A Probing Device for Quantitatively Measuring the Mechanical Properties of Soft Tissues during Arthroscopy
In This Article
Summary
Probing during arthroscopy surgery is normally done to assess the condition of the soft tissue, but this approach has always been subjective and qualitative. This report describes a probing device that can measure the resistance of the soft tissue quantitatively with a tri-axial force sensor during arthroscopy.
Abstract
Probing in arthroscopic surgery is performed by pulling or pushing the soft tissue, which provides feedback for understanding the condition of the soft tissue. However, the output is only qualitative based on the “surgeon’s feeling”. Herein is described a probing device developed to address this issue by measuring the resistance of soft tissues quantitatively with a tri-axial force sensor. Under both conditions (i.e., pull- and push-probing certain tissues mimicking the acetabular labrum and cartilage), this probing device is found to be useful for measuring some mechanical properties in joints during arthroscopy.
Introduction
The process of probing, which pulls (or hooks) or pushes soft tissues in joints with a metallic probe, allows for assessing the condition of soft tissues during arthroscopic surgery1,2. However, evaluation of the probing is very subjective and qualitative (i.e., the surgeon’s feeling).
On the basis of this context, if the resistance of the soft tissue (e.g., capsule or labrum in the hip joint, meniscus or ligament in the knee joint) during pulling could be measured quantitatively, it could be useful for surgeons to judge the necessity of a repair for the soft tissue and an indication of whether additional surgical intervention is necessary even after the primary repair is completed3,4,5. Furthermore, criteria for key quantitative variables to indicate necessary surgical intervention must be established for surgeons. Additionally, in the opposite direction, pushing the probe can be used to assess the mechanical properties of articular cartilage tissues. In the fields of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, such as the replacement of damaged, degenerate, or diseased cartilage tissues, in situ evaluation of push-probing can be critical2,6.
This article reports the development of a probing device with a tri-axial force sensor6 that can measure the resistance of soft tissue quantitatively during arthroscopy. This probing device consists of a probe component with a half-length size (200 mm) of a normal arthroscopic probe, and a grip component in which a strain gauge sensor is embedded to measure the resultant force of three axis at the tip of the probe (Figure 1).The strain gauge sensor was made specifically for probing. The strain gauge is embedded at the top of the grip component, which connects with the probe component. The resolution of this probing device is 0.005 N. The precision and accuracy were also measured by a commercialized weight with known weight (50 g). The precision was 0.013 N and the accuracy is 0.0035 N.
Furthermore, a sliding aspect of the grip component has been implemented to control the distance with the surgeon’s index finger or thumb while pulling or pushing the probe. During the process of measuring the resistance, the measured value is dependent on both the pulling distance of the probing device and the pulling force, which is why the pulling distance of the probing device is controlled by the sliding aspect. The sliding distance of the grip component of the probing device was set to 3 mm for the following representative cases in this study.
As shown in Figure 1, the resistance force of the soft tissues can thus be measured tri-axially. The first force is along the probe axis. The second is perpendicular to the probe axis along the direction of the hook of the probe, and the third is in the transversal direction. Measurement of the forces is done using the following general method: The three-axis force sensor includes three Wheatstone bridges corresponding to the x-, y-, and z-axes. The resistance value of the strain gauge changes according to the magnitude of the applied load, and the midpoint voltage of the bridge changes so that the force can be detected as an electrical signal. The measurement range of this device is 50 N in the direction of the probe axis and 10 N in the two remaining directions.
Dedicated software was developed for this probe in which the software shows the three forces in the x, y, and z directions (x is the transverse direction, y is the vertical direction (direction of the hook), and z is the probe axis) measured by the probing device in real time with a frequency of 50 Hz as three separate graphs (Figure 2). Optionally, a thin elastic cover normally used for intraoperative use of ultrasound devices can be used for waterproofing here.
This probing device can thus allow for assessing certain conditions of soft tissues. In addition, this probing device might allow for evaluating the mechanical properties of articular cartilage tissues. To this end, the reaction force on the articular cartilage surface while sliding the tip of this probing device forward on the surface might be correlated with the mechanical property of the articular cartilage.
The purpose of this study is to introduce how the probing device can be used. First are measurements of a mimic acetabular labrum as a representative tissue while pull-probing with a phantom hip model. Investigated is the difference in the resistance of the acetabular labrum in three surgical steps for a typical labral repair. Second are measurements of a representative mimic cartilage tissue through push-probing. Also investigated is a correlation between two different mechanical properties of the mimic cartilage tissue as measured by this probing device and a classical indentation device to validate the new method for measuring the mechanical properties of the articular cartilage.
Protocol
The protocol in the present study consists primarily of the following two aspects: 1) resistance force of the acetabular labrum with pull-probing and 2) measurement of the reaction force on the mimic cartilage sample with push-probing.
1. Resistance force of the acetabular labrum with pull-probing
- Phantom preparation for the measurements with pull-probing
- Fix a phantom hip, which consists of the left pelvis and femur bone, major muscles of the hip, acetabular labrum, hip capsule, and articular cartilage of the hip joint on a standard fixation device5.
- Abduct and internally rotate the femur bone slightly to distance it from the pelvis, generating joint space mimicking hip arthroscopy.
- Camera preparation for arthroscopy
- Prepare a 4 mm 70° autoclavable direct view arthroscope and connect a portable arthroscopy camera. Connect a portable arthroscopy camera light source to the 70° arthroscope. Connect USB cables from the arthroscopy camera and the light source to a PC. Then, open advanced screen recording software for the arthroscopy view on the PC.
- Preparation of portals
NOTE: The preparation is followed by the standard conventional hip arthroscopy method7.- Insert a cannulated needle and guide wire into the hip joint from the tip of the greater trochanter to make a normal anterolateral portal.
- Insert a 5.5 mm cannula with an obturator along the line of the guide wire. Then, remove the obturator, and insert the 70° arthroscope with the portable arthroscopy camera along the cannula, thus generating the first portal.
- Confirm whether the capsular triangle between the labrum and femoral head7 is seen in the view from this portal. Next, make the second portal as a modified anterior portal7.
- Capsulotomy, opening the hip capsule
- When the anterior portal has been generated, retain the arthroscope in the anterolateral portal. Insert a 4.5 mm cannula with an obturator along the guide wire, remove the obturator, and then insert an arthroscopic scalpel from the anterior portal. Perform a peri-portal capsulotomy around the anterior portal, moving the scalpel medially and laterally to generate more space for the anterior portal in the hip capsule.
- Place the arthroscope into the anterior portal. Rotate the camera view of the arthroscope until seeing the cannula at the anterolateral portal. Insert the arthroscopic scalpel from the anterolateral portal. Perform a transverse interportal capsulotomy, which connects between the two portals from approximately 10 o'clock to 2 o'clock. Then, leave this capsulotomy 5 mm from the labrum, measuring approximately 15 mm in length.
- Setup of the probing device
- Confirm the connection between the power supply unit and PC with a USB cable. Switch on the power supply unit. Open the software for the probing device, which is described in the Introduction.
- Input the matrix data for the first time, which is pre-calculated during calibration of the strain gauge sensor. Recalibrate if the measured value is not same as the default weight value when placed at the tip of the probe.
- Reset the measuring force value to zero immediately before each measurement. In addition, confirm whether the foot switch connected with the recording system of the probing device works well.
- Measurement of resistance of the acetabular labrum while pull-probing
- Place the arthroscope into the anterolateral portal. Insert the probing device from the anterior portal and go further into the hip joint until the tip of the device is below the inner side of the acetabular labrum.
- Zero the setting as above. Pull the tip of the probing device out in the direction of the joint (this is the first surgical step as “Labrum intact”) (Figure 3).
- Remove the probing device from the anterior portal and then insert the arthroscopic scalpel into the joint. Then, detach the anterior-superior labrum longitudinally (by 10 mm) from the acetabular rim sharply using the scalpel.
- Switch from the scalpel to the probing device in the anterior region. Hook the labrum along the probe axis at the same position of the labrum to measure the resistance force of the labrum (this is identified as the second step, “Labrum cut”). Again, remember to zero the setting before this measurement.
- Insert an anchor set for the labrum repair into the anterior portal. Place the anchor at the tip of the anchor set at the acetabular bony edge. Insert the suturing instrument into the anterior portal after removing the anchor set. Tighten the labrum at the acetabular edge. Repeat this repair procedure once more for making the second stitch.
- Measure the resistance force of the labrum by again hooking the labrum along the probing axis (this is as the third step, “Labrum repair”). Remember to press the foot pedal when recording each surgical step.
2. Measurement of the reaction force to mimic cartilage samples with push-probing
NOTE: In the second study, a vertical resistance force on each mimic cartilage surface was measured (Figure 4A) with push-probing on the cartilage surface at a 30° tilt to the horizontal line and identified as one element of the mechanical properties of articular cartilage.
- Preparation of the samples for measurements with push-probing.
- Prepare the cartilage samples. In the current study, five kinds of mimic cartilage samples were used, which were made from poly-vinyl alcohol hydrogels8.
- Reshape the samples from the bulk size of the provided samples to 15 mm x 20 mm x 3 mm as a mimic cartilage plate. Place each sample on a base plate, which has a tiny stopper toward the side of the push-probing.
- Measurement of cartilage resistance with push-probing
- Hold and fix the position and orientation of the probing device in which the tip of the device almost touches the surface of the mimic cartilage sample while maintaining a 30° tilt to the horizontal line.
- After zeroing the setting, push and pull the tip of the probing device on the mimic cartilage sample three times by pressing the foot pedal.
- Repeat this measurement step for the five samples after putting on each of the plates.
- Measurement of cartilage resistance by a classical indentation device
- Measure the conventional elastic modulus and stiffness of each sample using a classical indentation device (Figure 4B).
NOTE: The customized device for the classical indentation test to measure the elastic modulus of the mimic cartilage sample in the current study had a spherical indenter with a 1 mm diameter tip and an electromechanical actuator (resolution, 5 µm). The actuator, indenter, and load cell were assembled using custom 3D-printed brackets by PLA filaments on a 3D printer (Figure 4B) to function as a conventional uniaxial indentation system. Each sample was placed on the baseplate of the indentation device. The midpoint of the sample was aligned with the indenter tip. The indenter tip was brought into initial contact with the sample using a preload of 0.02 N. The indenter tip was then compressed 150 µm into the cartilage surface. The force and displacement were recorded during the indentation. The linear portion of the indentation force-displacement curve was used to calculate the stiffness and the elastic modulus as reported by Hayes et al.24 using the thickness of the sample. The data by this device was not validate, but the mechanical values of cartilage samples by this device were confirmed previously; the elastic modulus was 0.46 MPa (0.27 MPa standard deviation (SD)), which is consistent with that found in several previous literature studies11,16,19. - Calculate the coefficient value between the maximum value of the vertical reaction force with push-probing and the elastic modulus by the classical indentation device.
- Measure the conventional elastic modulus and stiffness of each sample using a classical indentation device (Figure 4B).
Representative Results
Resistance force of the acetabular labrum in the three surgical steps with pull-probing
The measurements recorded by this probing device at each step were repeated three times. The results show that the highest mean resultant forces of y and z for the acetabular labrum for the three steps were 4.4 N (0.2 N SD) at the intact labrum, 1.6 N (0.1 N SD) at the cut labrum, and 4.6 N (0.7 N SD) at the repaired labrum (Figure 5). The transverse force was just 2.8% of the highest resultant force while probing at the intact labrum.
Relationship between the two differently scaled mechanical properties by the probing device with push-probing and classical indentation device
The results show a significant positive relationship between the two mechanical properties obtained: probing sensor vs elastic modulus, r = 0.965 and p = 0.0044 (Figure 6); probing sensor vs stiffness, r = 0.975 and p = 0.0021).
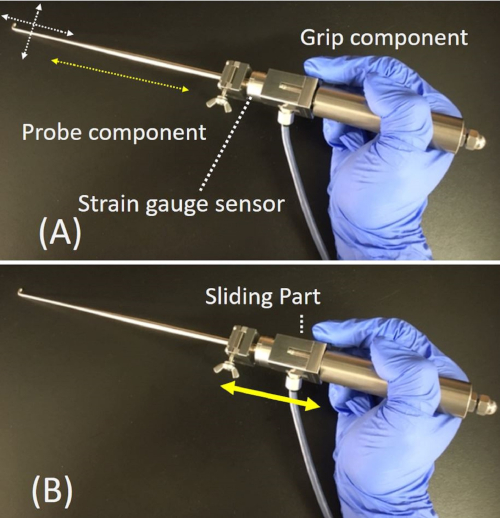
Figure 1: Probing device used in the current study (A) The probing device consists of a probe component and a grip component with an embedded strain gauge sensor that can tri-axially measure forces at the tip of the probe (one along the probe axis, dotted yellow arrow; other two perpendicular to the probe axis, dotted white arrows) (B) Because the grip component has a sliding piece, the probe component and the sliding aspect can be moved to the grip with the index finger, solid yellow arrow. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
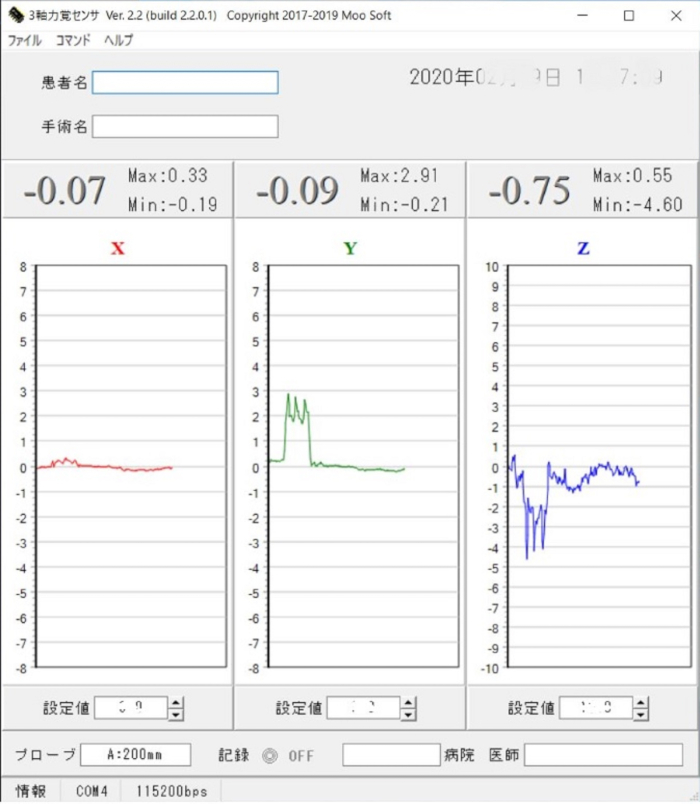
Figure 2: View of the software for the probing device. This view shows the real time tri-axially measured values of the resistance force of the soft tissues during probing. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
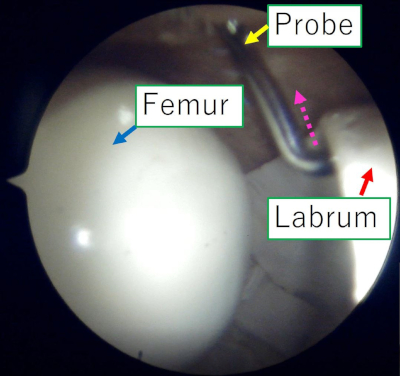
Figure 3: Representative operational view of the arthroscopy monitor during pull-probing of the acetabular labrum. This view is from a typical anterolateral portal. The probing device is inserted from a modified anterior approach. The pull-probing is performed along the axis of the probe (dotted arrow). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
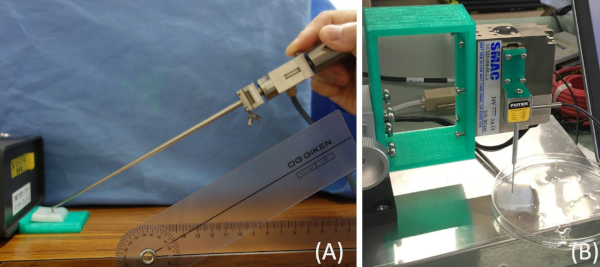
Figure 4: Two different scale tests for mechanical properties of mimic articular cartilage tissue (A) Measurement of the reaction force perpendicular to the cartilage surface while manually sliding the probe (B) Classical indentation test (compressed vertically to the cartilage surface) to understand the congruence between these two mechanical property tests. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
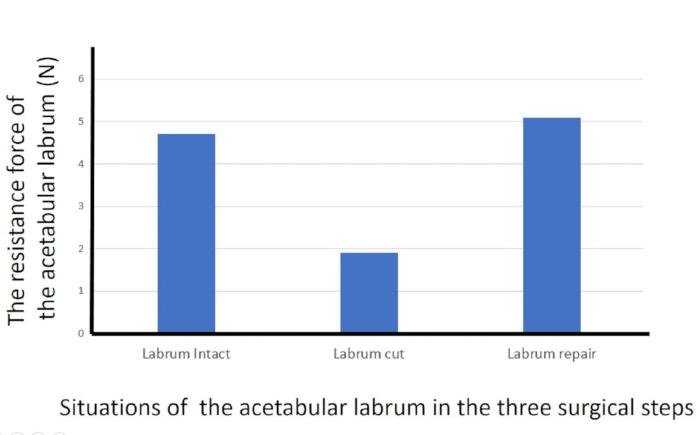
Figure 5: Resistance forces of the acetabular labrum with pull-probing. Resistance forces of the acetabular labrum with pull-probing for the three surgical steps. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
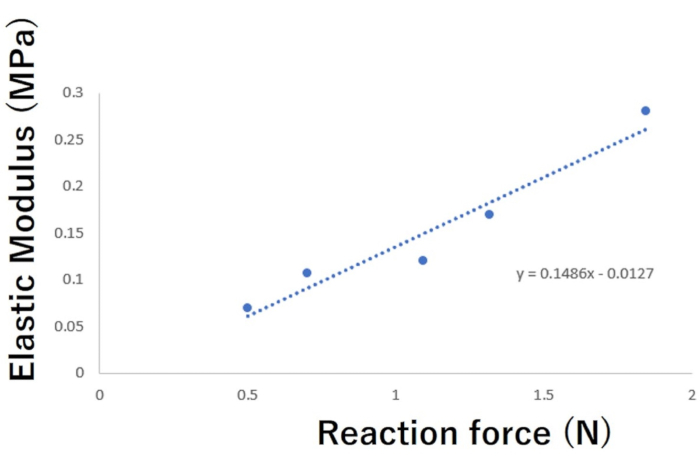
Figure 6: Relationship between the vertical reaction force on the cartilage surface with push-probing and elastic modulus by the classical indentation test. The vertical reaction force on the cartilage surface with push-probing had a strong positive correlation (r = 0.965, p = 0.0044) with the elastic modulus by the classical indentation test. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Discussion
This study demonstrates that the probing device is able to measure tri-axially the resistance of soft tissues in the joint during arthroscopic probing. Specifically, the following two things were investigated: 1) the difference in the resistance force of the acetabular labrum with pull-probing in the three surgical steps of a typical labral repair and 2) the relationship between two different mechanical properties of the mimic cartilage tissue with push-pulling.
According to this study, the quantitatively measured values by pull-probing with this device can be useful for evaluating the condition of the joint soft tissue. The highest resistance levels of the acetabular labrum decreased when the labrum was cut. Furthermore, the high resistance levels were recovered when the labrum was repaired. Thus, the probing force can also be useful for evaluating whether surgical intervention is sufficient. Furthermore, this pull-probing can be utilized for assessing other soft tissues as well, such as anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments for instability, medial and lateral collateral ligaments for valgus or varus balance in knee surgeries, labrum and rotator cuff in shoulder surgeries, as well as for other arthroscopic surgeries.
Similar results were previously reported using 10 fresh cadaver hip specimens with a similar probing device3. The highest resistance levels of the labrum were significantly reduced when the labrum was cut (intact labrum, 8.2 N; cut labrum, 4.0 N). Furthermore, the high resistance level of the labrum was significantly recovered when the labrum was repaired (cut, 4.0 N; repaired, 7.8N). Furthermore, resistance level for the cut labrum (3.0-5.0 N) was statistically separated with 95% confidence from those of the intact (6.5-9.9 N) and repaired labrum (6.7-9.1 N). Therefore, a threshold for detecting lesions in the labrum might be determined, which is approximately 5 N (4-6 N on cadavers) of the highest resistance level of the labrum. According to the current study, such a threshold on the phantom hip might be around 2-3 N.
Another interesting finding in the current study is the significant positive relationship between the reaction force on the mimic cartilage surface by the push-probing device and the elastic modulus by the classical indentation device. When push-probing is performed as shown in Figure 4 and then the tip of the probe is moving on the surface, a reaction force occurs. As a result, the tip of the probe is pushed up by the reaction force. This is measured as the perpendicular force of the probe axis. In this situation, if the mechanical property of the mimic cartilage tissue is small (i.e., soft), the force of the push-probing to the surface of the cartilage might be partially absorbed. Then, its reaction force on the surface to the tip of the probe should be weakened compared with that in the case of push-probing on hard cartilage tissue. As a result, the perpendicular force of the probe axis would be decreased. Therefore, if the angle of the probing axis to the mimic cartilage surface can be controlled by new technology, such as a wearable gyro sensor9,10, the in situ mechanical properties of the cartilage tissue can be evaluated.
Several research groups have tried to develop devices to quantitatively evaluate the quality of articular cartilage in vivo during arthroscopy11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22 using various methods, such as ultrasound bio-microscopy11, arthroscopic ultrasound imaging12, optical reflection spectroscopy13, pulsed laser irradiation14, near-infrared spectroscopy15, and ultrasound-based16, mechanical16,17,18,19,20,21, and electromechanical indentation devices22. Most of the devices except for the indentation ones11,12,13,14,15 can measure the thickness of the cartilage layer; however, they cannot measure related mechanical property values. Although ultrasound and mechanical-based indentation devices16,17,18 can measure some mechanical properties of articular cartilage, the surface of the tip of the device must be touched vertically to the articular cartilage surface, which is followed by conventional methods of compression testing. The remaining electromechanical indentation device22,23 that has been recently developed has a spherical shape at the tip of the device; here, it might be difficult to determine how to touch the tip to the cartilage surface during arthroscopy because of its relatively bigger size obscuring the measuring point by the tip itself. Additionally, the quantitative value (called as QP22,23) is not consecutive and rather seems to be a damage score (from 4 to 20 for cartilage assessment). For example, the 4 QP value is not worth twice the 2 QP value.
One important point is that the device adheres as much as possible to a shape of the classical probe. Furthermore, a conventional and known parameter unit (i.e., newton) for the probing device is applied in part because it is consecutively quantitative. In this context, the probing device described here can reproduce conditions of conventional probing based on the “surgeon’s feeling”. Thus, this probing device is shown to be useful for measuring certain mechanical properties in joints during arthroscopy.
In conclusion, the probing device described here, which can quantitatively measure the resistance of soft tissues with a tri-axial force sensor through both pull- and push-probing, can be useful for quantitatively evaluating comprehensive lesions or conditions of the joint soft tissues, which is an improvement of the current qualitative evaluation of conventional probing.
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by JSPS KAKENHI grants JP19K09658 and JP18KK0104 and a Japanese Foundation for Research and Promotion of Endoscopy (JFE) grant. The author would like to thank Professor Darryl D. D'Lima and Professional Scientific Collaborator Erik W. Dorthe in Shiley Center for Orthopaedic Research and Education at Scripps Clinic for the permission to duplicate the customized device for the classical indentation test at the institution, and for supporting the author with collaboration studies.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 4.5 mm ARTHROGARDE Hip Access Cannula GREEN | Smith&Nephew | 72201741 | Arthroscopy cannula |
| 70° Autoclavable, Direct View | Smith&Nephew | 72202088 | 70 degrees arthroscope |
| Bandicam | Bandicam Company | an advanced screen recording software | |
| da Vinci 2.0 A Duo | XYZ printing Japan | 3D printer | |
| Disposable Hip Pac | Smith&Nephew | 7209874 | A set of 3 guidewires and 2 arthroscopy needles |
| Hip phantom | Sawbones USA, A Pacific Research Company | SKU:1516-23 | The phantom model for hip arthroscopy |
| Labview | National Instruments | Systems engineering software for applications that require test, measurement, and control with rapid access to hardware | |
| LAC-1 | SMAC | Electromechanical actuator | |
| LSB200 | Futek | FSH00092 | A load cell |
| Nanopass | Stryker | CAT02298 | A suturing instrument for the labrum repair |
| Osteoraptor 2.3 Suture Anchor | Smith&Nephew | 72201991 | Anchor set for the labrum repair |
| PC software for Probing sensor | Moosoft | PC software for Probing sensor | |
| Poly-vinyl alcohol hydrogels | Sunarrow Limited | Poly-vinyl alcohol hydrogels | |
| portable arthroscopy camera | Sawbones USA, A Pacific Research Company | SKU:5701 | Portable arthroscopy camera |
| Probing sensor | Takumi Precise Metal Work Manufacturing Ltd | Probing device to measure resistance force to soft tissue in joint while probing | |
| Samurai Blade | Stryker | CAT00227 | Arthroscopic scalpel |
| Standard fixation device | Sawbones USA, A Pacific Research Company | SKU:1703-19 | The fixation device for the hip phantom |
| Strain gauge sensor | Nippon Liniax Co.,LTD | MFS20-100 | The sensor works with three Wheatstone bridges |
| Ultra-Hard C2 Tungsten Carbide Ball, 1 mm Diameter | McMaster-Carr | 9686K81 | Ultra-Hard C2 Tungsten Carbide Ball, 1 mm Diameter |
References
- Chami, G., Ward, J. W., Phillips, R., Sherman, K. P. Haptic feedback can provide an objective assessment of arthroscopic skills. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 466, 963-968 (2008).
- Tuijthof, G. J., Horeman, T., Schafroth, M. U., Blankevoort, L., Kerkhoffs, G. M. Probing forces of menisci: what levels are safe for arthroscopic surgery. Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, & Arthroscopy. 19 (2), 248-254 (2011).
- Hananouchi, T., Aoki, S. K. Quantitative evaluation of capsular and labral resistances in the hip joint using a probing device. Bio-Medical Materials and Engineering. 30 (3), 333-340 (2019).
- Hananouchi, T., et al. Resistance of Labrum using A Quantitative probing device in Hip Arthroscopy. Orthopaedic Research Society Annual Meeting. , (2017).
- Hananouchi, T. Evaluation of a quantitative probing to assess condition of soft tissue during arthroscopic surgery for regenerative medicine. Tissue Engineering International and Regenerative Medicine Society. (Termis-EU 2014). , (2014).
- Hananouchi, T., Dorthe, E. W., Chen, Y., Du, J., D'Lima, D. D. A Probing Device for in-situ Mechanical Property Evaluation of Cartilage Tissue. The 11th annual meeting of JOSKAS (Japanese Orthopaedic Society of Knee, Arthroscopy and Sports Medicine). , (2019).
- Aoki, S. K., Beckmann, J. T., Wylie, J. D. Hip Arthroscopy and the Anterolateral Portal: Avoiding Labral Penetration and Femoral Articular Injuries. Arthroscopy Techniques. 1 (2), 155-160 (2012).
- Sato, H., et al. Development and use of a non-biomaterial model for hands-on training of endoscopic procedures. Annals of Translational Medicine. 5 (8), 182 (2017).
- Boddy, K. J., et al. Exploring wearable sensors as an alternative to marker-based motion capture in the pitching delivery. PeerJ. 7, 6365 (2019).
- Aroganam, G., Nadarajah Manivannan, N., Harrison, D. Review on Wearable Technology Sensors Used in Consumer Sport Applications. Sensors. 19 (9), 1983 (2019).
- Gelse, K., et al. Quantitative ultrasound biomicroscopy for the analysis of healthy and repair cartilage tissue. European Cells & Materials. 19, 58-71 (2010).
- Virén, T., et al. Quantitative evaluation of spontaneously and surgically repaired rabbit articular cartilage using intra-articular ultrasound method in situ. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology. 36 (5), 833-839 (2010).
- Johansson, A., Sundqvist, T., Kuiper, J. H., Öberg, P. &. #. 1. 9. 7. ;. A spectroscopic approach to imaging and quantification of cartilage lesions in human knee joints. Physics in Medicine & Biology. 56 (6), 1865-1878 (2011).
- Sato, M., Ishihara, M., Kikuchi, M., Mochida, J. A diagnostic system for articular cartilage using non-destructive pulsed laser irradiation. Lasers in Surgery and Medicine. 43 (5), 421-432 (2011).
- Spahn, G., Felmet, G., Hofmann, G. O. Traumatic and degenerative cartilage lesions: arthroscopic differentiation using near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS). Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery. 133 (7), 997-1002 (2013).
- Kiviranta, P., Lammentausta, E., Töyräs, J., Kiviranta, I., Jurvelin, J. S. Indentation diagnostics of cartilage degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 16 (7), 796-804 (2008).
- Franz, T., et al. In situ compressive stiffness, biochemical composition, and structural integrity of articular cartilage of the human knee joint. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 9 (6), 582-592 (2001).
- Kitta, Y., et al. Arthroscopic measurement of cartilage stiffness of the knee in young patients using a novel indentation sensor. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 22, 110-111 (2014).
- Lyyra, T., Jurvelin, J., Pitkänen, P., Väätäinen, U., Kiviranta, I. Indentation instrument for the measurement of cartilage stiffness under arthroscopic control. Medical Engineering & Physics. 17 (5), 395-399 (1995).
- Niederauer, G. G., et al. Correlation of cartilage stiffness to thickness and level of degeneration using a handheld indentation probe. Annals of Biomedical Engineering. 32 (3), 352-359 (2004).
- Appleyard, R. C., Swain, M. V., Khanna, S., Murrel, G. A. C. The accuracy and reliability of a novel handheld dynamic indentation probe for analyzing articular cartilage. Physics in Medicine & Biology. 46, 541-550 (2001).
- Sim, S., et al. Non-destructive electromechanical assessment (Arthro-BST) of human articular cartilage correlates with histological scores and biomechanical properties. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 22 (11), 1926-1935 (2014).
- Mickevicius, T., Maciulaitis, J., Usas, A., Gudas, R. Quantitative Arthroscopic Assessment of Articular Cartilage Quality by Means of Cartilage Electromechanical Properties. Arthroscopy Techniques. 7 (7), 763-766 (2018).
- Hayes, W. C., Keer, L. M., Herrmann, G., Mockros, L. F. A mathematical analysis for indentation tests of articular cartilage. The Journal of Biomechanics. 5 (5), 541-551 (1972).
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2024 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved