Abstract
Biology
Isolatie van muizen megakaryocyten voorlopers
ERRATUM NOTICE
Important: There has been an erratum issued for this article. Read more …Beenmerg megakaryocyten zijn grote polyploïde cellen die zorgen voor de productie van bloedplaatjes. Ze ontstaan uit hematopoëtische stamcellen door megakaryopoiese. De laatste stadia van dit proces zijn complex en omvatten klassiek de bipotente Megakaryocyte-Erythrocyte Progenitors (MEP) en de unipotente Megakaryocyte Progenitors (MKp). Deze populaties gaan vooraf aan de vorming van bonafide megakaryocyten en als zodanig zou hun isolatie en karakterisering de robuuste en onbevooroordeelde analyse van megakaryocytenvorming mogelijk kunnen maken. Dit protocol presenteert in detail de procedure om hematopoëtische cellen uit het beenmerg van muizen te verzamelen, de verrijking van hematopoëtische voorlopercellen door magnetische depletie en ten slotte een celsorteerstrategie die sterk gezuiverde MEP- en MKp-populaties oplevert. Eerst worden beenmergcellen verzameld uit het dijbeen, het scheenbeen en ook de iliacale kam, een bot dat een groot aantal hematopoëtische voorlopers bevat. Het gebruik van iliacale kambotten verhoogt het totale celaantal per muis drastisch en draagt zo bij aan een ethischer gebruik van dieren. Een magnetische afstammingsdepletie werd geoptimaliseerd met behulp van 450 nm magnetische kralen die een zeer efficiënte celsortering door flowcytometrie mogelijk maakten. Ten slotte presenteert het protocol de etiketterings- en gatingstrategie voor het sorteren van de twee sterk gezuiverde megakaryocytenvoorloperpopulaties: MEP (Lin-Sca-1-c-Kit+CD16/32-CD150+CD9dim) en MKp (Lin- Sca-1-c-Kit+CD16/32-CD150+CD9bright ). Deze techniek is eenvoudig te implementeren en biedt voldoende cellulair materiaal om i) moleculaire karakterisering uit te voeren voor een diepere kennis van hun identiteit en biologie, ii) in vitro differentiatietests, die een beter begrip zullen geven van de mechanismen van rijping van megakaryocyten, of iii) in vitro modellen van interactie met hun micro-omgeving.
Erratum
Erratum: Isolation of Mouse Megakaryocyte ProgenitorsAn erratum was issued for: Isolation of Mouse Megakaryocyte Progenitors. A figure was updated.
Figure 2 was updated from:
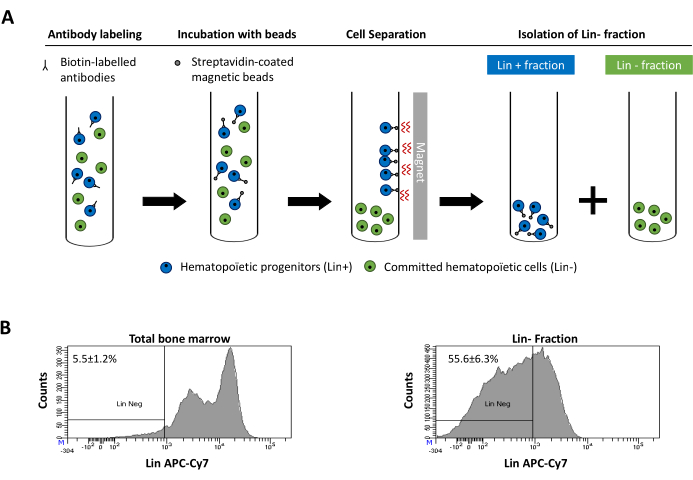
Figure 2: Magnetic depletion of lineage committed (Lin) cells. (A) Schematic representation of the magnetic depletion protocol. First, unsorted bone marrow cells are labeled with the biotin-conjugated rat anti-mouse antibody cocktail. Cells are then incubated with anti-rat Ig coated magnetic beads and subsequently subjected to the magnetic depletion using a strong magnet. The magnet will retain the labeled magnetic Lin+ fraction against the tube walls, while the unlabeled non-magnetic Lin- negative fraction will be collected in a new tube. (B) Lineage committed cells can be identified using fluorescent conjugated streptavidin. Typical analysis of the lineage expression in cells prior to magnetic depletion (total bone marrow) and after magnetic depletion (Lin- Fraction) N = 21. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
to:
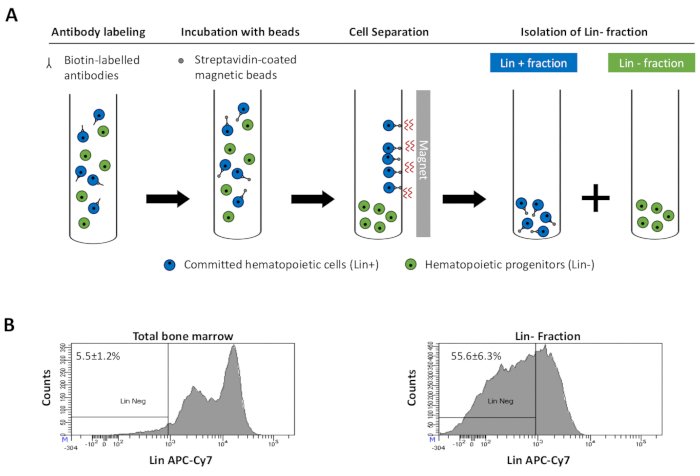
Figure 2: Magnetic depletion of lineage committed (Lin) cells. (A) Schematic representation of the magnetic depletion protocol. First, unsorted bone marrow cells are labeled with the biotin-conjugated rat anti-mouse antibody cocktail. Cells are then incubated with anti-rat Ig coated magnetic beads and subsequently subjected to the magnetic depletion using a strong magnet. The magnet will retain the labeled magnetic Lin+ fraction against the tube walls, while the unlabeled non-magnetic Lin- negative fraction will be collected in a new tube. (B) Lineage committed cells can be identified using fluorescent conjugated streptavidin. Typical analysis of the lineage expression in cells prior to magnetic depletion (total bone marrow) and after magnetic depletion (Lin- Fraction) N = 21. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Explore More Videos
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2024 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved