A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
White and Brown Adipose Depot Collection from Mouse Pup: A Surgical Procedure to Harvest the White Adipose Tissue and Brown Adipose Tissue from Mouse Pup
In This Article
Overview
In this video, we demonstrate the surgical procedure to isolate the subcutaneous white adipose tissue and interscapular brown adipose tissue from a newborn mouse.
Protocol
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board.
1. Collection and digestion of adipose depots (day 1)
- Prepare two 1.5 mL tubes for each pup: one for brown adipose tissue (BAT) and one for white adipose tissue (WAT). Add 250 µL of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) + 200 µL of 2x isolation buffer (123 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 1.3 mM CaCl2, 5 mM glucose, 100 mM 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES), penicillin-streptomycin, and 4% fatty acid-free bovine serum albumin) to each tube. Keep....
Results
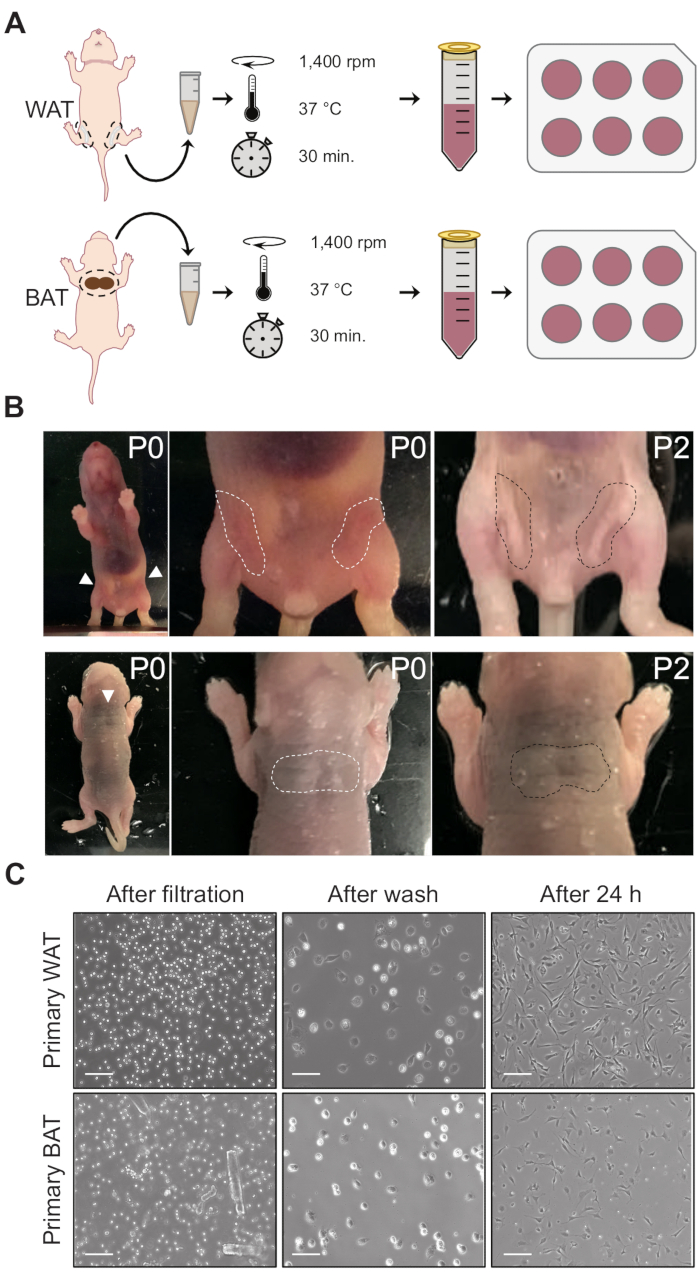
Figure 1: Collection and processing of fat pads. (A) Schematic representation of primary white (top) and brown (bottom) adipocyte isolation. (B) Subcutaneous white (top) and brown (bottom) adipose depots. In P0 mice, subcutaneous WAT is almost invisible, but becomes distinguishable on ~day 2 after birth. In contrast, BAT has a distinct dark color even at P0. In o.......
Disclosures
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 6-well plates | Corning | 353046 | |
| Fatty Acid-Free BSA | Sigma-Aldrich | A8806 | |
| CaCl2 | Sigma-Aldrich | C4901 | |
| Glucose | Sigma-Aldrich | G7021 | |
| HEPES | Sigma-Aldrich | H3375 | |
| KCl | Sigma-Aldrich | P9333 | |
| NaCl | Sigma-Aldrich | S7653 | |
| Pen/Strep | Gibco | 15140122 | |
| Surgical forceps | ROBOZ Surgical Instrument Co | RS-5158 | |
| Surgical Scissors | ROBOZ Surgical Instrument Co | RS-5880 | |
| DPBS, no calcium, no magnesium | Gibco | 14190144 |
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Source: Galmozzi, A. et al. Isolation and Differentiation of Primary White and Brown Preadipocytes from Newborn Mice. J. Vis. Exp. (2021)
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved