Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
Preparation of Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSC) from Naive and Pancreatic Tumor-bearing Mice using Flow Cytometry and Automated Magnetic Activated Cell Sorting (AutoMACS)
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
This is a rapid and comprehensive method of immunophenotyping Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSC) and enriching Gr-1+ leukocytes from mouse spleens. This method uses flow cytometry and AutoMACS Cell Sorting to enrich for viable Gr-1+ leukocytes prior to FACS sorting of MDSC for use in vivo and in vitro assays.
Streszczenie
MDSC are a heterogeneous population of immature macrophages, dendritic cells and granulocytes that accumulate in lymphoid organs in pathological conditions including parasitic infection, inflammation, traumatic stress, graft-versus-host disease, diabetes and cancer1-7. In mice, MDSC express Mac-1 (CD11b) and Gr-1 (Ly6G and Ly6C) surface antigens7. It is important to note that MDSC are well studied in various tumor-bearing hosts where they are significantly expanded and suppress anti-tumor immune responses compared to naïve counterparts7-10. However, depending on the pathological condition, there are different subpopulations of MDSC with distinct mechanisms and targets of suppression11,12. Therefore, effective methods to isolate viable MDSC populations are important in elucidating their different molecular mechanisms of suppression in vitro and in vivo.
Recently, the Ghansah group has reported the expansion of MDSC in a murine pancreatic cancer model. Our tumor-bearing MDSC display a loss of homeostasis and increased suppressive function compared to naïve MDSC 13. MDSC percentages are significantly less in lymphoid compartments of naïve vs. tumor-bearing mice. This is a major caveat, which often hinders accurate comparative analyses of these MDSC. Therefore, enriching Gr-1+ leukocytes from naïve mice prior to Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) enhances purity, viability and significantly reduces sort time. However, enrichment of Gr-1+ leukocytes from tumor-bearing mice is optional as these are in abundance for quick FACS sorting. Therefore, in this protocol, we describe a highly efficient method of immunophenotyping MDSC and enriching Gr-1+ leukocytes from spleens of naïve mice for sorting MDSC in a timely manner. Immunocompetent C57BL/6 mice are inoculated with murine Panc02 cells subcutaneously whereas naïve mice receive 1XPBS. Approximately 30 days post inoculation; spleens are harvested and processed into single-cell suspensions using a cell dissociation sieve. Splenocytes are then Red Blood Cell (RBC) lysed and an aliquot of these leukocytes are stained using fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies against Mac-1 and Gr-1 to immunophenotype MDSC percentages using Flow Cytometry. In a parallel experiment, whole leukocytes from naïve mice are stained with fluorescent-conjugated Gr-1 antibodies, incubated with PE-MicroBeads and positively selected using an automated Magnetic Activated Cell Sorting (autoMACS) Pro Separator. Next, an aliquot of Gr-1+ leukocytes are stained with Mac-1 antibodies to identify the increase in MDSC percentages using Flow Cytometry. Now, these Gr1+ enriched leukocytes are ready for FACS sorting of MDSC to be used in comparative analyses (naïve vs. tumor- bearing) in in vivo and in vitro assays.
Protokół
Prior to starting, prepare the following solutions:
3% Staining Media (SM):
-3% Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) in 1X Phosphate Buffer Saline (PBS)
MACS Buffer (MB):
- 0.5% Albumin from Bovine Serum (BSA) in 1XPBS
1. Harvest Spleens from Mice
- Subcutaneously inject 6-8 week of age C57BL/6 mice (Harlan) with 1.5 x 105 murine Panc02 cells suspended in 100 μl 1x PBS (tumor-bearing; TB). Control mice (Naïve) receive 100 μl 1XPBS.
- Approximately 4 weeks post injection, euthanize mice by carbon dioxide asphyxiation.
- Harvest spleens from mice by blunt dissection using forceps and scissors then weigh using a balance. Place spleens in separate, labeled 50 ml conical tubes containing 1 x PBS.
2. Generate a Single-cell Suspension of Leukocytes from Spleens
All procedures should be performed in a sterile environment under a Biological Safety Hood and cells and antibodies kept on ice.
- Assemble the cell dissociation sieve by inserting the mesh screen into the opening of the cup towards the bottom. Then, insert the retaining ring into the threaded area with the slotted side up and use the ring key to tighten the retaining ring, thus holding the screen in place. Place the assembled sieve in a Petri dish containing 10 ml 1 x PBS.
- Pool spleens and use glass pestle to grind spleens against the mesh screen of the cell dissociation sieve and into the Petri dish. Repeat for each treatment group of mice.
- Filter cell suspension into a 50 ml conical tube using a 70 μm cell strainer and a 5 ml serological pipette. Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm (250-300 x g) for 5 min.
- Remove supernatant and resuspend pellet in 5 ml 1 x RBC lysis buffer per spleen. Pipet up and down vigorously. Incubate at room temperature for 5 min. Stop the reaction by adding 20 ml of 1 x PBS. Pipet up and down vigorously. Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm (250-300 x g) for 5 min.
- Remove supernatant and resuspend pellet in 20 ml sterile 1 x PBS. Pipet up and down vigorously.
- Count cells using trypan blue and a hemacytometer and resuspend at desired concentration in 3% SM so that 50 μl is equivalent to 5x105-1x106 cells (1x107 cells/ml - 2x107 cells/ml).
3. Cell-surface Staining /Immunophenotyping of MDSC using Flow Cytometry
- Label the wells of a 96-well V bottom plate for control and experimental samples and single stains for compensation controls (No Stain, NS; Mac-1-FITC; Gr-1-APC and DAPI).
- Add 5x105-1x106 cells equivalent to 50 μl/well of splenocytes to their respective wells in the 96-well V-bottom plate. Centrifuge plate at 12,000 rpm (250-300 x g) for 5 min.
- Prepare "Master Mix" (MM) of Mouse BD Fc Block (Rat anti-mouse CD16/32 monoclonal antibody) diluted in 3% SM, in a 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube on ice. As a starting point, use 1 μg Fc Block in 3% SM for a final volume of 50 μl, per well.
- Carefully remove supernatant from each well of the 96-well V-bottom plate by quickly inverting the plate over and back, over a waste container or sink without disruption of the cell pellets.
- Vortex, briefly centrifuge Fc Block MM for 5 seconds and add 50 μl to all pellets in the 96-well V-bottom plate. Mix well by gently pipetting up and down, leaving samples in their wells. Incubate plate for 15 min in the dark on ice. Centrifuge plate at 12,000 rpm (250-300 x g) for 5 min.
- Prepare "Master Mix" (MM) of fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies diluted in 3% SM in a 1.5ml microcentrifuge tube on ice, while samples incubate with Fc Block. Antibodies should be titrated to determine optimal dilutions for staining procedures. As a starting point, combine a 1:25 dilution of Mac-1-FITC and 1:20 dilution of Gr-1-APC in 3% SM for a final volume of 50 μl, per sample well.
- Carefully remove supernatant from each well of the 96-well V -bottom as previously described.
- Vortex, briefly centrifuge MM of fluorescent-conjugated staining antibodies for 5 seconds and add 50 μl to control and experimental pellets. Mix well by gently pipetting up and down. For single-stain compensations, add a 1:25 dilution of Mac-1-FITC, 1:20 dilution of Gr-1-APC and 75 ng/ml of DAPI, in 3% SM for a final volume of 50 μl per well to their respective wells. Add 50 μl 3% SM to unstained well (No Stain). Mix well and incubate cells in 96-well V-bottom plate for 30 min in the dark on ice.
- Label FACS tubes (5 ml, 12 mm x 75 mm polystyrene round bottom tubes) to correspond to each well in the 96-well V-bottom plate. Add 200 μl 3% SM to each FACS tube.
- Centrifuge plate at 12,000 rpm (250-300 x g) for 5 min and remove supernatants. Wash pellets by adding 100 μl 3% SM to each pellet and mix well by gently pipetting up and down. Centrifuge plate at 12,000 rpm (250-300 x g) for 5 min. Repeat wash step once more.
- Carefully remove supernatant from each well of the 96-well V-bottom as previously described. Resuspend each pellet in 100 μl 3% SM and mix well.
- Transfer 100 μl resuspended pellet from each well of the 96-well V-bottom plate to their respectively labeled FACS tube.
- Prior to Flow cytometry analysis, add 75 ng/ml DAPI to control and experimental samples and DAPI single stain compensation control.
- Perform flow cytometric data acquisition of MDSC percentages. Perform compensation using the negative (no stain control) and the single positive controls. Set up a dot plot that displays the forward (FSC) versus side scatter (SSC) in log scale so that leukocyte populations of interest can be identified. Draw a large gate on all leukocytes, excluding debris and clumps with lowest forward and side scatter. From this parent gate, create a new dot plot that displays SSC versus DAPI and gate on DAPI- (live) cells. Select this newly gated population and create a dot plot that displays Mac-1 versus Gr-1 and gate on your double positive (Mac-1+ Gr-1+) MDSC.
4. Magnetic Enrichment of Gr-1+ Leukocytes
- Aliquot 1x107 remaining unstained leukocytes into appropriately labeled FACS tubes and centrifuge at 12,000 rpm (250-300 x g) for 5 min.
- Prepare MM of Gr-1-PE antibody in a 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube. For up to 107 cells, use a 1:10 dilution of Gr-1-PE antibody in 50 μl MB, per sample. For greater cell numbers, scale up volumes accordingly. Briefly centrifuge for 5 seconds, add to leukocytes in FACS tubes and incubate for 15 min at 4 °C in the dark.
- Add 2 ml of MB to FACS tubes, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm (250-300 x g) for 5 min and discard supernatant.
- Prepare MM of Anti-PE MicroBeads in a 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube. For up to 107 cells, use a 1:4 dilution of anti-PE MicroBeads in 200 μl MB, per sample. For greater cell numbers, scale up volumes accordingly. Briefly centrifuge for 5 seconds, add to leukocytes in FACS tubes and incubate for 15 min at 4 °C in the dark.
- Add 2 ml of MB to FACS tubes, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm (250-300 x g) for 5 min and discard supernatant. Resuspend pellet in 3 ml of SB. Filter through a 70 μm strainer into a new, labeled 50 ml conical tube.
- Prepare and prime Auto MACS Pro Separator. Refill all bottles with the appropriate solutions and empty the waste bottle, if necessary. Turn instrument on and examine status of fluid containers and column(s) after initialization. All symbols should be green. On the menu, select "Separation" from the upper menu bar followed by "Wash Now" from the lower menu bar. Select "Rinse" from the pop-up option followed by "Run" to start the priming process. Once the priming process is successfully completed, the instrument will then display that it is "Ready for Separation" under the Status menu.
- Choose suitable chilled tube rack for tube sizes and place 50 ml conical tube with magnetically labeled cells in row A, 50 ml conical tube for negative fraction collection in row B and 15 ml conical tube for positive fraction collection in row C.
- Choose "POSSEL_S" cell separation program for positive selection of labeled target cells in sensitive mode from samples. Magnetically labeled target cells are retained on the automats column; unlabeled cells are released into the negative fraction collection tube in row B. On automated retraction of the magnet, the labeled target cells will be released into the positive collection tube in row C of the tube rack.
5. Post-Sort Analysis of Gr-1+ Enriched Leukocytes
- Recount Gr-1+ and Gr-1- fractions using trypan blue and a hemacytometer. Resuspend cells at desired concentration in 3% staining medium so that 50 μl is equivalent to 5x105-1x106 cells (1x107 cells/ml - 2x107 cells/ml) and transfer 50 μl to correspondingly labeled FACS tubes.
- Prepare a MM of Mac-1 only, at a 1:25 dilution in 3% SM for a final volume of 50 μl per sample. Stain cells and prepare single stain compensations of Gr-PE, Mac-1 FITC and DAPI for flow cytometry analysis. Add 200 μl 3% SM and DAPI viability dye as previously described.
- Perform flow cytometric data acquisition to determine Gr-1+ and Gr-1- percentages and to also compare MDSC percentages pre- and post-autoMACS enrichment.
6. Representative Results
Here we show representative results for autoMACS enrichment of Gr-1+ leukocytes from pooled, naïve spleens for subsequent FACS sorting of MDSC (Figure 1). 1x106 naïve leukocytes were stained with Mac-1-FITC and Gr-1-APC antibodies to identify MDSC percentages using a BD LSRII instrument, prior to autoMACS sorting. 1x107 naïve leukocytes were then stained with anti-Gr-1-PE antibodies and PE-MicroBeads for enrichment of Gr-1+ leukocytes using an autoMACS Pro Separator. Post-autoMACS enrichment, Gr-1 percentages in Gr-1+ and Gr-1- collected fractions were evaluated using flow cytometry. 1x106 Gr-1+ leukocytes were removed and stained with Mac-1-FITC antibody to analyze and compare MDSC percentages of enriched, pooled naïve leukocytes to non-enriched, pooled tumor-bearing leukocytes by flow cytometry.
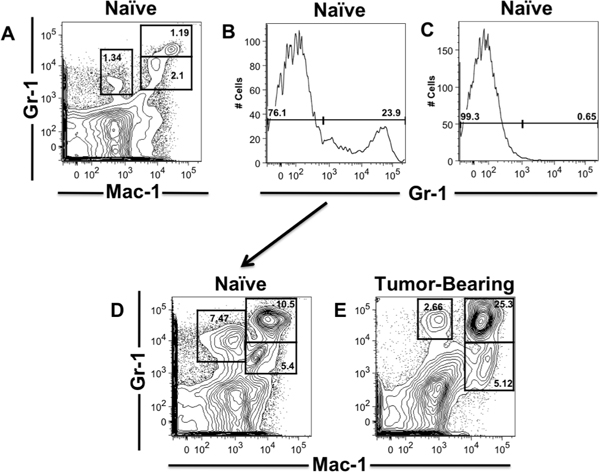
Figure 1. AutoMACS enrichment of Naïve Gr-1+ leukocytes for MDSC FACS Sorting. Spleens were harvested from pancreatic tumor-bearing and naïve mice and processed into single-cell suspensions. Flow cytometry analysis of naïve leukocytes surface stained with Mac-1 and Gr-1 fluorescent-conjugated antibodies, prior to autoMACS enrichment (A). Flow cytometry analysis of Gr-1+ (B) and Gr-1- (C) fractions post- autoMACS enrichment of Gr-1+ cells from pooled naïve leuckocytes stained with Gr-1-PE antibodies and anti-PE MicroBeads. Flow cytometry analysis of MDSC and Gr-1+ percentages post-autoMACS enrichment of Gr-1+ cells from pooled naïve leukocytes (D) compared to non-enriched pooled leukocytes from tumor-bearing mice (E) (naïve mice, n=5; tumor-bearing mice, n=3). MDSC and Gr-1 percentages are gated in the representative contour plots and histograms.
Dyskusje
This is a detailed method for processing and immunophentyping MDSC populations that is applicable to different lymphoid tissues from various animal models. In particular, autoMACS enrichment can be used for the isolation of various leukocyte populations including Gr-1 depletion of splenocytes 4, purification of myeloid subsets from splenocytes and lymph nodes 5, isolation of bone marrow neutrophils 14 and purification of CD8+ T cells from spleen and lymph nodes 15. ...
Ujawnienia
No conflicts of interest declared.
Podziękowania
We acknowledge the USF Flow Cytometry Core Facility. We would like to thank Dr. Denise Cooper for sharing resources. We would also like to thank Maya Cohen, Laura Pendleton and Diana Latour for their assistance in setting up and filming of this video. NN supported by NSF FG-LSAMP Bridge to the Doctorate Fellowship HRD #0929435. This work was funded by the American Cancer Society Institutional Research Grant# 93-032-13/Moffitt Cancer Center awarded to TG.
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 1X Phosphate Buffered Saline | Thermo Scientific Hyclone | SH30028.02 | Ca2+/Mg2+/Phenol Red-free |
| Albumin from Bovine Serum (BSA) | Sigma-Aldrich | A7906 | Let BSA dissolve undisturbed in PBS; Sterile Environment |
| Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) | Thermo Scientific Hyclone | SV3001403HI | Heat Inactivated; Sterile Environment |
| Rat anti-mouse CD16/32 monoclonal antibody (Fc Block) | BD Biosciences | 553142 | Sterile Environment |
| Anti-mouse CD11b (Mac-1) FITC | eBioscience | 11-0112 | Sterile Environment |
| Anti-mouse Ly6G (Gr-1) APC | eBioscience | 17-5931 | Sterile Environment |
| Anti-mouse Ly6G (Gr-1) PE | eBioscience | 12-5931 | Sterile Environment |
| DAPI | Invitrogen | D1306 | Serial Dilution Sterile Environment |
| Cell Dissociation Sieve | Sigma-Aldrich | CD1-1KT | Autoclave before use |
| 70-μm strainer | BD Biosciences | 352350 | Sterile Environment |
| 1X RBC Lysis Buffer | eBioscience | 00-4333-57 | Warm to room temperature before use; Sterile Environment |
| Petri dishes | Fisher Scientific | 08-757-12 | Sterile Environment |
| 50ml conical tubes | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. | 339652 | Sterile Environment |
| 5ml 12X75mm polystyrene round bottom tubes | BD Biosciences | 352054 | Known as FACS tubes; Sterile Environment |
| 96-well V-bottom plates | Corning | 3897 | Sterile Environment |
| Trypan Blue | Cellgro | 25-900-CI | Sterile Environment |
| PE MicroBeads | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-048-801 | Sterile Environment |
| AutoMACS Pro Separator | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-092-545 | |
| AutoMACS Columns | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-021-101 | |
| AutoMACS Running Buffer | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-091-221 |
Odniesienia
- Goni, O., Alcaide, P., Fresno, M. Immunosuppression during acute Trypanosoma cruzi infection: involvement of Ly6G (Gr1(+))CD11b(+) immature myeloid suppressor cells. Int. Immunol. 14, 1125-1134 (2002).
- Zhu, B. CD11b+Ly-6C(hi) suppressive monocytes in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 179, 5228-5237 (2007).
- Makarenkova, V. P., Bansal, V., Matta, B. M., Perez, L. A., Ochoa, J. B. CD11b+/Gr-1+ myeloid suppressor cells cause T cell dysfunction after traumatic stress. J. Immunol. 176, 2085-2094 (2006).
- Ghansah, T. Expansion of myeloid suppressor cells in SHIP-deficient mice represses allogeneic T cell responses. J. Immunol. 173, 7324-7330 (2004).
- Paraiso, K. H., Ghansah, T., Costello, A., Engelman, R. W., Kerr, W. G. Induced SHIP deficiency expands myeloid regulatory cells and abrogates graft-versus-host disease. J. Immunol. 178, 2893-2900 (2007).
- Yin, B. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells prevent type 1 diabetes in murine models. J. Immunol. 185, 5828-5834 (2010).
- Gabrilovich, D. I., Nagaraj, S. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 9, 162-174 (2009).
- Gallina, G. Tumors induce a subset of inflammatory monocytes with immunosuppressive activity on CD8+ T cells. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 2777-2790 (2006).
- Zhao, F. Increase in frequency of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in mice with spontaneous pancreatic carcinoma. Immunology. 128, 141-149 (2009).
- Greten, T. F., Manns, M. P., Korangy, F. Myeloid derived suppressor cells in human diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 11, 802-806 (2011).
- Youn, J. I., Nagaraj, S., Collazo, M., Gabrilovich, D. I. Subsets of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumor-bearing mice. J. Immunol. 181, 5791-5802 (2008).
- Ribechini, E., Greifenberg, V., Sandwick, S., Lutz, M. B. Subsets, expansion and activation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 199, 273-281 (2010).
- Pilon-Thomas, S. Murine Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Dampens SHIP-1 Expression and Alters MDSC Homeostasis and Function. PLoS One. 6, (2011).
- Panopoulos, A. D. STAT3 governs distinct pathways in emergency granulopoiesis and mature neutrophils. Blood. 108, 3682-3690 (2006).
- Preynat-Seauve, O. Extralymphatic tumors prepare draining lymph nodes to invasion via a T-cell cross-tolerance process. Cancer Res. 67, 5009-5016 (2007).
- Davies, D. Cell separations by flow cytometry. Methods Mol. Med. 58, 3-15 (2001).
- Maecker, H., Trotter, J. Selecting reagents for multicolor BD flow cytometry. Postepy Biochem. 55, 461-467 (2009).
- Bagwell, C. B., Adams, E. G. Fluorescence Spectral Overlap Compensation for Any Number of Flow Cytometry Parameters. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 677, 167-184 (1993).
- Perfetto, S. P. Amine reactive dyes: an effective tool to discriminate live and dead cells in polychromatic flow cytometry. J. Immunol. Methods. 313, 199-208 (2006).
- Safarik, I., Safarikova, M. Use of magnetic techniques for the isolation of cells. J. Chromatogr. B. Biomed. Sci. Appl. 722, 33-53 (1999).
- Collazo, M. M. SHIP limits immunoregulatory capacity in the T-cell compartment. Blood. 113, 2934-2944 (2009).
- Mack, E., Neubauer, A., Brendel, C. Comparison of RNA yield from small cell populations sorted by flow cytometry applying different isolation procedures. Cytometry. A. 71, 404-409 (2007).
- Strauss, L., Czystowska, M., Szajnik, M., Mandapathil, M., Whiteside, T. L. Differential responses of human regulatory T cells (Treg) and effector T cells to rapamycin. PLoS One. 4, e5994 (2009).
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaPrzeglądaj więcej artyków
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone