JoVE Science Education
Physics II
Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE.
RC/RL/LC Circuits
Przegląd
Source: Yong P. Chen, PhD, Department of Physics & Astronomy, College of Science, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN
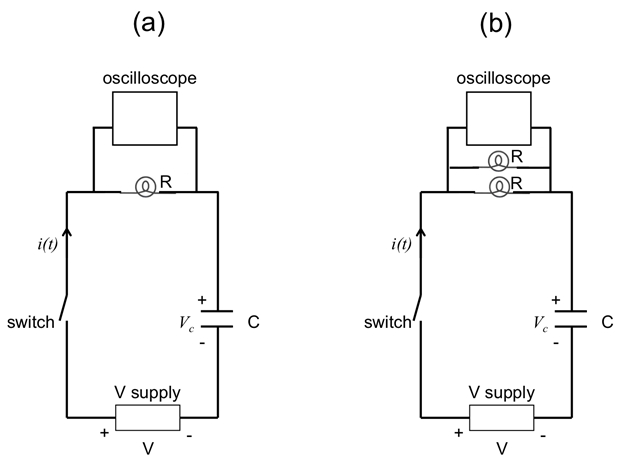
Capacitors (C), inductors (L), and resistors (R) are each an important circuit element with distinct behaviors. A resistor dissipates energy and obeys Ohm's law, with its voltage proportional to its current. A capacitor stores electrical energy, with its current proportional to the rate of change of its voltage, while an inductor stores magnetic energy, with its voltage proportional to the rate of change of its current. When these circuit elements are combined, they can cause the current or voltage to vary with time in various, interesting ways. Such combinations are commonly used to process time- or frequency-dependent electrical signals, such as in alternating current (AC) circuits, radios, and electrical filters. This experiment will demonstrate the time-dependent behaviors of the resistor-capacitor (RC), resistor-inductor (RL), and inductor-capacitor (LC) circuits. The experiment will demonstrate the transient behaviors of RC and RL circuits using a light bulb (resistor) connected in series to a capacitor or inductor, upon connecting to (and switching on) a power supply. The experiment will also demonstrate the oscillatory behavior of an LC circuit.
Procedura
1. Using an Oscilloscope
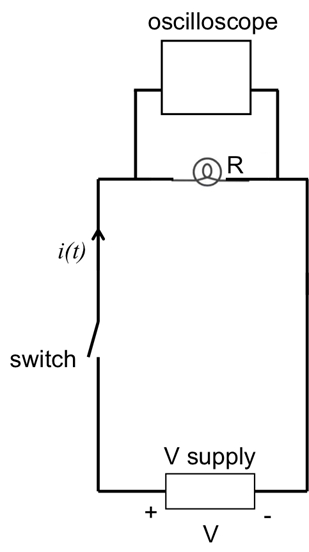
- Obtain an oscilloscope, a small light bulb (with resistance R of a few Ω), a switch, and a DC voltage supply (or alternatively a 1.5 V battery).
- Connect the circuit as shown in Figure 4, with the switch open. The connections in this experiment can be made with cables, clamps, or banana plugs into receiving ports on the instruments.
- Select the vertical scale of the oscilloscope to a range that is close to 1 V. Select the time scale
Wyniki
For step 1, the light bulb will "instantly" turn on and off when closing (step 1.4) and opening (in step 1.5) the switch. Representative oscilloscope traces are shown in Figure 8.
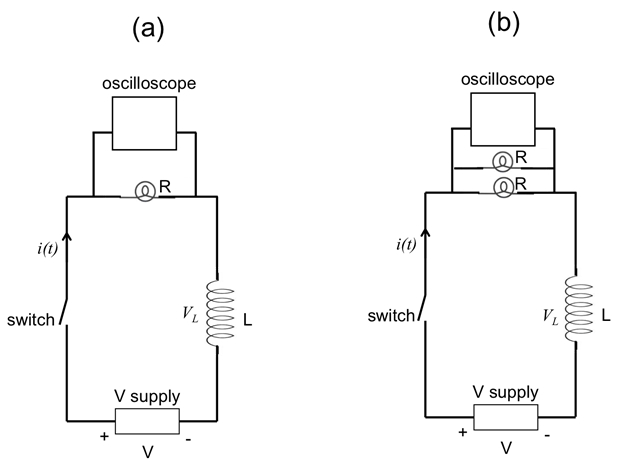
For step 2.3, after closing the switch, it can be observed that it takes a small but noticeable amount of time for the light bulb to turn on (instead of instantly as in step 1). When two parallel light bulbs are us
Wniosek i Podsumowanie
In this experiment, we have demonstrated the time dependent response (exponential turning on and off) in RC or RL circuits, and how changing the resistance affects the time constant. We also demonstrated the oscillatory response in an LC circuit.
RC, RL and LC circuits are essential building blocks in many circuit applications. For example, RC and RL circuits are commonly used as filters (taking advantage of the fact that capacitors tend to pass high frequency signals but block low frequency s
Przejdź do...
Filmy z tej kolekcji:

Now Playing
RC/RL/LC Circuits
Physics II
143.1K Wyświetleń

Electric Fields
Physics II
77.7K Wyświetleń

Electric Potential
Physics II
105.3K Wyświetleń

Magnetic Fields
Physics II
33.7K Wyświetleń

Electric Charge in a Magnetic Field
Physics II
33.7K Wyświetleń

Investigation Ohm's Law for Ohmic and Nonohmic Conductors
Physics II
26.3K Wyświetleń

Series and Parallel Resistors
Physics II
33.2K Wyświetleń

Capacitance
Physics II
43.8K Wyświetleń

Inductance
Physics II
21.6K Wyświetleń

Semiconductors
Physics II
29.9K Wyświetleń

Photoelectric Effect
Physics II
32.8K Wyświetleń

Reflection and Refraction
Physics II
36.3K Wyświetleń

Interference and Diffraction
Physics II
91.5K Wyświetleń

Standing Waves
Physics II
50.0K Wyświetleń

Sound Waves and Doppler Shift
Physics II
23.5K Wyświetleń
ISSN 2578-9082
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone
Używamy plików cookie, aby ulepszyć Twoje wrażenia z korzystania z naszej witryny.
Kontynuując korzystanie z naszej witryny lub klikając „Kontynuuj”, wyrażasz zgodę na akceptację naszych plików cookie.