live cells are distinct from debris or cell clusters.
- Using the autogate feature, select the live cell populations for each sample avoiding cell debris and cell clusters.
NOTE: All cell events (regardless of gating) are ultimately recorded by the cytometer. Therefore selecting a gate at this step is not critical. - Record the fluorescence intensity from each sample using the appropriate green or red lasers.
3. Flow cytometry analysis
- Gate cells using forward and side scatter parameters. Apply the same gate to all samples.
- Create histograms for fluorescence in each sample as in Figure 2B.
- Within each cell gate calculate the mean/median fluorescence intensity for all samples.
- Export data for appropriate statistical analysis.
NOTE: During data analysis, the mean/median fluorescence intensity of each sample should be normalized by subtracting the unstained sample values.
Results
Ritanserin inhibits macropinocytosis in TSC2-deficient cells
We have previously shown that macropinocytic uptake of nutrients is increased by three-fold in TSC2-deficient cells compared to TSC2-expressing cells16. In TSC and LAM, macropinocytosis is mediated via diacylglycerol kinase alpha (DGKA). The metabolic product of DGKA is phosphatidic acid (PA), a crucial component of cellular membranes. Therefore, we hypot...
Discussion
Here, we describe a quantitative approach to assess macropinocytosis using flow cytometry. This method provides an accurate and rapid measurement of the fluorescently labeled macropinocytic cargo dextran and albumin. Prior studies have carefully characterized the macropinocytic index of cancer cells using confocal microscopy approaches15,20. Although these methods accurately quantify the internalization, size and spacial distribution of macropinosomes, they ...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The LAM Foundation Career Development Award. Figure 1 was created with BioRender.com. Critical reading was performed by Hilaire C. Lam.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| DMEM | Gibco | 11965-092 | Growth media |
| EIPA (amiloride) | Sigma Aldrich | A3085 | Macropinocytosis inhibitor |
| FBS | R&D Systems | S11150 | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| FITC-Dextran | Invitrogen | D1822 | Fluorescent polysaccharide (70kDa) |
| Parafolmadehyde | Pierce | 28906 | Fixation agent |
| PBS | Gibco | 10010-023 | Phosphate Buffer Saline |
| Penicilin/Streptomycin | Sigma Aldrich | P4458-100ML | Cell culture antibiotics |
| Phosphatidic Acid | Avanti | 840101P | Phospholipid derived from egg |
| Ritanserin | Tocris | 1955 | DGKA inhibitor |
| TMR-BSA | Invitrogen | A23016 | Fluorescent albumin |
| Trypsin | Sigma Aldrich | 25300-054 | Dissociation agent |
References
- Yoshida, S., Pacitto, R., Inoki, K., Swanson, J. Macropinocytosis, mTORC1 and cellular growth control. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 75 (7), 1227-1239 (2018).
- Commisso, C., et al. Macropinocytosis of protein is an amino acid supply route in Ras-transformed cells. Nature. 497 (7451), 633-637 (2013).
- Maxson, M. E., Sarantis, H., Volchuk, A., Brumell, J. H., Grinstein, S. Rab5 regulates macropinocytosis by recruiting the inositol 5-phosphatases OCRL/Inpp5b that hydrolyze PtdIns(4,5)P2. Journal of Cell Science. , (2021).
- Bohdanowicz, M., et al. Phosphatidic acid is required for the constitutive ruffling and macropinocytosis of phagocytes. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 24 (11), 1712 (2013).
- Ramirez, C., Hauser, A. D., Vucic, E. A., Bar-Sagi, D. Plasma membrane V-ATPase controls oncogenic RAS-induced macropinocytosis. Nature. 576 (7787), 477-481 (2019).
- Kamphorst, J. J., et al. Human pancreatic cancer tumors are nutrient poor and tumor cells actively scavenge extracellular protein. Cancer Research. 75 (3), 544-553 (2015).
- Kim, S. M., et al. Targeting cancer metabolism by simultaneously disrupting parallel nutrient access pathways. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 126 (11), 4088-4102 (2016).
- Selwan, E. M., Finicle, B. T., Kim, S. M., Edinger, A. L. Attacking the supply wagons to starve cancer cells to death. FEBS Letters. 590 (7), 885-907 (2016).
- Henske, E. P., Jozwiak, S., Kingswood, J. C., Sampson, J. R., Thiele, E. A. Tuberous sclerosis complex. Nature Reviews Disease Primers. 2, 16035 (2016).
- Duvel, K., et al. Activation of a metabolic gene regulatory network downstream of mTOR complex 1. Molecular Cell. 39 (2), 171-183 (2010).
- Sancak, Y., et al. The Rag GTPases bind raptor and mediate amino acid signaling to mTORC1. Science. 320 (5882), 1496-1501 (2008).
- Choo, A. Y., et al. Glucose addiction of TSC null cells is caused by failed mTORC1-dependent balancing of metabolic demand with supply. Molecular Cell. 38 (4), 487-499 (2010).
- Kovalenko, A., et al. Therapeutic targeting of DGKA-mediated macropinocytosis leads to phospholipid reprogramming in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. Cancer Research. , (2021).
- Swanson, J. A. Phorbol esters stimulate macropinocytosis and solute flow through macrophages. Journal of Cell Science. 94, 135-142 (1989).
- Commisso, C., Flinn, R. J., Bar-Sagi, D. Determining the macropinocytic index of cells through a quantitative image-based assay. Nature Protocols. 9 (1), 182-192 (2014).
- Filippakis, H., et al. Vps34-mediated macropinocytosis in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex 2-deficient cells supports tumorigenesis. Scientific Reports. 8 (1), 14161 (2018).
- Li, L., et al. The effect of the size of fluorescent dextran on its endocytic pathway. Cell Biol Int. 39 (5), 531-539 (2015).
- Jachimska, B., Wasilewska, M., Adamczyk, Z. Characterization of globular protein solutions by dynamic light scattering, electrophoretic mobility, and viscosity measurements. Langmuir. 24 (13), 6866-6872 (2008).
- Armstrong, J. K., Wenby, R. B., Meiselman, H. J., Fisher, T. C. The hydrodynamic radii of macromolecules and their effect on red blood cell aggregation. Biophysical Journal. 87 (6), 4259-4270 (2004).
- Lee, S. W., Alas, B., Commisso, C. Detection and Quantification of Macropinosomes in Pancreatic Tumors. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1882, 171-181 (2019).
- Williams, T. D., Kay, R. R. The physiological regulation of macropinocytosis during Dictyostelium growth and development. Journal of Cell Science. 131 (6), (2018).
- Koivusalo, M., et al. Amiloride inhibits macropinocytosis by lowering submembranous pH and preventing Rac1 and Cdc42 signaling. Journal of Cell Biology. 188 (4), 547-563 (2010).
- Ohkuma, S., Poole, B. Fluorescence probe measurement of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 75 (7), 3327-3331 (1978).
- Murphy, R. F. Analysis and isolation of endocytic vesicles by flow cytometry and sorting: demonstration of three kinetically distinct compartments involved in fluid-phase endocytosis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 82 (24), 8523-8526 (1985).
- Williams, T., Kay, R. R. High-throughput Measurement of Dictyostelium discoideum Macropinocytosis by Flow Cytometry. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (139), e58434 (2018).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved