11.7 : Phase Transitions: Vaporization and Condensation
The physical form of a substance changes on changing its temperature. For example, raising the temperature of a liquid causes the liquid to vaporize (convert into vapor). The process is called vaporization—a surface phenomenon. Vaporization occurs when the thermal motion of the molecules overcome the intermolecular forces, and the molecules (at the surface) escape into the gaseous state. When a liquid vaporizes in a closed container, gas molecules cannot escape. As these gas phase molecules move randomly about, they will occasionally collide with the surface of the condensed phase, and in some cases, these collisions will result in the molecules re-entering the condensed phase. The change from the gas phase to the liquid is called condensation.
Vaporization is an endothermic process. The cooling effect is evident after a swim or a shower. When the water on the skin evaporates, it removes heat from the skin and cools the skin. The energy change associated with the vaporization process is the enthalpy of vaporization, ΔHvap. For example, the vaporization of water at standard temperature is represented by:

The reverse of an endothermic process is exothermic. And so, the condensation of a gas releases heat:
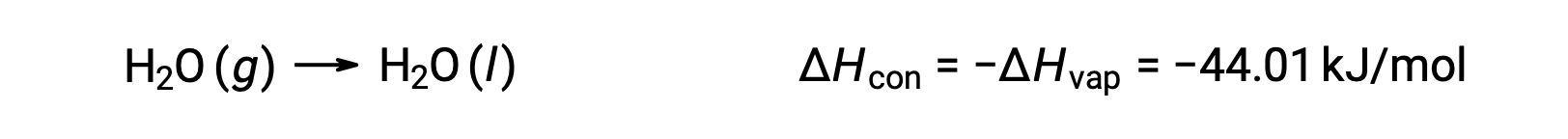
Vaporization and condensation are opposing processes; consequently, their enthalpy values are identical with opposite signs. While the enthalpy of vaporization is positive, the enthalpy of condensation is negative.
Different substances vaporize to different extents (depending on the strengths of their IMFs) and hence display different enthalpy of vaporization values. Relatively strong intermolecular attractive forces between molecules result in higher enthalpy of vaporization values. Weak intermolecular attractions present less of a barrier to vaporization, yielding relatively low values of enthalpies of vaporization.
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 10.3: Phase Transitions.
Z rozdziału 11:

Now Playing
11.7 : Phase Transitions: Vaporization and Condensation
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
17.0K Wyświetleń

11.1 : Porównanie molekularne gazów, cieczy i ciał stałych
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
40.1K Wyświetleń

11.2 : Siły międzycząsteczkowe i wewnątrzcząsteczkowe
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
84.9K Wyświetleń

11.3 : Siły międzycząsteczkowe
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
56.2K Wyświetleń

11.4 : Porównanie sił międzycząsteczkowych: temperatura topnienia, temperatura wrzenia i mieszalność
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
43.6K Wyświetleń

11.5 : Napięcie powierzchniowe, działanie kapilarne i lepkość
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
27.3K Wyświetleń

11.6 : Przejścia fazowe
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
18.6K Wyświetleń

11.8 : Ciśnienie pary
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
34.0K Wyświetleń

11.9 : Równanie Clausiusa-Clapeyrona
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
55.2K Wyświetleń

11.10 : Przemiany fazowe: topnienie i zamrażanie
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
12.2K Wyświetleń

11.11 : Przejścia fazowe: sublimacja i osadzanie
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
16.6K Wyświetleń

11.12 : Krzywe ogrzewania i chłodzenia
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
22.3K Wyświetleń

11.13 : Diagramy fazowe
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
39.0K Wyświetleń

11.14 : Struktury brył
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
13.6K Wyświetleń

11.15 : Molekularny i jonowy Brył
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
16.6K Wyświetleń
See More
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone