Immunization of Adult Zebrafish for the Preclinical Screening of DNA-based Vaccines
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
Here we describe a protocol for the immunization of the adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) with a DNA-based vaccine and demonstrate the validation of a successful vaccination event. This method is suitable for the preclinical screening of vaccine candidates in various infection models.
Abstract
The interest in DNA-based vaccination has increased during the past two decades. DNA vaccination is based on the cloning of a sequence of a selected antigen or a combination of antigens into a plasmid, which enables a tailor-made and safe design. The administration of DNA vaccines into host cells leads to the expression of antigens that stimulate both humoral and cell-mediated immune responses. This report describes a protocol for the cloning of antigen sequences into the pCMV-EGFP plasmid, the immunization of adult zebrafish with the vaccine candidates by intramuscular microinjection, and the subsequent electroporation to improve intake. The vaccine antigens are expressed as green fluorescent protein (GFP)-fusion proteins, which allows the confirmation of the antigen expression under UV light from live fish and the quantification of expression levels of the fusion protein with ELISA, as well as their detection with a western blot analysis. The protective effect of the vaccine candidates is tested by infecting the fish with Mycobacterium marinum five weeks postvaccination, followed by the quantification of the bacteria with qPCR four weeks later. Compared to mammalian preclinical screening models, this method provides a cost-effective method for the preliminary screening of novel DNA-based vaccine candidates against a mycobacterial infection. The method can be further applied to screening DNA-based vaccines against various bacterial and viral diseases.
Introduction
The first DNA vaccine studies were performed in the 1990s1, and since then, DNA vaccines have been tested against various infectious diseases, cancer, autoimmunity, and allergy2. In mammals, a DNA vaccine against West Nile virus in horses and a therapeutic cancer vaccine for canine oral melanoma have been licensed, but these are not currently in clinical use2. In addition to the interest evoked by mammalian studies, DNA vaccination has turned out to be a convenient way to immunize farmed fish against viral diseases. A vaccine against fish infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV) has been in commercial use since 2005, and a vaccine against infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV) was recently licensed3. In addition, several DNA vaccines against fish pathogens are being developed.
As traditional vaccines often contain inactivated or live attenuated pathogens, they pose a potential risk of transmitting the disease2. DNA vaccines, in turn, avert this risk, as they are based on the administration of plasmid encoding bacterial or viral antigens, rather than the whole pathogen itself2,4. DNA vaccines are produced with DNA recombination techniques, which allows the precise design of vaccine antigens and the flexible formulation of antigen combinations and adjuvants in a single vaccine construct5. Furthermore, the production of DNA vaccines is faster, easier and more cost-efficient than that of protein-based recombinant vaccines, which is a major advantage for vaccine candidate screening purposes, but also, for example, in the case of pandemic outbreaks2.
In fish, the most common administration routes for DNA vaccines are intraperitoneal, intramuscular, and oral3,6,7, while in mammals, subcutaneous and intradermal routes are additional options2. After an intramuscular injection, the administrated DNA plasmids enter the cells at the administration site (e.g., mostly myocytes, but also resident antigen-presenting cells [APCs]). The proportion of transfected cells can be significantly increased by electroporation2,8. After entering the cell, some plasmid DNA enters the nucleus, where the genes encoded by the plasmid are transcribed2. In this protocol, we utilize the pCMV-EGFP plasmid that has a strong ubiquitous promoter optimized for eukaryotic expression9. In this construct, the antigens are translated as a fusion protein with a GFP. The GFP enables the confirmation of a successful vaccination and the correct antigen product by the simple visualization of antigen expression with a fluorescence microscope in live fish.
In mammals, DNA vaccines have been shown to stimulate different types of immune responses depending on the transfected cell types2,5. Transfected myocytes secrete antigens into the extracellular space or release them upon cell death, and the antigens engulfed by APCs are, subsequently, presented on major histocompatibility complex II molecules2. This triggers CD4 and CD8 T cell responses, especially, in addition to B cell responses2,5,10. In fish, T and B lymphocytes, as well as dendritic cells (DCs), have been identified, yet their division of labor in antigen presentation is less well understood11. Zebrafish DCs, however, have been shown to share conserved phenotypic and functional characteristics with their mammalian counterparts12. Furthermore, DNA vaccination has been shown to elicit similar immune responses in fish and in mammals, including T and B cell responses6,13,14,15,16.
Both larvae and adult zebrafish are widely used to model different infectious diseases, such as the fish M. marinum infection model of tuberculosis used in this protocol17,18,19,20,21,22. In comparison with mammalian model organisms, the advantages of zebrafish include their small size, fast reproducibility, and low housing expenses23. These aspects make the zebrafish an ideal animal model for large-scale preclinical screening studies for novel vaccines and pharmaceutical compounds23,24,25.
In this protocol, we describe how novel vaccine antigen candidates against mycobacteriosis can be evaluated by the DNA-based vaccination of adult zebrafish. First, we describe how antigens are cloned into the pCMV-EGFP expression plasmid, followed by a detailed protocol for the intramuscular injection of vaccine plasmids and the subsequent electroporation into muscle. The expression of each antigen is confirmed by fluorescence microscopy one-week postimmunization. The efficacy of the antigen candidates is then tested by experimentally infecting vaccinated fish with M. marinum.
Protocol
Experiments including adult zebrafish require a permission for animal experimentation for both the vaccination and the subsequent studies with the infection model. All methods and experiments described here are approved by the Animal Experiment Board of Finland (ESAVI) and the studies are carried out in accordance with EU directive 2010/63/EU.
1. Cloning of DNA Vaccine Antigens
- Select an expression plasmid optimized for the eukaryotic expression of the antigen(s) of interest under a strong, constitutive promoter, such as the cytomegalovirus (CMV) immediate early promoter. To enable the in vivo verification of the antigen expression, select a vaccine plasmid that encodes a fluorescent tag, such as the pCMV-EGFP plasmid9 used in this protocol.
- Use appropriate web-based and bioinformatic tools to select a potentially immune-protective antigen sequence (or several sequences) of approximately 90–600 nt (30–200 aa)26 from the gene(s)-of-interest of the pathogen that will be used in the subsequent infection model.
- Use available software, or manually design primers to amplify the antigen genes from the pathogen genome and to clone the antigen sequence(s) into the multiple-cloning site of the expression plasmid. Make sure to preserve the correct reading frame when selecting the antigen.
- Include both a Kozak sequence (CCACC)27 and a start codon (ATG) in the 5’ primer. To preserve the C-terminal EGFP tag, avoid intervening stop codons (TAG, TAA, TGA) in the antigen sequence and the 3’ primer. Also, ensure that the GFP tag remains in the same reading frame with the antigen of interest.
- Use RNA or DNA extracted from the pathogen as a template to generate an adequate amount of PCR product with the cloning primers. Preferably, use a proofreading DNA polymerase to preserve the correct antigen sequence.
- Purify the PCR product and check the correct size of the product by gel electrophoresis. Digest and ligate the PCR product with the digested vaccine plasmid.
- Transform the ligation mix into competent bacterial cells according to a suitable protocol. Use an appropriate antibiotic selection for positive colonies and plasmid production in E. coli; the pCMV-EGFP plasmid, for example, contains an ampicillin resistance gene for this.
- Use Sanger sequencing to confirm the insertion of the correct antigen sequence. The following primers can be used for sequencing antigens in the pCMV-EGFP plasmid: CMV forward 5’- CGCAAATGGGCGGTAGGCGTG-3’ and EGFP-N reverse 5’ CGTCGCCGTCCAGCTCGACCAG-3’.
- Produce and purify a sufficient amount of the vaccine construct. Dissolve or elute the plasmid in sterile water. Make sure that the produced plasmid DNA is of high quality and the concentration is at least 0.72 µM or 2,000 ng/µL.
2. Pulling the Microinjection Needles
- Prepare microinjection needles in advance. Use 10-cm aluminosilicate glass capillaries. Note that borosilicate glass capillaries are too brittle for injecting adult fish.
- Pull the needles with a micropipette-needle-fabricating device.
NOTE: The needles should look similar to the one presented in Figure 1. With the device used in this protocol (Table of Materials), the following settings result in the desired kind of needles:- Set the glass capillary in the V-groove in the puller bar and tighten the clamping knob lightly.
- Move the holder next to the filament and gently push the capillary through the filament into the puller bar on the other side of the filament. Avoid touching the filament with the capillary.
- Tighten the clamping knobs, set down the safety glass, and press the pull button.
CAUTION: The filament is hot.
- Place the needles on a piece of reusable adhesive inside a 15-cm Petri dish plate to protect the needle tips. Keep the dish covered to keep the needles clean.
3. Filling the Micropipette Needles
- Prepare the vaccine mix. Use 0.5–12 µg of plasmid per dose. If combining several different plasmids in one vaccination mix, use a maximum total DNA concentration of 12 µg per fish.
- Calculate the volume of the vaccine “master mix” according to the number of fish in each group (see below). Add 1 µl of sterile-filtered phenol red to each injection dose to ease both the filling of the capillary needles and the observation of the injection. Add sterile 1x PBS up to a maximum total volume of 5–7 µl in one injection dose8.
NOTE: Injection volumes higher than 7 µL can result in the occasional leakage of the injection solution and should, therefore, be avoided. - Place a piece of tape, glue side up, on an appropriate holder, for example, the side of an empty tip box. Gently attach the capillary needles to the tape.
- Pipet a maximum of 7 µL of the vaccine mix onto a piece of laboratory film. Using a loading tip, transfer the vaccine from the film into the needle. Pipet slowly and carefully, avoid pipetting air bubbles into the needle.
- Let the needles settle for 15–30 min to remove possible remaining small air bubbles.
4. Setting the Microinjector and Electroporator for Immunization
- Set the micromanipulator and a light source into the right position. Switch the air pressure tap to the open position.
- Adjust the parameters for the pneumatic pump (see also Figure 2) as follows.
- Set the vent knob on the Eject port to hold to prevent backfilling of the pipette by capillary action. Set the tubing from the eject port to the micropipette. Do not use the Vacuum port in this protocol.
- Adjust the pulse length: use the timed mode, where an electronic timer controls the duration of the time the pressure solenoid stays open. Check that the green lamp next to the Eject pressure gauge illuminates when the pressure solenoid is open (energized).
- Set the pulse range to 10 s; with this setting, the pulses may be further set from 100 ms to 10.1 s. Use the 10-turn period dial for fine-tuning the pulse length—every turn of the dial is 1.0 s. If needed, this can also be adjusted during an injection.
- Use the pulse initiator (“start button”) on the front panel of the pneumatic pump, or a remote foot switch (recommended). This is connected to the front panel of the pneumatic pump.
- Set the needle onto the micropipette holder of the micromanipulator. Cut the tip of the needle with tweezers so that liquid can be pushed out, and use the microscope to view the correct position. Press the foot switch once to see that a 1-s pulse pushes a small droplet out of the needle.
- Use the following settings for the electroporator: voltage = 40 V; pulse length = 50 ms, number of pulses = 6. Connect the tweezers to the electroporator. See that the actual voltage and pulse length shown on the monitor do not differ significantly from the settings.
5. Injection of the DNA Vaccine and Electroporation
- For immunizations according to this protocol, use healthy, 6 to 12 month-old adult zebrafish. Keep the fish in a flow-through system with a 14/10 h light/dark cycle, with a maximum of seven fish per 1 L of water.
- Prepare a 0.02% 3-aminobenzoic acid ethyl ester (tricaine) solution (pH 7) in tank water for anesthetizing the fish28. Use a 10 cm Petri dish or something similar.
- Prepare a recovery tank by filling a 5 L beaker with 3 L of clean system water.
- Prepare a vaccination padding to keep the fish in a fixed position during the vaccination. Take a 5 x 7 cm2 piece of a 2 to 3 cm-thick sponge. Cut a groove into the sponge with a scalpel blade or sharp scissors.
NOTE: The same vaccination padding can be used in multiple experiments. Disinfect the sponge between the experiments by soaking it in 70% ethyl alcohol and allow to dry. - Thoroughly soak the sponge in the system water and set the sponge on a Petri dish.
- Fast the fish 24 h before the vaccinations.
- Anesthetize one zebrafish by placing it on a Petri dish containing 0.02% tricaine. Wait until the fish does not respond to touch stimulation and until there is no movement of the gills. Anesthetize a single fish at a time.
- Using a plastic spoon, transfer the anesthetized zebrafish onto the wet sponge and set the fish’s ventral side down into the groove. In the correct position, ensure that the head and most of the body of the fish are inside the groove and the dorsal fin and the tail are protruding out from the groove.
- Under the microscope, carefully place the needle in an approximately 45° angle close to the zebrafish’s dorsal muscle, using the x- and y-axis fine-tuning wheels on the micromanipulator.
- Find the small spot without scales in front of the dorsal fin, where pushing the needle does not demand force. If resistance is felt, try an adjacent spot. Avoid injuring the spine, the dorsal fin, or the scales.
NOTE: If the needle bends while pushing, shorten the needle slightly by cutting it. - Use the foot switch to gradually inject the vaccine solution into the muscle. Observe the injection through the microscope: phenol red is visible as it enters the muscle tissue. Adjust the duration of the pulse if needed.
NOTE: Alternatively, use the pulse initiator button on the front panel of the pneumatic pump for the injection. However, the use of a remote foot switch allows using the other hand for adjusting the pulse length by the 10-turn dial wheel. Avoid injecting the solution too fast, since this may cause excessive tissue damage. Make sure not to inject any air. - Electroporate the fish immediately after the injection. Make sure that the fish is still under anesthesia. Keep the fish on the sponge and set the fish between tweezer-type electrodes, so that the electrodes are located on each side of the injection site. Do not press the electrode tweezers too tight but keep both electrodes in contact with the fish.
- Press the start button on the electroporator to give six 40 V, 50 ms pulses.
- Gently transfer the fish to the recovery tank.
- Clean the electrodes after each electroporation by swiping them with 70% ethanol.
NOTE: Carefully monitor the well-being of the fish after the vaccination. Euthanize any fish showing signs of discomfort (a slow recovery from anesthesia, aberrant swimming, gasping) in 0.04% tricaine. After recovery, transfer the fish to the flow-through unit and feed it normally.
6. Visualization and Imaging of Antigen Expression
- Anesthetize the fish in 0.02 % tricaine 2–7 days after immunization, and use a UV-light to see EGFP expression near the injection site.
NOTE: Visual inspection under a UV light is an easy and non-invasive operation that is suitable for the routine verification of successful vaccinations, also in large-scale experiments. If no images of the fish are required, this step can also be performed in regular fish tanks without the need to anesthetize or move the fish. - To capture images, use a fluorescence microscope to visualize EGFP expression at the injection site8. Use a 2X objective lens and select the correct filter to visualize fluorescence or visible light views.
- Keep the anesthetized fish still by pressing the ventral fin gently with tweezers toward a Petri dish bottom. Take both light-microscope and fluorescence images of the same area.
- Merge the light-microscope and fluorescence images using the appropriate software29. Add a scale bar.
7. Quantification of the Expression Level and Size of the Antigens
- Euthanize the fish in 0.04% tricaine. Dissect the fluorescent part of the dorsal muscle with a scalpel and tweezers under UV-light. Extract proteins from the samples8.
- Verify the correct size of in vivo-produced proteins with a western blot analysis, using a horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated GFP antibody (or similar)8. Include a negative control (unimmunized fish) to exclude any background signals and unspecific binding, together with a control expressing EGFP without a fused antigen.
NOTE: For the western blot analysis, the expected size (in kDa) of the antigen-fusion proteins can be calculated, for example, by the equation:
Molecular Weight (MW) of dsDNA = (number of nucleotides x 607.4) + 157.9; or by using web-based tools. - Quantify the expression of each antigen using a GFP-ELISA8 (optional).
8. Combining the Vaccination Protocol with an M. marinum Infection Model
- Determine the group size required for the reliable determination of the effectiveness of a novel vaccine candidate in the infection model and the assay used (see, for example, Myllymaki et al.24 and Charan and Kantharia30). Carry out the appropriate power calculations while planning the experiments.
- To evaluate the effectiveness of vaccine candidates, infect the fish 5 weeks postimmunization. Use an intraperitoneal infection with approximately 30 colony-forming units (cfu) of M. marinum, which leads to a latent infection in most fish8,20,31.
NOTE: When using M. marinum, follow a BSL2 safety protocol. The preparation of the bacterium or virus depends on the pathogen. - Quantify the number of pathogens in each fish. Euthanize the fish 4 weeks postinfection and determine the bacterial burden in each fish from the extracted DNA with qPCR using primers specific for M. marinum20,24.
NOTE: Be sure to include an appropriate control group and use the correct statistical methods for analyzing the results. Generally, a group of fish immunized with the empty pCMV-EGFP plasmid is a suitable negative control. - Confirm positive results with antigens without the GFP tag. Clone the antigens as described in step 1 and repeat the vaccination experiment.
Representative Results
The steps involved in the DNA vaccination protocol of adult zebrafish are illustrated in Figure 3. At first, the selected antigen sequences are cloned into a pCMV-EGFP plasmid and plasmid DNA is produced and purified24 (Figure 3).Vaccine candidates are then injected intramuscularly with a microinjector and the injection site is electroporated to improve the intake of the plasmid into cells (Figure 3). The used vaccination dose was optimized by injecting different amounts of the pCMV-EGFP plasmid and measuring the GFP expression with ELISA (Supplementary Figure 1). Two to seven days postvaccination, the expression of the fusion protein is detected under UV light and visualized with fluorescence microscopy (Figure 3 and Figure 4). The expression levels of different antigens may vary from very intensive (antigen 1) to a faint expression (Figure 4). In addition, GFP expression can be observed across the dorsal muscle (antigen 1), or in a more limited area (antigen 2) (Figure 4). However, if no fluorescence is detected within 10 days, it is recommended to make sure that there are no mistakes in antigen cloning or primer design. To confirm that the expressed fusion protein is of the correct size, proteins can be extracted from the muscle tissue around the injection site and used for a western blot analysis.
The effect of the vaccine candidates is evaluated by challenging the fish with a low dose of M. marinum by an intraperitoneal injection (Figure 5). Four to five weeks postinfection, the bacterial counts are determined with qPCR and compared to bacterial loads in the control group (Figure 5). Furthermore, the effectiveness of the most promising vaccine candidates can be tested by monitoring the survival after a high dose M. marinum infection(Figure 5). However, in addition to giving a quantitative result on the progression of the infection, instead of merely a status of alive or dead, the qPCR-based cfu quantification requires less time and smaller group sizes and is, therefore, a more ethical approach for a primary screen. Overall, this protocol facilitates the screening of the effectiveness of novel vaccine antigens within 12 weeks (Figure 5).
Figure 1: Close-up (12X) of aluminosilicate needles used in the adult zebrafish intra muscular injections. The tip below has been cut with tweezers and is ready to be used for microinjections. This figure has been adapted from Oksanen35. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.

Figure 2: Microinjection equipment and set-up. The main components of the equipment needed for the DNA vaccination of adult zebrafish are highlighted in bold. The critical adjustments are indicated. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
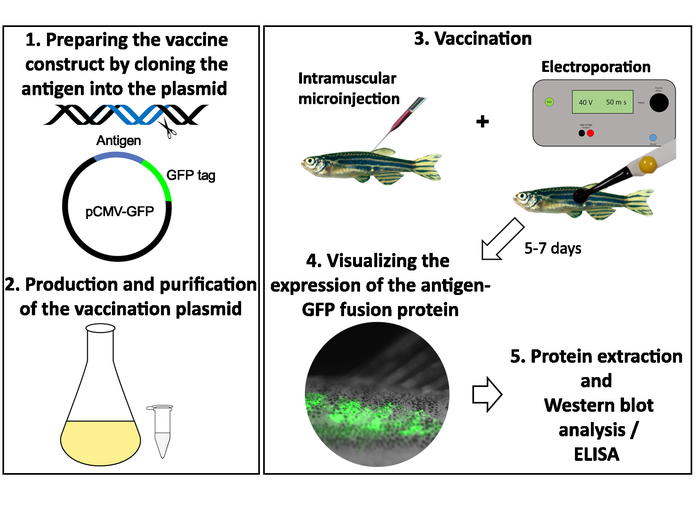
Figure 3: Preparing the DNA vaccine plasmids and the immunization procedure. (1) Selected antigens are cloned adjacent to the GFP tag in the pCMV-EGFP plasmid. (2) The vaccine construct is produced microbiologically, concentrated, and purified. (3) 12 µg of plasmid is injected into the dorsal muscle of an anesthetized adult zebrafish with a microinjector, and the injection site is subsequently electroporated with six 40-V, 50-ms pulses. (4) Two to seven days postvaccination, the GFP expression of the antigen-GFP fusion protein is visualized with a fluorescence microscope. (5) The fluorescent part of the dorsal muscle can be dissected and used for protein extraction. The size of the fusion protein is confirmed with a western blot analysis and the expression level with GFP-ELISA. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
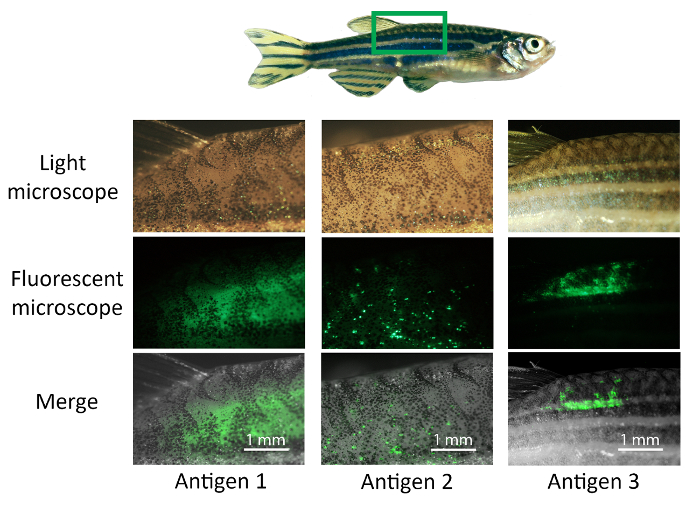
Figure 4: Visualizing the expression of the antigen-EGFP fusion protein. Anesthetized adult zebrafish are vaccinated with 12 µg of experimental vaccine antigens (antigen 1–3) and the injection site is electroporated, subsequently, with six 40 V, 50 ms pulses. Two to seven days postvaccination, the injection site is imaged with a microscope. First, the expression of GFP is detected under a fluorescence microscope. The area is inspected using a 2X magnitude objective and imaged and saved in .tiff form. The light microscope image of the same area is merged with the fluorescence image using the ImageJ software. The quantity and position of the antigen expression may vary between antigens and individual fish. For example, the expression of antigen 1 is observed across the dorsal muscle and the expression of antigen 2 is seen as small spots, whereas antigen 3 is strongly expressed in a more limited area. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
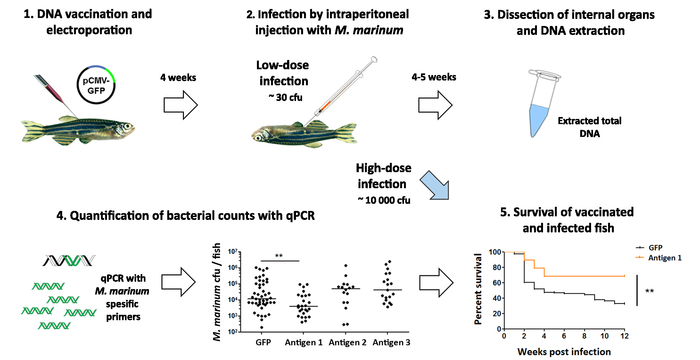
Figure 5: Testing the effectiveness of vaccine candidates against a mycobacterial infection. (1) Adult zebrafish are vaccinated with experimental DNA vaccines against mycobacteriosis. (2) Five weeks postvaccination, the fish are infected with a low dose of Mycobacterium marinum (~30 cfu). (3) Four weeks later, the internal organs are dissected and used for DNA extraction. (4) The bacterial count in each fish is quantified with qPCR using M. marinum-specific primers. Immunization with antigen 1 led to a significant decrease in the bacterial counts (p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA), while antigens 2 and 3 had no effect. (5) The protective effect of the most promising vaccine candidate (antigen 1) is further evaluated in a survival experiment, where fish are infected with a high dose (~10,000 cfu) of bacteria and their survival is monitored for 12 weeks. Consistent with the decrease in the bacterial burden observed in panel 4, vaccination with antigen 1 also improved the survival of the fish upon an M. marinum infection (p <0.01), suggesting this antigen could be a promising candidate for a novel vaccine against tuberculosis. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
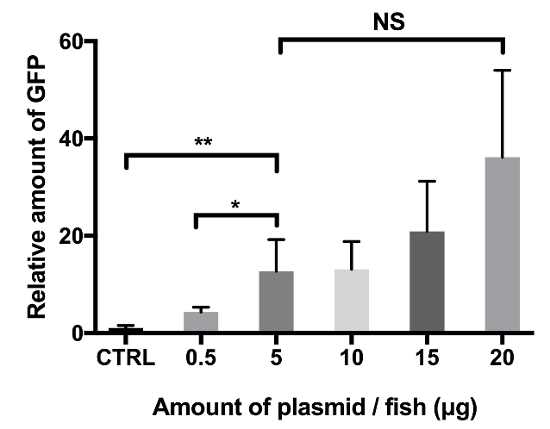
Supplementary Figure 1: Amount of plasmid DNA affects plasmid-derived EGFP expression in adult zebrafish. Groups of fish (n = 5 in each group) were injected with 0.5–20 μg of pCMV-EGFP, and electroporation (six pulses of 50 V) was used to enhance the transfection. Control fish (CTRL) were injected with 2 μg of the empty pCMV plasmid not containing the EGFP gene. GFP-ELISA was performed 3 days postinjection to define the relative EGFP expression in fish homogenates. P-values: *p <0.03, **p <0.004. The error-bars represent standard deviations. NS = not significant. This figure has been adapted from Oksanen35. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Discussion
The procedure of immunizing adult zebrafish with DNA-based vaccines requires some technical expertise. Even for an experienced researcher, vaccinating a single fish takes approximately 3 min, excluding preparations. Thus, a maximum of roughly 100 fish can be immunized within a day. If more than 100 fish are required for the experiment, the immunizations can be divided between up to 3 days. In addition to the quality of the experiment, sufficient training of the researcher(s) for handling the fish and performing the immunization is essential for the well-being of the fish. Make sure to follow local legal and animal welfare rules and guidelines when it comes to housing the fish, planning the experiments, and the qualifications required for the personnel carrying out the experiments.
In summary, there are several critical steps to avoid complications in the immunization protocol. For the successful immunization, ensure that 1) the fish to be immunized are healthy and sufficient in age and size (the immunization of more juvenile fish can require down-scaling the vaccine volume and the electroporation settings); 2) the fish are properly anesthetized with no stronger than 0.02% 3-aminobenzoic acid ethyl ester, and they remain anesthetized throughout the entire procedure (anesthesia should be kept as short as possible to ensure the recovery of the fish); 3) the sponge pad is properly soaked; 4) liquid is injected in each pulse from the pneumatic pump and, if not, the pulse length is adjusted (pulling the needle slightly backwards along the y-axis can help); 5) there are no air bubbles with the vaccine solution; 6) the electroporation settings and the actual pulse voltage and length are correct; 7) the electrodes do not cause skin damage on the electroporation site (during the electroporation, keep the electrodes in gentle contact with the fish, and release the fish immediately into the recovery tank after electroporation).
It is important to monitor the fish after the electroporation in the recovery tank and to euthanize any fish showing signs of discomfort. Furthermore, it is necessary to practice the procedure before starting a large-scale experiment, to ensure a fluent workflow. If possible, ask a sufficiently trained colleague for assistance with filling the needles and the electroporation.
The DNA vaccination method enables the tailor-made design of vaccine antigens. It is possible to clone the whole antigen or, preferably, select parts of the antigen based on cellular localization and immunogenicity24. In addition, the method enables combining several antigens or adjuvants into one vaccine construct or injecting several separate plasmids at the same time2. By including a stop codon after the antigen sequence or by excising the EGFP gene from the plasmid, it is possible to utilize the same plasmid vector also to express the antigen without the subsequent N-terminal GFP tag. This may be reasonable in confirming the positive screening results, as the relatively large size of GFP can affect the folding of the antigen and, thus, restrict humoral responses potentially evoked by the vaccination.
A higher antigen expression has been linked to DNA vaccine immunogenicity2. Electroporation after injection has, thus, been included in this protocol, as it has been shown to increase the expression of antigens or reporter genes from fourfold to tenfold in zebrafish32. Furthermore, electroporation as a technique causes moderate tissue injury, thus inducing local inflammation that further promotes the vaccine-induced immune responses2. On the other hand, electroporation is generally well-tolerated. With the equipment used here, practically 100% of adult zebrafish will recover well from the six pulses of 40 V used in this protocol35.
In addition to using electroporation to enhance the entry of the vaccine plasmid into the cells, we use a strong ubiquitous promoter in the vaccine plasmid and a polyA tail at the 3' end of the antigen to improve antigen expression in the transfected fish cells. In some cases, if the codon usage of the target pathogen significantly differs from the vaccinated species, codon optimization has been found useful in further increasing target gene expression2. In this zebrafish-M. marinum model, however, codon optimization had no significant effect on the expression levels of two mycobacterial model genes, ESAT-6 and CFP-10, and has, thus, been deemed unnecessary in this model35.
Target gene expression profiles have some temporal variation between the antigens, depending, for instance, on the size and the structure of the antigens in question. However, antigen expression is usually similar within a group of fish immunized with the same vaccine. Typically, the brightest EGFP expression is observed four days to one-week postvaccination, but a scale of 2–10 days is possible. It is recommended to validate the expression of each antigen-EGFP fusion protein in a small group of fish (2–3) before including the antigen in a large-scale experiment. If no GFP expression is observed at any point 2–10 days after immunization, make sure that 1) the immunization protocol was carefully followed. Always have a group of fish immunized with the empty pCMV-EGFP plasmid as a positive control and make sure that 2) the antigen design and molecular cloning was carried out correctly (adequate primer design; the antigen and the EGFP tag are both in the same reading frame and no intervening stop codons are included). In some cases, despite the correct antigen design, GFP cannot be detected. This may be due to the incorrect folding or rapid breakdown of the fusion protein. In these circumstances, it may be necessary to redesign the antigen.
In vaccines that are used to immunize farmed fish, the plasmid dose used is typically 1 µg or less7,33,34. In zebrafish, reporter gene expression can also be detected after at least a 0.5 µg plasmid injection following electroporation; however, the relative target gene expression significantly increases with a higher amount of plasmid per fish (Supplementary Figure 1). In fish injected with the pCMV-EGFP reporter plasmid, an injection with 5–20 µg of plasmid resulted in four to eight times higher EGFP levels in comparison with fish injected with 0.5 µg. Therefore, to ensure a high enough target gene expression, yet have injection volumes that are small enough (≤7 µL) to prevent any excess tissue damage or vaccine leakage, we chose to use 5 to 12 µg per fish for the preliminary screening purposes. In addition to vaccine immunogenicity, a high enough target gene expression is required to detect reporter gene expression with a fluorescence microscope and with western blot, which is necessary for screening purposes to confirm the correct in vivo translation of the target antigen. However, lower plasmid doses (0.5–1 µg) can be useful for other types of experimental uses.
In conclusion, this protocol for the immunization of adult zebrafish with a DNA plasmid can be used in the preclinical testing of novel vaccine candidates against various bacterial or viral infections. The expression of the vaccine antigen as a GFP-fusion protein allows the visualization of a successful immunization event and antigen expression. We apply this method for the preclinical screening of novel vaccine antigen candidates against tuberculosis. For this, we infect the zebrafish five weeks postvaccination and determine the bacterial counts in each fish with qPCR20,24.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the members of the Experimental immunology research group, and especially to Leena Mäkinen and Hannaleena Piippo, for all the work they have done in developing and optimizing the vaccination protocol, and their help in actual experiments using the protocol.
This work was supported by Jane ja Aatos Erkon Säätiö (Jane and Aatos Erkko Foundation; to M.R.), Sigrid Juséliuksen Säätiö (Sigrid Juselius Foundation; to M.R.), the Competitive State Research Financing of the Expert Responsibility area of Tampere University Hospital (to M.R.), Tampereen Tuberkuloosisäätiö (Tampere Tuberculosis Foundation; to M.R., H.M., and M.N.), Suomen Kulttuurirahasto (Finnish Cultural Foundation; to H.M.), Suomen Tuberkuloosin Vastustamisyhdistyksen Säätiö (Finnish Anti-Tuberculosis Foundation; to H.M.), Väinö ja Laina Kiven säätiö (Väinö and Laina Kivi Foundation; to M.N.) and the Tampere City Science Foundation (to M.N.).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| pCMV-GFP plasmid | Addgene | #11153 | |
| 2-propanol | Sigma-Aldrich | 278475-2L | DNA extraction |
| Ampicillin sodium salt | Sigma-Aldrich | A0166-5G | |
| Chloroform | Merck | 1.02445.2500 | DNA extraction |
| ECM Electro Square Porator | BTX Harvard apparatus | BTX ECM 830 | |
| FastPrep-24 5G | MP Biomedicals | 116005500 | homogenizer |
| Flaming/brown micropipette puller | Sutter Instrument Co. | P-97 | Pulling of needles |
| GeneJet PCR Purification kit | ThermoFischer Scientific | K0701 | |
| GFP ELISA kit | Cell Biolabs, Inc. | AKR-121 | |
| Guanidine thiocyanate (FW 118.2) | Sigma-Aldrich | G9277-500G | DNA extraction |
| ImageJ2 | imagej.net/Downloads | freely available software | |
| LB Agar | Sigma | L2897-1kg | |
| LB Broth (Miller) | Sigma | L3522-1kg | |
| Micromanipulator | Narishige | MA-153 | |
| Microscope | Nikon | AZ100 | fluorescense microscope |
| Microscope | Olympus | ZS61 | |
| Nightsea Full adapter system w/Royal Blue Color light head | Electron Microscopy Sciences | SFA-RB | |
| PBS tablets | VWR Chemicals | E404-200TABL. | |
| Phenol red sodium salt | Sigma-Aldrich | 114537-5G | |
| PV830 Phneumatic Pico Pump | WPI | SYS-PV830 | |
| QIAGEN Plasmid Maxi kit | Qiagen | ID:12163 | plasmid extraction |
| Sodium citrate (FW294.1) | VWR Chemicals | 27833.294 | DNA extraction |
| Tri Reagent | Molecular Research Center, Inc. | TR 118 | DNA extraction |
| Tricaine (ethyl 3-aminobenzoate methanesulfonate salt) | Sigma | A5040-100g | anestesia and euthanasia solution |
| Tris (free base) (FW121.14) | VWR Life Science | 0497-500G | DNA extraction |
| Tweezertrodes Electrodes (7mm) Kits | BTX Harvard apparatus | BTX 450165 | tweezer type electrodes |
| 2.8 mmCeramic beads | Omni International | 19-646-3 | DNA extraction |
| 2ml Tough tubes with caps | Omni International | 19-649 | DNA extraction |
| Aluminosilicate capillaries | Harvard apparatus | 30-0108 | |
| Microloader 20 µl | eppendorf | 5242956.003 | loading tips |
| Petri dishes, 16 mm | Sarsted | 82.1473 | |
| Scalpels | Swan Morton | 0501 | |
| Parafilm | Bemis | laboratory film | |
| Pins | |||
| Plastic spoon | |||
| Spatula | |||
| Sponge | |||
| Styrofoam workbench | |||
| Tweezers |
References
- Tang, D. C., DeVit, M., Johnston, S. A. Genetic immunization is a simple method for eliciting an immune response. Nature. 356 (6365), 152-154 (1992).
- Tregoning, J. S., Kinnear, E. Using Plasmids as DNA Vaccines for Infectious Diseases. Microbiology Spectrum. 2 (6), (2014).
- Evensen, O., Leong, J. A. DNA vaccines against viral diseases of farmed fish. Fish Shellfish Immunology. 35 (6), 1751-1758 (2013).
- Sommerset, I., Lorenzen, E., Lorenzen, N., Bleie, H., Nerland, A. H. A DNA vaccine directed against a rainbow trout rhabdovirus induces early protection against a nodavirus challenge in turbot. Vaccine. 21 (32), 4661-4667 (2003).
- Li, L., Petrovsky, N. Molecular mechanisms for enhanced DNA vaccine immunogenicity. Expert Review of Vaccines. 15 (3), 313-329 (2016).
- Embregts, C. W. E., et al. Intramuscular DNA Vaccination of Juvenile Carp against Spring Viremia of Carp Virus Induces Full Protection and Establishes a Virus-Specific B and T Cell Response. Frontiers in Immunology. 8, 1340 (2017).
- Lorenzen, N., LaPatra, S. E. DNA vaccines for aquacultured fish. Revue scientifique et technique (International Office of Epizootics). 24 (1), 201-213 (2005).
- Oksanen, K. E., et al. An adult zebrafish model for preclinical tuberculosis vaccine development. Vaccine. 31 (45), 5202-5209 (2013).
- Matsuda, T., Cepko, C. L. Electroporation and RNA interference in the rodent retina in vivo and in vitro. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 101 (1), (2004).
- Cho, J. H., Youn, J. W., Sung, Y. C. Cross-priming as a predominant mechanism for inducing CD8(+) T cell responses in gene gun DNA immunization. The Journal of Immunology. 167 (10), 5549-5557 (2001).
- Lewis, K. L., Del Cid, N., Traver, D. Perspectives on antigen presenting cells in zebrafish. Developmental & Comparative Immunology. 46 (1), 63-73 (2014).
- Shao, T., et al. Characterization of surface phenotypic molecules of teleost dendritic cells. Developmental & Comparative Immunology. 49 (1), 38-43 (2015).
- Utke, K., et al. Cell-mediated immune responses in rainbow trout after DNA immunization against the viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus. Developmental & Comparative Immunology. 32 (3), 239-252 (2008).
- Cuesta, A., et al. An active DNA vaccine against infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV) with a different mode of action than fish rhabdovirus DNA vaccines. Vaccine. 28 (19), 3291-3300 (2010).
- Castro, R., et al. DNA vaccination against a fish rhabdovirus promotes an early chemokine-related recruitment of B cells to the muscle. Vaccine. 32 (10), (2014).
- Iwanami, N. Zebrafish as a model for understanding the evolution of the vertebrate immune system and human primary immunodeficiency. Experimental Hematology. 42 (8), 697-706 (2014).
- Patterson, H., et al. Adult zebrafish model of bacterial meningitis in Streptococcus agalactiae infection. Developmental & Comparative Immunology. 38 (3), 447-455 (2012).
- Cronan, M. R., Tobin, D. M. Fit for consumption: zebrafish as a model for tuberculosis. Disease Model & Mechanisms. 7 (7), 777-784 (2014).
- Tobin, D. M., Ramakrishnan, L. Comparative pathogenesis of Mycobacterium marinum and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cellular Microbiology. 10 (5), 1027-1039 (2008).
- Parikka, M., et al. Mycobacterium marinum causes a latent infection that can be reactivated by gamma irradiation in adult zebrafish. PLoS Pathogens. 8 (9), e1002944 (2012).
- Rounioja, S., et al. Defense of zebrafish embryos against Streptococcus pneumoniae infection is dependent on the phagocytic activity of leukocytes. Developmental & Comparative Immunology. 36 (2), 342-348 (2012).
- Myllymaki, H., Bauerlein, C. A., Ramet, M. The Zebrafish Breathes New Life into the Study of Tuberculosis. Frontiers in Immunology. 7, 196 (2016).
- Myllymaki, H., Niskanen, M., Oksanen, K. E., Ramet, M. Animal models in tuberculosis research - where is the beef?. Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery. 10 (8), 871-883 (2015).
- Myllymaki, H., et al. Identification of novel antigen candidates for a tuberculosis vaccine in the adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). PLoS One. 12 (7), e0181942 (2017).
- Myllymaki, H., Niskanen, M., Luukinen, H., Parikka, M., Ramet, M. Identification of protective postexposure mycobacterial vaccine antigens using an immunosuppression-based reactivation model in the zebrafish. Disease Model & Mechanisms. 11 (3), (2018).
- Ingolotti, M., Kawalekar, O., Shedlock, D. J., Muthumani, K., Weiner, D. B. DNA vaccines for targeting bacterial infections. Expert Review of Vaccines. 9 (7), 747-763 (2010).
- Kozak, M. Recognition of AUG and alternative initiator codons is augmented by G in position +4 but is not generally affected by the nucleotides in positions +5 and +6. The EMBO Journal. 16 (9), 2482-2492 (1997).
- Matthews, M., Varga, Z. M. Anesthesia and euthanasia in zebrafish. ILAR Journal. 53 (2), 192-204 (2012).
- Schneider, C. A., Rasband, W. S., Eliceiri, K. W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nature Methods. 9 (7), 671-675 (2012).
- Charan, J., Kantharia, N. D. How to calculate sample size in animal studies?. Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics. 4 (4), 303-306 (2013).
- Hammaren, M. M., et al. Adequate Th2-type response associates with restricted bacterial growth in latent mycobacterial infection of zebrafish. PLoS Pathogens. 10 (6), e1004190 (2014).
- Rao, N. M., Rambabu, K. M., Rao, S. H. Electroporation of adult zebrafish. Methods in Molecular Biology. 423, 289-298 (2008).
- McCaffrey, J., Donnelly, R. F., McCarthy, H. O. Microneedles: an innovative platform for gene delivery. Drug Delivery and Translational Research. 5 (4), 424-437 (2015).
- Lorenzen, E., Lorenzen, N., Einer-Jensen, K., Brudeseth, B., Evensen, O. Time course study of in situ expression of antigens following DNA-vaccination against VHS in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum) fry. Fish and Shellfish Immunology. 19 (1), 27-41 (2005).
- Oksanen, K. Adult Zebrafish Model for Studying DNA-based Vaccination against Mycobacterial Disease. Tampereen yliopisto. , (2011).
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved