An Oligonucleotide-based Tandem RNA Isolation Procedure to Recover Eukaryotic mRNA-Protein Complexes
In This Article
Summary
A tandem RNA isolation procedure (TRIP) for recovery of endogenously formed mRNA-protein complexes is described. Specifically, RNA-protein complexes are crosslinked in vivo, polyadenylated RNAs are isolated from extracts with oligo(dT) beads, and particular mRNAs are captured with modified RNA antisense oligonucleotides. Proteins bound to mRNAs are detected by immunoblot analysis.
Abstract
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) play key roles in the post-transcriptional control of gene expression. Therefore, biochemical characterization of mRNA-protein complexes is essential to understanding mRNA regulation inferred by interacting proteins or non-coding RNAs. Herein, we describe a tandem RNA isolation procedure (TRIP) that enables the purification of endogenously formed mRNA-protein complexes from cellular extracts. The two-step protocol involves the isolation of polyadenylated mRNAs with antisense oligo(dT) beads and subsequent capture of an mRNA of interest with 3'-biotinylated 2'-O-methylated antisense RNA oligonucleotides, which can then be isolated with streptavidin beads. TRIP was used to recover in vivo crosslinked mRNA-ribonucleoprotein (mRNP) complexes from yeast, nematodes and human cells for further RNA and protein analysis. Thus, TRIP is a versatile approach that can be adapted to all types of polyadenylated RNAs across organisms to study the dynamic re-arrangement of mRNPs imposed by intracellular or environmental cues.
Introduction
Post-transcriptional gene regulation is driven through the interactions between RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) and mRNAs, which direct the processing, localization, translation and decay of every transcript within cells1,2. The identification of the RBPs and ncRNA interacting with particular mRNAs, establishing what is known as ribonucleoprotein complexes/particles (RNPs), is therefore key to understanding the fate of mRNAs and gene expression control. Complementary approaches are undertaken for biochemical characterization of RNP complexes3,4: while the "protein-centric" approach is based on the purification of specific RBPs, the "RNA-centric" approach involves the isolation of subpopulations or individual RNAs and subsequent analysis of interacting proteins or RNAs. Recently, an RNA-centric approach for the identification of the RBP repertoire interacting with polyadenylated (poly(A)) RNAs5 has become increasingly popular by incorporating an ultraviolet (UV) light crosslinking step to stabilize protein-RNA interactions prior the isolation of mRNAs, which dramatically extended the catalogue of RBPs in human cells6,7,8,9,10,11, Caenorhabditis elegans12, Saccharomyces cerevisiae12,13,14, and other organisms15,16,17,18,19,20. However, the mapping of proteins and/or ncRNAs assembled on particular transcripts is still a great challenge. To this end, two main approaches are currently used: on the one hand, RNA aptamer tags are fused to the RNA of interest to enable affinity purification. Thereby, the RNA aptamers bind with high affinity to aminoglycoside antibiotics including tobramycin and streptomycin21,22,23,24, or to proteins, such as the coat protein from the R17/MS2 bacteriophage or bacterial streptavidin S125,26,27,28,29. Although this approach was shown to be relatively robust and versatile, it requires cloning to design the RNA under investigation, and thus cannot be used to capture natural mRNAs. On the other hand, antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) were used early on for the recovery and characterization of highly expressed native RNPs30,31 and viral RNAs32. More recently, ASOs were applied to capture long non coding RNAs33,34,35 and in vitro formed mRNPs36. One major limiting factor with all RNA centric approaches is the copy number of the RNA of interest, making the recovery of low-expressed mRNAs more problematic. This limitation can be overcome by upscaling the reaction; however, this can potentially lead to increasing the background.
Herein, we describe our recently developed ASO-based tandem RNA isolation procedure (TRIP) to isolate native mRNA-protein complexes with high selectivity37 (Figure 1). The protocol involves two sequential ASO-based purification steps, namely the isolation of poly(A) mRNAs with commercially available oligo(dT) coupled beads followed by capturing of specific mRNAs using specifically designed short biotinylated 2'-methoxy RNA ASOs. This two-step procedure helps eliminating contaminating proteins and adds opportunities for adjustment and optimization. In this instance, TRIP was applied on selected mRNAs from yeast, nematodes, and human cells to confirm in vivo formed mRNA-protein complexes.
Protocol
1. Design Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs)
- Analyze the secondary structure of the mRNA or a fragment thereof using available online tools38. Therefore, enter the nucleotide (nt) sequence in the empty box. In the basic options box, select Minimum free energy (MFE) and partition function and Avoid isolated base pairs. In the output options box, select Interactive RNA secondary structure plot and finally click the Proceed button. A new window will pop-up that displays the secondary structure of the mRNA of interest.
- Select at least three different 21 - 24 nts long sequences within the mRNA of interest, preferentially in regions lacking detectable secondary structures (e.g., in unstructured loops) and in 3’ untranslated regions (UTR).
Note: It has been observed that ASOs annealing to sequences in the 3’ untranslated regions (UTR) performed best. One possibility is that ribosomes bound to the coding sequence (CDS) may occasionally obstruct the annealing of ASOs. ASOs annealing to 5’UTRs were not tested.- Select the regions with a guanidine/cytosine ratio close to 50% and lacking nucleotide tandem repeats to avoid potential formation of hairpins or self-annealing.
- Manually design 2’-methoxy modified RNA oligonucleotides bearing a biotin moiety at the 3’, fully complementary to the selected regions (step 1.2) within the desired target mRNA.
Note: 2’-methoxy modifications render the RNA resistant to cellular RNases and increases the duplex melting temperature, which allows for stringent washing. The biotin moiety is required for capturing ASOs with streptavidin.- Adjust the melting temperature of the RNA hybrids to ~60-65 °C and ensure that it has a high linguistic sequence complexity (>60%) as determined with suitable online tools39.
- Use the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool40 to search for potential ASO cross-hybridization with other mRNAs in the transcriptome. Select Nucleotide BLAST, insert the sequences in the empty box and select the organism of interest. Keep the remaining parameters as default and click BLAST.
Note: Even partial continuous alignment of 8-10 nts can lead to cross-hybridization and recovery of this mRNA.
2. Cell Culture, UV Irradiation and Cell Lysis
Note: In the following, the procedure is described for budding yeast S. cerevisiae, nematodes C. elegans, and human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293). Nevertheless, it can be adapted to other organisms as well, although it was not explicitly tested yet.
- S. cerevisiae
- Grow yeast cells (e.g., strain BY4743 derivate; MATa/α his3Δ1/his3Δ1 leu2Δ0/leu2Δ0 LYS2/lys2Δ0 met15Δ0/MET15 ura3Δ0/ura3Δ0 PFK2:TAP/PFK2) in 500 mL of YPD media (1% yeast extract, 2% peptone, 2% D-glucose) at 30 °C with constant shaking at 220 rpm.
- Collect the cells at mid-log phase (optical density at 600 nm (OD)600 ~ 0.6) by filtration using 0.45 µm nylon filters or by centrifugation at 3,000 × g for 2 min at room temperature (RT). Discard the flow-through or the supernatant, respectively.
- Wash the cells three times with 25 mL of phosphate-buffered-saline (PBS) using the 0.45 µm nylon filter or collect by centrifugation at 3,000 × g for 2 min at RT and discard the supernatant. Collect the cells as quickly as possible as the imposed stress could have an impact on RNA-protein interactions.
- Resuspend the cells in 25 mL of PBS and then pour the suspension in a 15 cm Petri dish. Place the dish on ice, remove the lid, and expose the cells three times with 400 mJ cm-2 of 254 nm UV light in a UV-crosslinker with 2-min breaks on ice between each exposure cycle with gentle mixing.
- Transfer the cells to a 50 mL tube and collect the cells by centrifugation at 3,000 × g for 3 min at 4 °C. Discard the supernatant and keep the pellet.
Note: Cells can be snap frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80 °C. - Resuspend the cells in 4 mL of chilled lysis buffer A (LB-A; 100 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 500 mM LiCl, 10 mM EDTA, 1% Triton X-100, 5 mM DTT, 20 U ml-1 DNase I, 100 U ml-1 RNasin, complete EDTA-free protease-inhibitor cocktail).
- Transfer the cells into two 2 mL tubes. Add max. ⅔ volumes of chilled glass beads and disrupt the cells in a tissue lyser at 30 Hz for 10 min at 4 °C.
- Punch a hole in the bottom of the tube with a hot needle and transfer the lysate to a fresh 1.5 mL tube by centrifugation at 600 × g for 30 s.
- Clear the lysate by three sequential centrifugations at 4 °C at 3,000 × g for 3 min, then 5,000 × g and 10,000 × g for 5 min each.
Note: Extracts can be snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80 °C.
- C. elegans
- Culture Bristol N2 worms at 20 °C on Nematode Growth Medium (NGM) plates (0.3% NaCl, 1.7% agar, 0.25% peptone, 1 mM CaCl2, 5 µg/mL cholesterol, 1 mM MgSO4, 25 mM KPO4 buffer, pH 6.0) seeded with the OP50 Escherichia coli strain41.
- Add 5 mL of M9 buffer41 (0.3% KH2PO4, 0.6% Na2HPO4, 0.5% NaCl, 1 mM MgSO4) to each plate, shake the plate to resuspend the worms and transfer the worms to a 15 mL tube. Place 2 µL of the suspension in a slide and count the worms in the suspension with a microscope. Then apply the factor to calculate the number of worms per plate.
- Collect ~ 120,000 worms by centrifugation at room temperature (400 × g, 2 min, RT) and discard the supernatant.
- Wash the worms three times. Therefore, add 10 mL of M9 buffer, mix by inversion and collect the worms by centrifugation at 400 × g for 2 min at RT.
- Add 15 mL of M9 buffer to the worms and place on a rotatory wheel for 15 min at RT.
- Transfer the worms to NGM plates (~4,000 worms per plate) and expose to UV-light (254 nm) at 300 mJ cm-2 in a UV-crosslinker.
- Add 5 mL of M9 buffer directly to the plate and shake the plate to resuspend the worms in the buffer. Transfer the suspension with a pipette to a 15 mL tube and collect the worms by centrifugation at 400 × g for 2 min at RT.
- Resuspend the worms in 2 mL of lysis buffer B (LB-B; 100 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 0.75% IGEPAL, 1 mM DTT, 20 U mL-1 DNase I, 100 U mL-1 RNasin, complete EDTA-free protease-inhibitor cocktail).
- Grind the worms in a mortar filled with liquid nitrogen. Collect the powder in a 50 mL tube and thaw at RT.
Note: Liquid nitrogen must be handled according to safety procedures (e.g., fume hood and safety gloves) - Clear the lysate including the fat layer by centrifugation at 14,000 × g for 10 min and subsequently pass the clarified lysate through a 0.45 μm filter with a syringe.
- Human cultured cells
Note: The following description is based on transient transfection of HEK293 cells with pGL3-CDKN1B-3’UTR reporter plasmid that expresses the 3′UTR of CDKN1B/27 downstream of the firefly luciferase gene42.- Culture HEK293 cells in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) containing 25 mM glucose and 1 mM sodium pyruvate, supplemented with 100 U mL-1 penicillin, 100 µg mL-1 streptomycin and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), and incubate at 37 °C in a humidified chamber (incubator) containing 5% CO2.
- Seed ~3×106 HEK293 cells in a standard 10 cm tissue culture dish the day before the transfection. Count the cells with a hemocytometer.
- Mix 2 µg of the reporter gene (e.g., pGL3-p27-3’UTR) with 20 µL of transfection reagent and transfect the cells at 70% confluency (~7×106 cells).
- Place the cells in an incubator at 37 °C for further 48 h before harvesting.
- Remove the medium with a serological pipette and quickly wash the cells twice with 10 mL of PBS pre-warmed at 37 °C. Remove PBS with a serological pipette.
- Add 6 mL of PBS to the dish, place on ice and then expose the cells to UV light (254 nm) at 100 mJ cm-2 in an UV-crosslinker.
Note: The plate must be kept on ice during UV-light exposure. - Scrape off the cells (in total ~107 cells) in PBS and transfer to a 15 mL tube.
- Spin down the cells at 250 × g for 10 min at 4 °C and then remove the supernatant with a pipette.
Note: The cell pellet can be snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80 °C until use. - Resuspend the cells in 2 mL of pre-chilled lysis buffer (LB-A) by pipetting up and down for 5-6 times, while keeping the tube on ice.
- Transfer the lysate with a pipette to a 5 mL tube placed on ice.
- Subject the lysate to three rounds of sonication consisting of 20 s bursts at 10 μm amplitude with 30 s of cooling periods on ice.
Note: Sonication is recommended as it completes lysis of cells and fragments the DNA. - Transfer the lysate to 2 mL tubes and centrifuge at 15,000 × g for 10 min at 4 °C. Collect the supernatant (=extract) and transfer to a new tube. Remove an analytical sample (5-10%) for further protein and RNA analysis.
Note: This step is critical to remove any remaining cell debris and can be repeated.
3. First Step: Poly(A) RNA Isolation
- Equilibrate 1 mg of oligo(dT)25-coupled magnetic beads in 500 µL of the respective lysis buffer.
- Combine 5 mg, 10 mg or 4 mg (protein) of S. cerevisiae, C. elegans or HEK293 extracts, respectively, with 1 mg of oligo(dT)25 -coupled magnetic beads. Mix the samples vigorously for 10 min at 25 °C in a mixer.
Note: Protein concentrations of extracts can be determined with Bradford assay using bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a reference standard. Vigorous shaking of samples prevents sedimentation of beads. To evaluate the specificity of mRNA isolation, a control experiment can be performed in parallel by adding an excess (20 µg) of polyadenylic acids (pA). - Place the tubes on a magnetic stand for 10 s and remove the supernatant. Keep the supernatant on ice for subsequent rounds of recovery (step 3.7).
- Add 500 µL of wash buffer A (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 600 mM LiCl, 1 mM EDTA, 0.1% Triton X-100) to the beads and vortex for 5 s.
Note: The concentration of LiCl in the wash buffers can vary. 600 mM LiCl is recommended but lower concentrations were also tested (500 mM for C. elegans, 300 mM for HEK293). - Collect the beads with a magnet and then wash the beads twice with 500 µL of wash buffer B (WB; 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 600 mM LiCl, 1 mM EDTA).
- Elute the RNA in 30 µL of 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5 at 80 °C for 2 min with continuous shaking (1,000 rpm) in a mixer. Immediately place the tube in the magnetic stand and collect the eluate after 10 s. Save the beads for additional rounds of purification.
Note: Collect the eluate as quickly as possible to prevent potential rebinding of mRNAs to the beads at lower temperatures. - Add the beads from previous step to the supernatant collected at step 3.3, and repeat the capture, washing and elution of mRNAs twice (steps 3.3-3.6). The eluates from repeated rounds are then combined and can be stored at -80 °C.
4. Second step: Capturing of Specific mRNAs with 3’-Biotinylated 2’-Methoxy Modified Antisense RNA Oligonucleotides
Note: To test the suitability of ASOs, the following procedure can be performed with total RNAs isolated from cells.
- Equilibrate 30 µL of streptavidin-coupled magnetic beads in 1 mL of binding and wash buffer (B&W buffer; 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM EDTA, pH 8.0) containing 0.1 mg mL-1 Escherichia coli transfer RNA (tRNA) on a rotator for 1 h at RT.
- Wash the beads three times with 750 µL of B&W buffer.
- Resuspend the beads in 30 µL of B&W buffer and keep on ice until use.
- Dilute ~35 µg of total protein from the previous poly(A) isolation (see 3) in 100 µL of B&W buffer in a 1.5 mL tube.
Note: To test the specificity of ASOs with total RNA, add 600 ng of purified total RNA to 100 µL of B&W buffer. - Add 200 pmol of the respective ASO and incubate at 70 °C for 5 min.
Note: The elevated temperature resolves secondary structures in the RNA facilitating the annealing of the ASO. - Remove the entire heat-block from the device and place it at RT for 10 min to cool down slowly.
- Add 30 µL of equilibrated streptavidin-coupled magnetic beads from step 4.1 to the sample.
- Incubate the mixture for 30 min at 25 °C with constant shaking at 950 rpm in a mixer.
Note: It is recommended to flick the tubes every 10 min to prevent sedimentation of beads. - Place the tubes on the magnetic stand, remove the supernatant and wash the beads three times with 750 µL of pre-warmed B&W buffer at 55 °C.
Note: The optimal wash temperature may slightly differ/vary between different ASOs. It is recommended to adjust this condition with non-crosslinked total RNA prior performing the experiment with cell extracts. - Elute the RNA in 20 µL of 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5 at 90 °C for 10 min with constant shaking at 950 rpm in a mixer. Place the tubes in the magnetic stand and immediately collect the eluate.
Note: For protein analysis, add 20 µL of 1× Laemmli buffer to the beads and incubate at 95 °C for 5 min. Proteins are monitored by immunoblot analysis following standard laboratory protocols.
Representative Results
We developed an ASO-based RNA isolation strategy, termed TRIP, to capture particular mRNAs with their bound proteins from three different organisms37. Essentially, RNA-protein complexes were crosslinked in vivo by UV-irradiation of cells at 254 nm, and poly(A) RNAs were recovered with commercially available oligo (dT) coupled-magnetic beads, then the mRNA of interest was isolated with 3'-biotinylated 2-0'-methoxy modified antisense RNA oligonucleotides (Figure 1). We therefore designed several 21-24 nts modified ASOs with full-complementarity to regions in the selected mRNAs from yeast, C. elegans and human, and tested their suitability to recover the mRNA of interest (a list of primers and ASOs is given in Table 1). The efficiency and specificity of individual ASOs were first evaluated with non-crosslinked total RNA isolated from the respective organism. In these experiments, RNA ASOs were coupled to streptavidin-conjugated paramagnetic beads and incubated with non-crosslinked total RNA prepared from the corresponding organism. After the release of captured mRNAs from the beads, the presence of mRNA targets as well as unrelated control mRNAs was monitored by reverse transcription (RT)-polymerase chain reaction (PCR)37. We noticed that two variables, the salt concentration and temperature of wash buffers, played critical roles in the efficiency of the capture of PFK2 mRNA from yeast that was tested with three different ASOs (Figure 2A). Lowering the salt (NaCl) concentration to 25 mM reduced the recovery of the negative control mRNA (PFK1) to non-detectable levels with all ASOs, but it also reduced the recovery of the desired target mRNA PFK2 (10-15% of the input). Conversely, an increase of the salt concentrations to physiological levels (150 mM NaCl) increased the recovery of PFK2 mRNAs up to 75% with the ASO PFK2-2, exceeding that of the control PFK1 mRNA by at least 5-fold (Figure 2A). Of further note, the different ASOs showed great variation of mRNA target capture efficacies at physiological salt-concentrations, emphasizing the need for empirical validation of ASOs. The dependence of mRNA recovery on the temperature of the wash buffer is exemplified for C. elegans cep-1 and yeast RPS20 mRNAs, using respective ASOs (Table 1). We observed that the optimal wash temperature was between 50 °C and 55 °C, as evident from the low background with unrelated mRNAs and the efficient recovery of mRNAs target (Figure 2B). At this point,we wish to emphasize the possibility of cross-hybridization of ASOs with other mRNAs. For example, the DNM1 ASO is fully complementary to a sequence within the DNM1 coding sequence, but it also partially anneals with ACT1 mRNA. DNM1 ASOs recovered both mRNAs irrespective of the washing temperature, showing strong propensity for cross-hybridization (Figure 2C). Finally, we have used the above described tests and optimizations to select three ASOs that were suitable for the recovery of respective target mRNAs from total RNA isolated from S. cerevisiae, C. elegans and human cells (Figure 2D).
After initial selection of suitable ASOs in vitro, we performed TRIP with cell extracts obtained from UV-crosslinked organisms/cells (Figure 1). Specifically, we tested the recovery of three different mRNAs from three different organisms: PFK2 mRNA from the yeast S. cerevisiae, cep-1 from the nematode C. elegans, and a reporter mRNA (pGL3-CDKN1B-3'UTR) bearing the 3'UTR sequence of human CDKN1B/p27 mRNA fused to a luciferase (luc) reporter for transient expression in human HEK293 cells. To control the specificity of the RNA isolation, we monitored the recovery of several unrelated mRNAs, and we performed competition experiments by the addition of an excess of pA to cell extracts, which competes with the binding of cellular mRNAs to oligo(dT)25 beads during the first step purification step. As previously seen with non-crosslinked total RNA samples (Figure 2), RT-PCR confirmed the enrichment of the respective mRNAs target mRNA during TRIP, whereas several non-related control mRNAs were not enriched (Figure 3A). Moreover, neither mRNAs were detected on beads without ASOs, indicating appropriate blocking procedures that avoid unspecific binding. On this line, unrelated/scrambled ASOs may also be used as control, although the potential for cross-hybridization with certain mRNAs and the inferred capture of bound proteins has then to be taken into account. Since proteins in the final eluate could be hardly visualized on silver-stained polyacrylamide gels (data not shown), the presence of previously known mRNA interacting proteins was further assessed by immunoblot analysis. This includes Pfk2p from S. cerevisiae, which binds selectively to PFK2 mRNA in a ribosome independent manner12; C. elegans GLD-1, a canonical RBP that binds to 3'UTR sequences of cep-1 mRNA for translational regulation43; and HuR, an RBP that regulates mRNA stability and translation of p27/CDKN1B mRNA44. As expected, all of these proteins were identified in the TRIP eluates of respective mRNAs by Western Blot analysis (Figure 3B).
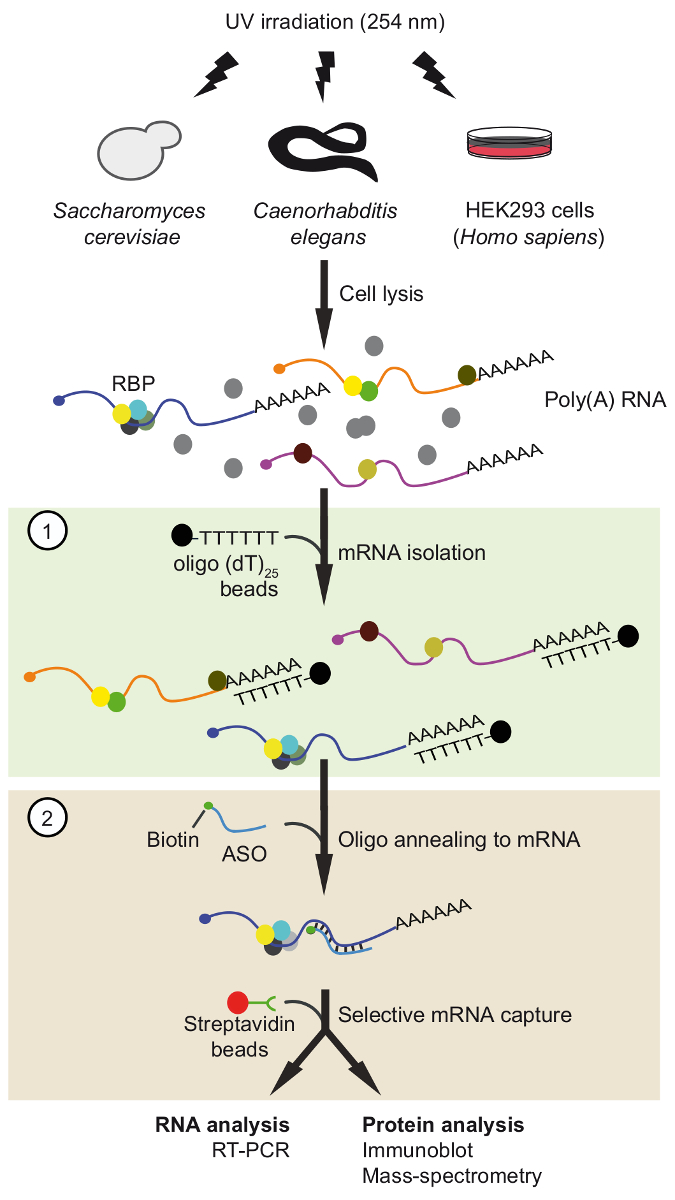
Figure 1. Schematic representation of TRIP. Proteins are crosslinked to RNA in vivo by UV-irradiation. In the first step (light green box), poly(A) RNA-protein complexes are recovered with oligo(dT)25 beads applying stringent washing conditions to remove unbound proteins. In the second step (pink box), the target mRNP is pulled-out with biotinylated antisense RNA oligonucleotides and streptavidin beads. The purified mRNPs are then analyzed by RT-PCR and immunoblot/mass-spectrometry (MS) to identify RNAs and proteins interacting with the mRNA of interest, respectively. The figure was modified from previous publication37 with permission. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
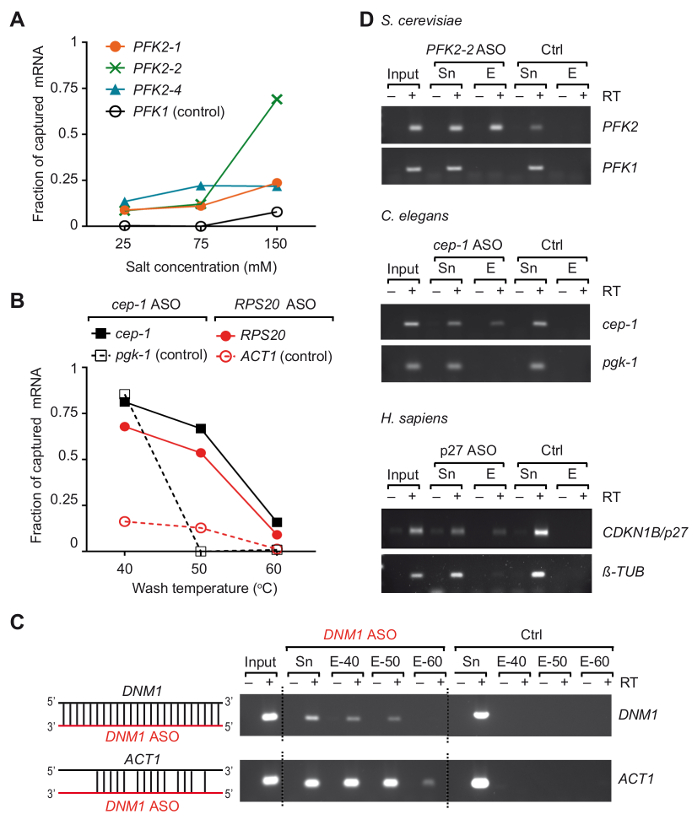
Figure 2. Isolation of selected mRNAs from total RNA of non-crosslinked cells/organisms using modified antisense RNA capture probes. (A) Impact of salt concentrations on the capturing efficiency of the yeast PFK2 mRNA with ASOs. Total RNA from yeast cells was combined with the indicated ASOs and washed with buffer containing the specified salt (NaCl) concentration at 55 °C. Green, blue and orange lines represent PFK2 mRNA recovery with different ASOs as determined by RT-PCR37: PFK2-1 and PFK2-2 anneal in the 3'UTR, PFK2-4 in the CDS. PFK1 is a negative control mRNA. PCR was performed with 32 amplification cycles and quantified as previously described37. (B) Fraction of C. eleganscep-1 and yeast RPS20 ASO bound mRNAs at different wash temperatures, represented in black and red lines, respectively. C. eleganspgk-1 and yeast ACT1 are non-target (control) mRNAs. 30 and 32 PCR cycles were applied for detection of yeast and C. elegans mRNAs, respectively. (C) Schematic representation of the hybridization of DNM1 ASO (red) with sequences in the DNM1 mRNA as well as potential cross-hybridization with ACT1 mRNA is shown to the left. An agarose gel showing products from RT-PCR reactions (30 cycles) for the detection of yeast DNM1 and ACT1 mRNAs eluted from beads is shown to the right. Input, total RNA; Sn, supernatant after incubation with ASOs; E, eluates from beads washed at indicated temperatures prior elution (40 °C, 50 °C and 60 °C). A control experiment (Ctrl) was performed in parallel without adding ASO. (D) Agarose gel showing RT-PCR products for the detection of mRNAs (right) captured from total RNA of yeast S. cerevisiae, C. elegans, and human HEK293 cells (H. sapiens). Input, total RNA; Sn, supernatant; E, eluates from the beads. PCR was performed by 30 amplification cycles for yeast mRNAs, 32 cycles for C. elegans mRNAs, and 28 and 30 cycles for human tubulin and p27 mRNAs, respectively. The figure was modified from previous publication37 with permission. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
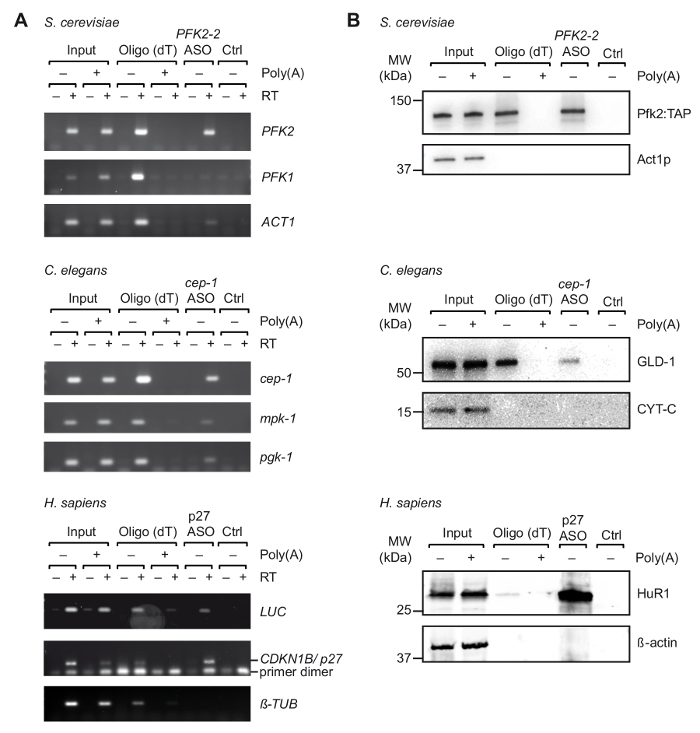
Figure 3. Capture of specific mRNA-protein complexes from extracts derived from UV crosslinked cells with TRIP. (A) Agarose gels for the detection of mRNAs (right) with RT-PCR upon capture with oligo(dT) and indicated ASOs from S. cerevisiae, C. elegans and human (H. sapiens) cell extracts. Input, total RNA from crosslinked cells/organisms; Ctrl, control without ASO. Poly(A), competition with poly(A). RT-PCR was performed as described37 with 35 amplification cycles for LUC, 32 cycles for p27, and 29 cycles for tubulin. (B) Immunoblot analysis of mRNA-bound proteins with indicated antibodies (right). Loaded fractions are as follows: 0.1%, 2.5% and 1% for yeast, nematode and human inputs; 10%, 10% and 5% for yeast, nematode and human oligo(dT) lanes; and 66% for all ASOs lanes. Molecular weights (MW) are indicated in kilodaltons (kDa). Figure republished with permission37. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
| Primer name | Sequence | Target | Size | |
| Pfk2_Fwd | GTGTTAAGGGTTCACATGTCG | PFK2 S. cerevisiae | 133 bp | |
| Pfk2_Rev | CTTCCAACCAAATGGTCAGC | PFK2 S. cerevisiae | 133 bp | |
| Pfk1_Fwd | GGTGATTCTCCAGGTATGAATG | PFK1 S. cerevisiae | 97 bp | |
| Pfk1_Rev | CTTCGTAACCTTCGTAAACAGC | PFK1 S. cerevisiae | 97 bp | |
| Act1_Fwd | GTCTGGATTGGTGGTTCTATC | ACT1 S. cerevisiae | 85 bp | |
| Act1_Rev | GGACCACTTTCGTCGTATTC | ACT1 S. cerevisiae | 85 bp | |
| Dnm1_Fwd | CTGTGTTCGATGCATCAGAC | DNM1 S. cerevisiae | 156 bp | |
| Dnm1_Rev | CGCACTCCAATTCTTCTCTC | DNM1 S. cerevisiae | 156 bp | |
| Rps20_Fwd | CGCTGAACAACACAACTTGG | RPS20 S. cerevisiae | 228 bp | |
| Rps20_Rev | GGAAGCAACAACAACTTCGAC | RPS20 S. cerevisiae | 228 bp | |
| Cep1_Fwd | CGATGAAGAGAAGTCGCTGT | cep-1 C. elegans | 110 bp | |
| Cep1_Rev | ATCTGGGAACTTTTGCTTCG | cep-1 C. elegans | 110 bp | |
| Pgk1_Fwd | GCGATATTTATGTCAATGATGCTTTC | pgk-1 C. elegans | 74 bp | |
| Pgk1_Rev | TGAGTGCTCGACTCCAACCA | pgk-1 C. elegans | 74 bp | |
| Mpk1_Fwd | TGCTCAGTAATCGGCCATTG | mpk-1 C. elegans | 74 bp | |
| Mpk1_Rev | TCCAACAACTGCCAAAATCAAA | mpk-1 C. elegans | 74 bp | |
| p27_Fwd | TTTAAAAATACATATCGCTGACTTCATGG | p27 H. sapiens | 212 bp | |
| p27_Rev | CAAAGTTTATGTGCTACATAAAAGGTAAAAA | p27 H. sapiens | 212 bp | |
| Luc_Fwd | AATGGCTCATATCGCTCCTGGAT | Luciferase P. pγralis | 117 bp | |
| Luc_Rev | TGGACGATGGCCTTGATCTTGTCT | Luciferase P. pγralis | 117 bp | |
| β-TUBULIN_Fwd | CTGAACCACCTTGTCTCAGC | β-TUBULIN H. sapiens | 136 bp | |
| β-TUBULIN_Rev | AGCCAGGCATAAAGAAATGG | β-TUBULIN H. sapiens | 136 bp | |
| PFK2-1 ASO | AAUAGAAAGUGUAAUAAAAGGUCAU | 3' UTR PFK2 S. cerevisiae | - | |
| PFK2-2 ASO | GUUUCAUGGGGUAGUACUUGU | 3' UTR PFK2 S. cerevisiae | - | |
| PFK2-4 ASO | CUUGAAGAGGAGCGUUCAUA | ORF PFK2 S. cerevisiae | - | |
| DNM1 ASO | UCGGUCAGUGGAGGUUCAGCGUUU | ORF DNM1 S. cerevisiae | - | |
| RPS20 ASO | GUCGGUAAUAGCCUUCUCAUUCUUG | ORF RPS20 S. cerevisiae | - | |
| cep-1 ASO | GUGAGAAAUGCGGUGCUUUGAAA | 3' UTR cep-1 C. elegans | - | |
| p27 ASO | UCAUACCCCGCUCCACGUCAGUU | 3' UTR p27 H. sapiens | - | |
Table 1. Oligonucleotide sequences. List of PCR primers and ASOs used in this work, primer sequence, gene target and expected fragment size after amplification.
Discussion
TRIP permits the analysis of proteins bound to specific mRNAs in vivo with biochemical means. While we have used the method to validate the interaction of particular RBPs with mRNA targets from different organisms/cells, TRIP could also be applicable to study other types of poly(A) RNAs, such as cytoplasmic long ncRNAs. Furthermore, systematic analysis of bound proteins and/or RNAs with MS or RNA sequencing could be achieved by an up-scaling of the procedure. In this regard, our preliminary data indicates that 1 L of yeast cultures and at least 100 million of human HEK293 cells could provide sufficient starting material to obtain reliable MS data for well-expressed mRNAs (unpublished results).
The described TRIP protocol includes the irradiation of cells with UV-light at 254 nm to crosslink RNA-protein interactions. This enables the implementation of stringent wash conditions during purification. Nevertheless, although not explicitly tested, we wish to note that crosslinking is optional and active RNPs may also be recovered with physiological buffers. However, in this case, the potential re-arrangement of proteins and or RNAs on the target RNA in lysates should be taken into account. Conversely, if UV or other crosslinking procedures are applied (e.g., formaldehyde), the integrity of the RNA should be evaluated as RNA degradation could lead to diminished recovery of mRNPs. Additionally, UV-crosslinking is rather inefficient (~5%) and even less so for proteins interacting with double-stranded RNA, which could introduce bias for the detection of certain classes of RBPs12. Finally, UV irradiation can also induce protein-protein and protein-DNA crosslinks that should be considered for data interpretation45,46. Therefore, alternative crosslinking procedures, for example with formaldehyde, could also be of particular interest to capture larger protein assemblies on mRNAs.
One key feature of TRIP is the two-step ASO-based purification procedure to recover particular RNAs, thereby increasing selectivity and decreasing the probability of co-purifying contaminants. For instance, one concern relates to adding biotinylated ASOs directly to cell extracts, which could lead to co-purification of biotin-binding proteins. This is circumvented in TRIP by implementing a first round of purification of poly(A) RNAs using covalently coupled oligo-(dT)25 magnetic beads, which allows for stringent purification conditions as done for RNA-protein interactome capture. Furthermore, poly(A) RNA selection removes highly abundant ncRNAs, such as ribosomal RNAs and tRNAs, and therefore reduces the complexity of the sample and potential sources for cross-hybridization and contamination. In the second step, particular mRNAs are recovered with biotinylated and modified ASOs that anneal with regions on the mRNA targets. Alternatively, modified ASOs could also be directly covalently attached to magnetic beads via an amine-linker, reducing the propensity to capture biotin binding proteins. However, in our experience, the incubation of the poly(A) RNA fraction with ASOs prior to the addition of streptavidin beads recovered mRNPs more efficiently than direct addition of ASO-coupled beads. Possibly, free oligos are kinetically favored with better access to sequences in structured RNA as compared to immobilized oligos. Hence, the covalent coupling of ASOs to beads prior to the incubation with the sample could be detrimental for recovery of the RNA target and has to be tested empirically.
One drawback with ASO based methods is inefficient recovery of some target mRNAs. We therefore recommend the evaluation of several ASOs that anneal to different regions of the transcript. Specifically, we suggest the design of 2-3 ASOs that anneal with sequences in the 3'-UTR or the CDS of the mRNA of interest. Each ASO may exhibit a different efficiency for the recovery of the respective mRNA target and should be empirically tested (Figure 2A, B, data not shown). At the end, we found that ASOs annealing to the 3'UTRs performed better compared to the ones annealing to CDS. This could be due to increased accessibility of binding sites in UTRs because of the absence of translating ribosomes, whereas ribosomes may obstruct efficient hybridization within CDS. We also experienced that combination of several ASOs could lead to increased contamination from abundant non-target mRNAs and reduced pull-down efficiency. In any case, the selectivity of the chosen oligos can be controlled by competition experiments (e.g., addition of competing oligos).
A further concern relates to potential cross-hybridization with unrelated RNAs, as we observed that even partial hybridization with other mRNAs can lead to the recovery of that mRNA (Figure 2C). To evaluate the suitability of the designed ASOs, we therefore recommend performing initial in vitro testing with total RNAs to optimize salt concentrations and washing temperature of buffers. In our hands, washing of streptavidin-coupled magnetic beads in buffers containing 150 mM NaCl at 55 °C performed best, but we recommend independent tests of the conditions for each designed ASO. Noteworthy, we found that all ASOs selected from in vitro experiments (Figure 2D) were appropriate for capturing the respective mRNA target from crosslinked cell extracts (Figure 3), further substantiating the validity of in vitro testing. Besides designing suitable ASOs for mRNA capture, additional factors could impact on selectivity. Therefore, comprehensive blocking procedures with BSA and/or tRNA according to the bead type specifications can prevent unspecific binding to beads. To further reduce unspecific absorption of proteins, we also recommend the use of Lo-bind tubes, especially when working with low amounts of samples.
Generally, TRIP can complement previously established approaches to capture RNAs with ASOs. For instance, the non-coding RNA Xist was isolated with bound proteins from nuclear extracts derived from 200-800 million UV crosslinked cells by using an array of long (90-mer) biotinylated DNA oligonucleotides that covered the entire transcript34,35. However, the chosen tiling approach could become problematic in light of the great potential for cross-hybridization with unrelated RNAs, and it cannot be used to select specific transcript, e.g., alternatively spliced forms. Recently, specifically designed locked nucleic acid (LNA) or DNA ASO mixmers were covalently attached to a magnetic resin to recover in vitro transcript or highly expressed ribosomal RNAs from cell-free extracts; however, it was not tested for the recovery of in vivo formed mRNA-protein complexes36. In light of the increased recognition of post-transcriptional gene control by RBPs and ncRNA, we believe that TRIP is a useful method to investigate the composition and dynamics of RNP complexes within cells upon intracellular and environmental cues and its impact in health and disease.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Jonathan Hall and Mauro Zimmermann (ETH Zurich) for the synthesis of PFK2 and cep-1 ASOs, Dr. Maikel Wouters for the design of p27/CDKN1B ASOs, and Dr. Rafal Ciosk (Friedrich Miescher Institute for Biomedical Research, Basel) for anti-GLD-1 antibodies. This work was supported by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BB/K009303/1) and a Royal Society Wolfson Research Merit Award (WM170036) to A.P.G.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| MaxQ 5000 Large Incubated and Refrigerated Orbital Shaker | Thermo Fisher Scientific | SHKE5000-8CE | Floor shaker to grow yeast cells |
| BBD 6220 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | CO2 incubator to grow human cells | |
| Sonicator Soniprep150 | MSE | MSS150.CX4.5 | Sonicator/cell disruptor. Used to shear DNA in human cell lysates |
| Stratalinker 1800 | Stratagene | Stratalinker to expose cells to UV light at 254 nm | |
| Tissue Lyser | Qiagen | RETSCH MM200 | Device to mechanically disrupt yeast cells |
| Refrigerated Centrifuge | Eppendorf | 5810R | Centrifuge to spin down cells, lysates |
| Shaking incubator, Thriller | Peqlab | Thermoshaker for 1.5 mL tubes | |
| Glass beads 0.5mm | Stratech Scientific Limited | 11079105 | Lysis of yeast cells |
| Nylon Filter, 0.41 μm | Millipore | NY4104700 | Collection of yeast cells |
| Millex-HA Filter, 0.45 µm | EMD Millipore | SLHA02510 | Filter to clear nematode lysate |
| Eppendorf LoBind microcentrifuge tubes Protein 1.5 mL | Sigma-Aldrich | 22431081 | Minimise protein loss |
| 2 mL microfuge tube | Ambion | AM12425 | Yeast extract preparation and other applications |
| 5 mL tube | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 129A | Collection of HEK293 cell lysate |
| 15 mL tube | Sarstedt | 62.547.254 | Collection C. elegans |
| 50 mL plastic tube | Sarstedt | 62.554.502 | Collection yeast cells |
| DMEM, high glucose, pyruvate | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 41966 | Media for culturing HEK293 cells |
| Penicillin-Streptomycin | Sigma-Aldrich | P4333 | Used to supplement cell culture media to control bacterial contamination |
| Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) | Sigma-Aldrich | F7524 | Used to supplement cell culture media |
| Lipofectamine 2000 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 11668027 | Transfection reagent |
| RQ1 RNase-Free DNase | Promega | M6101 | DNAse I to degrade DNA from cell lysate |
| RNasin Plus RNase Inhibitor | Promega | N2611 | RNase inhibitor to avoid RNA degradation |
| cOmplete, Mini, EDTA-free Protease Inhibitor Cocktail | Roche | 11836170001 | Protease inhibitor cocktail to avoid protein degradation |
| Dynabeads Oligo (dT)25 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 61011 | Magnetic beads required for the first step of mRNA-protein complex purification |
| Dynabeads M-280 Streptavidin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 11205D | Magnetic beads required for the second step of mRNA-protein complex purification |
| E. coli tRNA | Sigma-Aldrich | 10109550001 | transfer RNA from E. coli used for blocking streptavidin beads and avoid unsepecific interactions |
| Quick Start Bradford 1x Dye Reagent | BioRad | 5000205 | To determine protein concentration within lysates, using BSA as reference |
| Bovine Serum Albumin | Sigma | A7906-100G | Used to perform the standard curve that will be used as reference for protein concentration determination |
| mouse anti-Act1 | MP Biomedicals | 869100 | Antibody for detection of yeast actin in Western blot (1:2,500) |
| mouse anti-Act1 | Sigma | A1978 | Antibody for detection of human actin in Western blot (1:2,000) |
| mouse anti-HuR | Santa Cruz | sc-5261 | Antibody for detection of HuR in Western blot (1:500) |
| mouse anti–CYC-1 | Invitrogen | 456100 | Antibody for detection of Cyc-1 in Western blot (1:1,000) |
| peroxidase anti-peroxidase soluble complex | Sigma | P1291 | Detection of Pfk2:TAP in Western blot (1:5,000) |
| HRP-conjugated sheep anti-mouse IgG | Amersham | NXA931 | HRP-coupled secondary antibody |
References
- Mitchell, S. F., Parker, R. Principles and properties of eukaryotic mRNPs. Molecular Cell. 54 (4), 547-558 (2014).
- Iadevaia, V., Gerber, A. P. Combinatorial Control of mRNA Fates by RNA-Binding Proteins and Non-Coding RNAs. Biomolecules. 5 (4), 2207-2222 (2015).
- McHugh, C. A., Russell, P., Guttman, M. Methods for comprehensive experimental identification of RNA-protein interactions. Genome Biology. 15 (1), 203 (2014).
- Matia-González, A. M., Gerber, A. P., Sesma, A., von der Haar, T. Ch. 14. Fungal RNA Biology. , 347-370 (2014).
- Tsvetanova, N. G., Klass, D. M., Salzman, J., Brown, P. O. Proteome-wide search reveals unexpected RNA-binding proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS One. 5 (9), (2010).
- Castello, A., et al. Insights into RNA biology from an atlas of mammalian mRNA-binding proteins. Cell. 149 (6), 1393-1406 (2012).
- Baltz, A. G., et al. The mRNA-bound proteome and its global occupancy profile on protein-coding transcripts. Molecular Cell. 46 (5), 674-690 (2012).
- Castello, A., et al. System-wide identification of RNA-binding proteins by interactome capture. Nature Protocols. 8 (3), 491-500 (2013).
- Liao, Y., et al. The Cardiomyocyte RNA-Binding Proteome: Links to Intermediary Metabolism and Heart Disease. Cell Reports. 16 (5), 1456-1469 (2016).
- Liepelt, A., et al. Identification of RNA-binding Proteins in Macrophages by Interactome Capture. Molecular Cell Proteomics. 15 (8), 2699-2714 (2016).
- Conrad, T., et al. Serial interactome capture of the human cell nucleus. Nature Communications. 7, 11212 (2016).
- Matia-Gonzalez, A. M., Laing, E. E., Gerber, A. P. Conserved mRNA-binding proteomes in eukaryotic organisms. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology. 22 (12), 1027-1033 (2015).
- Mitchell, S. F., Jain, S., She, M., Parker, R. Global analysis of yeast mRNPs. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology. 20 (1), 127-133 (2013).
- Beckmann, B. M., et al. The RNA-binding proteomes from yeast to man harbour conserved enigmRBPs. Nature Communications. 6, 10127 (2015).
- Wessels, H. H., et al. The mRNA-bound proteome of the early fly embryo. Genome Research. 26 (7), 1000-1009 (2016).
- Sysoev, V. O., et al. Global changes of the RNA-bound proteome during the maternal-to-zygotic transition in Drosophila. Nature Communications. 7, 12128 (2016).
- Despic, V., et al. Dynamic RNA-protein interactions underlie the zebrafish maternal-to-zygotic transition. Genome Research. 27 (7), 1184-1194 (2017).
- Zhang, Z., et al. UV crosslinked mRNA-binding proteins captured from leaf mesophyll protoplasts. Plant Methods. 12, 42 (2016).
- Reichel, M., et al. In Planta Determination of the mRNA-Binding Proteome of Arabidopsis Etiolated Seedlings. Plant Cell. 28 (10), 2435-2452 (2016).
- Koster, T., Marondedze, C., Meyer, K., Staiger, D. RNA-Binding Proteins Revisited - The Emerging Arabidopsis mRNA Interactome. Trends Plant Sciences. 22 (6), 512-526 (2017).
- Hamasaki, K., Killian, J., Cho, J., Rando, R. R. Minimal RNA constructs that specifically bind aminoglycoside antibiotics with high affinities. Biochemistry. 37 (2), 656-663 (1998).
- Bachler, M., Schroeder, R., von Ahsen, U. StreptoTag: a novel method for the isolation of RNA-binding proteins. RNA. 5 (11), 1509-1516 (1999).
- Vazquez-Pianzola, P., Urlaub, H., Rivera-Pomar, R. Proteomic analysis of reaper 5' untranslated region-interacting factors isolated by tobramycin affinity-selection reveals a role for La antigen in reaper mRNA translation. Proteomics. 5 (6), 1645-1655 (2005).
- Hartmuth, K., Vornlocher, H. P., Luhrmann, R. Tobramycin affinity tag purification of spliceosomes. Methods Molecular Biology. 257, 47-64 (2004).
- Beach, D. L., Keene, J. D. Ribotrap : targeted purification of RNA-specific RNPs from cell lysates through immunoaffinity precipitation to identify regulatory proteins and RNAs. Methods Molecular Biology. 419, 69-91 (2008).
- Slobodin, B., Gerst, J. E. A novel mRNA affinity purification technique for the identification of interacting proteins and transcripts in ribonucleoprotein complexes. RNA. 16 (11), 2277-2290 (2010).
- Slobodin, B., Gerst, J. E. RaPID: an aptamer-based mRNA affinity purification technique for the identification of RNA and protein factors present in ribonucleoprotein complexes. Methods Molecular Biology. 714, 387-406 (2011).
- Yoon, J. H., Gorospe, M. Identification of mRNA-Interacting Factors by MS2-TRAP (MS2-Tagged RNA Affinity Purification). Methods Molecular Biology. 1421, 15-22 (2016).
- Leppek, K., Stoecklin, G. An optimized streptavidin-binding RNA aptamer for purification of ribonucleoprotein complexes identifies novel ARE-binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Research. 42 (2), 13 (2014).
- Blencowe, B. J., Sproat, B. S., Ryder, U., Barabino, S., Lamond, A. I. Antisense probing of the human U4/U6 snRNP with biotinylated 2'-OMe RNA oligonucleotides. Cell. 59 (3), 531-539 (1989).
- Lingner, J., Cech, T. R. Purification of telomerase from Euplotes aediculatus: requirement of a primer 3' overhang. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences U S A. 93 (20), 10712-10717 (1996).
- Upadhyay, A., Dixit, U., Manvar, D., Chaturvedi, N., Pandey, V. N. Affinity capture and identification of host cell factors associated with hepatitis C virus (+) strand subgenomic RNA. Molecular Cell Proteomics. 12 (6), 1539-1552 (2013).
- Imig, J., et al. miR-CLIP capture of a miRNA targetome uncovers a lincRNA H19-miR-106a interaction. Nature Chemical Biology. 11 (2), 107-114 (2015).
- Chu, C., et al. Systematic discovery of Xist RNA binding proteins. Cell. 161 (2), 404-416 (2015).
- McHugh, C. A., et al. The Xist lncRNA interacts directly with SHARP to silence transcription through HDAC3. Nature. 521 (7551), 232-236 (2015).
- Rogell, B., et al. Specific RNP capture with antisense LNA/DNA mixmers. RNA. 23 (8), 1290-1302 (2017).
- Matia-Gonzalez, A. M., Iadevaia, V., Gerber, A. P. A versatile tandem RNA isolation procedure to capture in vivo formed mRNA-protein complexes. Methods. , 93-100 (2017).
- Gruber, A. R., Lorenz, R., Bernhart, S. H., Neubock, R., Hofacker, I. L. The Vienna RNA websuite. Nucleic Acids Research. 36 (Web Server issue), W70-W74 (2008).
- Kalendar, R., Khassenov, B., Ramankulov, Y., Samuilova, O., Ivanov, K. I. FastPCR: An in silico tool for fast primer and probe design and advanced sequence analysis. Genomics. 109 (3-4), 312-319 (2017).
- Altschul, S. F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E. W., Lipman, D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. Journal of Molecular Biology. 215 (3), 403-410 (1990).
- Stiernagle, T. Maintenance of C. elegans. WormBook. , 1-11 (2006).
- Kedde, M., et al. A Pumilio-induced RNA structure switch in p27-3' UTR controls miR-221 and miR-222 accessibility. Nature Cell Biology. 12 (10), 1014-1020 (2010).
- Schumacher, B., et al. Translational repression of C. elegans p53 by GLD-1 regulates DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Cell. 120 (3), 357-368 (2005).
- Ziegeler, G., et al. Embryonic lethal abnormal vision-like HuR-dependent mRNA stability regulates post-transcriptional expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 285 (20), 15408-15419 (2010).
- Itri, F., et al. Femtosecond UV-laser pulses to unveil protein-protein interactions in living cells. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 73 (3), 637-648 (2016).
- Zhang, L., Zhang, K., Prandl, R., Schoffl, F. Detecting DNA-binding of proteins in vivo by UV-crosslinking and immunoprecipitation. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 322 (3), 705-711 (2004).
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved