Abstract
Behavior
Visual Classical Conditioning in Wood Ants
ERRATUM NOTICE
Important: There has been an erratum issued for this article. Read more …Abstract
Several species of insects have become model systems for studying learning and memory formation. Although many studies focus on freely moving animals, studies implementing classical conditioning paradigms with harnessed insects have been important for investigating the exact cues that individuals learn and the neural mechanisms underlying learning and memory formation. Here we present a protocol for evoking visual associative learning in wood ants through classical conditioning. In this paradigm, ants are harnessed and presented with a visual cue (a blue cardboard), the conditional stimulus (CS), paired with an appetitive sugar reward, the unconditional stimulus (US). Ants perform a Maxilla-Labium Extension Reflex (MaLER), the unconditional response (UR), which can be used as a readout for learning. Training consists of 10 trials, separated by a 5-minute intertrial interval (ITI). Ants are also tested for memory retention 10 minutes or 1 hour after training. This protocol has the potential to allow researchers to analyze, in a precise and controlled manner, the details of visual memory formation and the neural basis of learning and memory formation in wood ants.
Erratum
Erratum: Visual Classical Conditioning in Wood AntsAn erratum was issued for: Visual Classical Conditioning in Wood Ants. The Acknowledgments section was updated, and a supplemental figure was added.
The Acknowledgments sections was updated from:
The authors thank Tom Collett and Cornelia Buehlmann for sharing valuable information regarding collection and maintenance of wood ant colonies. The authors also thank Justine Crevel for commenting on previous versions of this article.
to:
The authors thank Tom Collett and Cornelia Buehlmann for sharing information regarding collection and maintenance of wood ant colonies. The authors also thank Justine Crevel for commenting on previous versions of this article, and Nora Nevala for measuring the spectrum intensity of the visual stimulus. This work was supported by a BBSRC grant to JEN (grant number BB/R005036/1). All the data pertaining to this manuscript are published in the University of Sussex Research Data Repository online database (10.25377/sussex.5794386).
The following supplemental figure was added to the end of the Representative Results section:
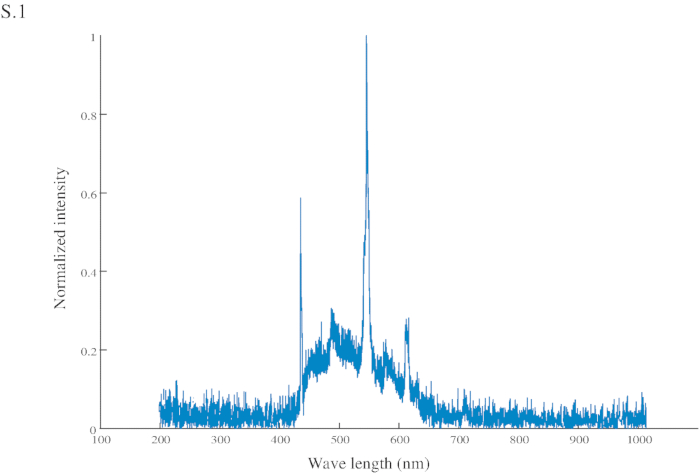
Figure S1: Normalized intensity of the conditional stimuli (CS). The CS has a peak intensity at 545 nm (in the green range) and another at 435 nm (in the blue range).
Explore More Videos
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2024 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved