A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
A Continuous-flow Photocatalytic Reactor for the Precisely Controlled Deposition of Metallic Nanoparticles
In This Article
Summary
For a continuous and scalable synthesis of noble-metal-based nanocomposites, a novel photocatalytic reactor is developed and its structure, operation principles, and product quality optimization strategies are described.
Abstract
In this work, a novel photocatalytic reactor for the pulsed and controlled excitation of the photocatalyst and the precise deposition of metallic nanoparticles is developed. Guidelines for the replication of the reactor and its operation are provided in detail. Three different composite systems (Pt/graphene, Pt/TiO2, and Au/TiO2) with monodisperse and uniformly distributed particles are produced by this reactor, and the photodeposition mechanism, as well as the synthesis optimization strategy, are discussed. The synthesis methods and their technical aspects are described comprehensively. The role of the ultraviolet (UV) dose (in each excitation pulse) on the photodeposition process is investigated and the optimum values for each composite system are provided.
Introduction
Metallic nanoparticles, especially noble metals (e.g., Pt, Au, Pd) have vast applications in catalysis1. In general, decreasing the size of the nanoparticles (NPs) increases their catalytic activity while maintaining the cost (weight) constant, but it also makes their application more difficult. NPs (usually smaller than 10 nm) have great tendencies to aggregation, which degrades their catalytic activity; however, immobilization on suitable substrates can mostly resolve this problem. Furthermore, depending on the application type (e.g., electrocatalysis), it is sometimes necessary to immobilize the NPs on conductive substrates2,3. NPs can also be hybridized with semiconductors to form a Schottky barrier and avoid (delay) the electron-hole recombination (acting as electron traps)4,5. Hence, in most of the applications, the noble metal NPs (NNPs) are deposited either on a conductive (e.g., graphene) or a semiconductive (e.g., TiO2) substrate. In both cases, metal cations are usually reduced in the presence of the substrate, and the reduction technique differs from one method to another.
For the deposition of NNPs via a reduction of their cations, electrons (with proper electrical potential) should be provided. That can be done in two ways: by oxidation of other chemical species (a reducing agent)6,7 or from an external power source8. In any case, for the homogeneous deposition of monodispersed NPs, it is necessary to impose a strict control on the generation and transfer of the (reducing) electrons. This is very difficult when a reducing agent is used since there is virtually no control over the reduction process once the reactants (cations and reducing agent) are mixed. Furthermore, NPs can form anywhere and not necessarily on the target substrate. When using an external power source, the control over the number of the provided electrons is much better, but NPs can only be deposited on an electrode surface.
Photocatalytic deposition (PD) is an alternative approach, which offers more control over the number of the (photo)generated electrons since it is directly related to the dose of the illuminated photons (with a proper wavelength). In this method, the substrate material has a dual role; it provides the reducing electrons9 and stabilizes the formed NPs10. Moreover, NPs form only on the substrate since the electrons are generated by the substrate. A proper electrical connection between composite components (made by the photocatalytic reduction method) is also guaranteed11. Nevertheless, in conventional photocatalytic deposition methods in which the whole batch of reactants (photocatalyst and metal cation) is illuminated simultaneously, there is no control over the nucleation of the NNPs. Indeed, once a few particles (nuclei) are formed, they act as preferred transfer sites for the photogenerated electrons5 and act as a preferred growth site. This superior electron transfer promotes the growth of the existing particles and disfavors the formation of new nuclei, which results in the formation of large NNPs. This problem can be addressed by the pulsed illumination of UV light in a special continuous-flow reactor (Figure 1) that has recently been developed by our group12. The unique feature of this reactor is that it allows researchers to control both NP-size-determining factors, namely, nucleation and growth. In this reactor, a very small portion of reactants is illuminated for a very short period of time, promoting the formation of nuclei (more nuclei are formed) and restricting the growth (smaller particles are attained). In this method, by controlling the illumination dose (i.e., by adjusting the exposure duration [changing the length of uncovered parts of the reaction tube; Figure 1C] or intensity of the incident light [number of the lamps]), a very precise control over the number of photogenerated electrons and, consequently, on the reduction process (NNP deposition) can be exerted.
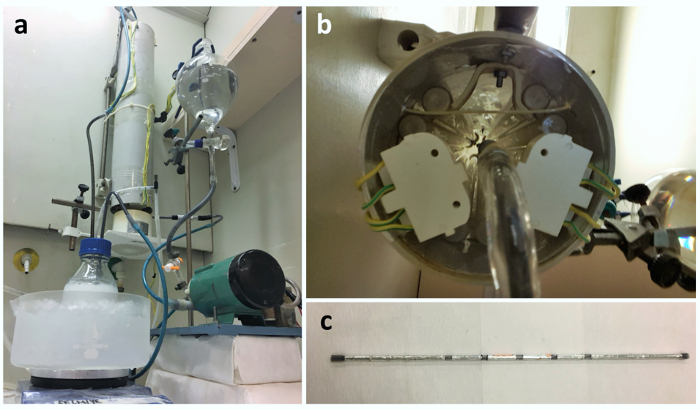
Figure 1: The fabricated photocatalytic deposition reactor. (A) The reactor. (B) Inside the illumination chamber. (C) A quartz tube with 5 cm x 1 cm illumination exposure length. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Despite the great potential of the PD method for the controlled deposition of NNPs, its application is limited to semiconducting materials. Fortunately, it is possible to open a wide band gap in graphene (one of the best-conducting substrates13) by its simple chemical functionalization. Afterward, these functional groups (FGs) can be mostly removed and the resulting graphene will still be conductive enough for most of the applications. Among numerous functionalized derivatives of graphene, graphene oxide (GO), which exhibits considerable semiconducting properties14, is the most promising candidate for this purpose. This is mainly due to the fact that GO's production has the highest production yield among the others. Nevertheless, since GO consists of different types of FGs, its chemical composition varies continuously under UV illumination. We have recently shown that by a selective removal of weakly bonded FGs (partial reduction; PRGO), the chemical structure and electronic properties of GO can be stabilized, which is an essential requirement for homogeneous depositions of the NNPs12. In this report, we describe the structure of the reactor and provide detailed information for its replication and operation. The deposition mechanism (working mechanism of the reactor) and possible optimization strategies are also discussed in great detail. To validate the applicability of the developed PD reactor for both types of common substrates (conductor and semiconductor) and different NNPs, the deposition of platinum on PRGO and TiO2, as well as of gold on TiO2, is demonstrated. It is noteworthy that by a proper selection of the metal, photocatalyst and precursor materials (e.g., salt, hole scavenger), and the dispersion media, several other metallic particles (such as Ag and Pd15) can also be deposited. In principle-since, in the photodeposition of NNPs, the cations of the metal are reduced by the photoexcited electrons-the energy level of the semiconductor's conduction band minimum (CBM) should match with (be more negative than) the reduction potential of the aimed cations. Due to the extensive technical production aspects, the synthesis of PRGO is also described in detail. For further information regarding the chemical structure and electronic properties of PRGO, please refer to previous work12.
The detailed structure of the reactor is schematically depicted in Figure 2. The reactor has two main components: a UV illumination and a reservoir compartment. The illumination section consists of a quartz tube, which is exactly fixed along the central axis of a cylindrical tube with a polished aluminum liner. The reservoir consists of a 1 L sealed-cap glass bottle with gas and liquid (reactants) inlets and outlets. Use a silicon septum with an open-top screw cap for inserting the tubes. To take samples during the reaction without letting oxygen enter the reactor, an outlet with a valve is also installed. It should be mentioned here that the samplings on specific time intervals are not a part of the nanocomposite production process, and sampling only needs to be done once to obtain the concentration-time curves for each set of synthesis parameters (the application of these curves will be discussed in the Discussion section). The reservoir is placed inside an ice-water bath while being vigorously mixed on a magnetic stirrer. A magnetic pump circulates the reactant from the reservoir to the reaction chamber (illumination section) and back to the reservoir. A magnetic one is used since high flow rates are necessary (the flow rate in this work = 16 L·min-1) and peristaltic pumps (or other similar pumps) can hardly provide those flows. When using a magnetic pump, care should be taken to completely fill the impeller casing (pump housing) with the reactant liquid and evacuate any trapped air (oxygen source). The trapped air can also decrease the pump's real flow rate.
For a pulsed excitation of the photocatalyst material, specific lengths of the quartz tube are covered by a thick aluminum foil, leaving equal lengths between them uncovered (Figure 2). The duration of the pulsed excitation can be adjusted by changing the length of the uncovered parts (exposure length). The optimum exposure length is determined by various parameters, such as the quantum yield of the photocatalyst and the intended NP loading (concentration of the precursors; see Discussion).
Protocol
1. Fabrication and operation of the photocatalytic deposition reactor
CAUTION: When UV lamps are turned on, use UV-C protective glasses.
- Fabrication of the photocatalytic deposition reactor
- Cover the inner surface of a polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipe (diameter x length = 15 cm x 55 cm; other materials can also be used) with a thick, polished, and adhesive-backed aluminum foil. Install five 55 W UV-C lamps (see Table of Materials) on the inner surface of the tube at equal distance.
- Fix a quartz tube (diameter x length = 0.5 cm x 55 cm) along the central axis of the PVC tube (concentric configuration). For the pulsed excitation of the photocatalyst, cover the desired equal lengths of the quartz tube with the same adhesive-backed aluminum foil (in this work, for the Pt/graphene composites: 5 cm x 0.4 cm, 5 cm x 2 cm, and 1 cm x 50 cm, and for the Pt/TiO2 and Au/TiO2 composites: 5 cm x 1 cm). Note that 2.5 cm of the quartz tube on each side is used for connecting the plastic tubes.
- Install a heavy-duty fan at one end of the PVC tube (to cool down the whole illumination chamber).
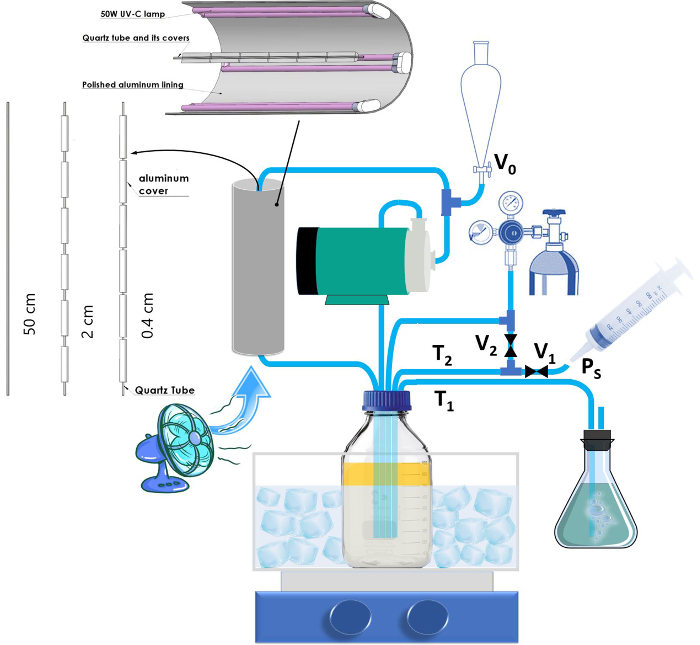
Figure 2: Schematic illustration of the photocatalytic deposition reactor. T1 is the N2 gas outlet that goes into the bubbler. T2 is the sampling tube and Ps is the point for attachment of the syringe (for sampling). V0 is the initial feeding valve and V1 and V2 are the sampling and tube evacuation valves (after sampling), respectively. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Feeding the reactants to the reactor
- Use a setup like the one shown in Figure 2. Place a separation funnel in a higher vertical position than the pump and the reservoir (the pump should also be in a higher vertical position than the bottom of the reservoir) and fill the reactants into the separation funnel.
- Open the valve V0 to feed the reactant to the reactor and close the valve (V0) immediately when the funnel is depleted (otherwise, air will also enter the pump).
NOTE: The flow rate of the magnetic pumps is affected by the gravitational forces exerted on the liquid, meaning that any alteration in the position of the reactor parts (vertical displacements) will change the flow rate (thus, do not displace the reactor parts once they are set up).
2. Synthesis of partially reduced GO
CAUTION: All the following experiments should be carried out inside a fume hood.
- Synthesis of GO
- Add 100 mL of 98% sulfuric acid and 2 g of graphite to a 500 mL Erlenmeyer flask. Cool down the flask to ~0 °C in an ice-water bath while mixing its contents on a magnetic stirrer.
NOTE: Use a big magnetic stir bar, since the suspension will become very viscous at the end of the reaction. - Gradually add 6 g of potassium permanganate (over a period of 30 min) as it is a very exothermic reaction. Remove the ice-water bath and continue stirring for 6 h.
- Put the flask inside an ice-water bath and continue stirring for 15 min. Add 250 mL of distilled water dropwise, using a separation funnel. Remove the ice-water bath, gradually add 30 mL of hydrogen peroxide, and keep stirring for 30 min.
- Centrifuge the suspension at 3,500 x g for 15 min and discard the supernatant. Wash the precipitates with distilled water. Repeat this process (wash-centrifuge) till pH reaches 5.
NOTE: Higher rotational speeds (if available) would be better but lower speeds should be compensated with longer centrifugation times. Also note that when the pH value rises to above 3-4, even long-time centrifugation (and also higher rotational speeds) cannot precipitate all the particles16 and a considerable part of the suspension will be lost (roughly 1 g will remain at the end). The reaction can be paused here (store the reactants in an amber bottle, or wrap a normal bottle with aluminum foil). - Add the product of the previous step to 0.5 L of 1 M hydrochloric acid and stir it for 1 h. Wash the product as described in step 2.1.3 until the pH reaches 5. Add the product to 1 L of distilled water and sonicate it in a bath-sonicator for 3 h (add ice to the bath during the sonication to avoid a temperature rise).
- Centrifuge the product for 3x 20 min at 3,500 x g and, each time, discard the precipitates. Store the obtained GO suspension in a capped glass bottle (use an amber bottle, or wrap a normal bottle with aluminum foil).
NOTE: If necessary, the centrifuge times can be broken down to shorter intervals (with cooling periods in between) to avoid temperature rises (higher than room temperature [RT]) of the suspension since, otherwise, the unwanted precipitates will not settle down. - Weigh three dry crystallizing dishes (of a volume of 100-200 mL) with an analytical grade balance (0.01 mg readability), each of them 3x. Shake the GO suspension well and, after 1 min, add exactly (with the highest possible accuracy) 100 mL of it to each of the crystallizing dishes. Leave the dishes in a 70-80 °C oven to dry completely.
- By means of the final dry weight (weigh each dish 3x on the same analytical balance) and empty dish weight, determine the solid content of the GO suspension by averaging the values obtained from the three dishes. Adjust the concentration to 0.2 g/L by adding the required amount of distilled water.
NOTE: To check if the drying is complete or not, check the weight changes during two consecutive days. The weighing should be done immediately after taking the dishes out of the oven (before the temperature falls below 50 °C) since, otherwise, considerable weight increase will be observed. Although this process is time-consuming, since the solid content is not high, it is more accurate than other solid-content-determination methods.
- Add 100 mL of 98% sulfuric acid and 2 g of graphite to a 500 mL Erlenmeyer flask. Cool down the flask to ~0 °C in an ice-water bath while mixing its contents on a magnetic stirrer.
- Partial reduction of GO (synthesis of PRGO)
- Gradually add the diluted GO suspension (the product of step 2.1.5) to an equal volume of a 4 M sodium hydroxide solution in a round-bottom flask. Attach a condenser to the flask and reflux-stir the suspension at 90 °C for 8 h (with a heater mantle).
- After cooling down, "wash-centrifuge" the precipitates with distilled water (as described in step 2.1.4) to near neutral pH (~7-8).
NOTE: Since PRGO has much less hydrophilicity than GO, all the precipitates should settle down during the centrifugation and the supernatant should be a completely clear solution. If this is not the case for any reason (e.g., not sufficient rotational speed), the solid content measurement (see step 2.1.8) should be conducted at this stage too.
3. Photocatalytic deposition of NNPs
- Synthesis of Pt/graphene composite
- Adjust the concentration of the product from section 2.2 to 50 mg·L-1 and sonicate the suspension with a probe sonicator for 1 h in an ice-water bath. Take 540 mL of the product and add 60 mL of ethanol (hole scavenger) and continue the sonication (in ice) for an extra 1 h. For a 20 wt% Pt/graphene composite, add 169 microliters of 8 wt% hexachloroplatinic acid aqueous solution (commercially available) to the product and stir it at room temperature for 15 min (for other Pt loadings, calculate the amount accordingly).
NOTE: It is advised to use aqueous solutions of the noble metal salts (if commercially available) or initially prepare a highly concentrated stock solution from the powder-form salts. These salts are hygroscopic materials and, due to their extensive water absorption, precise weighing and obtaining reproducible results will be difficult or even impossible. - Fill the ice-water bath with ice and feed the product of the previous step to the reactor, as described in section 1.2. Start the magnetic pump and open the N2 gas inlet valve with a high flow. Put and fix the gas outlet tube (T1 in Figure 2) in a 1 L Erlenmeyer flask and fill it with ~0.7 L of water so that the gas bubbles out.
- To flush out the dissolved O2 gas from the system and cool down the suspension, vigorously mix the suspension with the magnetic stirrer for 30 min. Reduce the N2 gas flow and turn on the five UV lamps.
NOTE: The N2 gas flow has no effect on the synthesis process itself and, hence, has no specific value. However, it is continuously applied to maintain a positive pressure inside the system and avoid O2 penetration. Bubble formation at the endpoint of the T1 tube inside the water-filled Erlenmeyer flask is the only requirement for the flow adjustment.
- Adjust the concentration of the product from section 2.2 to 50 mg·L-1 and sonicate the suspension with a probe sonicator for 1 h in an ice-water bath. Take 540 mL of the product and add 60 mL of ethanol (hole scavenger) and continue the sonication (in ice) for an extra 1 h. For a 20 wt% Pt/graphene composite, add 169 microliters of 8 wt% hexachloroplatinic acid aqueous solution (commercially available) to the product and stir it at room temperature for 15 min (for other Pt loadings, calculate the amount accordingly).
- Sampling Pt/graphene deposition (and reduction of PRGO to RGO)
CAUTION: Although wearing goggles in a chemistry lab is always mandatory, it is worth it to be reminded again, since in this experiment, there is a high risk of splashing.- Increase the N2 gas flow 5 min after turning on the UV lights. Attach a syringe to point PS (Figure 2). While holding the syringe piston to prevent it from coming out, open the valve V1, fill the syringe with 20 mL of the suspension, and close the valve (V1). Detach the syringe and open the valve V2 to evacuate the remaining suspension inside the tube T2, and close it (V2) afterward. Reduce the N2 gas flow to the previous level.
- Centrifuge the product of the previous step at 10,000 x g for 10 min. Store the supernatant for inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) analysis. Wash the precipitates with distilled water and centrifuge it at 10,000 x g for 10 min (discard the supernatant this time). Repeat the washing process 1x more.
- Disperse the product of the previous step in 50 mL of distilled water by gentle sonication in a bath sonicator for 1 h. Dissolve 30 mg of ascorbic acid and heat-stir it at 90 °C for 1 h. Centrifuge the product at 10,000 x g for 10 min, take the precipitates, and discard the supernatant.
- Repeat the washing process 2x more and store the precipitates for characterization purposes.
- Repeat steps 3.2.1 and 3.2.2 for sampling times of 10, 15, 20, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90, 105, and 120 min (after turning on the UV lights).
- Synthesis of Pt/TiO2 composite
- Add 200 mg of TiO2 nanoparticles (commercially available, ~100-150 nm in particle size) to 570 mL of distilled water and 30 mL of ethanol and sonicate it with a probe sonicator in an ice-water bath for 1 h.
- For a 5 wt.% Pt/TiO2 composite, add 21 mg of 8 wt.% hexachloroplatinic acid aqueous solution to the prepared suspension and stir it at room temperature for 15 min (for other Pt loadings, calculate the amount accordingly). Repeat step 3.1.2 for the prepared mixture, with four and two UV lamps.
- Sampling Pt/TiO 2 deposition
- Repeat section 3.2 for the products of section 3.3 at time intervals of 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, 20, and 40 min.
- Synthesis of Au/TiO 2 composite
- For a 5 wt.% Au/TiO2 composite, add 345 µL of a 50 g·L-1 hydrogen tetrachloroaurate(III) aqueous solution to the product of step 3.3.1 and stir it at room temperature for 15 min (for other Au loadings or other Au sources, calculate the amount accordingly). Repeat step 3.1.2 for the prepared mixture, with four and two UV lamps.
NOTE: Since the gold salt used here was in powder form, we initially prepared a 50 g·L-1 hydrogen tetrachloroaurate(III) solution in distilled water.
- For a 5 wt.% Au/TiO2 composite, add 345 µL of a 50 g·L-1 hydrogen tetrachloroaurate(III) aqueous solution to the product of step 3.3.1 and stir it at room temperature for 15 min (for other Au loadings or other Au sources, calculate the amount accordingly). Repeat step 3.1.2 for the prepared mixture, with four and two UV lamps.
- Sampling Au/TiO 2 deposition
- Repeat section 3.2 for the products of section 3.5 at time intervals of 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, 20, and 40 min.
4. Sample preparation for characterizations
- For ICP-OES analysis of supernatants, simply filter the liquids with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) syringe filters with a 0.2 µm pore size. For more information on ICP-OES of the solid samples, refer to Ma and Wei17.
NOTE: When the samples are in solution form, ICP-OES is a very simple and fast technique, but for solid samples, especially for noble metals, it requires multiple microwave digestion processes with aqua regia, hydrogen peroxide, and hydrochloric acid, which makes it very time-consuming (at least 12 h for each sample preparation). Hence, for monitoring the photodeposition rate and process optimization, concentration changes of the metallic cations in the supernatant can be monitored. - For transmission electron microscopy (TEM) imaging, disperse collected precipitates in distilled water (a very dilute suspension) and drop-cast them on TEM grids (or dip-coat the grid into the suspension). For X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis, simply drop-cast concentrated dispersions of the precipitates on oxygen-plasma-treated glass substrates and dry them on a hot plate.
Results
XPS is one of the most powerful techniques for confirming the formation of metallic NPs and study their chemical states. For this purpose, both survey spectra and high-resolution spectra (of Pt4f and Au4f) were recorded, which confirms the complete reduction of the metallic cations and successful deposition of the NNPs (Figure 3). For the deconvolution of both Pt4f and Au4f, initially, a Shirley background subtracti...
Discussion
Nanoparticles are the most widely used form of noble-metal-based catalysts. In almost all cases, NNPs are deposited either on a conductive or a semiconductive support material. This hybridization is mostly done by the reduction of the cations of the noble metal in the presence of the intended substrate (material). Hence, a successful synthesis method for the production of NNP-based nanocomposite should meet at least two main requirements: 1) the reduction of the cations should be efficient and complete; 2) the deposition...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Sabanci University and Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology (Empa) for all the support provided.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Chloroplatinic acid solution | Sigma Aldrich | 262587-50ML | |
| Hydrogen tetrachloroaurate(III) hydrate | Alfa Aesar | 12325.03 | |
| TiO2 Nanopowder (TiO2, anatase, 99.9%, 100nm) | US research nanomaterials | US3411 | |
| Graphite powder | Alfa Aesar | 10129 | |
| Sulfuric acid | Sigma Aldrich | 1120802500 | |
| Hydrogen peroxide | Sigma Aldrich | H1009-100ML | |
| L-Ascorbic acid | Sigma Aldrich | A92902-500G | |
| Hydrochloric acid | Sigma Aldrich | 320331-2.5L | |
| Sodium hydroxide | Sigma Aldrich | S5881-1KG | |
| Potassium permanganate | Merck | 1050821000 | |
| Corning® Silicone Septa for GL45 Screw Cap | Sigma Aldrich (Corning) | CLS139545SS | |
| Polyvinyl chloride pipe | Koctas | UV-Reactor casing | |
| Fuded silica (Quartz) tube | Technical Glass Products | ||
| UV−C lamps | Philips | TUV PL-L 55W/4P HF 1CT/25 |
References
- Okitsu, K., Mizukoshi, Y., Ashokkumar, M. Catalytic Applications of Noble Metal Nanoparticles Produced by Sonochemical Reduction of Noble Metal Ions. Handbook of Ultrasonics and Sonochemistry. , 325-363 (2016).
- Shakoori Oskooie, M., Menceloglu, Y. Z., Unal, S., Hayat Soytas, S. Rapid Microwave-assisted Synthesis of Platinum Nanoparticles Immobilized in Electrospun Carbon Nanofibers for Electrochemical Catalysis. ACS Applied Nano Materials. , (2018).
- Kaplan, B. Y., et al. Graphene: A Promising Catalyst Support for Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. ECS Meeting Abstracts. , (2018).
- Iliev, V., Tomova, D., Bilyarska, L., Eliyas, A., Petrov, L. Photocatalytic properties of TiO2 modified with platinum and silver nanoparticles in the degradation of oxalic acid in aqueous solution. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 63, 266-271 (2006).
- Bumajdad, A., Madkour, M. Understanding the superior photocatalytic activity of noble metals modified titania under UV and visible light irradiation. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 16, 7146 (2014).
- Şanlı, L. I., Bayram, V., Yarar, B., Ghobadi, S., Gürsel, S. A. Development of graphene supported platinum nanoparticles for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells: Effect of support type and impregnation-reduction methods. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 41, 3414-3427 (2016).
- Işıkel Şanlı, L., Bayram, V., Ghobadi, S., Düzen, N., Gürsel, S. A. Engineered catalyst layer design with graphene-carbon black hybrid supports for enhanced platinum utilization in PEM fuel cell. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 42, 1085-1092 (2017).
- Domínguez-Domínguez, S., Arias-Pardilla, J., Berenguer-Murcia, &. #. 1. 9. 3. ;., Morallón, E., Cazorla-Amorós, D. Electrochemical deposition of platinum nanoparticles on different carbon supports and conducting polymers. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry. 38, 259-268 (2008).
- Pan, X., Xu, Y. -. J. Defect-Mediated Growth of Noble-Metal (Ag, Pt, and Pd) Nanoparticles on TiO2 with Oxygen Vacancies for Photocatalytic Redox Reactions under Visible Light. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C. 117, 17996-18005 (2013).
- Zhang, Y., Zhang, N., Tang, Z. -. R., Xu, Y. -. J. Graphene Oxide as a Surfactant and Support for In-Situ Synthesis of Au-Pd Nanoalloys with Improved Visible Light Photocatalytic Activity. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C. 118, 5299-5308 (2014).
- Abdolhosseinzadeh, S., Asgharzadeh, H., Sadighikia, S., Khataee, A. UV-assisted synthesis of reduced graphene oxide-ZnO nanorod composites immobilized on Zn foil with enhanced photocatalytic performance. Research on Chemical Intermediates. 42, 4479-4496 (2016).
- Abdolhosseinzadeh, S., Sadighikia, S., Gürsel, S. A. Scalable Synthesis of Sub-Nanosized Platinum-Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite by an Ultraprecise Photocatalytic Method. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering. 6, 3773-3782 (2018).
- Zhang, N., Yang, M. -. Q., Liu, S., Sun, Y., Xu, Y. -. J. Waltzing with the Versatile Platform of Graphene to Synthesize Composite Photocatalysts. Chemical Reviews. 115, 10307-10377 (2015).
- Han, C., Zhang, N., Xu, Y. -. J. Structural diversity of graphene materials and their multifarious roles in heterogeneous photocatalysis. Nano Today. 11, 351-372 (2016).
- Abdolhosseinzadeh, S. . Bandgap Modulation of Graphene Oxide and Its Application in the Photocatalytic Deposition of Metallic Nanoparticles. , (2017).
- Abdolhosseinzadeh, S., et al. Fast and fully-scalable synthesis of reduced graphene oxide. Scientific Reports. 5, 10160 (2015).
- Ma, Y., Wei, X. Determination of platinum in waste platinum-loaded carbon catalyst samples using microwave-assisted sample digestion and ICP-OES. AIP Conference Proceedings. 1829 (1), 020008 (2017).
- Sevilla, M., Sanchís, C., Valdés-Solís, T., Morallón, E., Fuertes, A. B. Highly dispersed platinum nanoparticles on carbon nanocoils and their electrocatalytic performance for fuel cell reactions. Electrochimica Acta. 54, 2234-2238 (2009).
- de Sá, D. S., et al. Intensification of photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes and phenol by scale-up and numbering-up of meso- and microfluidic TiO2 reactors for wastewater treatment. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry. 364, 59-75 (2018).
- Kononova, O. N., Leyman, T. A., Melnikov, A. M., Kashirin, D. M., Tselukovskaya, M. M. Ion exchange recovery of platinum from chloride solutions. Hydrometallurgy. 100, 161-167 (2010).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved