A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
An Intragastric Gavage Technique for Controlled Helicobacter Infection in Mice
Overview
This video demonstrates the establishment of Helicobacter pylori infection through the intragastric gavage technique in a mouse model. The bacterial suspension is administered via a catheter inserted through the mouth into the stomach. Inoculated bacteria colonize and establish an infection in the stomach, which can be used to study the host-pathogen interaction.
Protocol
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board.
1. Growth and Preparation of Bacterial Inocula
- Thaw glycerol stocks of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) or H. felis from -80 °C and subculture on horse blood agar (HBA) plates comprising: Blood Agar Base No.2 (see Table of Materials); a modified "Skirrow's antibiotic s.......
Representative Results
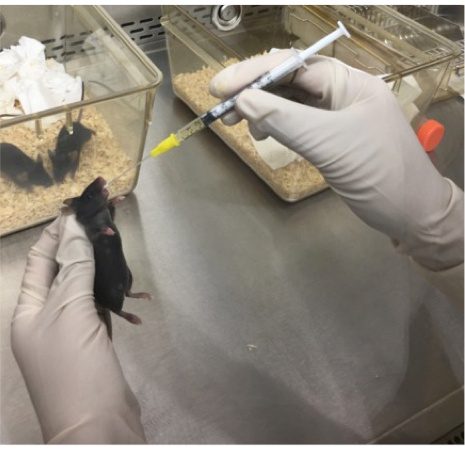
Figure 1: Image demonstrating the oral gavage technique. A disposable 1 mL syringe and flexible catheter are used to deliver ≥105 CFU of bacterial inocula to a mouse via the intragastric route. The mouse was anesthetized using methoxyflurane and held in a firm grip at the neck, allowing for access of the catheter to the stomach via the esophagus.
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Source: D'Costa, K. et al., Mouse Models Of Helicobacter Infection And Gastric Pathologies. J. Vis. Exp. (2018)
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved