Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Measurement of Extracellular Fluorescent Glucose Analog Depletion: A Surrogate Measurement Technique to Assess Glucose Uptake in Mouse Organs Ex Vivo
W tym Artykule
Overview
In this video, we demonstrate an ex vivo technique to measure extracellular glucose analog depletion in harvested mouse organs. It involves incubating the mouse tissue in a solution containing fluorescently-labeled deoxyglucose, which is taken up by the cells. The glucose analog uptake can be indirectly determined by measuring the fluorescence of the incubated medium.
Protokół
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board.
NOTE: All procedures must be done in a class II biosafety cabinet with the blower on and the lights off.
1. Preparation of materials
NOTE: All materials are listed in the Table of Materials.
- Prepare Medium 1, centrifugation Medium 2, and storage and working solutions of fluorescent 2-deoxy-2-[(7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazol-4-yl) amino]-D-glucose (2-NBDG or FD-glucose) according to Table 1 in a Class II biosafety cabinet. Protect FD-glucose from light throughout the experiment by turning off all the lights under the hood.
- Use ready-to-use cell culture reagents: Trypsin-EDTA, phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and glucose-free and phenol red-free Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (hereafter, glucose-free DMEM).
2. Ex vivo measurement of extracellular FD-glucose depletion in organs
- Pretreat mice with compounds stimulating glucose metabolism before the organ dissection, as follows.
- Use nine-week-old Lepob male mice (n = 11). Feed all mice with a regular chow diet before the experiment.
- Assign mice randomly into three groups for intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections.
- Inject mice from the control Lepob group with 0.1 mL of sterile PBS (n = 4).
- Inject mice from the insulin Lepob group with 0.1 mL of sterile PBS, containing 12 IU human insulin per gram of body weight (BW) (n= 3).
- Inject mice from the AAC2 Lepob group with 0.1 mL of sterile PBS, containing 0.1 nmol AAC2 per gram of body weight (BW) (n = 4).
- After 15 min, subject mice to inhalation of 5% isoflurane and exsanguinate blood by cardiac puncture from the anesthetized animals.
- Dissect visceral epidydimal white adipose tissue (200 mg), liver (200 mg), and whole brain from each animal. Use a Class II biosafety hood for tissue handling.
- Prepare FD-glucose (0.29 mM) working solution in glucose-free DMEM in a Class II Biosafety cabinet without light.
- Measure the fluorescence of FD-glucose working solution (0.29 mM) at excitation and emission wavelengths of 485 and 535 nm, respectively, using a microplate reader.
- Incubate the harvested tissues/organs in a 6-well plate containing PBS for 1 min. Handle each tissue or organ in a separate well.
- After 1 min, place each tissue on a sterile paper towel to absorb PBS. Transfer tissues/organs into a separate 6-well plate containing 4,000 µL of glucose-free DMEM and incubate for 2 min.
- After 2 min, remove and transfer the tissues into wells of a 6-well plate containing 0.29 mM FD-glucose working solution (1 mL/well). Incubate the 6-well plates containing tissues in FD-glucose working solution at 37 °C (5% CO2 and 95% humidity).
- Collect 100 µL of FD-glucose working solution from each well after 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 60, 90, and 120 min of incubation, to analyze the kinetics of extracellular FD glucose depletion. Shake before and after collection.
- Transfer 100 µL of FD-glucose working solution into 96-well plates to measure the fluorescence at excitation and emission wavelengths of 485 and 535 nm, respectively, using a microplate reader.
- Normalize fluorescence to the 0 min value (100%) for each organ in each animal (Figure 1).
Table 1: Preparation of culture media and FD-glucose solutions.
| Solution/Medium | Components |
| Ethanol:DMSO (1:1/v/v) | Ethanol (200 µL) and DMSO (200 µL) in 1-1.5 mL tube; use cell culture grade ethanol and DMSO |
| Medium 1 | DMEM (89 mL), Penicillin/streptomycin (1%) (1 mL) and Calf serum (10%) (10 mL) in sterile 50 mL tube |
| Centrifugation Medium 2 | DMEM (89 mL), Penicillin/streptomycin (1%) (1 mL) and Bovine serum (10%) (10 mL) in sterile 50 mL tube |
| Storage FD-glucose solution 5 mg/mL (14.5 mM) | FD glucose (1 mg) and Ethanol:DMSO (1:1/v/v) (200 µL) in 0.5 mL tube; store at -80 °C, preferentially under argon or nitrogen atmosphere |
| Working FD-glucose solution 5 µg/mL (14.5 mM) | Storage FD glucose solution 5 mg/mL (1 µL), Glucose free DMEM (999 µL); prepare immediately before experiment. |
Wyniki
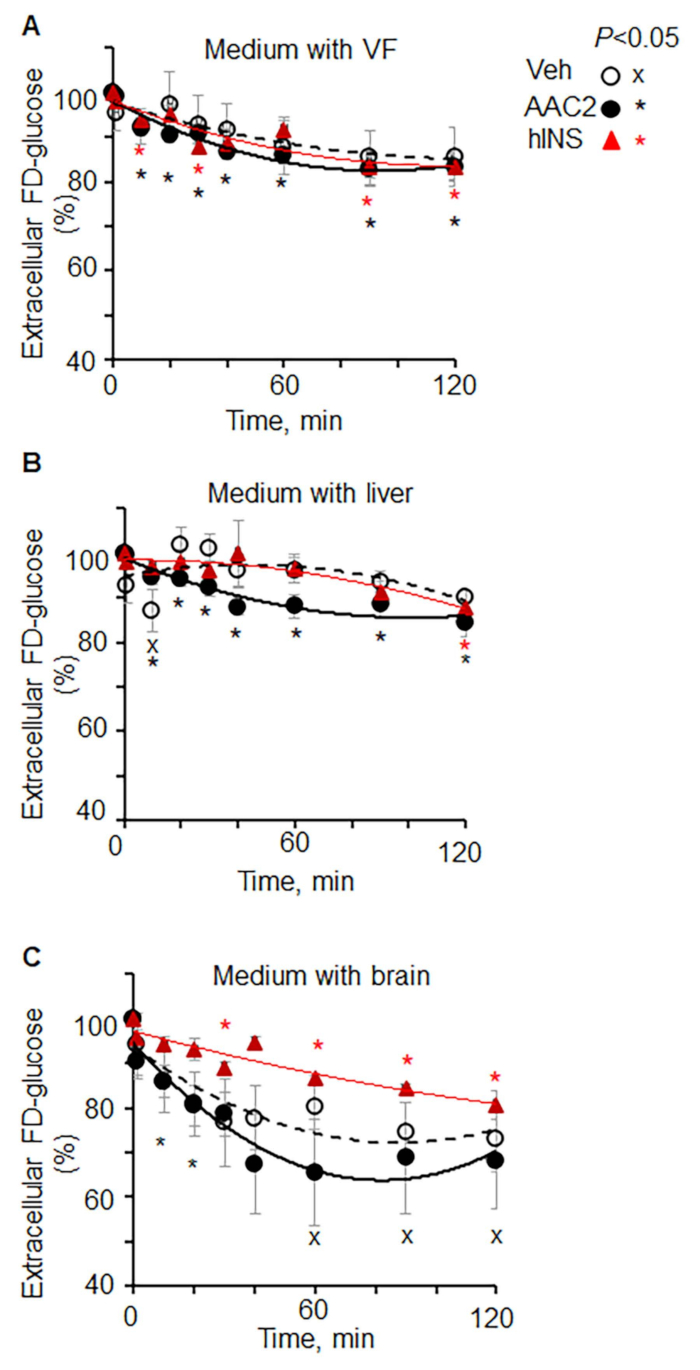
Figure 1: Kinetics of extracellular FD-glucose depletion in different organs ex vivo. (A-C) Lepob mice were injected with vehicle (PBS, n = 4), insulin (12 IU/kg BW, n = 3), and AAC2 (1 nmol/g BW, n = 3). After 15 min, tissues were dissected and isolated. Explants of (A) visceral fat, (B) liver, an...
Ujawnienia
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 96-well plates | Falcon | 353227 | Plastic ware |
| B6.V-Lepob/J male mice | Jackson Laboratory | stock number 000632 | Mice |
| BioTek Synergy H1 modular multimode microplate reader (Fisher Scientific, US) | Fisher Scientific, US | Fisher Scientific, US | Device |
| Cell incubator | Forma | Series II Water Jacket | Device |
| Diet (mouse/rat diet, irradiated) | Envigo | Teklad LM-485 | Diet |
| Isoflurane, 5% | Henry Schein | NDC 11695-6776-2 | Anestaetic |
| Phosphate buffered solution | Sigma-Aldrich | DA537-500 mL | Cell culture |
| Penicillin/streptomycin (P/S) | Gibco/ThermoFisher | 15140-122 | Cell culture |
| Glucose-free and phenol red-free DMEM | Gibco/ThermoFisher | A14430-01 | Cell culture |
| Fluorescent 2-deoxy-2-[(7-nitro-2,1,3- benzoxadiazol-4-yl) amino]-Dglucose) | Sigma | 72987-1MG | Assay |
| Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium | Gibco/ThermoFisher | 11965-092 | Cell culture |
| Bovine serum | Gibco/ThermoFisher | 161790-060 | Cell culture |
| Ethanol | Sigma-Aldrich | E7023-500mL | Reagent |
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Source: Kumar, S. B. et al., Extracellular Glucose Depletion as an Indirect Measure of Glucose Uptake in Cells and Tissues Ex Vivo. J. Vis. Exp. (2022)
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone