A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Assessing the Antimicrobial Potential of Bacteriocin-Producing Murine Fecal Bacterial Isolates
In This Article
Overview
This video demonstrates the detection of bacteriocin-producing lactic acid bacteria derived from mouse fecal matter. The assay determines the antimicrobial activity of bacteriocin on specific bacterial strains.
Protocol
1. LAB Counting and Bacteriocin Activity
- Weigh one fecal pellet of each sample in a 1.5 mL tube and add an adequate volume of ice-cold 0.9% NaCl to achieve a 10% (w/v) solution. Use sterile micro pestles for 1.5 mL tubes to homogenize the fecal suspension and prepare ten-fold serial dilutions in ice-cold 0.9% NaCl.
- Count the total number of LAB cells.
- Transfer diluted cells (100 µL) to 4 mL of prewarmed Man Rogosa Sharpe (MRS) soft agar (50 °C, 0.8% agar). Mix by vortexing before pouring the cells onto a solid MRS agar plate (1.5% agar).
- Dry the plate by taking the lid off for 5 - 10 min in the st....
Representative Results
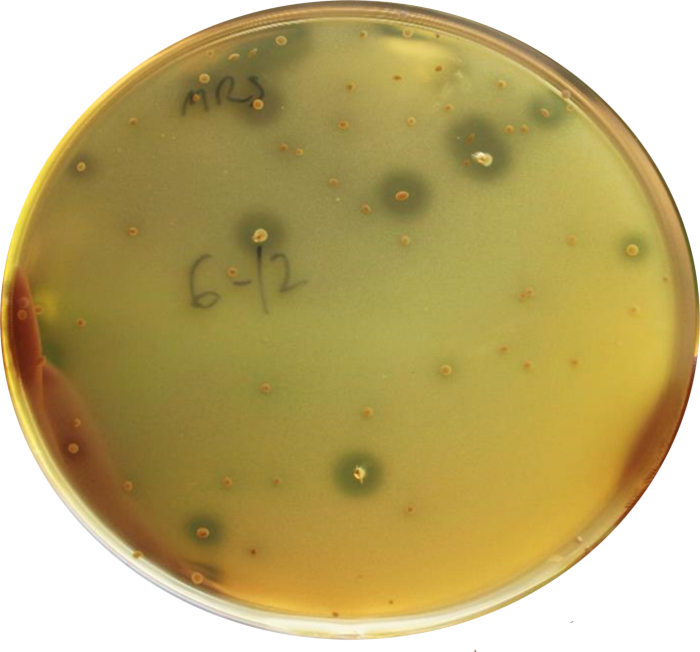
Figure 1: Detection of Bacteriocin Production in LAB Recovered from Feces by a Three-layer Protocol (as described in the procedure)
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Source: Bäuerl, C., et al. A Method to Assess Bacteriocin Effects on the Gut Microbiota of Mice. J. Vis. Exp. (2017).
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved