Method Article
クロマチンレギュレータと米国でのゲノムワイドスナップショット
要約
生体内でゲノムにどのような影響を与えるかクロマチン制御因子とクロマチンの状態の問題は、細胞運命決定が発生中の胚になっている様子を、早期の我々の理解の鍵である。 ChIPの-SEQ-グローバルレベル-さアフリカツメガエル胚のためにここで概説でクロマチンの機能を調査するための最も一般的なアプローチ。
要約
The recruitment of chromatin regulators and the assignment of chromatin states to specific genomic loci are pivotal to cell fate decisions and tissue and organ formation during development. Determining the locations and levels of such chromatin features in vivo will provide valuable information about the spatio-temporal regulation of genomic elements, and will support aspirations to mimic embryonic tissue development in vitro. The most commonly used method for genome-wide and high-resolution profiling is chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by next-generation sequencing (ChIP-Seq). This protocol outlines how yolk-rich embryos such as those of the frog Xenopus can be processed for ChIP-Seq experiments, and it offers simple command lines for post-sequencing analysis. Because of the high efficiency with which the protocol extracts nuclei from formaldehyde-fixed tissue, the method allows easy upscaling to obtain enough ChIP material for genome-wide profiling. Our protocol has been used successfully to map various DNA-binding proteins such as transcription factors, signaling mediators, components of the transcription machinery, chromatin modifiers and post-translational histone modifications, and for this to be done at various stages of embryogenesis. Lastly, this protocol should be widely applicable to other model and non-model organisms as more and more genome assemblies become available.
概要
The first attempts to characterize protein-DNA interactions in vivo were reported about 30 years ago in an effort to understand RNA polymerase-mediated gene transcription in bacteria and in the fruit fly1,2. Since then, the use of immunoprecipitation to enrich distinct chromatin features (ChIP) has been widely adopted to capture binding events and chromatin states with high efficiency3. Subsequently, with the emergence of powerful microarray technologies, this method led to the characterization of genome-wide chromatin landscapes4. More recently, chromatin profiling has become even more comprehensive and high-resolution, because millions of co-immunoprecipitated DNA templates can now be sequenced in parallel and mapped to the genome (ChIP-Seq)5. As increasing numbers of genome assemblies are available, ChIP-Seq is an attractive approach to learn more about the genome regulation that underlies biological processes.
Here we provide a protocol to perform ChIP-Seq on yolk-rich embryos such as those of the frog Xenopus. Drafts of the genomes of both widely used Xenopus species—X. tropicalis and X. laevis—have now been released by the International Xenopus Genome Consortium6. The embryos of Xenopus species share many desirable features that facilitate and allow the interpretation of genome-wide chromatin studies, including the production of large numbers of high-quality embryos, the large size of the embryos themselves, and their external development. In addition, the embryos are amenable to classic and novel manipulations like cell lineage tracing, whole-mount in situ hybridisation, RNA overexpression, and TALEN/CRISPR-mediated knockout technology.
The following protocol builds on the work of Lee et al., Blythe et al. and Gentsch et al.7-9. Briefly, Xenopus embryos are formaldehyde-fixed at the developmental stage of interest to covalently bind (cross-link) proteins to their associated genomic DNA. After nuclear extraction, cross-linked chromatin is fragmented to focus subsequent sequencing on specific genomic binding or modification sites, and to minimize the contributions of flanking DNA sequences. Subsequently, the chromatin fragments are immunoprecipitated with a ChIP-grade antibody to enrich those containing the protein of interest. The co-immunoprecipitated DNA is stripped from the protein and purified before creating an indexed (paired-end) library for next-generation sequencing (NGS). At the end, simple command lines are offered for the post-sequencing analysis of ChIP-Seq data.
プロトコル
注:すべてのアフリカツメガエルの仕事は英国動物 (科学的処置)医療研究のためのMRC研究所が実施されるように法1986に完全に準拠しています。
1.準備
- (説明を参照してください)ChIP実験に必要な胚の数を推定します。
- 7.5に調整し、オートクレーブ滅菌EDTA、pHをせずに500ミリリットル10xのMarcの修正リンガー(MMR)(1MのNaCl、20のKCl、20のCaCl 2、10mMのMgSO 4を、:RTで保存されている次のソリューションを準備SDS溶出緩衝液50mMのHEPES pH7.5)に10を1ml(50mMトリス-HCl pH8.0,1mMのEDTA、1%SDS)および5×DNAローディング緩衝液1ml(0.2%オレンジG、30%グリセロール、60のEDTA pHは8.0)。
- 4℃で保存され、次の溶液を調製する:50 HEG緩衝液(50mM HEPES-KOH pH7.5,1mMのEDTA pH8.0で、20%グリセロール)、抽出緩衝液E1(50mMのHEPES-KOH pHを500mlのミリリットル7.5、150mMのNaCl、1mMのEDTA。 10%グリセロール、0.5%のIgepal CA-630、0.25%トリトンX-100)、E2(10mMのpH8.0のトリス-HCl、150mMのNaCl、1mMのEDTA、0.5mMのEGTA)、及びE3(10mMのトリス-HCl pH8.0で、150mMのNaCl、1mMのEDTA、1%のIgepal CA-630、0.25%のNa-デオキシコレート、0.1%SDS)、RIPA緩衝液(50mM HEPES-KOH pH7.5の500mMのLiClを、1mMのEDTAを500ml 1%のIgepal CA-630、0.7%デオキシコール酸ナトリウム)およびTEN緩衝液(10mMのTris-HCl pH8.0,1mMのEDTA、150mMのNaCl)50mlの。
- スコアと7ミリリットルマークで15ミリリットルコニカルポリスチレンチューブをクリップ。超音波処理を受けて核抽出物を含むように、このチューブを使用してください。
- ポスト配列決定分析のために、少なくとも8 GBのRAMと500ギガバイトの空きディスク容量とマルチコアのUnixスタイルのオペレーティングコンピュータを使用。局部的にそのうちのほとんどは、コマンドラインで使用されている次のソフトウェアをインストールします。FastQC、イルミナCASAVA-1.8品質のフィルタ、ボウタイ11、SAMtools 12、ホーマー13、MACS2 14、IGV 15,16、Cluster3 17、Javaのツリービュー、BLAST + 18、とb2g4pipe 19。コンパイラおよびサードパーティ製のソフトウェアのインストール手順と要件を確認してください。
- 短いNGSを整列させるためのボウタイインデックスを構築アフリカツメガエルのゲノムに読み込みます。例はXのためにここに示されているXenbase ftpサーバ(/パブ/ゲノミクス/ JGI)からFASTAファイル(genome.fa)としてダウンロードすることができトロピカゲノムV7.1(2011年11月)、。ボウタイのインデックスサブディレクトリに FASTAファイルを移動します。
- xenTro7インデックスファイルを生成するために(ここではプロンプト文字の後に>)次のコマンドラインを使用します。
>ボウタイビルド/path/to/bowtie/index/genome.fa xenTro7
>輸出BOWTIE_INDEXES = /パス/に/蝶ネクタイ/インデックス/
- xenTro7インデックスファイルを生成するために(ここではプロンプト文字の後に>)次のコマンドラインを使用します。
- UCSCゲノムブラウザまたはツール/テーブルブラウザを経由して、最新のゲノムのバージョン(genomes.nimr.mrc.ac.uk)用NIMRサーバ上のミラーサイトからの遺伝子注釈ファイル(GTF)をダウンロードします。 Hをカスタマイズするために、ゲノムFASTAファイルとGTFファイルを使用して、アフリカツメガエルのためトメール( 例えば、X.トロピカゲノムV7.1、 - xenTro7に名前を付ける )。
- また、アフリカツメガエルのゲノムの一部の古いバージョンの構築済みのHOMERパッケージを使用。
> loadGenome.pl -name xenTro7 -orgヌル-fasta /path/to/genome.fa -gtfパス/に/ genes.gtf
- また、アフリカツメガエルのゲノムの一部の古いバージョンの構築済みのHOMERパッケージを使用。
- と注釈ファイル(genes.gtf)(同じフォルダにgenome.fa.faiファイルとgenome.fa)インデックス付きFASTAファイルをアップロードしてゲノムブラウザIGVのためのゲノムトラック(.genomeファイル ) を作成します。次のようにアフリカツメガエルのゲノムのためのゲノム足場指数(genome.fa.fai)を作成します。
> samtools faidx /path/to/genome.fa - 次のようにアフリカツメガエルの遺伝子上にいくつかのモデル種(ヒト、マウス、ゼブラフィッシュ、ショウジョウバエおよび酵母)からの遺伝子オントロジー(GO)の用語を渡すために+ BLASTを使用します。
- ツール経由UCSCゲノムブラウザから単一FASTAファイル(cds.fa)として、すべてのコード配列(CDS)をダウンロード/テーブルブラウザと非冗長タンパク質(NR)の事前にフォーマットBLASTデータベースで更新BLAST +:
> update_blastdb.pl NR - ヒト(txid9606)を検索する、マウス(txid10090)、ゼブラフィッシュ(txid7955)、フルーツフライ(txid7227)及び酵母(txid4932)、その高度な検索機能を経由してNCBIサイトからのタンパク質(HTTP://www.ncbi.nlm.nih。 GOV /タンパク質/高度)と、コンピュータに生じたGI(シーケンス識別子)リスト(sequence.gi.txt)を送る。
- 一定の期待(E)値のカットオフ(ここでは10 -20)でBLASTxのを実行することにより、GIリストから最も類似したタンパク質にアフリカツメガエルの遺伝子を割り当てます。出力フォーマットは、(-outfmt 5 -out blastx_results.xml)XMLであることを確認してください。利用可能なコンピュータのコア数と相関時間節約のスレッド(-num_threads)をご利用ください。
> BLASTX -db /パス/に/ NR -gilist /path/to/sequence.gi.txt -query /パス/ TO / cds.fa -evalue 1E-20
-outfmt 5 -out /path/to/blastx_results.xml -num_threads [#スレッド] - テキストエディタでb2g4pipeフォルダのb2gPipe.propertiesファイルを開き、Dbacces.dbname = b2go_sep13とDbacces.dbhost = publicdb.blast2go.comへのデータベースのプロパティを更新。インストールフォルダから実行しますb2g4pipe。
> javaのXmx1000m -cp *:EXT / *:es.blast2go.prog.B2GAnnotPipe -in /path/to/blastx_results.xml
-out結果/ xenTro7 -prop b2gPipe.properties -v -annot
注:このプログラムの抽出物は、各BLASTヒットのための条件をGOと対応するアフリカツメガエルの遺伝子(xenTro7.annot)に割り当てます。最も更新されたデータベースの設定は(9.11.1を参照)Blast2GO Java Web Startアプリケーションのツール/一般設定/のDataAccess設定]で見つけることができます。
- ツール経由UCSCゲノムブラウザから単一FASTAファイル(cds.fa)として、すべてのコード配列(CDS)をダウンロード/テーブルブラウザと非冗長タンパク質(NR)の事前にフォーマットBLASTデータベースで更新BLAST +:
2.クロマチン架橋
- アフリカツメガエルの卵を受精、デゼリーと文化のembryos標準的なプロトコル20に記載の方法。
- キャップ8ミリリットルのガラス製サンプルバイアルに興味のある発達段階でdejellied胚(最大2500 アフリカツメガエルまたは10,000 X.トロピカ ) を転送し、0.01XのMMRで一度簡単にそれらを洗う。
- (固定時間と必要な胚の数のための議論を参照してくださいRTで15から40分間0.01X MMR( 例えば 、8ミリリットルの0.01XのMMRに36.5から38パーセントホルムアルデヒドの225μlを添加)の1%ホルムアルデヒドで胚を修正)ChIP実験あたり。
注:ホルムアルデヒドは、腐食性及び毒性が高い。それは、目や皮膚に接触、消化不良、及び吸入した場合に危険である。バイアルにホルムアルデヒドを追加するときにヒュームフードを使用してください。 - 簡単に冷たい0.01XのMMRで胚を3回洗浄することにより固定を停止します。表面張力が破裂するためにそれらを引き起こすためエン ブリーOSが液面に接触しないようにしてください。
- 氷上で2 mlのマイクロチューブに胚を分注し孵化する前に、約250μL(X.トロピカ )または600μL( アフリカツメガエル )の容積を占めるチューブあたり250の胚、最大で。
- 離れてピペットできるだけ多くの0.01XのMMR。あなたはセクション3ですぐに続ける場合は、次の手順をスキップします。
- 冷たいHEGバッファー250μlの中で胚を平衡化する。胚がチューブの底に沈降した後、できるだけ多くの液体を除去し、スナップ凍結し、液体窒素中で。 -80℃で保管してください。
3.クロマチンの抽出
注: アフリカツメガエル胚から架橋されたクロマチンの以下の抽出は、固定工程2.3に示す時間と50から80 Xで最も効率的に動作しますトロピカまたは25から40 X.抽出バッファーE1、E2及びE3の1ml当たりの胚ツメガエル 。バッファの回計算された量が必要とされるように、各抽出工程は、繰り返される。アップスケーリングのために、複数の2ミリリットルmicrocentriを使用フーガ管または50ミリリットル遠心管。クロマチン抽出中に氷の上のサンプルとバッファーを保管してください。
- 1mMのDTTおよびプロテアーゼ阻害剤錠剤バッファE1、E2及びE3の適切なボリュームを補う。 5 mMのNaFをおよび2 mMのNa 3 VO 4とリン酸化特異的抗体を用いたChIP、さらにサプリメントバッファを行う場合は。
- ピペッティングによりE1と固定胚を均質化する。 2分(50 mlチューブを使用する場合には5分)、1,000×gで冷却遠心機(4℃)で遠心ホモジネート。上清と壁に接続された任意の脂質を吸引除去する。
- E1中のペレットを再懸濁。 10分間氷上でサンプルを保管してください。ステップ3.2のように上清を遠心分離し、廃棄します。
- E2中のペレットを再懸濁。ステップ3.2のように上清を遠心分離し、廃棄します。
- 手順を繰り返し3.4が、遠心分離前に10分間氷上でサンプルを続ける。
- E3でペレットを再懸濁。少なくとも10分間氷上でサンプルを保管してください。遠心分離して廃棄し、SUステップ3.2とpernatants。
注:この段階で、再懸濁はかなり透明になる必要があります。 E3でのアニオン性界面活性剤は水溶性の残りの卵黄血小板の大部分をレンダリングすることによって架橋された核を抽出します。 - E3 1mlの総容量に再懸濁し、架橋された核のプールペレット(通常は不溶化顔料顆粒から茶色に着色)。それは非常に粘性が表示され、ピペットが困難な場合には2または3 mlのE3でサンプルを希釈する。同じまたは次の日の手順4を続行するために氷の上または4℃で保管してください。後で使用するために-80℃で液体窒素とストア内のスナップ凍結。
4.クロマチン断片化
注:超音波処理は可溶化することおよび架橋クロマチンをせん断の両方に使用される。ここでは1/16インチテーパーマイクロチップやサウンドエンクロージャを搭載したミソニックスソニケーター3000を実行するためのパラメータである。他の超音波処理器を使用する場合は、せん断するメーカーの推奨事項に従ってください架橋されたクロマチンまたは合計で4〜8分間12 Wに6を使用しています。
- 超音波処理(ステップ1.4)のために特注のチューブにステップ3.7からの核サンプルを転送します。短い温度計クランプを経由して氷水で満たされた800ミリリットルのプラスチックビーカーに添付管を使用したことにより、超音波処理中冷やしサンプルを保管してください。
- 実験用ジャッキにビーカーを置きます。超音波処理器のマイクロチップは、容積の深さの約2/3サンプルに浸漬し、管壁に触れることなくセンタリングされるように、ジャックを調整する。
- 合計で7分間のサンプルを超音波処理、1分間の一時停止を30秒毎に中断。 1.0に電源を設定します。サンプルが泡に始めた場合、超音波処理を起動し、すぐに9から12の読みに到達するために電力設定(通常は2〜4)を大きくW.はすぐに一時停止します。チューブを再配置し、泡が完全に消失した場合に再起動します。
- >(フルスピードで予備冷却し1.5ミリリットルマイクロチューブやスピンに断片化したクロマチンを移し15,04℃で5分間00 XG)。
- 1.5ミリリットルのマイクロチューブに予め冷やした上清を移し。クロマチン断片化(セクション5)の程度を可視化するために(理想的に周りに40万以上の核のクロマチンを含む)を50μlの上清を収集します。チップ(セクション6)のために上清の残りの部分を使用してください。
- 最大1日4℃で保存サンプル。 -80℃での長期保存のために液体窒素中でアリコート(ChIP実験ごとに1つ)としてスナップ凍結サンプル。
5.イメージングクロマチン断片化
- ステップ4.6から上清50μlにSDS溶出緩衝液50μl、5 M NaClを4μLおよびプロテイナーゼK(20μgの/μL)の1を添加する。
- オーブン65℃に設定し、ハイブリダイゼーションで6から15時間(O / N)インキュベートする。
- 商業PCR精製キットを用いてDNAを精製する。必要であれば、製造業者によって推奨されるようにpHを調節するために酢酸ナトリウム(pH5.2)の3 Mを使用する。溶出溶出緩衝液の11μlの(10mMトリス-HCl pH8.5)中でのDNA二回。
- 100 bpおよび電気泳動による1.4%アガロースゲル上の1キロバイトのDNAラダーと一緒に全体のサンプルを実行する前に、RNアーゼA(20μgの/μL)の0.4μLを追加し、5倍のDNAローディングバッファー5μlの。電気泳動後の安全な核酸染色溶液で最適な結果が、染色ゲルである。
6.クロマチン免疫沈降
注:4℃で5分間、磁気ビーズを洗浄するために、このセクションでは、低保持1.5mlの微小管を使用し、チューブあたり、指示バッファの少なくとも1ミリリットル。溶液が透明になるまでビーズからバッファを削除する前に、または20から30秒間、磁気ラックに毎回チューブを残す。
- ChIPのために使用される総クロマチンの約1%に相当する入力サンプルとして後で使用するために新しいチューブにステップ4.6からの転送上清(断片化クロマチン)の10〜30μlの。 4で保存ChIPサンプルは、架橋を逆転させるための準備ができるまで、C°。
- 新しいチューブに残りのクロマチンを転送します。抗体コントロールを必要とするのChIP-qPCR実験のために、2管にクロマチンの等容量を配布。
- クロマチンにChIPグレード抗体(または対応する抗体コントロール)を追加します。おおよその目安としては、目的のエピトープを発現する1つの百万個の細胞あたり約1μgの抗体を使用しています。
- より正確に(参照、ChIP実験ごとに必要な抗体の量を推定する抗体の様々な量( 例えば 、0.25μgの、1μgから2.5μgの)と同じチップを実行するとチップqPCRによりネガティブとポジティブコントロール遺伝子座での収量を比較するために、セクション10)。抗体対照として、抗体と同一のアイソタイプおよび宿主動物種の正常血清を使用しています。
- 4℃で回転体(10 RPM)O / Nでインキュベートする。
- 5分間のaのためのE3で一度抗体互換の磁気ビーズの十分な量を洗うT 4°C。チェック ビーズ(通常はビーズの5から20μlのIgG抗体1μgのをバインド)の抗体結合容量のために製造業者の仕様。
- 抗体プレインキュベートクロマチンに洗浄したビーズを追加します。さらに4時間、回転体(10 RPM)でインキュベートする。
- 洗浄は、あらかじめ冷却RIPAバッファーで4回(のChIP-qPCRに)または10倍(のChIP-配列)のビーズ、及び一旦予め冷却TEN緩衝液である。
- ChIPの-配列実験を実施する場合にのみ、このステップを実行する。
- 再懸濁は、チューブあたりTEN緩衝液50μlにビーズを洗浄した。 1新しいチューブにそれらを転送することにより、単一チップ実験からのプールは、すべてのビーズ。チューブの底にビーズを収集するための磁気ラック1000×gで冷蔵(4℃)遠心分離を使用する。ビーズのペレットを中断することなく、できるだけ多くの液体できるだけ捨てる。
- SDS溶出バッファーとvortの50から100μlのビーズを再懸濁することによりビーズ取り除くチップ材65℃で15分間サーモミキサー(1,000回転)で連続してexing。 30秒間フルスピード(> 15000 XG)でその遠心した後。新しいチューブに上清(チップ溶出液)を転送します。
- 最後のステップを繰り返し、チップ溶出液を兼ね備えています。
7.クロマチンリバースクロスリンクとのDNA精製
- 100〜200μlの(段階6.10)でのChIP試料の体積に到達するために、入力サンプル(ステップ6.1)に十分なSDS溶出緩衝液を加える。 5 M NaClを1/20容量を有するチップと入力サンプルの両方を補完する。ハイブリダイゼーションオーブン中で65℃で6〜15時間(O / N)のためのサンプルをインキュベートする。
- 200μgの/ mlのTEバッファーおよびRNase Aの1ボリュームを追加します。 37℃で1時間インキュベートする。
- 200μgの/ mlのプロテイナーゼKを追加します。 55℃で2から4時間インキュベートする。
- フェノールによってDNAを精製:クロロホルム:イソアミルアルコール抽出以前に9を概説したようにエタノール沈殿が続く。 ChIPの-配列の場合は、32を追加溶出緩衝液(10mMトリス-HCl、pH8.5)中のμlのDNAペレットを溶解する。 DNAが完全に溶解されることを保証するために30分間氷上でのサンプルのままにしておきます。
注:商業PCR精製キットは低いDNA回収率を有するが、より便利であり、のChIP-qPCRのサンプルのために使用することができる。 - ChIPの-配列の場合は、蛍光光度法に基づく方法を使用して、チップと入力DNAの1μlの濃度を決定する。メーカーの指示に従って、DNAの濃度は、蛍光光度計の信頼性の高い検出範囲内にあることを確認してください。
8.のChIP-のSeqライブラリー構築と検証
注:DNAライブラリーを調製するための現在の方法は、1〜2 ngのからNGS用複雑度の高いライブラリーの構築を可能にする。いくつかの複雑さを犠牲にして、ライブラリは、DNAのわずか50 PG(特定の材料/機器の表を参照)から作成することができる。チップと入力ライブラリの両方に同量のDNAを使用してください。簡単に説明すると、MAKへ電子インデックス付きのChIP-配列のライブラリは、チップと入力DNAが末端修復する必要がある(ペアエンド)は、(特定の材料/機器の表を参照)特殊なアダプターに連結し、サイズ選択とPCR増幅。
- ChIPの-配列のライブラリを作るために、メーカーのガイドラインに従ってください。さらに推奨事項について説明を参照してください。
- 溶出バッファーの12μlの各ライブラリを溶出し、蛍光光度計を使用して各チップと入力ライブラリの1μlの濃度を決定する。 5から25 ng /μLでの濃度を期待しています。濃度は25 ng /μLでより高い場合PCRサイクル(18サイクルよりも少ない)の数を減らすことを検討してください。
注:正確な定量は、最適なNGS結果を達成するための鍵である。 18回のPCRサイクル後に1 ng /μLで程度の低濃度のライブラリは、配列決定されますが、頻繁に低い複雑であることができます。 - 断片サイズ分布を決定するために、ライブラリの1μLを使用して、Cですべてのアダプターダイマー汚染(バンド約120 bp)をチェックするヒップベースのキャピラリー電気泳動。 1:1のビーズ対サンプル比で固相可逆固定化精製を繰り返します(代わりに、1.6:1)ライブラリはアダプターダイマーが含まれている場合。
- 類似のDNA濃縮の傾向は前に、ライブラリ調製後に観察されているかどうかをチェックするために検証され、正と負の制御遺伝子座(セクション10を参照)上のqPCRを実行します。配列決定のために品質管理承認されたライブラリを提出してください。
9.後の配列決定分析とデータの可視化
注:今日では、NGSは、多くの場合、社内または商用シング施設(一部NGSのガイドラインについての説明を参照)によって行われる。標準出力シーケンシングの保存数百万人が読み込む(.fastq.gz *)単一または複数のgzipで圧縮FASTQファイルです。通常、多重化は、すでに彼らのインデックスに応じて分離されている読み取り、各読み取りは、各BASのためのシーケンス識別子及び品質管理スコア(イルミナ1.8+のためのPhred + 33)が含まれていますEコール。このアプローチは、ここでNGSデータを分析するための多くの方法のうちの唯一のものである。読者は、この分野が急速に進んでいるとの更新が定期的に発生しているとして、次のコマンドラインのいずれかが変更を必要とするかどうかを確認することが推奨されている。
- gzipで圧縮FASTQファイルを連結し、FastQCスクリプトを使用して配列決定データの品質をチェック。これを実行し、チップと入力シーケンシングデータの両方のために、次のコマンドのほとんど 端末からの(例としては、ChIPのために示されている)。
>猫/path/to/*.fastq.gz> ChIP.fastq.gz
> fastqc ChIP.fastq.gz
注:高複雑チップ-配列ライブラリの成功したシークエンシングからの生データは、ほとんどのテストに合格する必要があります。障害は貧しいシングが実行され、そのようなバイアスされたPCR増幅またはアダプタ汚染などの実験の工芸品から主に由来する。重複(冗長性)ある程度の冗長読み取りとして善意の DNA濃縮を表すことができ期待されている 21。しかしながら、後で読み取りタグを制限することができる- 5 '末端または読み取る-塩基対ごとに1つの任意の冗長を除去するためには、ピークの検出感度(ステップ9.4)21に影響を与えずに読み取る。 - アダプタ汚染を除去するための前処理配列決定データ(homerToolsトリム-3 <アダプター配列を>)は、1つのミスマッチ(-mis 1)を可能にする。 (インデックス化)アダプタの最初の20塩基(5 'から3')(特定の材料/機器の表に記載されているアダプターのために示さ)ライゲーションの際に目的のDNA断片に近接して使用してください。
> gzipの-cd ChIP.fastq.gz | fastq_illumina_filter -vn> ChIP.fastq
> homerToolsはトリム-3 GATCGGAAGAGCACACGTCTは1 -min 36 ChIP.fastqを-mis
注:フィルタリング(-N)を読み取るの除去は、唯一のイルミナ1.8で生成されたFASTQファイルのデフォルトによって必要とされている。 fastq_illumina_filterコマンドを省略( すなわち 、。 '| fastq_illumina_filter -Vn')1.8より古いバージョンでは、シーケンス識別子を生成した場合。 - 揃える前処理されたが、ボウタイを用いて基準ゲノム(xenTro7)に読み込みます。 IEのみ、最初の28拠点で最大の2つのミスマッチとSAM形式で最大の70レポートのアライメント(-S)の読み取りあたりのすべてのミスマッチの合計のPhred + 33品質スコア、デフォルト設定を使用して(-m 1)読み込みマッピングされた一意に保つ。チャンクメモリが使い果たされている場合、スレッドあたりのメガバイト(--chunkmbs)の数を増やします。
>ボウタイ-m 1 -S -p [#スレッド] --chunkmbs [例えば200] xenTro7 ChIP.fastq.trimmed> ChIP.sam
注:ボウタイはデフォルトでのPhred + 33品質スコアを期待しています。 FASTQファイルが1.8よりも古いイルミナによるのPhred + 64品質スコアで生成された場合phred64-quals -オプションを含めます。 - 大物ファイル(.bw)にアライメント(SAM)ファイルを変換するために2ホーマーのコマンドを使用します。
> makeTagDirectoryのChIP / -single -TBP 1 ChIP.sam
> makeUCSCfileのChIP /ChIP.bw -o -bigWig /パス/に/ genome.fa.fai -fsize 1E20ノルム1E7
注:変換は、参照ゲノム(ステップ1.8)の足場指数(genome.fa.fai)が必要です。ここで、プロファイルは、塩基対ごとに1つのタグに制限(-TBP 1)及び千万に正規化される( ノルム1E7)を読み出す。大物は、動的にそのようなIGV(ステップ9.12)などのゲノムブラウザでクロマチンプロファイルを視覚化するための推奨フォーマットの一つです。 - ゲノムのランドマーク( 例えば 、25塩基対のビン、-si ZE 20000 -hist 25と+/- 10キロバイト)などの転写開始(TSS、ここに示す例)、および終了など(でのタグの分布(-dチップ/)を決定TTS)のサイト。 アフリカツメガエルの注釈xenTro7(ステップ1.7)でHOMER perlスクリプトのannotatePeaks.plを実行します。
> annotatePeaks.pl TSS xenTro7 -size 20000 -hist 25 -dのChIP /> ChIP_tagDensity.tss - チップとの間のDNA濃縮の有意なピークを探す(ChIP.sam -t)とXの入力(-c Input.sam)トロピカゲノムモデル構築のための200 bpの(--bw = 200)の(0.01 -q)1%のFDRカットオフと(超音波処理後)のDNA断片とMACS2を使用。そのようなヒストンマークまたはRNAポリメラーゼのような目的のクロマチン機能の広い分布を期待している場合は、このコマンドラインにフラグ--broadを追加します。
> macs2 callpeak -t ChIP.sam -c Input.sam -f SAM -nのChIP -g 1.4376e9 -q 0.01 --bw = 200
注:Xの有効サイズトロピカゲノムアセンブリV7.1は約14.376億BP(-g 1.4376e9)です。 MACS2は彼らのゲノム位置にピークを入隊BEDファイル(ChIP_peaks.bed)を生成します。 - クラスタ化されたヒートマップの形でいくつかのクロマチンのプロファイルを比較します。
- 興味のあるタグ密度ディレクトリからタグ分配マトリクスを作成します(-dのChIP / other_ChIP /)MACS2ピーク(AT 例えば 、25塩基対のビン、-size 2000 -hist 2と+/- 1キロバイト5 -ghist):
> annotatePeaks.pl ChIP_peaks.bed xenTro7 -size 2000 -hist 25 -ghist -dのChIP / other_ChIP /> ChIP.matrix - ChIP.matrixファイルをアップロードし、階層的に最も近い重心に対して最小のユークリッド距離に基づいて、これらのタグ密度をクラスタ化するCluster3のグラフィカル·ユーザ·インタフェースを使用してください。クラスタリングを可視化するためにJavaのツリービューで生成されたCTDファイルを開きます。
- 興味のあるタグ密度ディレクトリからタグ分配マトリクスを作成します(-dのChIP / other_ChIP /)MACS2ピーク(AT 例えば 、25塩基対のビン、-size 2000 -hist 2と+/- 1キロバイト5 -ghist):
- ピークサミットで濃縮されている小説と以前から知られている結合モチーフ、+/- 100塩基対(200 -size)検索。モチーフの発生をマップするとモチーフ密度をプロットするannotatePeaks.plを使用します。
> findMotifsGenome.pl ChIP_peaks.bed xenTro7 ChIP_motifs / -size 200 -p [#スレッド]
> annotatePeaks.pl ChIP_peaks.bed xenTro7 -m motif1.motif> ChIP_peaks.motif1
> annotatePeaks.pl ChIP_peaks.bed xenTro7 -m motif1.motif -size 800 -hist 25> motif1.density
注:findMotifsGenome.plスクリプトinfe比較ランダムに選択される遺伝子を中心としたバックグラウンド配列から濃縮をRS。最も濃縮された小説のモチーフは、位置重み行列の形式でmotif1.motifで保存されます。読者はそのようなcisFinder 22とMEME 23などの他のde novoモチーフ発見方法と、これらの結果を実証することが奨励されている。 - 最寄りの遺伝子への距離を計算することにより、400 bpの窓(400 -size)内での正規化されたリード回数を決定することによって、ピークを注釈:
> annotatePeaks.pl ChIP_peaks.bed xenTro7 -size 400 -dのChIP /入力/> ChIP_peaks.genes - 数(N)、個々の位置と正規化された読み取り回数(R)と最寄りのあたりのすべて(LR)のピーク(ターゲット)遺伝子をリストするには、次のawkコマンドを使用して出力をまとめる。
> awkは> = -5000 && 7ドル<= 1000 '{ t'の7ドルをFSは=} BEGIN」
{N [8ドル] + = 1; R [8ドル] + = 9ドル。 LR [8ドル]は、「LR [$ 8] =&#39; 7ドル(I N)のための '(' $ 9 ')'} END {
{プリントi 'は T' N [i]は ' t'のR [i]は ' t'のSUBSTR(LR [I]、2)}} 'ChIP_peaks.genes> ChIP_peaks.summary
注:$の後の数字は、前の手順で作成したChIP_peaks.genesファイルに合うように修正する必要があるかもしれない列番号を指す。このスクリプトの模範は、上流の5キロバイトとTSSの下流1キロバイトを超えたピークを除外します。7ドル、8ドルと9ドルがそれぞれ、TSS、遺伝子識別子とピークあたりの正規化された読み取り回数までの距離を参照してください。 - 次のように標的遺伝子の中で濃縮されたGOタームの分析を実行します。
- Java Web Startは(のjavaws)19を介してコマンドラインからBlast2GOのグラフィカル·ユーザ·インタフェースを起動します。
>のjavaws http://blast2go.com/webstart/blast2go1000.jnlp - 注釈をアップロードする開発者の指示に従ってくださいアフリカツメガエル 1.9.4で生成されたように遺伝子(xenTro7.annot)と同定された標的遺伝子のフラットファイルのファイル。同じ遺伝子識別子は両方のファイルで使用されていることを確認します。
- Java Web Startは(のjavaws)19を介してコマンドラインからBlast2GOのグラフィカル·ユーザ·インタフェースを起動します。
- トラックとしてIGVに大物(ChIP.bw、Input.bw)とBEDファイル(ChIP_peaks.bed)を添加することによりクロマチンのプロファイルを視覚化する。利用可能な場合は、開発の同じステージのためにRNA-配列トラックとデータを補完します。セッションとして結果を保存します。
- プログラミングのプラットフォームのR使用(www.r-project.org)上記生成されたように、さらにデータを操作し、視覚化する、またはMATLABを。また、Excelと小さなデータセットをプロットする。
テストチップとの確認のChIP-配列のための10のChIP-QPCR
- 陽性(ピーク特異的)および陰性対照遺伝子座の両方のために60°C(T mの )、約100 bpのDNAを取り囲むプライマーを設計するためにオンラインプラットフォームプライマー3を使用。 インシリコ使用したプライマー特異性を確認のPCR検索はUCSCゲノムブラウザに実装。
- 約1%の入力から始まる3倍希釈の8点標準曲線を作成するか、または2を使用-のDNA濃縮の定量化のためのΔΔC(T)メソッド8,24を 。
- すべてのサンプルのための技術的な三連でリアルタイムPCRを実行し、 すなわち 、チップ、コントロールと、必要があることも、標準曲線サンプル。
- 入力されたDNAの割合として、または陽性および陰性対照遺伝子座の両方で、コントロールサンプルに対するChIPのの比としてプロットDNA濃縮。
結果
プロトコルがうまく実行された場合、ここで提示されたものと同等の結果が予想され、使用中の抗体はChIPグレードの品質(議論を参照)である。このプロトコルは、ホルムアルデヒド固定アフリカツメガエル胚からの核の抽出と超音波処理によるクロマチンの効率的なせん断( 図1A-C)を可能にする。断片化したクロマチンは、主に100〜1,000塩基対までの範囲とBP( 図1C)300〜500ピーキングDNA断片の非対称の分布を示している。免疫沈降したDNAの最小限の50 PGが成功した同様のサイズのDNAインサート( 図2A)とインデックス付きペアエンドチップ-配列ライブラリーを作製するために必要とされている。図書館は、約120bpの電気泳動図で見ることができるアダプターダイマー、の大部分が欠けている必要があります。
シークエンシング·バイ·合成の際に、読み取る前処理は、ゲノム( 図2B、C)にマッピングされる。に成功した実験では、 X。トロピカリス胚は、シングルエンドの、通常50から70パーセントは、40塩基対の読み取り、最大2つのミスマッチをバージョン7.1のゲノムアセンブリに一意にマッピングすることができる。入力はゲノム全体に非常に均一に揃える読み込みますが、チップの位置合わせは、対象のクロマチン機能に隣接する鎖特異的濃縮度で結果を読み取ります。すべての断片は5 '末端( 図2C)25から配列決定されているためである。平均断片サイズに方向を読んで整列を拡張するような転写因子結合事象のような単一のクロマチン機能の正確なプロファイルを生成します。 IGVまたはその他の互換性のあるゲノムブラウザで可視化すると、これらのDNA占有率は、ピークとして表示されます。 MACSようなピークの発信者は、これらのピーク( 図3A)の位置を決定するために使用される。十結合部位の数千のこの方法は、Xに決定されているトロピカリスゲノムなどVegT 26とTボックス転写因子。 ChIPの-qPCRのexperiメンツは、チップ配列( 図3B)によって発見ローカル濃縮を確認する必要があります。
ChIPの-配列の実験は、クロマチン機能のゲノムワイドな特性を探ることができます。例えば、このような転写開始および終結部位ゲノムの要素を読み出し分布を算出する遺伝子( 図3C)の周りに空間的な結合優先を強調表示することができる。同様に、ピーク位置でリード分布のヒートマップは、ゲノムワイドスケール( 図3D)で異なるクロマチンの特徴を比較するために使用される。特定の転写因子は、DNA配列に特異的に結合する。ピークは潜在的な補因子( 図3E)の共富むモチーフを含むこの種の情報を取得することができ、基礎となるゲノムDNAのデノボモチーフ分析。標的遺伝子の大部分は、低いというよりも高いレベル( 図3F)におけるDNAの占有率を示す。このスケールフリーの特徴は、TRの間で非常に一般的であると思われるanscription因子と標的遺伝子のごく一部を直接生物学的関連27,28で規制されていることを示唆している。濃縮されたGOタームまたはそのような標的遺伝子の発現差異などの他の属性、さらにアフリカツメガエル胚 ( 図3G)におけるクロマチン機能の生物学的機能への洞察を明らかにすることができるの分析。
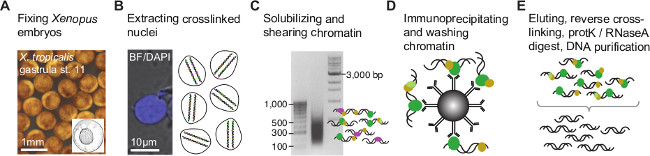
アフリカツメガエル胚図1.クロマチン免疫沈降手順。 (A)胚は、ホルムアルデヒド固定共有結合(架橋)に関心ゲノムDNAに関連するすべてのタンパク質の発達段階にある。核抽出(B)の際に、架橋されたクロマチンに隣接するDNを最小化することにより、ゲノムDNAの結合またはクロマチン修飾部位を絞り込むために断片化される配列(C)。続いて、クロマチンの断片は、関心(D)のエピトープを含むものを豊かにするChIPグレード抗体で免疫沈降される。共免疫沈降したDNAはNGS( 図2)のためのChIPフラグメントライブラリーを作成する前に、(E)タンパク質から剥離して精製される。 この図の拡大版をご覧になるにはこちらをクリックしてください。

図2.チップ-のSeqライブラリ準備、シークエンシング·バイ·合成、マッピングおよびピーク呼出し。 (A)電気泳動図は、250から450までのDNAテンプレートを持つ良品チップ-配列のライブラリが表示されます。これらのテンプレートは、ユニバーサル(58 BP)が隣接して目的のDNAインサートとインデックス化(63 bp)のアダプタを必要とする。(B) の何百万人も、同一のテンプレートを含む各クラスタに、可逆、明確な蛍光体と同一の終端特性を有するすべての4つのヌクレオチドの存在下で塩基により塩基を配列決定する。蛍光画像は、最終的に読み込むに組み立てられる対応する塩基を呼び出すためにリアルタイムで処理されている。(C)のみを一意アフリカツメガエルのゲノムにマップが保存されていることを読み取ります。すべての断片は、5 '末端から配列決定されたように、ChIPのマッピングは、対象のクロマチン機能に隣接する鎖特異的なピークで結果を読み取る。これにより、ピーク発信者が正確にクロマチンの機能をローカライズするために、平均断片長に読み込み、免疫沈降から発信され、延長濃縮を検出する。 この図の拡大版をご覧になるにはこちらをクリックしてください。
図3.接合体T-ボックス転写因子VegT(zVegT)により、後の配列決定分析とデータの可視化の例。すべてはここに示されている数は一意千万に正規化マッピングされ、非冗長読み取っているお読みください。(A)抜粋Xに結合zVegTのゲノムワイドプロファイルのトロピカ原腸胚(Nieuwkoopとフェイバー29の後、ステージ11から12.5)。各ピークは、拡張のパイルアップを読み出し、一つの結合部位を表す。これらのピークは、1%未満の偽発見率(FDR)でMACS2によって呼び出される。各MESP遺伝子(30 RNA-配列データ)を非常に近位端および上流zVegT結合を示しているが、唯一mespaとmespbは 、その段階で表される。(B)zVegTのDNA占有レベル(非含むいくつかの遺伝子座でのChIP-qPCRにより決定される結合型地域β アクチンの上流0.5キロバイト)CONFIのChIP-配列によって発見特定の濃縮をrm汎用。 (A)に(赤いバー)と呼ばれるピークとmespaための結果を比較します。 DNAの占有レベルは、VegT抗体(IgGアイソタイプのウサギポリクローナル)を用いたChIP及び抗体対照(正常ウサギIgG)とのChIP両方の入力のパーセンテージとして可視化される。エラーバーは、2つの生物学的複製物の標準偏差を反映している。(C)Metagene分析は周辺で他のゲノム領域へと遺伝子本体内のプロモーターへの結合を優先zVegTを(タグは25bpの上でビニング)を示しています。(D)は、ヒートマップは、k平均を示しているクラスタ化された(K = 5)DNA占有レベルが原腸段階ですべてのzVegT結合領域へのzVegT及び酸化Smad2 / Smad3の(チップ配列データ31)の相対的な(タグは、25塩基対の上ビニング)。ヒートマップは、ログ2ベースとBPあたり5タグを中心とするある。(E) デノボモチーフ分析はzVegT-の38%に結合モチーフ標準的なT-ボックス転写因子を発見基礎となるモチーフスコアはバックグラウンド配列中の5%の発見率に正規化された場合に領域を結合した。正規のSmad2 / Smad3の結合モチーフはほとんど濃縮されていないのに対し、密度マップは、zVegT結合部位の中央にT-boxモチーフのための最高の富化を示す。(F)ヒストグラムは、各標的遺伝子について計算されるzVegTのDNA占有レベルを示す[ - ]。上流の5キロバイトの間に全てのピーク(+/- 200 bp)のからの転写開始部位の対応すると1キロバイト下流[+](G)トップ300の遺伝子が最も高いDNA占有レベル-5 KBと1キロバイト以内である初期胚発生の生物学的プロセスについて濃縮。これらの用語はzVegTの推定機能に沿ったものであるGO。 FDRは、両側フィッシャーの正確確率検定に基づいて、複数のテストのために補正している。 この図の拡大版をご覧になるにはこちらをクリックしてください。
ディスカッション
私たちのプロトコルは、 アフリカツメガエル胚からゲノムワイドなクロマチンのプロファイルを作成し、分析する方法について説明します。それは、 生体内で内因性遺伝子座への架橋タンパク質からのin silicoで濃縮されたゲノムのサイトを表す読み取る数百万を処理するすべてのステップをカバーしています。ゲノムのドラフトの増加数が利用可能なので、このプロトコルは、他のモデルと非モデル生物に適用可能であるべきである。前作8,31,33,34から離れて、このプロトコルを設定し、最も重要な実験の項では、架橋された核を抽出するためのポスト固定手順です。それは、効率的なクロマチンの可溶化及びせん断および容易なアップスケーリングが容易になります。一緒に図書館準備の改良効率を有するこのプロトコルは半分から関心のクロマチン関連エピトープを表す2百万個の細胞に高複雑チップ-配列ライブラリーの構築を可能にします。 ChIPの-qPCR実験のために、これらの細胞のいくつか1万は、通常は十分です多分6つの異なるゲノム遺伝子座でDNA濃縮をチェックする。これらの数値は、保守的な見積もりであるが、タンパク質発現レベルは、抗体の品質、架橋効率、およびエピトープのアクセシビリティに依存して変化し得る。目安として、単一のアフリカツメガエル胚は、中期胞胚期で約4000細胞(Nieuwkoopとフェイバー29の後8.5)、後半の原腸段階(12)で、40,000細胞や初期尾芽段(20)に100,000細胞が含まれています。
効率的な免疫沈降のための正確な固定時間は、ChIPの、定量PCR(セクション10)によって経験的に決定される必要がある。実験はXを含む場合、一般的には、より長い固定時間が必要とされている胚、初期の発達段階、および弱い(または間接的な)DNA結合特性をツメガエル 。しかし、クロマチン断片化が少なく効率的になるように、40分よりも長いアフリカツメガエル胚を固定し、又は指示(セクション3)よりも多くの胚を処理してお勧めしません。それは重要ではありません非常に困難な卵黄に富む胚からの核抽出を行うことができ、ホルムアルデヒドを急冷するためのこの一般的なステップとして、定着後にグリシンを使用する。現在、この理由は不明である。これは、ホルムアルデヒド-グリシン付加物は、さらに、N末端 アミノ基またはアルギニン残基35と反応することが考えられる。
抗体は、任意のChIP実験の鍵であると十分な対照(Landt ら 36によるガイドラインを参照)、目的のエピトープに対する特異性を示すために行われる必要がある。何ChIPグレード抗体が利用可能でない場合、エピトープタグ融合タンパク質を、対応の導入は、これらのタンパク質は、内因性の結合部位37を占めることができるような合法的な代替手段であってもよい。この場合には、非注入胚は、陰性対照ではなく、非特異的血清でのChIPとして使用することが最善である。目的のタンパク質は、当研究所の乏しい回復をもたらす低レベルで発現される場合、この戦略を適用することも可能であるCHED DNA。
なぜなら、使用中のDNAの少量ののChIP-配列のライブラリーを作製するためのように、洗浄工程の数を減らし、最低限DNAの損失を維持するために反応を結合するための手順を選ぶことが推奨される。アダプターおよびプライマーは、(特定の材料/機器の表を参照)の多重配列決定およびNGSプラットフォームと互換性がある必要があります。 (長い一本鎖アームを含む)Y-アダプタを使用する場合、それは、サイズを選択するDNAインサートの前にPCR 3~5回と予め増幅するライブラリに重要である( 例えば 、100〜300 bp)のゲル電気泳動。一本鎖末端は、DNA断片が不均一に移行させる。試験は、PCRサイクル数を決定するために推奨されている入力DNA( 例えば 、0.1、0.5、1、2、5、10および20 ng)を種々の量で実行され(以下で18サイクルに等しい)のサイズを作るために必要な100から200 ngのの-selectedライブラリ。 PCRサイクルの数を減らすことのReduの配列をレンダリングndantは可能性が低い読み取る。固相可逆固定化ビーズは、効率的に目的のDNAを回復し、確実に連結およびPCR反応からの任意の空きアダプターと二量体を除去するための試薬をクリーンアップ良いです。
、読み込みの数、種類や長さの点では周りの20から30000000シングルエンドが36塩基対の読み取りに十分な深さで全体のアフリカツメガエルのゲノムをカバーするための最ものChIP-配列の実験のために十分である。最も一般的なNGSマシンは、これらの基準を満たすことが日常的に可能である。しかし、読み込みの広い分布が予想される場合に読み取るのではなく鋭いピークではなく、ヒストン修飾と観察されたように、数を増加させることが有益であり得る。多くのChIP-配列の実験のために、4~5異なってインデックス付きのライブラリをプールすることができ、高性能のNGS機を用いて一つのフローセルレーンに配列決定した。時々mappability wのを高めるために、リードの長さおよび配列のDNA鋳型(ペアエンド)の両端を拡張することも推奨される反復的なゲノム領域内のクロマチンを分析鶏。
このプロトコルは、そのような転写因子、シグナル伝達メディエーターおよび翻訳後ヒストン修飾として、クロマチン機能の多種多様な正常に適用された。彼らが開発し、クロマチンプロファイルを解釈するのが困難になるとしかし、胚は、細胞の不均一性の増加度合いを取得する。有望な手順は、細胞型特異的な核38,39を抽出することにより、組織特異的プロファイルクロマチン風景にシロイヌナズナおよびショウジョウバエにおいてなされている。私たちのプロトコルは、他の胚における組織特異的のChIP-配列への道を開くことができ、核抽出工程が含まれています。
開示事項
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
謝辞
We thank Chris Benner for implementing the X. tropicalis genome (xenTro2, xenTro2r) into HOMER and the Gilchrist lab for discussions on post-sequencing analysis. I.P. assisted the GO term analysis. G.E.G and J.C.S. were supported by the Wellcome Trust and are now supported by the Medical Research Council (program number U117597140).
資料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 1/16 inch tapered microtip | Qsonica | 4417 | This microtip is compatible with Sonicator 3000 from Misonix and Q500/700 from Qsonica. |
| 8 ml glass sample vial with cap | Wheaton | 224884 | 8 ml clear glass sample vials for aqueous samples with 15-425 size phenolic rubber-lined screw caps. |
| Adaptor | e.g., IDT or Sigma | NA | TruSeq universal adaptor,
AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAG ATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACAC GACGCTCTTCCGATC*T. TruSeq indexed adaptor, P-GATCGGAAGAGCACACGTC TGAACTCCAGTCAC ‐NNNNNN‐ ATCTCGTATGCCGTCT TCTGCTT*G. *, phosphorothioate bondphosphate group at 5' end. NNNNNN, index (see TruSeq ChIP Sample Preparation Guide for DNA sequence). Order adaptors HPLC purified. Adaptors can be prepared by combining equimolar amounts (each 100 µM) of the universal and the indexed adaptor and cooling them down slowly from 95 °C to room temperature. Use 1.5 pmol per ng of input DNA. Store at -20 °C. |
| b2g4pipe (software) | Blast2GO | non-commercial | http://www.blast2go.com/data/blast2go/b2g4pipe_v2.5.zip |
| BLAST+ (software) | Camacho et al. | non-commercial | http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PAGE_TYPE=BlastDocs& DOC_TYPE=Download |
| Bowtie (software) | Langmead et al. | non-commercial | http://bowtie-bio.sourceforge.net/index.shtml |
| cisFinder (software) | Sharov et al. | non-commercial | http://lgsun.grc.nia.nih.gov/CisFinder/ |
| Chip for capillary electrophoresis | Agilent Technologies | 5067-1504 | Load this chip with 1 µl DNA for library quality control. Store at 4 °C. |
| Chip-based capillary electrophoresis system | Agilent Technologies | G2940CA | The Agilent 2100 BioAnalyzer is used to check the quality of ChIP-Seq libraries. Keep reagents at 4 °C. |
| ChIP-Seq library preparation kit (KAPA Hyper Prep Kit) | Kapa Biosystems | KK8504 | Kit contains KAPA end repair and A-tailing enzyme mix, end Repair and A-tailing buffer, DNA ligase, ligation buffer, KAPA HiFi HotStart ReadyMix (2X), and KAPA library amplification primer mix (10X) (see also PCR primers). Adaptors are not included. Store at -20 °C. |
| ChIP-Seq library preparation kit (alternative, ThruPLEX-FD Prep Kit) | Rubicon Genomics | R40048 | Kit uses their own stem-loop adaptors and primers. This kit eliminates intermediate purification steps and is as sensitive as the KAPA Hyper Prep Kit. Store at -20 °C. |
| Cluster3 (software) | de Hoon et al. | non-commercial | http://bonsai.hgc.jp/~mdehoon/software/cluster |
| FastQC (software) | Simon Andrews | non-commercial | http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc |
| Fluorometer | life technologies | Q32866 | Qubit 2.0 Fluorometer |
| Fluorometer reagents | life technologies | Q32851 | The kit provides concentrated assay reagent, dilution buffer, and pre-diluted DNA standards for the Qubit fluorometer. Store DNA standards at 4 °C, buffer and dye at room temperature. |
| Formaldehyde | Sigma | F8775-4X25ML | Formaldehyde solution, for molecular biology, 36.5-38% in H2O, stabilised with 10-15% methanol. Store at room temperature. CAUTION: Formaldehyde is corrosive and highly toxic. |
| Gel (E-Gel EX agarose , 2%) | life technologies | G4010 | Pre-cast gel with 11 wells, openable format. Leave one lane between ladder and library empty to avoid cross-contamination. Store gels at room temperature. |
| Gel electrophoresis system | life technologies | G6465 | E-Gel iBase and E-Gel Safe Imager combo kit for size-selecting ChIP-Seq libraries. |
| Gel extraction kit | Qiagen | 28706 | Store all reagents at room temperature. Use 500 µl of QG buffer per 100 mg of 2% agarose gel slice to extract DNA. Use MinElute columns (from MinElute PCR purification kit) to elute DNA twice. |
| HOMER (software) | Chris Benner | non-commercial | http://homer.salk.edu/homer/index.html |
| Hybridization oven | Techne | FHB1D | Hybridizer HB-1D |
| IGV (software) | Robinson et al. | non-commercial | http://www.broadinstitute.org/igv/home |
| Illumina CASAVA-1.8 quality filter (software) | Assaf Gordon | non-commercial | http://cancan.cshl.edu/labmembers/gordon/fastq_illumina_filter |
| Java TreeView (software) | Alok Saldanha | non-commercial | http://jtreeview.sourceforge.net |
| Laboratory jack | Edu-Lab | CH0642 | This jack is used to elevate sample in sound enclosure for sonication. |
| Ladder, 100 bp | New England BioLabs | N3231 | Keep 1x solution at room temperature. Store stock at -20 °C. |
| Ladder, 1 kb | New England BioLabs | N3232 | Keep 1x solution at room temperature. Store stock at -20 °C. |
| Low-retention 1.5-ml microcentrifuge tubes | life technologies | AM12450 | nonstick, RNase-free microfuge tubes, 1.5 ml |
| MACS2 (software) | Tao Liu | non-commercial | https://github.com/taoliu/MACS |
| Magnetic beads | life technologies | 11201D | These Dynabeads are superparamagnetic beads with affinity purified polyclonal sheep anti-mouse IgG covalently bound to the bead surface. Store at 4 °C. |
| Magnetic beads | life technologies | 11203D | These Dynabeads are superparamagnetic beads with affinity purified polyclonal sheep anti-rabbit IgG covalently bound to the bead surface. Store at 4 °C. |
| Magnetic beads | life technologies | 10001D | These Dynabeads are superparamagnetic beads with recombinant protein A covalently bound to the bead surface. Store at 4 °C. |
| Magnetic beads | life technologies | 10003D | These Dynabeads are superparamagnetic beads with recombinant protein G covalently bound to the bead surface. Store at 4 °C. |
| Magnetic rack | life technologies | 12321D | DynaMag-2 magnet |
| MEME | Bailey et al. | non-commercial | http://meme.nbcr.net/meme/ |
| Na3VO4 | New England BioLabs | P0758 | Sodium orthovanadate (100 mM) is a commonly used general inhibitor for protein phosphotyrosyl phosphatases. Store at -20 °C. |
| NaF | New England BioLabs | P0759 | Sodium fluoride (500 mM) is commonly used as general inhibitor of phosphoseryl and phosphothreonyl phosphatases. Store at -20 °C. |
| NGS machine | Illumina | SY-301-1301 | Genome Analyzer IIx |
| NGS machine (high performance) | Illumina | SY-401-2501 | HiSeq |
| Normal serum (antibody control) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-2028 | Use as control for goat polyclonal IgG antibodies in ChIP-qPCR experiments. Store at 4 °C. |
| Normal serum (antibody control) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-2025 | Use as control for mouse polyclonal IgG antibodies in ChIP-qPCR experiments. Store at 4 °C. |
| Normal serum (antibody control) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-2027 | Use as control for rabbit polyclonal IgG antibodies in ChIP-qPCR experiments. Store at 4 °C. |
| Nucleic acid staining solution | iNtRON | 21141 | Use RedSafe nucleic acid staining solution at 1:50,000. Store at room temperature. |
| Orange G | Sigma | O3756-25G | 1-Phenylazo-2-naphthol-6,8-disulfonic acid disodium salt. Store at 4 °C. |
| PCR primers | e.g., IDT or Sigma | Primers to enrich adaptor-ligated DNA fragments by PCR: AATGATACGGCGACCACCGA*G and CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGA*G, phosphorothioate bond. Primers designed by Ethan Ford. Combine primers at 5 µM each. Use 5 µl in a 50 µl PCR reaction. Store at -20 °C. | |
| MinElute PCR purification kit | Qiagen | 28006 | for purification of ChIP-qPCR and shearing test samples. Store MinElute spin columns at 4 °C, all other buffers and collection tubes at room temperature. |
| Phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1, pH 7.9) | life technologies | AM9730 | Phenol:Chloroform:IAA (25:24:1) is premixed and supplied at pH 6.6. Use provided Tris alkaline buffer to raise pH to 7.9. Store at 4 °C. CAUTION: phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol is corrosive, highly toxic and combustible. |
| Primer3 (software) | Steve Rozen & Helen Skaletsky | non-commercial | http://biotools.umassmed.edu/bioapps/primer3_www.cgi |
| Protease inhibitor tablets | Roche | 11836170001 | cOmplete, Mini, EDTA-free. Use 1 tablet per 10 ml. Store at 4 °C. |
| Protease inhibitor tablets | Roche | 11873580001 | cOmplete, EDTA-free. Use 1 tablet per 50 ml. Store at 4 °C. |
| Proteinase K | life technologies | AM2548 | proteinase K solution (20 µg/µl). Store at -20 °C. |
| RNase A | life technologies | 12091-039 | RNase A (20 µg/µl). Store at room temperature. |
| Rotator | Stuart | SB3 | Rotator SB3 |
| SAMtools (software) | Li et al. | non-commercial | http://samtools.sourceforge.neta |
| Solid phase reversible immobilisation beads | Beckman Coulter | A63882 | The Agencourt AMPure XP beads are used to minimise adaptor dimer contamination in ChIP-Seq libraries. Store at 4 °C. |
| Sonicator 3000 | Misonix/Qsonica | Newer models are now available. Q125, Q500 or Q700 are all suitable for shearing crosslinked chromatin. | |
| Sound enclosure | Misonix/Qsonica | optional: follow the manufacturer's recommendation to obtain the correct sound enclosure. | |
| Thermomixer | eppendorf | 22670000 | Thermomixer for 24 x 1.5 mL tubes. Precise temperature control from 4 °C above room temperature to 99 °C. |
参考文献
- Gilmour, D. S., Lis, J. T. Detecting protein-DNA interactions in vivo: distribution of RNA polymerase on specific bacterial genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 81 (14), 4275-4279 (1984).
- Gilmour, D. S., Lis, J. T. In vivo interactions of RNA polymerase II with genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 5 (8), 2009-2018 (1985).
- Solomon, M. J., Larsen, P. L., Varshavsky, A. Mapping protein-DNA interactions in vivo with formaldehyde: evidence that histone H4 is retained on a highly transcribed gene. Cell. 53 (6), 937-947 (1988).
- Ren, B., et al. Genome-wide location and function of DNA binding proteins. Science. 290 (5500), 2306-2309 (2000).
- Johnson, D., Mortazavi, A., Myers, R., Wold, B. Genome-wide mapping of in vivo protein-DNA interactions. Science. 316 (5830), 1497-1502 (2007).
- Hellsten, U., et al. The genome of the Western clawed frog Xenopus tropicalis. Science. 328 (5978), 633-636 (2010).
- Lee, T. I., Johnstone, S. E., Young, R. A. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and microarray-based analysis of protein location. Nature Protocols. 1 (2), 729-748 (2006).
- Blythe, S. A., Reid, C. D., Kessler, D. S., Klein, P. S. Chromatin immunoprecipitation in early Xenopus laevis embryos. Dev Dyn. 238 (6), 1422-1432 (2009).
- Gentsch, G. E., Smith, J. C. Investigating physical chromatin associations across the Xenopus genome by chromatin immunoprecipitation. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2014 (5), (2014).
- Ubbels, G. A., Hara, K., Koster, C. H., Kirschner, M. W. Evidence for a functional role of the cytoskeleton in determination of the dorsoventral axis in Xenopus laevis eggs. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 77, 15-37 (1983).
- Langmead, B., Trapnell, C., Pop, M., Salzberg, S. L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 10 (3), R25 (2009).
- Li, H., et al. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 25 (16), 2078-2079 (2009).
- Heinz, S., et al. Simple combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime cis-regulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell identities. Mol Cell. 38 (4), 576-589 (2010).
- Zhang, Y., et al. Model-based analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol. 9 (9), R137 (2008).
- Robinson, J. T., et al. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat Biotechnol. 29 (1), 24-26 (2011).
- Thorvaldsdottir, H., Robinson, J. T., Mesirov, J. P. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief Bioinform. 14 (2), 178-192 (2013).
- Imoto, S., Nolan, J., Bioinformatics Miyano, S. . 20 (9), 1453-1454 (2004).
- Camacho, C., et al. BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinformatics. 10, 421 (2009).
- Conesa, A., et al. Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics. 21 (18), 3674-3676 (2005).
- Sive, H., Grainger, R., Harland, R. . Early development of Xenopus laevis: A laboratory manual. , (2000).
- Chen, Y., et al. Systematic evaluation of factors influencing ChIP-seq fidelity. Nat Methods. 9 (6), 609-614 (2012).
- Sharov, A. A., Ko, M. S. H. Exhaustive search for over-represented DNA sequence motifs with CisFinder. DNA Res. 16 (5), 261-273 (2009).
- Bailey, T. L., et al. MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucl Acids Res. 37 (2), W202-W208 (2009).
- Livak, K. J., Schmittgen, T. D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25 (4), 402-408 (2001).
- Park, P. J. ChIP-seq: advantages and challenges of a maturing technology. Nat Rev Genet. 10 (10), 669-680 (2009).
- Gentsch, G. E., et al. In vivo T-box transcription factor profiling reveals joint regulation of embryonic neuromesodermal bipotency. Cell Rep. 4 (6), 1185-1196 (2013).
- Barabasi, A. L., Oltvai, Z. N. Network biology: understanding the cell's functional organization. Nat Rev Genet. 5 (2), 101-113 (2004).
- Biggin, M. D. Animal transcription networks as highly connected, quantitative continua. Dev Cell. 21 (4), 611-626 (2011).
- Nieuwkoop, P. D., Faber, J. . Normal table of Xenopus laevis (Daudin): a systematical and chronological survey of the development from the fertilized egg till the end of metamorphosis. , (1994).
- Akkers, R. C., et al. A hierarchy of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 acquisition in spatial gene regulation in Xenopus embryos. Dev Cell. 17 (3), 425-434 (2009).
- Yoon, S. J., Wills, A. E., Chuong, E., Gupta, R., Baker, J. C. . HEB and E2A function as SMAD/FOXH1 cofactors. Genes Dev. 25 (15), 1654-1661 (2011).
- Jallow, Z., Jacobi, U. G., Weeks, D. L., Dawid, I. B., Veenstra, G. J. Specialized and redundant roles of TBP and a vertebrate-specific TBP paralog in embryonic gene regulation in Xenopus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 101 (37), 13525 (2004).
- Buchholz, D. R., Paul, B. D., Shi, Y. -. B. Gene-specific changes in promoter occupancy by thyroid hormone receptor during frog metamorphosis. Implications for developmental gene regulation. J Biol Chem. 280 (50), 41222-41228 (2005).
- Wills, A. E., Guptaa, R., Chuonga, E., Baker, J. C. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and deep sequencing in Xenopus tropicalis and Xenopus laevis. Methods. 66 (3), 410-421 (2014).
- Metz, B., et al. Identification of formaldehyde-induced modifications in proteins: reactions with model peptides. J Biol Chem. 279 (8), 6235-6243 (2004).
- Landt, S. G., et al. ChIP-seq guidelines and practices of the ENCODE and modENCODE consortia. Genome Res. 22 (9), 1813-1831 (2012).
- Mazzoni, E. O., et al. Embryonic stem cell-based mapping of developmental transcriptional programs. Nat Methods. 8 (12), 1056-1058 (2011).
- Deal, R. B., Henikoff, S. A simple method for gene expression and chromatin profiling of individual cell types within a tissue. Dev Cell. 18 (6), 1030-1040 (2010).
- Bonn, S., et al. Tissue-specific analysis of chromatin state identifies temporal signatures of enhancer activity during embryonic development. Nat Genet. 44 (2), 148-156 (2012).
転載および許可
このJoVE論文のテキスト又は図を再利用するための許可を申請します
許可を申請さらに記事を探す
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2023 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved