Optimized Staining and Proliferation Modeling Methods for Cell Division Monitoring using Cell Tracking Dyes
In This Article
Summary
Successful use of cell tracking dyes to monitor immune cell function and proliferation involves several critical steps. We describe methods for: 1) obtaining bright, uniform, reproducible label-ing with membrane dyes; 2) selecting fluorochromes and data acquisition conditions; and 3) choosing a model to quantify cell proliferation based on dye dilution.
Abstract
Fluorescent cell tracking dyes, in combination with flow and image cytometry, are powerful tools with which to study the interactions and fates of different cell types in vitro and in vivo.1-5 Although there are literally thousands of publications using such dyes, some of the most commonly encountered cell tracking applications include monitoring of:
- stem and progenitor cell quiescence, proliferation and/or differentiation6-8
- antigen-driven membrane transfer9 and/or precursor cell proliferation3,4,10-18 and
- immune regulatory and effector cell function1,18-21.
Commercially available cell tracking dyes vary widely in their chemistries and fluorescence properties but the great majority fall into one of two classes based on their mechanism of cell labeling. "Membrane dyes", typified by PKH26, are highly lipophilic dyes that partition stably but non-covalently into cell membranes1,2,11. "Protein dyes", typified by CFSE, are amino-reactive dyes that form stable covalent bonds with cell proteins4,16,18. Each class has its own advantages and limitations. The key to their successful use, particularly in multicolor studies where multiple dyes are used to track different cell types, is therefore to understand the critical issues enabling optimal use of each class2-4,16,18,24.
The protocols included here highlight three common causes of poor or variable results when using cell-tracking dyes. These are:
- Failure to achieve bright, uniform, reproducible labeling. This is a necessary starting point for any cell tracking study but requires attention to different variables when using membrane dyes than when using protein dyes or equilibrium binding reagents such as antibodies.
- Suboptimal fluorochrome combinations and/or failure to include critical compensation controls. Tracking dye fluorescence is typically 102 - 103 times brighter than antibody fluorescence. It is therefore essential to verify that the presence of tracking dye does not compromise the ability to detect other probes being used.
- Failure to obtain a good fit with peak modeling software. Such software allows quantitative comparison of proliferative responses across different populations or stimuli based on precursor frequency or other metrics. Obtaining a good fit, however, requires exclusion of dead/dying cells that can distort dye dilution profiles and matching of the assumptions underlying the model with characteristics of the observed dye dilution profile.
Examples given here illustrate how these variables can affect results when using membrane and/or protein dyes to monitor cell proliferation.
Protocol
1. General Membrane Labeling with PKH26 Cell Tracking Dye (Ref. 25; Figure 1)
- Use sterile technique for steps 1.1 - 1.9. Prepare ~107 human peripheral blood mononuclear cells or lymphocytes (hPBMC, hPBL) using the laboratory's standard method with addition of a final 300 x g spin to minimize platelet contamination. Resuspend cells at 107/ml in HBSS+1% BSA and place on ice, reserving a 500 μl aliquot (5x106 cells) for use in Step 2.
- Place 5x106 cells (500 μl) in a 12 x 75 mm conical polypropylene tube. Wash once with 3.5 ml HBSS. Carefully aspirate the supernatant, leaving no more than 15-25 μl of residual fluid, but taking care not to remove cells. Use this tube to prepare a 2x cell suspension in Step 1.4.
- During the cell washing in Step 1.2, add 0.5 ml of Diluent C labeling vehicle (from the PKH26GL kit) to a 12 x 75 mm conical polypropylene tube. Use this tube to prepare a 2x PKH26 solution in Step 1.5.
- Add 0.5 ml of Diluent C labeling vehicle to the washed cell pellet from Step 1.2 and aspirate and dispense 3-4 times to obtain a single cell suspension (2x cells). Avoid bubble formation and excessive mixing, which may reduce cell viability and recovery.
- Immediately after preparing the 2x cell suspension in Step 1.4, prepare a 2x (4 μM) dye solution by adding 2.0 μl of 1.0 mM PKH26 dye stock in ethanol (from the PKH26GL kit) to the Diluent C tube prepared in Step 1.3 and vortex to disperse uniformly.
- Immediately after preparing the 2x dye solution in Step 1.5, rapidly pipette the 2x cell suspension from Step 1.4 into the 2x dye solution and simultaneously aspirate and dispense 3-4 times to completely disperse cells in dye. Do not: add 1.0 mM dye directly to cells; pour 2x cells into 2x dye; or add 2x cells to 2x dye while vortexing. Because staining is nearly instantaneous, such methods yield less uniform intensities than the recommended method (Figure 2).
- After 1 min, add 1.0 ml of heat inactivated serum or HBSS+5% BSA to stop dye uptake into cell membranes. Failure to use enough protein risks the formation of dye aggregates, which can pellet with cells during the washing steps and cause unintended labeling of other cells present in an experiment. If medium with 10% heat inactivated serum (CM) or HBSS+1% BSA is to be used as the stop reagent, carry out staining in a 15 ml conical polypropylene tube and add at least 5.0 ml of stop reagent to insure adsorption of all unincorporated dye.
- Centrifuge the labeled cells for 5 min @ ~400 x g. Carefully aspirate the supernatant without removing cells. Wash the pellet twice with 4 ml of CM or HBSS+1% BSA, dispersing the pellet well before recentrifugation. To minimize carryover of dye adsorbed on tube walls and maximize washing efficiency, transfer the cells to a fresh polypropylene tube after the first resuspension. Note: adequately stained cells will exhibit a distinct pink tinge in the pellet.
- Resuspend the washed cell pellet in 1.0 ml HBSS+1% BSA. Count the cells, determine cell recovery, and adjust volume to give a final concentration of 107/ml. With careful aspiration, cell recovery should be ≥85%. If cell recovery is < 70%, determine the cause before proceeding further. Withdraw a 150 μl aliquot (1.5x106 cells) and place on ice for use in Step 2.
2. Preparation of Instrument and Assay Setup Controls (Table 1)
- Aliquot 50 μl (5x105) of unstained cells from the cell suspension saved in Step 1.1 into each of five 1.8 ml Eppendorf tubes: 1, 3, 4, 5, and 7. Aliquot 50 μl (5x105) of PKH26pos cells from Step 1.9 into each of three tubes: 2, 6 and 8.
- Add 10 μl IgG block (100 μg/tube of IgG; see table of Reagents) to Tubes 1-8 and incubate for 10 min at ambient temperature (20-25 °C).
- Add a saturating amount of the antibody(ies) indicated in Table 1 to Tubes 4, 5, 7, and 8 and incubate all samples (Tubes 1-8) for 30 min at ambient temperature and protected from light.
- Add 1.5 ml of HBSS+1% BSA to all samples, pellet the cells by centrifugation (5 min @ 400 x g) and wash once with 1.5 ml of HBSS+1% BSA, with careful aspiration to avoid cell loss.
- Resuspend each sample in 500 μl of HBSS+1% BSA. If required for samples to be analyzed on your cytometer, transfer to a 12 x 75 mm round bottom tube. Add 10 μl of 100 μg/ml 7-AAD daily working stock (see table of Reagents) to Tubes 3, 6, 7 and 8 as indicated in Table 1. Incubate on ice for 30 min prior to use in flow cytometer setup and staining verification (Step 3).
3. Flow Cytometer Setup and Staining Verification
- Verify that the flow cytometer is operating properly, using the laboratory's established procedures for daily quality control. Verify that signals can readily be detected in each spectral window to be used, and that detector responses are linearly proportional to signal intensity in the window to be used for proliferation monitoring14.
- Acquire FSC vs. SSC data for Tube 1 using linear display scales. Adjust each detector's amplification such that the lymphocyte population falls in the lower left quadrant of the dot plot, is not off-scale in either parameter, and is not interrupted due to thresholding. Collect ungated FSC vs. SSC data for all samples in Steps 3.3 - 3.7.
- Acquire data for Tube 1, using no color compensation and logarithmic display scales for all 4 fluorescence detectors. Adjust each detector's high voltage (HV) to place the autofluorescence of unstained lymphocytes on scale with few/no cells accumulating in the first channel. Set an analysis boundary for each histogram corresponding to the brightest 2% of unstained cells.
- Using no color compensation and the HV settings established in Steps 3.2 and 3.3, acquire data for Tube 2, collecting FSC, SSC and signals in all 4 fluorescence detectors. For the detector used to monitor PKH26 fluorescence, verify that all PKH26pos cells appear on scale as a single symmetrical peak in the 3rd-4th decade, with few/no cells in the last channel. If there are multiple peaks or peak shape is skewed, repeat Step 1 with careful attention to salt minimization and mixing technique (Figure 2). If necessary, adjust dye concentration.
- Using settings established in Step 3.3, acquire data for Tube 3, collecting FSC, SSC and signals in all 4 fluorescence detectors. For the detector used to monitor 7-AAD fluorescence, verify that 7-AADpos cells fall above the 2% boundary established in Step 3.3 (i.e., that non-viable cells are well resolved from viable 7-AADneg cells).
- Using settings established in Step 3.3, acquire data for Tube 4, collecting FSC, SSC and signals in all 4 fluorescence detectors. Verify that CD8pos cells are well resolved from unstained cells (i.e., fall above the 2% boundary established in Step 3.3 for the FITC detector). Repeat with Tube 5 and verify that CD8pos cells are well resolved from unstained cells (i.e. fall above the 2% boundary established in Step 3.3 for the APC detector).
- Using settings established in Step 3.3, acquire data for Tubes 6, 7 and 8, collecting FSC, SSC and signals in all 4 fluorescence detectors.
- Use the list mode files collected for Tubes 1-5 and your color compensation software to establish a color overlap matrix for each fluorochrome in the detectors being used to monitor the three other fluorochromes. Apply this matrix to the list mode file for Sample 6 and verify that the presence of PKH26 labeling does not alter the ability to detect 7-AADpos cells.
- Apply the color overlap matrix from Step 3.8 to the list mode file for Sample 7 and verify that: a) 3 well resolved subpopulations (CD3negCD4neg, CD3posCD4neg and CD3posCD4pos) can be identified on an FITC vs. APC dot plot; and b) the presence of anti-CD3-FITC and anti-CD4-APC does not alter the ability to detect 7-AADpos cells. If the presence of anti-CD3-FITC alters the upper 2% boundary for data collected on the PKH26 detector, readjust the boundary as required.
- Apply the color overlap matrix from Step 3.8 to the list mode file for Sample 8. If the presence of PKH26 labeling alters the 2% boundary for the FITC, 7-AAD or APC detectors from those set using the autofluorescence control in Step 3.3, readjust the boundary(ies) as needed using Tube 7 of Table 1 and verify that it is still possible to distinguish CD3posCD4pos, CD3posCD4neg, and CD3negCD4neg cells using the adjusted boundary(ies).
4. Proliferation Model Selection for Cell Division Monitoring by Dye Dilution
- Determine the spacing between generations, which is dependent on the number of channels and logarithmic decades on your cytometer. For digital instruments, this value, typically 4 or 5 decades, is determined by the number of bins in the digital signal processor. On analog instruments, where the number of decades is rarely a whole number, accurate modeling requires the precise number of decades to be experimentally determined. To do this, data from a mixture of calibrated fluorescent beads with manufacturer-assigned relative intensities is acquired at the same detector high voltage settings used in the experiment. The position of the bead peaks allows for the calibration of the logarithmic scale in terms of intensity range per log decade. Specifically, this is done by plotting the channel number for each bead type against the log of the manufacturer-assigned value. The slope of a best-fit straight line for the bead data values gives the number of relative intensity units per channel. Multiplied by the number of channels, this value will then be the number of log decades for the full scale, from which the number of channels corresponding to a two-fold decrease in intensity (i.e., daughter generation spacing) can be calculated14.
- Decide whether to use a fixed spacing between generations or to allow the spacing to float. A Standard (fixed) setting will use the generational spacing value determined in Step 4.5 to assign the location of each generation, and is typically used when the histogram lacks distinct peaks. A Float setting allows each generational peak position to be determined by the histogram shape and is typically used when distinguishable generational peaks are evident.
- Decide whether to use a fixed peak width for all generations or a floating width. A fixed width uses the SD calculated for the unstimulated control sample to model all generations and is typically chosen when the sample lacks distinguishable generational peaks. A floating width allows the program to independently vary the SD for each generation and is best used with distinguishable generational peaks.
- Run a program containing a proliferation analysis module (here ModFit LT Version 3.3). Load the stimulated PKH26pos file from the data set to be analyzed (e.g., an stimulated 96 hr culture of PKH26pos cells counterstained as for Tube 8 in Table 1).
- Select the parameters for analysis, in this case PKH26 (585/42) gated on viable (7-AADneg) CD3pos lymphocytes and FSC vs. SSC to exclude small debris and large aggregates (Figure 3). In defining these regions be careful to include the high forward scatter area where blasts are typically found and note that CD3 expression may be down-modulated in stimulated cultures.
- Create a new proliferation model using the Proliferation Wizard. Using the Open Data File (Start tab), load the unstimulated PKH26pos control file and define the location of the peak channel in the parental distribution corresponding to undivided cells.
- Analyze the file for the unstimulated PKH26pos control, noting the values for parental peak position and width (standard deviation). If a fixed peak width (SD) is desired, check Lock SD.
- Load the PKH26neg control (e.g., a 96 hr culture of PKH26neg cells counterstained as for Tube 7 in Table 1). Adjust the number of generations by setting the peak channel for the dimmest generation above the PKH26neg control. This determines the number of daughter generations the model can accurately fit and is typically 6-9 generations.
- Open the data file for the stimulated sample (e.g., a stimulated 96 hr culture of PKH26pos cells counterstained as for Tube 8 in Table 1) and confirm that the regions for the parental peak position and the SD as defined in Step 4.7 remain unchanged. If fixed generational spacing is desired, select Standard model option; otherwise select the Floating option.
- Analyze each experimental file in the data set, using the same model defined in Step 4.9. Minor adjustments to the parental peak position may be necessary for the very best fit as defined both visually and by the reduced chi square (RCS) value.
- Record the desired proliferation metrics resulting from the best-fit for each experimental file in the data set. For a comprehensive description of possible metrics see Ref. 22.
Representative Results
Membrane dyes like PKH26 stain by near-instantaneous partitioning into cell membranes rather than by chemical reaction (for CFSE) or equilibrium binding (for antibodies). Lack of attention to the critical issues outlined in Figure 1 may result in dim or heterogeneous staining of the type shown in Figure 2. In contrast, use of optimized labeling conditions (Figure 1, Table 2) results in bright homogeneous distributions suitable for a variety of cell tracking applications including cell division monitoring based on dye dilution (Figure 3). Dead/dying cells lose varying amounts of tracking dye, which can broaden and/or skew daughter generation intensities and complicate proliferation modeling based on dye dilution3,4,16,18. Use of a viability dye is therefore recommended when collecting dye dilution data under conditions where significant numbers of dead cells may be present, such as stimulated cultures (Figure 3) or older specimens (Figure 4).
Because tracking dye labeling typically gives fluorescence intensities several orders of magnitude greater than immunophenotyping, it is important to include appropriate compensation controls (Table 1) and to verify that the presence of tracking dye does not impair ability to resolve antibody positive and negative cells (Figure 4). To avoid the need for excessive color compensation, it is preferable to place a bright fluorochrome, or one not found on cells of interest such as a dye excluded by live cells, in the spectral channel(s) adjacent to the tracking dye (Figure 4A&B vs. 4C&D). When using peak modeling software to quantify extent of proliferation, obtaining a good fit requires matching assumptions within the model to the characteristics of the dye dilution profiles being analyzed (Figure 5 and Table 3). With appropriate selection of tracking dyes and viability reagents, it is also possible to characterize proliferative responses in multiple lymphocyte subpopulations simultaneously. For example, as illustrated in Figure 6, addition of a 2nd tracking dye simplifies discrimination between regulatory T cells (labeled with CellVue Claret) and highly proliferated effector T cells (labeled with CFSE) and provides much greater detail about their interactions than could be obtained using 3H-thymidine labeling18,27.
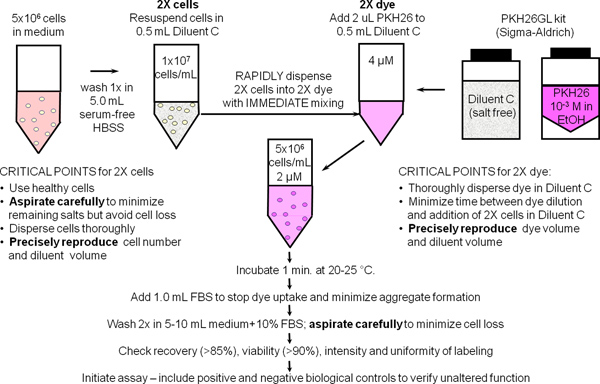
Figure 1. General membrane labeling protocol for PKH26, PKH67 and CellVue dyes. Partitioning of these highly lipophilic dyes into cell membranes occurs essentially instantly upon mixing with cells when staining is carried out in the salt-free Diluent C vehicle provided to maximize dye solubility and staining efficiency. As summarized in this schematic for general membrane labeling with PKH26, bright, uniform and reproducible staining is therefore most easily obtained by: 1) minimizing the amounts of protein and/or salts present in the staining step and 2) using a mixing technique that insures rapid homogeneous dispersal of cells in dye (i.e., simultaneously exposes all cells to the same concentration of dye).
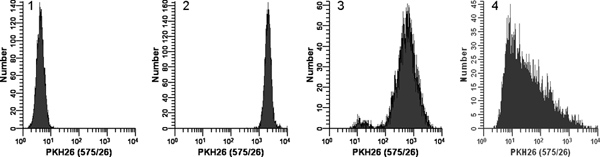
Figure 2. Effect of staining conditions on PKH26 fluorescence distributions (reprinted from Ref. 18). Replicate samples of logarithmically growing, cultured U937 cells were stained with PKH26 (final concentrations: 1 x 107 cells/ml, 12 - 15 μM PKH26) for 3 min at ambient temperature, with or without immediate mixing upon the addition of 2x cells to 2x dye. After washing, stained cells were analyzed on a Beckman Coulter CyAn flow cytometer using constant instrument settings. Histogram 1: unstained control with PKH26 detector voltage adjusted to place all cells on scale in the first decade with few/no cells accumulating in the first channel. Histogram 2: staining at 15 μM dye using addition of 2x cells to 2x dye with immediate mixing resulted in a bright, homogenously stained, symmetrical population of cells placed in the fourth decade, with few/no cells accumulating in the last channel (gMFI = 2548, gCV = 26.2%). Histogram 3: staining at 15 μM dye using addition of 2x cells to 2x dye but without immediate mixing resulted in a reduced intensity and a broader CV (gMFI = 505, gCV = 116%) as well as a dimly stained subpopulation, possibly due to a drop of cells dispensed on the wall of the tube rather than into the 2x dye solution. Histogram 4: a staining error led to 3 μl of concentrated ethanolic dye stock being added directly to 2x cells in Diluent C without further mixing rather than being used to prepare a 2x dye solution in Diluent C. This resulted in a final dye concentration of 12 μM but gave extremely dim and heterogeneous staining (gMFI = 32.9, gCV = 1020%). The observed right skew most likely reflects the combined effects of: i) poor mixing due to widely disparate cell and dye volumes; and ii) the fact that cells closest to the dye dispensing point would be exposed to a higher concentration of dye than those farther away. Click here to view larger figure.
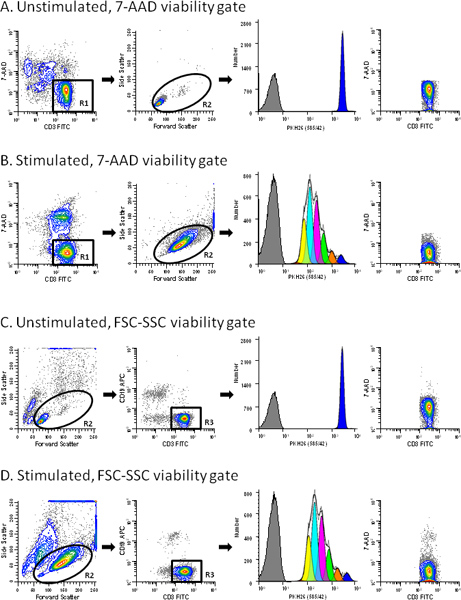
Figure 3. Use of a viability probe simplifies gating of T cell proliferation profiles. hPBMC were labeled with PKH26 (final cell concentration: 3x107/ml; final dye concentration: 10 μM). After culture for 96 hr in the presence (stimulated) or absence (unstimulated) of anti-CD3 and IL-2, cells were counterstained with anti-CD3-FITC, anti-CD19-APC and 7-AAD, and were analyzed on a FACSCalibur flow cytometer (see Reference 13 for details). Color compensation was performed at the time of data acquisition using hardwired compensation circuitry. The extent of proliferation was modeled as described in Step 4 using the Proliferation Wizard in ModFit LT3.3. Data from the PKH26neg control (Table 1, Tube 7) are overlaid for reference (gray filled histograms in column 3). Viabilities for unstimulated and stimulated cultures were 76% and 62% (ungated data for panels A and B, respectively). Panel A. PKH26 stained cells cultured for 96 hr in medium were gated to include viable (7-AADneg) CD3pos cells (R1). In addition to the antibody inclusion and 7-AAD dead cell exclusion gate, a forward scatter (FSC) versus side scatter (SSC) gate (R2) was used to exclude debris and aggregates. Note the absence of dead cells in the last plot in this panel. The best fit model for the PKH26 proliferation profile (column 3) gave a single peak with RCS = 2.1 (Donor 6, Table 3), indicating good symmetry, and was used to define the parental position and starting peak width for analysis of the stimulated sample from this data set (Panel B). Panel B. A replicate aliquot of PKH26 stained cells was cultured with anti-CD3 and IL-2 for 96 hr and gated in the same way as in Panel A. A model with floating peak position and floating peak width gave the best fit for this data with RCS = 1.3 (Donor 6, Table 3). Panel C. The same data file as in Panel A was analyzed without the use of 7-AAD data. When a primary FSC vs. SSC was used to partially exclude dead cells and aggregates (R2) and a secondary gate to select CD3 positive events (R3), a small residual population of dead cells remained (0.2% of gated events). The best fit model gave a single peak with RCS = 2.2. Panel D. The same data file as in Panel B was gated as in Panel C. Note the larger residual population of dead cells in the stimulated sample (1.29% of gated events) for this gating strategy. The best fit model was one with floating peak position and floating peak width (RCS = 1.3). Click here to view larger figure.
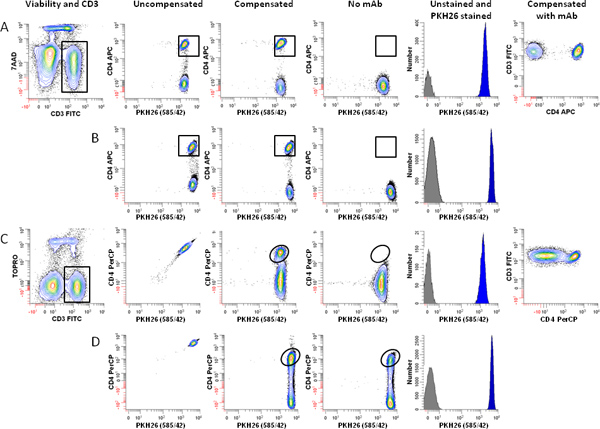
Figure 4. Effect of fluorochrome choice and dye concentration on ability to immunophenotype lymphocytes labeled with PKH26. hPBMC were isolated from 24-hr old blood and labeled with PKH26 as described in Step 1, with the exception that staining was carried out in 12 x 75 mm round bottom polystyrene tubes rather than 12 x 75 mm conical polypropylene tubes. Immediately after labeling with PKH26, cells were counterstained with the indicated immunophenotypic and viability reagents, and analyzed on an LSRFortessa flow cytometer using the gating strategy of Figure 3A and the following optical configuration: 488 nm laser: FSC-A (488 nm); SSC-A (488/10 BP), FITC-A (530/30 BP); PKH26-A (575/26 BP); 7-AAD-A or PerCP-A (695/40 BP). 640 nm laser: APC-A or TOPRO-3-A (670/14 BP). Color compensation was performed at the time of data acquisition using BD DiVa software. "Auto" indicates autofluorescence of the no-antibody control in the relevant spectral window (APC for panels A and B, PerCP for Panels C and D). Data from the PKH26neg control (Table 1, Tube 7) are overlaid for reference (gray filled histograms, column 5). Post-staining viabilities were similar for all samples (88-92%). Panel A. Cells labeled with PKH26 at a final concentration of 2 μM were counterstained using anti-CD3-FITC, anti-CD4-APC, and 7-AAD (Tube 8 of Table 3). After gating on viable (7-AADneg) CD3pos lymphocytes (Column 1) and exclusion of debris and aggregates based on FSC and SSC (see Figure 3A), PKH26 intensity was evaluated in combination with APC CD4 (Columns 2 and 3). Whether uncompensated (Column 2) or compensated (Column 3), this fluorochrome combination resulted in good resolution between CD4pos T cells and CD4neg T cells), as verified both by a no-antibody, autofluorescent control (Tube 6 of Table 1; Column 4) and the two-color plot of CD3 vs. CD4 (Column 6). Panel B. Using the same fluorochrome combination as in Panel A, but increasing the final PKH26 concentration to 4 μM did not adversely affect the ability to resolve CD4pos T cells from CD4neg T cells. Panel C. A replicate aliquot of cells independently labeled with PKH26 at a final concentration of 2 μM was counterstained using anti-CD3-FITC, anti-CD4-PerCP, and TOPRO-3. After gating on viable (TOPRO-3neg) CD3pos lymphocytes (Column 1) and exclusion of debris and aggregates based on FSC and SSC (see Figure 3A), PKH26 intensity was evaluated in combination with anti-CD4-PerCP (Columns 2 and 3). Substantial spectral overlap of PKH26 into the PerCP channel is evident in the uncompensated data (Column 2), and resolution between PKH26pos CD4pos and PKH26pos CD4neg events is marginal after compensation is applied (compare column 3 with the no-antibody, autofluorescent control shown in Column 4). Panel D. When PKH26 concentration is increased to 4 μM, it is no longer possible to use the fluorochrome combination of Panel C. Spectral overlap from PKH26 into the PerCP channel exceeds the intensity of the signal from CD4 (Column 2) and CD4posPKH26pos events can no longer be resolved from CD4negPKH26pos T cells (Column 3 vs. Column 4). Click here to view larger figure.
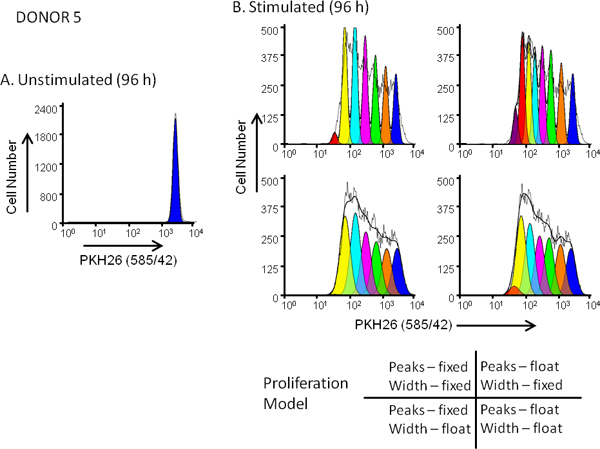
Figure 5. Effect of proliferation model selection on goodness of fit for dye dilution profiles. hPBMC were labeled with PKH26 (final cell concentration: 3x107/ml; final dye concentration: 10 μM). After culture for 96 hr in the presence (stimulated) or absence (unstimulated) of anti-CD3 and IL-2, cells were harvested counterstained with anti-CD3-FITC, anti-CD19-APC and 7-AAD and analyzed on a FACSCalibur flow cytometer (see Reference 13 for detailed methods). Color compensation was performed at the time of data acquisition using hardwired compensation circuitry. Panel A. The PKH26 intensity profile from an unstimulated 96 hr culture for Donor 5, a moderate responder, was gated as shown in Figure 3A and used to provide the ModFit Proliferation Wizard with a first estimate of position and width for the peak representing undivided parental cells. Panel B. The PKH26 intensity profile from a parallel stimulated 96 hr culture was analyzed using the starting estimates from Panel A and 4 different combinations of 'Proliferation Wizard' settings, corresponding to fixed or floating peak intensities, and fixed or floating peak widths for successive daughter generations as shown. As summarized in Table 3, the model that gave the best fit to the observed data (lowest reduced chi-square; RCS) was the "floating/floating" combination in which not only peak positions but also standard deviations of daughter generation peaks were allowed to vary (RCS = 1.5). The same model gave the best fit for Donor 6, a high responder (Figure 3B and Table 3).
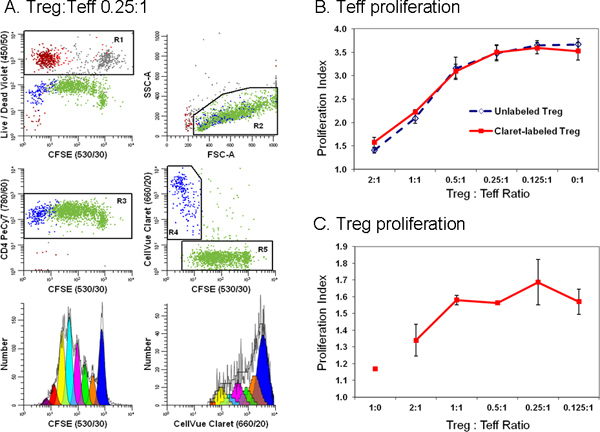
Figure 6. Addition of a second cell tracking dye simplifies discrimination between effector and regulatory T cells in a flow cytometric suppression assay (adapted from Ref. 18). Monocyte-depleted lymphocytes prepared from TRIMA leukapheresis filters were stained with anti-CD127-PE, anti-CD4-PE-Cy7, and anti-CD25-APC and flow sorted into populations of effector (Teff; CD4pos CD127bright CD25dim), regulatory (Treg; CD4pos CD127dim CD25pos), and accessory (CD4neg) cells. Sorted Treg cells labeled with CellVue Claret (final cell concentration: 1x106/ml; final dye concentration: 1 μM) and sorted Teff labeled with CFSE (final cell concentration: 5 × 107/ml; final dye concentration, 5 μM) were co-cultured at varying ratios in the presence of anti-CD3, anti-CD28 and irradiated accessory cells. After 96 hr, cultures were harvested, counterstained with anti-CD4-PE-Cy7 and LIVE/DEAD Fixable Violet, and analyzed on an LSRII flow cytometer and color compensation was performed at the time of data acquisition using BD DiVa software (see Reference 18 for details including compensation controls). The Proliferation Indices for Teff and Treg were modeled as described in Step 4, using the Proliferation Wizard in ModFit LT3.3. Data points in panels B and C represent the mean ± 1 standard deviation of triplicate samples. Panel A. Representative data are shown for one of three triplicate samples at a Treg:Teff ratio of 0.25:1. LIVE/DEAD Fixable Violet reagent was used to exclude dead cells (R1, upper left plot; accessory cells = red-brown, nonviable Teff = gray and nonviable Treg = red) from all other data plots. CellVue Claret staining was used to distinguish viable Treg (R4, center right plot; blue) from viable but highly proliferated Teff (R5, center right plot; green). A single parameter CFSE proliferation profile for Teff (lower left plot) was generated by gating on cells that were CFSEpos (R5), CD4pos (R3), viable (not R1), and had lymphocyte scatter properties (R2). A single parameter CellVue Claret proliferation profile for Treg was generated by gating on cells that were CellVue Claretpos (R4), CD4pos (R3), viable (not R1), and had lymphocyte scatter properties (R2). Note the generous lymphocyte region (R2) defined to include lymphocyte blasts. Note also that total number of cells to be collected depends upon the lowest frequency population of interest. In a cell proliferation experiment where the population of interest may be distributed over a broad range of intensities representing up to seven or eight generations a large number of cells should be collected in order to accurately model and calculate the number of cells in each generation. When studying rare cells, it may be necessary to simply run the sample tube nearly dry in order to collect the maximum possible number of events. For the sample shown here, doing this resulted in a total of ~25,000 events, of which 11,923 were Teff (Proliferation Index 3.85) and 1,380 were Treg (Proliferation Index 1.83). Panel B. As expected, increasing the proportion of Tregs present in co-cultures led to greater suppression of Teff cell proliferation. Similar results were obtained with both CellVue Claret-stained (solid line) or unstained (dashed line) Treg, indicating that staining with the CellVue Claret tracking dye did not affect Treg potency. Panel C. Treg are relatively anergic and, as expected, did not proliferate when incubated with anti-CD3, anti-CD28, and accessory cells in the absence of Teff cells (Treg:Teff ratio of 1:0). However, as the proportion of Teff present in co-cultures increased (i.e., as the Treg:Teff ratio decreased), the extent of Treg proliferation also increased. The generally larger error bars for these data at least in part reflect the limited extent of proliferation, leading to smaller numbers of events collected relative to Teff and greater uncertainty in modeling the number of cells in each generation. Click here to view larger figure.
| Tube No. (Purpose) | PKH26 | Antibody(ies) | 7-AAD |
| 1 (Setup, compensation) | - | - | - |
| 2 (Setup, compensation) | + | - | - |
| 3 (Setup, compensation) | - | - | + |
| 4 (compensation) | - | CD8-FITCb | - |
| 5 (compensation) | - | CD8-APCb | - |
| 6 (no Ab control) | + | - | + |
| 7 (no tracking dye control) | - | CD3-FITC CD4-APC or CD19-APCc | + |
| 8 (T0 control) | + | CD3-FITC CD4-APC or CD19-APCc | + |
Table 1. Instrument Setup Controlsa. a Controls listed are appropriate for a 4-color CD4 T cell proliferation monitoring assay using: PKH26 (proliferation dye), CD3-FITC (pan-T cell marker), CD4-APC (T-helper cell marker), 7-aminoactinomycin D (7-AAD; dead cell exclusion). b Brighter surrogates for CD3-FITC and CD4-APC (better ability to detect compensation errors). c Figure 3: CD3-FITC and CD19-APC. d Figure 4: CD3-FITC and CD4-APC.
| Cell type | Final Cell Concentration | Final Dye Concentration | Reference |
| hPBMCb | 1 x 107/ml | 2 μM PKH67 | 10,17 |
| 5 x 106/ml | 2 μM PKH26 | 12 | |
| 3 x 107/ml | 10 μM PKH26 | 13 | |
| 5 x 107/ml | 30 μM PKH26 | 18 | |
| 1 x 106/ml | 1 μM CellVue Claretc | 18 | |
| 3 x 107/ml | 4 μM CellVue Claret | 13 | |
| 5 x 107/ml | 5 μM CellVue Claret | 18 | |
| Cells in culture | 5 x 105/ml | 0.1 μM PKH26 (1°mammary cells) | 8 |
| 1 x 107/ml | 15 μM PKH26 (U937) | 18 | |
| 1 x 107/ml | 12.5 -15 μM PKH26 (U937) | 15 | |
| 1 x 107/ml | 1 μM PKH67 (K562) | 18 | |
| 1 x 107/ml | 1 μM PKH67 (T cell lines) | 9 | |
| 1 x 107/ml | 10 μM CellVue Claret (YAC-1) | 23 |
Table 2. Non-Perturbing Membrane-Dye Staining Conditionsa. a Adapted and updated from Ref. 18. b A low speed wash (300 x g) was used to minimize platelet contamination. c Treg cells (flow sorted CD4posCD25posCD127neg lymphocytes).
| Model Settings | Model Results | ||||||||
| Donor | Treatment | Peak Position | SD | Parental Position | Parental SD | # of Peaks Fitted | RCS | PI | PF |
| 5 | Unstimulated | Float | Float | 209 | 4.5 | 1 | 5.1 | 1.0 | 0 |
| 5 | Stimulated | Fixed | Fixed | 209 | 4.5 | 7 | 35 | 3.9 | 31 |
| 5 | Stimulated | Float | Fixed | 209 | 4.5 | 8 | 19 | 4.3 | 30 |
| 5 | Stimulated | Fixed | Float | 209 | 9.2 | 6 | 1.9 | 3.8 | 30 |
| 5 | Stimulated | Float | Float | 209 | 9.0 | 7 | 1.5 | 3.7 | 29 |
| 6 | Unstimulated | Float | Float | 205 | 4.0 | 1 | 2.1 | 1.0 | 0 |
| 6 | Stimulated | Fixed | Fixed | 205 | 4.0 | 6 | 42 | 6.6 | 60 |
| 6 | Stimulated | Float | Fixed | 205 | 4.0 | 7 | 12 | 7.4 | 60 |
| 6 | Stimulated | Fixed | Float | 205 | 8.6 | 6 | 6.9 | 6.8 | 62 |
| 6 | Stimulated | Float | Float | 205 | 6.5 | 6 | 1.3 | 6.5 | 59 |
Table 3. Impact of Proliferation Model on Goodness of Fit (RCS) and Proliferation Metrics a. a Sample staining, data collection and gating as described in Figure 3A & B.
Discussion
The methods described here are those found in our combined laboratories to most reliably give optimal results for hPBMC labeling using membrane dyes13,16,18 and for lymphocyte subset phenotyping and proliferation tracking using either membrane or protein dyes2,11,13,16,18. As illustrated in Figures 1 and 2, bright uniform labeling is most readily achieved by limiting the presence of physiologic salts and using a mixing technique that results in rapid, homogeneous exposure of all cells to the same concentration of dye. Because staining with membrane dyes occurs by partitioning into the lipid bilayer, other variables that alter free dye concentration can also impact labeling efficiency. For example, labeling in round bottom polystyrene tubes results in less efficient washout of salts prior to resuspension in Diluent C and also in reduced free dye concentration due to dye adsorption on tube walls, particularly at lower dye concentrations. Both factors tend to give broader staining distributions than when labeling is done using conical bottom polypropylene tubes (Figures 3, 4 and unpublished results). Sample age and type can also affect peak width even when optimized staining procedures are used. For example, CVs for PKH26pos lymphocytes isolated from freshly drawn blood range from 14-20% (Figure 3, Ref. 13 and unpublished results) whereas CVs for lymphocytes isolated from 24 hr old blood samples or TRIMA pheresis filters range from 25-30% (Figure 4 and Ref. 18).
Staining uniformity and the extent to which non-viable cells can be excluded from analysis both affect whether distinguishable daughter peaks are evident in the dye dilution profile, which in turn affects choice of a proliferation model to fit the observed data (Figures 5 and 6). Although ModFit (Verity Software House, Topsham, ME) is used here as an example of software used to generate metrics such as Proliferation Index and Precursor Frequency (Figures 3, 5 and 6; Table 3), other software packages also contain modules to analyze proliferation data. These include FCSExpress (De Novo Software, Los Angeles, CA) and FlowJo (Tree Star, Inc., Ashland, OR). All of these programs use a non-linear least squares analysis to iteratively find the best fit to the raw data by changing the position, height and SD (or width) of Gaussian peaks representing sequential daughter generations. Proliferative Index (PI) and Precursor Frequency (PF) are the most commonly used measures of extent of proliferation. PI, as defined by ModFit, is a measure of the increase in cell number over the course of the assay, analogous to the 'stimulation index' of a thymidine uptake assay. PF returns the fraction of cells in the initial population that responded to the stimulus by proliferating. Caution is advised, however, when reading the literature since terminology varies somewhat among software packages (e.g., FlowJo and ModFit use different definitions and calculations for what is meant by "Proliferation Index")22.
The critical issues discussed here for labeling and proliferation analysis with membrane dyes are also encountered when using protein dyes. For example, careful attention to mixing technique must also be observed, along with exclusion of dead/dying cells, in order to obtain uniform distributions and distinguishable daughter peaks when using CFSE (Figure 6)2-4,13,18,24. Appropriate choice of fluorochromes for phenotyping and viability assessment is also important to avoid excessive spectral overlap and inability to recognize antibody positive cells, particularly with visible emitting protein dyes such as CFSE2-4,11,13,16,18. Reducing the concentration of tracking dye decreases compensation problems in adjacent spectral channels but also limits the number of cell divisions that can be monitored before daughter cell intensities begin to overlap with autofluorescence. Alternatively, use of newer cell tracking dyes such as the far red emitting CellVue Claret (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) or violet emitting CellTrace Violet (Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY) may reduce compensation problems (Figure 6). Finally, although membrane dyes generally tend to exhibit less toxicity11,26, it is possible to over-label cells with either class of dye. It is therefore always necessary to verify that the concentration of tracking dye used has not altered the functionality of the cells to be tracked (Figure 6)3,13,16,18.
Acknowledgements
The authors would particularly like to thank the following individuals for their technical and intellectual contributions to the development of these methods through the years: Bruce Bagwell (Verity Software House), Nadège Bercovici (IDM), Lizanne Breslin (Zynaxis Cell Science and PTI Research), Brian Gray (PTI Research), Jan Fisher (Dartmouth Medical School), Alice Givan (Dartmouth Medical School), Betsy Ohlsson-Wilhelm (SciGro, Inc.), and Mary Waugh (Dartmouth Medical School). They would also like to thank the Bowdoin class of 2006 from the Annual Courses in Research Methods and Applications of Flow Cytometry, which generated the data shown in Figure 2.
Flow cytometry was performed at Roswell Park Cancer Institute's Flow Cytometry Laboratory, which was established in part by equipment grants from the NIH Shared Instrument Program, and receives support from the Core Grant (5 P30 CA016056-29) from the National Cancer Institute to the Roswell Park Cancer Institute, and at the Abramson Cancer Center Flow Cytometry and Cell Sorting Resource Laboratory of the University of Pennsylvania, which was established in part by equipment grants from the NIH Shared Instrument Program, and receives support from NIH #2P30 CA016520 from the National Cancer Institute. The work shown in Figures 3 and 5 was also supported in part by SBIR grant EB00228 from the National Institutes of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) awarded to PTI Research, Inc.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Reagent or equipment | Company | Catalogue number | Comments |
| Commercially Purchased | |||
| 7-Aminoactinomycin D | Sigma-Aldrich | A9400 | |
| Bovine serum albumin (BSA) | Sigma-Aldrich | A4503 | |
| Fetal bovine serum (FBS) | Atlanta Biologicals | S11150 | |
| Hanks balanced salt solution (HBSS) | Life Technologies | 14175-079 | Calcium and magnesium free, without phenol red |
| Human IgG Cohn fraction II and III globulins | Sigma-Aldrich | G-4386 | |
| Mouse anti-human CD3-FITC | BD Biosciences | 349201 | Saturating concentration as determined by laboratory titration |
| Mouse anti-human CD4-APC | BD Biosciences | 340672 | Saturating concentration as determined by laboratory titration |
| Mouse anti-human CD4-PECy7 | BD Biosciences | 348799 | Saturating concentration as determined by laboratory titration |
| Mouse anti-human CD8-FITC | BD Biosciences | 347313 | Saturating concentration as determined by laboratory titration |
| Mouse anti-human CD8-APC | Caltag (Life Technologies) | MHCD0805 | Saturating concentration as determined by laboratory titration |
| Mouse anti-human CD19-APC | Caltag (Life Technologies) | MHCD1905 | Saturating concentration as determined by laboratory titration |
| Mouse anti-human CD25-APC | BD Biosciences | 340938 | Saturating concentration as determined by laboratory titration |
| Mouse anti-human CD127-PE | BD Biosciences | 557938 | Saturating concentration as determined by laboratory titration |
| Mouse anti-human CD3 | eBiosciences | 16-0037-85 | 1.0 mg/ml; azide free |
| Mouse anti-human CD28 | eBiosciences | 16-0289-85 | 1.0 mg/ml; azide free |
| PBS | Gibco | 21300-058 | |
| PKH26 red fluorescent cell linker kit containing 10-3M PKH26 in EtOH and Diluent C | Sigma-Aldrich | PKH26GL-1KT or MINI26-1KT | Procedures in Step 1 also apply to kits containing PKH67 or other CellVue dyes |
| CellVue Claret far red fluorescent cell linker kit containing 10-3M CellVue Claret in EtOH and Diluent C | Sigma-Aldrich | MINCLARET-1KT or MIDCLARET-1KT | |
| 5-(and-6)-carboxyfluorescein diacetate, succinimidyl ester (CFDA-SE) | Invitrogen (Life Technologies) | C34554 | Non-fluorescent; cleaved by membrane esterases to form fluorescent amino-reactive carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE) |
| LIVE/DEAD Fixable Violet | Invitrogen (Life Technologies) | L34955 | |
| Sterile 12 x 75 mm conical polypropylene tubes & caps | VWR | 60818-102 | Gives better membrane dye staining efficiency (reduced dye adsorption; less cell loss during supernatant aspiration) |
| 12 x 75 mm round bottom polystyrene tubes | Becton Dickinson | 21008-936 | |
| Flow cytometer | BD Bioscience | FACSCalibur LSRFortessa | Any cytometer able to detect FITC, PKH26, and 7-AAD (ex. 488 nm; em. 520 nm, 567 nm, and 655 nm, respectively) and APC ex. 633-640 nm; em. 660 nm) |
| Flow cytometer | Beckman Coulter | LSRII CyAn | Any cytometer able to detect FITC, PKH26, and 7-AAD (ex. 488 nm; em. 520 nm, 567 nm, and 655 nm, respectively) and APC ex. 633-640 nm; em. 660 nm) |
| Laboratory Prepared | |||
| 7-Aminoactinomycin D, concentrated stock | NA | NA | 1 mg/ml in PBS. Freeze in aliquots and store at -20 °C. |
| 7-Aminoactinomycin D, working stock | NA | NA | 100 μg/ml in PBS; prepare daily from 1 mg/ml frozen stock. |
| IgG block | NA | NA | HBSS + 10 mg/ml Human IgG Cohn fraction II and III globulins + 10 mg/ml BSA. |
References
- Poon, R. Y., Ohlsson-Wilhelm, B. M., Bagwell, C. B., Muirhead, K. A., Diamond, R. A., DeMaggio, S. Use of PKH Membrane Intercalating Dyes to Monitor Cell Trafficking and Function. Living Color: Flow Cytometry and Cell Sorting Protocols. , 302-352 (2000).
- Wallace, P. K., Muirhead, K. A. Cell Tracking 2007: A Proliferation of Probes and Applications. Immunol. Invest. 36, 527-562 (2007).
- Hawkins, E. D., Hommel, M., Turner, M. L., Battye, F. L., Markham, J. F., Hodgkin, P. D. Measuring lymphocyte proliferation, survival and differentiation using CFSE time-series data. Nat. Protoc. 2, 2057-2067 (2007).
- Quah, B. J., Warren, H. S., Parish, C. R. Monitoring lymphocyte proliferation in vitro and in vivo with the intracellular fluorescent dye carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester. Nat. Protoc. 2, 2049-2056 (2007).
- Bolton, D. L., Minang, J. T., Trivett, M. T., Song, K., Tuscher, J. J., Li, Y., Piatak, M., O'Connor, D., Lifson, J. D., Roederer, M., Ohlen, C. Trafficking, Persistence, and Activation State of Adoptively Transferred Allogeneic and Autologous Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Specific CD8+ T Cell Clones during Acute and Chronic Infection of Rhesus Macaques. J. Immunol. 184, 303-314 (2010).
- Juopperi, T. A., Sharkis, S. J. Isolation of Quiescent Murine Hematopoietic Stem Cells by Homing Properties. Meth. Mol. Biol. 430, 21-30 (2008).
- Kusumbe, A. P., Bapat, S. A. Cancer stem cells and aneuploid populations within developing tumors are the major determinants of tumor dormancy. Cancer Res. 69, 9245-9253 (2009).
- Pece, S., Tosonim, D., Confalonieri, S., Mazzarol, G., Vecchi, M., Ronzoni, S., Bernard, L., Viale, G., Pelicci, P. G., Fiore, P. P. D. i. Biological and Molecular Heterogeneity of Breast Cancers Correlates with Their Cancer Stem Cell Content. Cell. 140, 62-73 (2010).
- Gertner-Dardenne, J., Poupot, M., Gray, B. D., Fournié, J. -. J. Lipophilic fluorochrome trackers of membrane transfers between immune cells. Immunol. Invest. 36, 665-685 (2007).
- Bercovici, N., Givan, A. L., Waugh, M. G., Fisher, J. L., Vernel-Pauillac, F., Ernstoff, M. S., Abastado, J. P., Wallace, P. K. Multiparameter precursor analysis of T-cell responses to antigen. J. Immunol. Methods. 276, 5-17 (2003).
- Givan, A. L., Fisher, J. L., Waugh, M. G., Bercovici, N., Wallace, P. K. Use of cell-tracking dyes to determine proliferation precursor frequencies of antigen-specific T cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 263, 109-124 (2004).
- Schwaab, T., Tretter, C. P., Gibson, J. J., Cole, B. F., Schned, A. R., Harris, R., Fisher, J. L., Crosby, N., Stempkowski, L. M., Heaney, J. A., Ernstoff, M. S. Tumor-related immunity in prostate cancer patients treated with human recombinant granulocyte monocyte-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF). Prostate. 66 (6), 667-674 (2006).
- Bantly, A. D., Gray, B. D., Breslin, E., Weinstein, E. G., Muirhead, K. A., Ohlsson-Wilhelm, B. M., Moore, J. S. CellVue Claret, a New Far-Red Dye, Facilitates Polychromatic Assessment of Immune Cell Proliferation. Immunol. Invest. 36, 581-605 (2007).
- Givan, A. L. A flow cytometric assay for quantitation of rare antigen-specific T-cells: using cell-tracking dyes to calculate precursor frequencies for proliferation. Immunol. Invest. 36, 563-580 (2007).
- Tario, J. D., Gray, B. D., Wallace, S. S., Muirhead, K. A., Ohlsson-Wilhelm, B. M., Wallace, P. K. Novel lipophilic tracking dyes for monitoring cell proliferation. Immunol Invest. 36, 861-885 (2007).
- Wallace, P. K., Tario, J. D., Fisher, J. L., Wallace, S. S., Ernstoff, M. S., , ., Muirhead, K. A. Tracking Antigen-Driven Responses by Flow Cytometry: Monitoring Proliferation by Dye Dilution. Cytometry. 73, 1019-1034 (2008).
- Barth, R. J., Fisher, D. A., Wallace, P. K., Channon, J. Y., Noelle, R. L., Gui, J., Ernstoff, M. S. A Randomized Trial of Ex vivo CD40L Activation of a Dendritic Cell Vaccine in Colorectal Cancer Patients: Tumor-Specific Immune Responses Are Associated with Improved Survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 16, 5548-5556 (2010).
- Tario, J. D., Muirhead, K. A., Pan, D., Munson, M., Wallace, P. K. Tracking Immune Cell Proliferation and Cytotoxic Potential Using Flow Cytometry. Meth. Mol. Biol. 699, 119-164 (2011).
- Fuse, S., Underwood, E. Simultaneous Analysis of In Vivo CD8+ T Cell Cytotoxicity Against Multiple Epitopes using Multicolor Flow Cytometry. Immunol. Invest. 36, 829-845 (2007).
- Schütz, C., Fleck, M., Mackensen, A., Zoso, A., Halbritter, D., Schneck, J. P., Oelke, M. Killer artificial antigen-presenting cells: a novel strategy to delete specific T cells. Blood. 111, 3546-3552 (2008).
- Zaritskaya, L., Shurin, M. R., Sayers, T. J., Malyguine, A. M. New flow cytometric assays for monitoring cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Expert Rev. Vaccines. 9, 601-616 (2010).
- Roederer, M. Interpretation of cellular proliferation data: Avoid the panglossian. Cytometry. 79A, 95-101 (2011).
- Quah, B. J. C., Parish, C. R. The Use of Carboxyfluorescein Diacetate Succinimidyl Ester (CFSE) to Monitor Lymphocyte Proliferation. J. Vis. Exp. (44), e2259 (2010).
- Houlihan, D. D., Newsome, P. N. Critical Review of Clinical Trials of Bone Marrow Stem Cells in Liver Disease. Gastroenterology. 135, 438-450 (2008).
- Brusko, T. M., Hulme, M. A., Myhr, C. B., Haller, M. J., Atkinson, M. A. Assessing the In Vitro Suppressive Capacity of Regulatory. T Cells. Immunol. Invest. 36, 607-628 (2007).
Explore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved