Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
Double Fluorescence in situ Hybridization in Fresh Brain Sections
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
This protocol involves a non-radioactive in-situ hybridization procedure that enables the simultaneous identification of two transcript species, at a single cell resolution, in thin sections of the vertebrate brain.
Streszczenie
Protokół
This protocol was developed and refined based on standard radioactive and non-radioactive in-situ hybridization methods, previously developed by us and others to detect one or two transcript species in brain tissue 1-7. The protocol described below has a total length of 2 or 3 days, depending on the number of procedural interruptions chosen by the end user. All steps detailed below are to be conducted at room temperature, with the exception of the riboprobe hybridization step and post-hybridization washes. The solutions and buffers required for all steps involved in this method can be found at the end of this protocol.
1. Tissue Preparation and Sectioning
- Decapitate and extract subject's brain rapidly, and place it into a plastic mold of adequate size.
- Cover brain with Tissue-Tek embedding medium and rapidly place the plastic mold in a dry-ice/alcohol bath for rapid freezing. Frozen tissue can be stored at -80°C until use.
- Using a cryostat, collect 2 or 3 brain sections per slide onto charged Superfrost Plus slides. Thickness of the sections should be 10-12 μm. Slides can be stored at -80°C until use.
2. Preparation of Sephadex G50 Columns for Probe Purification
"Sephadex columns can be purchased from commercial sources, however, we provide below a low-cost alternative for the generation of columns, which will be required for probe purification.
- Hydrate adequate amount of Sephadex G50 powder with RNase-free, DEPC-treated water (for example, 2 g of powder in 100 ml of DEPC-treated water), mix solution briefly and store at room temperature to precipitate excess Sephadex G50.
- Remove supernatant (upper layer of water) following Sephadex G50 precipitation.
- Repeat the process above 3- 5 times.
- After the final wash, re-suspend the Sephadex G50 solution in TE buffer (1:1 ratio), and store at 4°C until use.
- Place autoclaved glass wool into a sterile 1 ml syringe and compress it with the plunger to make a compact layer at the bottom, and then place the syringe into a 15 ml Falcon tube.
- Mix well the solution of Sephadex G50 in TE. Fill the syringe/column with this solution.
- Centrifuge the column for 30 sec at 1000 rpm.
- Repeat this procedure until the column is almost completely filled with Sephadex G50 beads.
- Apply 200 μl of column washing buffer to the column and centrifuge it for 2 min at 1000 rpm. Discard flow-through.
- Apply 200 μl of column blocking buffer to the column and spin it for 2 min at 1000 rpm. Repeat this step 4-5 times to equilibrate column. Columns can be stored at 4°C until use if sealed with Parafilm.
3. Labeling and Purification of Riboprobes
Below we detail the generation and purification of a single riboprobe. For dFISH, the preparation of each probe will involve the same methodology, except that one of the probes will be labeled with digoxigenin (DIG)-tagged UTP whereas the other with biotin-tagged UTP.
- Prepare a concentrated ( > 150 ng/μl) and purified linearized cDNA solution of interest to generate either sense (control) or antisense riboprobes.
- In a 1.5 ml microfuge tube, add 0.5-1 μg of purified cDNA template, 2 μl of 5X probe labeling buffer, 1 μl of 10X DIG (or biotin)-labeling mix, 0.5 μl of RNasin and 1 μl of the appropriate RNA polymerase, and bring the final volume of the solution to 10 μl with RNAse-free (DEPC-treated) water.
- Incubate the solution in a water bath at 37°C for 2 hr.
- Add 1 μl of tRNA (stock; 20 μg/μl), and 39 μl of column blocking buffer to the solution.
- Prepare the Sephadex G50 column for probe purification. To this end, add 50 μl blocking buffer to the column and spin it for 10 sec at 1000 rpm.
Repeat this step 2-3 times to equilibrate the column (i.e., the full 50 μl applied to the column are recovered after cycle of centrifugation). - Apply the probe solution to the Sephadex G50 column, position a new microfuge tube at the bottom of the column, and spin it for 3 min at 1000 rpm to obtain the purified 50 μl of riboprobe solution.
- Assess quality and yield of labeled riboprobe using either a standard formaldehyde-agarose RNA gel, or a spectrophotometer.
4. Post-fixation, Acetylation and Hybridization
- Remove sections from the -80°C freezer and allow for a room temperature to equilibrate. Subsequently, incubate sections in a cold, freshly-made 3% paraformaldehyde solution for 5 min.
- Briefly rinse sections in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) twice.
- Dehydrate sections through a standard alcohol series (70, 95, and 100%; 2 min each), and let them air-dry.
- Incubate sections in an acetylation solution for 10 min.
- Rinse sections 3 times in 2X SSPE.
- Dehydrate sections once again through the standard alcohol series described above, and allow them to air-dry.
- Prepare an adequate volume of hybridization solution and add both riboprobes to the solution (probe concentration: 1 ng/μl for each probe). Total volume of the hybridization solution is determined based on the number of sections to be hybridized (16 μl of hybridization solution per section).
- Apply adequate volume of the hybridization solution to tissue and coverslip slides ensuring that no air bubbles overlay the tissue.
- Place slides in a metal slide holder. Immerse holder in a mineral oil bath set at 65°C overnight. Ensure that coverslips are facing upward (i.e., the lateral aspect of the slide holder should be in contact with the bottom of the mineral oil container).
5. Post-Hybridization Washes
- The following day, carefully remove the slide holder from the mineral oil bath and briefly rinse it in chloroform to remove excess oil from the slides.
- Place slides in a 2X SSPE solution for 5-10 min. Coverslips should detach from slides while in solution.
- Transfer the slides to a new 2X SSPE solution, and keep them for 1 hr at room temperature.
- Transfer sections into a solution containing 2X SSPE plus 50% formamide. The temperature of this solution should match the temperature used in the overnight hybridization procedure. Keep slides in this solution for 1.5 hr.
- Transfer sections to a 0.1X SSPE solution pre-warmed to the same temperature of the hybridization step. Incubate sections in this solution for 30 min. Repeat this step for an additional 30 min.
6. Detection and Visualization of Riboprobes
- Transfer slides to TNT buffer to which 0.3% hydrogen peroxide has been added, for 10 min.
- Wash sections in TNT buffer, 3 times (10 min each).
- Using a DAKO pen, draw a well around the area containing the brain sections. Importantly, caution should be exercised to ensure that sections do not dry.
- Apply 150 μl of TNB buffer to each slide, and incubate sections in this solution for 30 min, in a humid chamber.
- Remove excess TNB solution by tilting slides.
- Apply 150 μl of TNB solution containing peroxidase-conjugated anti-DIG antibody, and store slides in a humid chamber for 2 hr. Antibody concentration should be determined individually for each transcript of interest prior to carrying out dFISH.
- Wash sections in TNT buffer; 3 times, 10 min each.
- Apply 150 μl of Alexa 594-conjugated tyramide working solution to each slide, and store them in a humid chamber for 1 hr. This solution should be prepared according to the manufacturer's directions.
- Wash sections in TNT buffer; 3 times, 10 min each.
- Incubate sections in TNT buffer to which 0.3% hydrogen peroxide has been added for 10- 30 min.
- Wash sections in TNT buffer; 3 times, 10 min each.
- Apply 150 μl of TNB buffer per slide, and keep them in a humid chamber for 30 min.
- Remove excess TNB solution by tilting slides.
- Add 150 μl of TNB solution containing peroxidase-conjugated anti-biotin antibody, and store slides in a humid chamber for 2 hr.
- Wash sections in TNT buffer; 3 times, 10 min each.
- Apply 150 μl of an Alexa 488-conjugated tyramide working solution to the slides and incubate sections for 1 hr. This solution should be prepared according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
- Wash sections in TNT buffer; 3 times, 10 min each.
- Add 150 μl of Hoechst solution (1:1000 in TNT buffer) to the sections and keep them in the humid chamber for 2 min.
- Wash the sections in TNT buffer; 3 times, 5 min each.
- Coverslip sections with a fluorescence-compatible mounting medium (e.g., Vectashield or ProLong antifade).
7. Representative Results
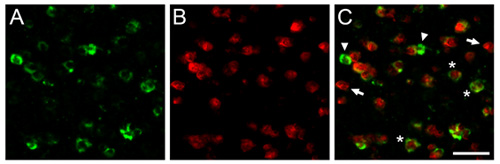
Figure 1. We show here representative dFISH results obtained in the zebra finch brain. Shown are photomicrographs obtained from the caudomedial nidopallium (NCM), the songbird analogue of the mammalian auditory cortex. Brain sections were hybridized with a biotinylated riboprobe directed against parvalbumin (A), a marker for a sub-population of inhibitory neurons, and a DIG-labeled riboprobe directed against the activity-dependent gene zenk (B), a reliable marker for song-driven neurons. C) Overlay of (A) and (B) shows a population of inhibitory neurons that are activated by auditory experience. Arrows and arrowheads indicate cells labeled exclusively with each of the two riboprobes, and asterisks show representative neurons co-expressing both transcripts of interest. Scale bar = 25 μm.
Dyskusje
We have used this protocol to study how the vertebrate brain is neurochemically and functionally organized, and to determine how behaviorally-relevant sensory stimuli impact the genomic machinery of neurons in the adult brain 8-10. We have successfully used this method in brain tissue from mice, rats and songbirds, but anticipate that this protocol will be easily adaptable to brain sections obtained from an array of vertebrate species and, perhaps, non-neural tissues. Key controls required to obtaining reliabl...
Ujawnienia
No conflicts of interest declared.
Podziękowania
Work supported by grants of NIH/NIDCD and the Schmitt Foundation to RP.
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| DEPC | VWR international | IC15090225 | toxic substance |
| PCR purification kit | Qiagen | 28104 | |
| Formaldehyde | VWR international | BDH0506-4LP | toxic substance |
| T3 RNA polymerase | Roche Group | 11031163001 | |
| T7 RNA polymerase | Roche Group | 10881767001 | |
| Tris-HCl (1 M, pH 7.5) | VWR international | IC816124 | |
| MgCl2 (1 M) | Sigma-Aldrich | 449172 | |
| Spermidine (1 M) | Sigma-Aldrich | S0266 | |
| DIG RNA labeling mix | Roche Group | NC9380805 | |
| Biotin RNA labeling mix | Roche Group | NC9440104 | |
| RNasin | Promega Corp. | N2111 | |
| BSA | Sigma-Aldrich | 05491 | |
| DTT | Sigma-Aldrich | D5545 | |
| Sephadex G50 | VWR international | 95016-772 | |
| EDTA | VWR international | 101384-758 | |
| SDS | Sigma-Aldrich | L4390 | |
| Transfer (t)RNA | Invitrogen | 15401011 | |
| 10X MOPS | VWR international | 14221-398 | toxic substance |
| Paraformaldehyde | VWR international | AAAL04737-36 | toxic substance |
| Sodium phosphate monobasic | Sigma-Aldrich | S3139 | |
| Sodium phosphate dibasic | Sigma-Aldrich | S3264 | |
| NaOH | VWR international | SX0600-1 | |
| Triethanolamine | VWR international | IC15216391 | |
| Acetic anhydride | VWR international | MK242002 | toxic substance |
| SSPE | VWR international | 82021-488 | |
| Formamide | VWR international | JT4028-1 | toxic substance |
| Poly A | Invitrogen | POLYA.GF | |
| Mineral oil | VWR international | IC15169491 | |
| Chloroform | VWR international | BDH1109 | organic solvent |
| Deionized formamide | Sigma-Aldrich | F9037 | toxic substance |
| Hydrogen peroxide | VWR international | VW36901 | toxic substance |
| Tween 20 | Sigma-Aldrich | P1379 | |
| Triton X-100 | JT Baker | X198-05 | |
| Anti-DIG HRP | Roche Group | 11093274910 | |
| Anti-biotin peroxidase | Vector Laboratories | SP3010 | |
| TSA Alexa Fluor 594 | Invitrogen | T20935 | |
| TSA Alexa Fluor 488 | Invitrogen | T20932 | |
| H–chst | VWR international | 200025-538 | |
| Vectashield | Vector Laboratories | H-1000 | |
| embedding mold | VWR international | 15160-157 | |
| cryostat | Leica Microsystems | CM 1850 | |
| Superfrost plus slide | VWR international | 89033-052 | |
Solutions
| |||
Odniesienia
- Jin, L., Lloyd, R. V. In situ hybridization: methods and applications. J Clin Lab Anal. 11, 2-9 (1997).
- Stoler, M. H. In situ hybridization. Clin Lab Med. 10, 215-236 (1990).
- Komminoth, P., Werner, M. Target and signal amplification: approaches to increase the sensitivity of in situ hybridization. Histochem Cell Biol. 108, 325-3233 (1997).
- Kessler, C. The digoxigenin:anti-digoxigenin (DIG) technology--a survey on the concept and realization of a novel bioanalytical indicator system. Mol Cell Probes. 5, 161-205 (1991).
- Panoskaltsis-Mortari, A., Bucy, R. P. In situ hybridization with digoxigenin-labeled RNA probes: facts and artifacts. Biotechniques. 18, 300-307 (1995).
- Qian, X., Lloyd, R. V. Recent developments in signal amplification methods for in situ hybridization. Diagn Mol Pathol. 12, 1-13 (2003).
- Mello, C. V., Jarvis, E. D., Denisenko, N., Rivas, M. Isolation of song-regulated genes in the brain of songbirds. Methods Mol Biol. 85, 205-217 (1997).
- Pinaud, R. GABAergic neurons participate in the brain's response to birdsong auditory stimulation. Eur J Neurosci. 20, 1318-1330 (2004).
- Velho, T. A., Pinaud, R., Rodrigues, P. V., Mello, C. V. Co-induction of activity-dependent genes in songbirds. Eur J Neurosci. 22, 1667-1678 (2005).
- Tremere, L. A., Jeong, J. K., Pinaud, R. Estradiol shapes auditory processing in the adult brain by regulating inhibitory transmission and plasticity-associated gene expression. J Neurosci. 29, 5949-5963 (2009).
- Pinaud, R., Mello, C. V., Velho, T. A., Wynne, R. D., Tremere, L. A. Detection of two mRNA species at single-cell resolution by double-fluorescence in situ hybridization. Nat Protoc. 3, 1370-1379 (2008).
- Pinaud, R., Jeong, J. K. Duplex fluorescence in situ hybridization in the study of gene co-regulation in the vertebrate brain. Methods Mol Biol. 611, 115-129 (2010).
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaPrzeglądaj więcej artyków
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone