A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
A Model of Experimental Steatosis In Vitro: Hepatocyte Cell Culture in Lipid Overload-Conditioned Medium
In This Article
Summary
This protocol is intended to be a tool to study steatosis and the molecular, biochemical, cellular changes produced by the over exposure of hepatocytes to lipids in vitro.
Abstract
Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), previously known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is the most prevalent liver disease worldwide due to its relationship with obesity, diabetes type 2, and dyslipidemia. Hepatic steatosis, the accumulation of lipid droplets in the liver parenchyma, is a key feature of the disease preceding the inflammation observed in steatohepatitis, fibrosis, and end-stage liver disease. Lipid accumulation in hepatocytes might interfere with proper metabolism of xenobiotics and endogenous molecules, as well as to induce cellular processes leading to the advance of the disease. Although the experimental study of steatosis can be performed in vivo, in vitro approaches to the study of steatosis are complementary tools with different advantages. Hepatocyte culture in lipid overload-conditioned medium is an excellent reproducible option for the study of hepatic steatosis allowing the identification of cellular processes related to lipid accumulation, such as oxidative and reticular stresses, autophagia, proliferation, cell death, etcetera, as well as other testing including drug effectiveness, and toxicological testing, among many other possible applications. Here, it was aimed to describe the methodology of hepatocyte cell culture in lipid overload-conditioned medium. HepG2 cells were cultured in RMPI 1640 medium conditioned with sodium palmitate and sodium oleate. Importantly, the ratio of these two lipids is crucial to favor lipid droplet accumulation, while maintaining cell proliferation and a moderate mortality rate, as occurs in the liver during the disease. The methodology, from the preparation of the lipid solution stocks, mixture, addition to the medium, and hepatocyte culture is shown. With this approach, it is possible to identify lipid droplets in the hepatocytes that are readily observable by Oil-red O staining, as well as curves of proliferation/mortality rates.
Introduction
Fatty liver associated with metabolic dysfunction is highly prevalent worldwide1,2; it is estimated that up to 25% of the population is affected3. This disease previously known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), has updated its nomenclature to metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) to accurately reflect the pathogenesis related with obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes type 2, and dyslipidemia, as well as the possible managements of the disease3,4.
Regardless of the name, the disease includes a wide spectrum of histopathological changes characterized by abnormally high accumulation of lipids in the liver (>5% of fat in the hepatocytes5) and might progress through the lipid accumulation typically found in simple steatosis to steatohepatitis, which in turn might lead to the development of fibrosis, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and liver failure5,6,7,8. Due to its increasing prevalence, MAFLD is expected to become the first indication of liver transplantation and the leading cause of hepatocellular carcinoma9.
Although it has been considered as a benign or mild form of fatty liver disease, hepatic steatosis is in fact the metabolic key in MAFLD10. Different metabolic pathways are affected by lipid accumulation in the liver, including but not limited to lipid synthesis, exportation, and metabolism10. Insulin resistance, oxidative stress, reticular stress, and cellular dysfunction are strongly associated to hepatic lipotoxicity11,12. On the other hand, fatty hepatocytes are the target of reactive oxygen species, rendering metabolites as lipid peroxides, protein carbonyls, and adducts of nucleic acids13. At the cellular level, fatty hepatocytes might undergo mitochondrial damage14, cellular senescence15, apoptosis16, pyroptosis12, and autophagia17, among other events.
Hepatocytes are highly responsible for metabolism, detoxification, and synthesis of a wide range of molecules. Many of these functions might be compromised by the lipid accumulation observed in steatosis. Therefore, it is of great importance to have reproducible tools that allow an accurate evaluation of steatosis. In this sense, in vitro models are readily applicable and highly reproducible. Steatosis in vitro has been used with different goals16,18,19. The HepG2 cells are widely used as hepatocyte cell line. It has advantages such as being easy to culture and well characterized. Perhaps, the only disadvantage of HepG2 cells is the fact that it is a carcinogenic cell line, so this must be considered when analyzing the outcomes. Here, the application of a mixture of fatty acids widely used in cell culture: palmitic acid (PA) and oleic acid (OA) is shown. Both PA and OA offer different outcomes in culture20. PA (C 16:0) is the most common saturated fatty acid obtained from the diet16. PA is considered as a biomarker of de-novo lipogenesis, a crucial step in the development of NAFLD21. PA is shown to be highly toxic22; therefore, it might not be recommended to induce steatosis in vitro. OA (C 18:1) is a monounsaturated fatty acid. In contrast to PA, OA has been suggested to possess anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties, being able to counteract PA12. Both PA and OA are the main fatty acids present in the triglycerides, regardless of the condition of health or disease16. Table 1 provides examples of the hepatocyte culture with PA, OA, and their mixture, as well as the outcomes reported12,23,24,25,26,27. Other fatty acids have also been used in hepatocyte culture, including stearic acid (C 18:0)28,29,30, linoleic acid (C 18:1)28,30,31 and its conjugates (CLA)28,32, palmitoleic acid (C 16:1)29. However, their use is least frequently reported in the literature, perhaps because their hepatic abundance is lower than PA and OA16.
In conjunction, both fatty acids resemble steatosis in vitro, providing proliferating cells, with increased cell death and lower viability compared with control conditions. It is worth mentioning that the respective salts of these fatty acids are available and can be used as well. One of the main problems when assessing lipid overload in hepatocyte cell culture is given in the differentiation between toxicological models and a model that best represent steatosis. Many models can be accounted in the first case. In fact, the use of PA alone might be considered among them, and the high mortality is the most evident outcome12,16,23,24,25,26,27. The use of high doses even in the case of OA can also be considered as a toxicologic model. The protocol shown here is in higher accordance with steatosis development since it shows low mortality compared with that observed in other models and allows it to be followed during several days with progressive lipid accumulation as it occurs in NAFLD. The possibility to assess mild and severe steatosis through experimental conditions is considered another advantage.
| Fatty acids | Conditions | Outcomes | Reference | ||
| PA | Concentration: 200 μM | Lipid accumulation | Yan et al, 201925. | ||
| Time exposure: 24 h | Hepatocyte damage | ||||
| Transaminases elevation | |||||
| PA | Concentration: 50, 100 and 200 μM | Lipid accumulation | Xing et al, 201924. | ||
| Time exposure: 24 h | |||||
| PA | Concentration: 250 μM , 500 μM , 750 μM and 1,000 μM | Lipid accumulation | Wang et al, 202026. | ||
| Time exposure: 24 h | Progressive reduction of cell viability | ||||
| Mix of OA/PA | Concentration: 1 mM | Lipid accumulation | Xiao et al, 202027. | ||
| Time exposure: 24 h | Does not report lipotoxicity | ||||
| Rate: 2OA:1PA | |||||
| Mix of OA/PA | First stimulation with 200 μM and 400 μM of PA and then second stimulation with 200 μM of OA | Lipid accumulation. | Zeng et al, 202012. | ||
| Concentration:400 μM PA: 200 μM OA | Evidence of lipotoxicity induced by PA was reduced by stimulation of OA. | ||||
| Rate: 2PA:1OA | |||||
| Time exposure: 24 h | |||||
| Mix of OA/PA | Concentration: 400 μM PA: 200 μM OA | Lipid accumulation | Chen et al, 201823. | ||
| Rate: 2PA:1OA | |||||
| Time exposure: 24 h | |||||
| Mix of OA/PA | Concentration :50 and 500 μM | Generation of two types of steatosis: mild steatosis and severe steatosis. | Campos and Guzmán 2021 | ||
| Rate: 2PA:1OA | Simulates chronic exposition of lipid overload | ||||
| Time exposure: 24 h, 2 days,3 days and 4 days. | |||||
Table 1. Hepatocyte culture in steatogenic conditions. The table presents the type of fatty acid used, the conditions maintained, and the observed outcomes in hepatocyte culture. PA: Palmitic acid. OA: Oleic acid.
Finally, this model is applicable not only to the study of steatosis and fatty liver, but also to the hepatic metabolic, synthetic, and detoxification pathways in the context of steatosis. Also, in vitro induced steatosis might provide evidence for the identification of potential markers of the disease as well as therapeutic targets.
Protocol
1. Standard and conditioned medium preparation
- To prepare standard RPMI 1640, supplement RPMI 1640 culture medium with 10% (v/v) of fetal bovine serum (FBS, previously heat inactivated) and 1% (v/v) of Penicillin-Streptomycin solution. Store the medium at 4 °C.Sterilize by using 0.22 µm filters.
- To prepare palmitate stock solution, prepare a 50 mM solution of palmitate in the standard RPMI 1640 previously supplemented with 1% of bovine serum albumin (lipid free). A volume of 5-10 mL of this stock will be sufficient. Sterilize the stock solution by using 0.22 µm filters. Store at 4 °C protected from light for up to 1 month.
- To prepare oleate stock solution, prepare a 50 mM solution of oleate in the standard RPMI 1640 previously supplemented with 1% of bovine serum albumin (lipid free). A volume of 10 mL will be sufficient. Sterilize the stock solution by using 0.22 µm filters. Store at -20 °C protected from light for up to 1 month.
- To prepare steatogenic medium from the previously prepared stocks, prepare a 1-part palmitate: 2-part oleate steatogenic medium at two possible levels: mild and severe steatosis.
- Mild Steatosis: Prepare 100 mL of a 1-part palmitate: 2-part oleate (50 µM) mix in standard RPMI 1640. Sterilize by using 0.22 µm filters. Store at 4 °C for up to 1 week.
- Severe Steatosis: Prepare 100 mL of a 1-part palmitate: 2-part oleate (500 µM) mix in standard RPMI 1640. Sterilize by using 0.22 µm filters. Store at 4 °C for up to 1 week.
- Alternative preparation for the stock solutions.
- Prepare both stock solutions using the respective fatty acids by using free lipid albumin as indicated above.
- When lacking free lipid albumin, use palmitate and oleate salts.
- Dissolve either palmitate or oleate in 2 mL of absolute ethanol and then mix in the final volume of standard RPMI 1640 (5-10 mL). Dissolve oleate directly by stirring in standard RPMI 1640 culture medium.
- Allow evaporation of ethanol by incubating in a water bath at 70 °C; mix thoroughly.
- In every case, sterilize both stock solutions using 0.22 µm filters. Store palmitate stock solution at 4 °C and oleate stock solution at - 20 °C. Protect both solutions from light. These solutions are stable for 1 month.
2. Pre-culture
- Seed 100,000 HepG2 cells per well in a 24-well plate. Add 1 mL of standard RPMI 1640.
- Pre-incubate at 37 °C and 5% CO2 for 24 h, allowing cell attachment.
3. Steatogenic culture
- After pre-culture, discard the standard RPMI 1640 medium and add the steatogenic medium accordingly.
- Discard the supernatant and add fresh steatogenic medium every 24 h.
4. Viability and mortality assessment
- Seed 100,000 HepG2 cells per well in a 24-well plate. Add 1 mL of standard RPMI 1640.
- Pre-incubate for 24 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
- Change standard RPMI 1640 medium for the steatogenic medium.
- Incubate for 24 h, 2 days, 3 days, and 4 days refreshing the steatogenic medium every 24 h.
- After the appropriate time, discard the supernatant.
- Detach cells from the well by adding 500 µL of 0.05% Trypsin-EDTA. Incubate for 5 min at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
- Collect the resuspended cells in a microtube.
- Centrifuge at 300 x g and discard the supernatant.
- Add 200 µL of standard RPMI 1640 and resuspend the cells.
- Add 15 µL of 0.4% Trypan blue solution in a fresh microtube. Mix with 15 µL of the previous cell suspension.
- Count the stained and non-stained cells in a hemocytometer.
- Calculate the viability and mortality rates accordingly.
Viability =
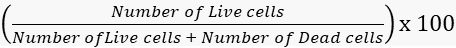
Mortality =
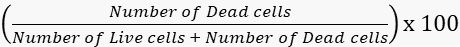
5. Lipid staining with Oil-Red O
- Put a cell culture coverslip in every well in a 24-well plate.
- Seed 100,000 HepG2 cells per well. Add 1 mL of standard RPMI 1640.
- Pre-incubate at 37 °C and 5% CO2 for 24 h.
- Change standard RPMI 1640 medium for the steatogenic medium.
- Incubate for 24 h, 2 days, 3 days, and 4 days, refreshing the steatogenic medium every 24 h.
- After the appropriate time, discard the supernatant.
- Wash with 1 mL of phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Discard the supernatant.
- Fix with 1 mL of 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS.
- Incubate for 1 h at room temperature.
- Discard the excess of paraformaldehyde.
- Rinse the cells with 1 mL of distilled water.
- Add 1 mL of 70% isopropanol and incubate for 5 min.
- Discard the excess of isopropanol. A PBS wash is not needed at this point.
- Add 1 mL of Oil-red O solution and incubate for 30 min.
- Discard the excess of the Oil-red O solution.
- Rinse with 1 mL of distilled water.
- Add 500 µL of hematoxylin solution. Incubate for 3 min.
- Discard the excess of hematoxylin solution.
- Rinse with 1 mL of distilled water.
- Observe under the microscope at a magnification of 400x (Objective 40x, Ocular 10x).
6. Morphometric assessment of lipid contents
- Randomly select and capture photographs of 10 optical fields from the complete area of the well. Repeat for every well.
- Assess the percentage of red stained area using the Color Threshold tool in the ImageJ software according to Ferreira and Rasband33.
- Compare the stained area with the complete area of the optical field using the Analyze Particles tool in the ImageJ software according to Ferreira and Rasband33.
- Calculate the average percentage of every well.
Results
Hepatocytes cultured in the steatogenic medium display growth all over the surface of the well; however, fatty hepatocytes show lower growth rate compared with cells cultured in control medium. The proposed ratio and concentration of OA and PA, guarantee cell survival during culture. Seeding 1 x 105 cells per well in 24-well plates provides optimum confluence as shown in Figure 1.
Viability in cultured cells was lower in the steatogenic groups, Mild and...
Discussion
This protocol is intended to provide a strategy to study steatosis in vitro. Cell culture is a powerful tool to study cellular, molecular, biochemical, and toxicological aspects of the cells exposed to different conditions. With this approach, steatosis can be visualized not only as a stage of the complex disease that is MAFLD, but also as the hepatocyte overexposure to lipids and the possible outcomes resulting from such exposure. Therefore, its application is not restricted to the physiopathology of MAFLD, but...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (Conacyt, CB-221137). Adriana Campos is a doctoral student at Programa de Doctorado en Ciencias Biomédicas, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, and was supported by Conacyt (CVU: 1002502).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Biosafety cabinet | ESCO Airstream | AC2-452+C2:C26 | Class II Type A2 Biological Safety Cabinet |
| Bottle top filter | Corning, US | 430513 | Non-pyrogenic, polystyrene, sterile. 1 filter/Bag. 0.22 μm, 500 mL. |
| Bovine serum albimun (BSA) | Gold Biotechnology, US | A-421-10 | BSA Fatty Acid Free for cell culture |
| Culture media RPMI 1640 | ThermoFisher-Gibco, US | 31800-022 | - |
| Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) | ThermoFisher-Gibco, US | A4766801 | - |
| Hemocytometer | Marienfeld, DE | 640010 | - |
| HepG2 cell line | ATCC, US | HB-8065 | Hepatocellular carcinoma human cells. |
| Humidified incubator | Thermo Electronic Corporation,US | Model: 3110 | Temperature (37 °C ± 1 °C), humidity (90% ± 5%) , CO2 (5% ± 1%) |
| Inverted microscope Eclipse | NIKON, JPN | Model: TE2000-S | - |
| Isopropanol | Sigma-Aldrich, US | I9030-4L | - |
| Oil Red O Kit | Abcam, US | ab150678 | Kit for histological visualization of neutral fat. |
| Paraformaldehyde | Sigma-Aldrich, US | P6148-500G | - |
| Penicillin/streptomycin | ThermoFisher-Gibco, US | 15140-122 | Antibiotics 10,000 U/mL Penicillin, 10,000 μg/mL Streptomycin |
| pH meter | Beckman, US | Model: 360 PH/Temp/MV Meter | - |
| Phosphate buffered saline | ThermoFisher-Gibco, US | 10010-023 | - |
| Serological Pipettes | Sarstedt, AUS | 86.1253.001 | Non-pyrogenic, sterile, 5 mL |
| Serological Pipettes | Sarstedt, AUS | 86.1254.001 | Non-pyrogenic, sterile, 10 mL |
| Sodium bicarbonate | Sigma-Aldrich, US | S5761-1KG | Preparation of culture media |
| Sodium oleate | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, US | sc-215879A | - |
| Sodium palmitate | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, US | sc-215881 | - |
| Syring filter | Corning, US | 431219 | Non-pyrogenic, sterile, 28 mm, 0.2 μm. |
| Trypan Blue | Sigma-Aldrich, US | T6146-25G | - |
| Trypsin 0.05% /EDTA 0.53 mM | Corning, US | 25-052-Cl | - |
| 24 well cell culture cluster | Corning, US | 3524 | Flat bottom with lid. Tissue culture treated. Nonpyrogenic, polystyrene, sterile. 1/Pack. |
| 96 well cell culture cluster | Corning, US | 3599 | Flat bottom with lid. Tissue culture treated. Nonpyrogenic, polystyrene, sterile. 1/Pack. |
References
- Younossi, Z. M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease - a global public health perspective. Journal of Hepatology. 70 (3), 531-544 (2019).
- Younossi, Z., et al. Global perspectives on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 69 (6), 2672-2682 (2019).
- Eslam, M., et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. Journal of Hepatology. 73 (1), 202-209 (2020).
- Eslam, M., Sanyal, A. J., George, J. MAFLD: A consensus-driven proposed nomenclature for metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 158 (7), 1999-2014 (2020).
- Chalasani, N., et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology. 67 (1), 328-357 (2018).
- Calzadilla Bertot, L., Adams, L. A. The natural course of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. International Journal of Molecular Science. 17 (5), 774 (2016).
- Reccia, I., et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A sign of systemic disease. Metabolism. 72, 94-108 (2017).
- Tomita, K., et al. Free cholesterol accumulation in hepatic stellate cells: Mechanism of liver fibrosis aggravation in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Hepatology. 59 (1), 154-169 (2014).
- Byrne, C. D., Targher, G. Nafld: A multisystem disease. Journal of Hepatology. 62, 47-64 (2015).
- Ipsen, D. H., Lykkesfeldt, J., Tveden-Nyborg, P. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic lipid accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 75 (18), 3313-3327 (2018).
- Diehl, A. M., Day, C. Cause, pathogenesis, and treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. New England Journal of Medicine. 377 (21), 2063-2072 (2017).
- Zeng, X., et al. Oleic acid ameliorates palmitic acid induced hepatocellular lipotoxicity by inhibition of ER stress and pyroptosis. Nutrition and Metabolism. 17, 11 (2020).
- Ore, A., Akinloye, O. A. Oxidative stress and antioxidant biomarkers in clinical and experimental models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Medicina (Kaunas). 55 (2), 26 (2019).
- Paradies, G., Paradies, V., Ruggiero, F. M., Petrosillo, G. Oxidative stress, cardiolipin and mitochondrial dysfunction in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 20 (39), 14205-14218 (2014).
- Aravinthan, A., et al. Hepatocyte senescence predicts progression in non-alcohol-related fatty liver disease. Journal of Hepatology. 58 (3), 549-556 (2013).
- Gomez, M. J., et al. A human hepatocellular in vitro model to investigate steatosis. Chemico Biological Interactions. 165 (2), 106-116 (2007).
- Wu, W. K. K., Zhang, L., Chan, M. T. V. Autophagy, NAFLD and NAFLD-related HCC. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. 1061, 127-138 (2018).
- Levy, G., Cohen, M., Nahmias, Y. In vitro cell culture models of hepatic steatosis. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1250, 377-390 (2015).
- Kanuri, G., Bergheim, I. In vitro and in vivo models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). International Journal of Molecular Science. 14 (6), 11963-11980 (2013).
- Ricchi, M., et al. Differential effect of oleic and palmitic acid on lipid accumulation and apoptosis in cultured hepatocytes. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 24 (5), 830-840 (2009).
- Lee, Y., et al. Serial biomarkers of de novo lipogenesis fatty acids and incident heart failure in older adults: The cardiovascular health study. Journal of the American Heart Association. 9 (4), 014119 (2020).
- Alnahdi, A., John, A., Raza, H. Augmentation of glucotoxicity, oxidative stress, apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction in Hepg2 cells by palmitic acid. Nutrients. 11 (9), 1979 (2019).
- Chen, X., et al. Oleic acid protects saturated fatty acid mediated lipotoxicity in hepatocytes and rat of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Life Sciences. 203, 291-304 (2018).
- Xing, J. H., et al. NLRP3 inflammasome mediate palmitate-induced endothelial dysfunction. Life Sciences. 239, 116882 (2019).
- Yan, H., et al. Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 7 accelerates hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology. 46 (12), 1101-1110 (2019).
- Wang, J., Hu, R., Yin, C., Xiao, Y. Tanshinone IIA reduces palmitate-induced apoptosis via inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress in Hepg2 liver cells. Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology. 34 (2), 249-262 (2020).
- Xiao, Z., Chu, Y., Qin, W. IGFBP5 modulates lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity through activating ampk pathway in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Life Sciences. 256, 117997 (2020).
- Avila, G., et al. In vitro effects of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) on inflammatory functions of bovine monocytes. Journal of Dairy Science. 103 (9), 8554-8563 (2020).
- Malhi, H., Bronk, S. F., Werneburg, N. W., Gores, G. J. Free fatty acids induce JNK-dependent hepatocyte lipoapoptosis. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 281 (17), 12093-12101 (2006).
- Oh, J. M., et al. Effects of palmitic acid on TNF-alpha-induced cytotoxicity in SK-Hep-1 cells. Toxicology In Vitro: An International Journal Published in Association with BIBRA. 26 (6), 783-790 (2012).
- Stellavato, A., et al. In vitro assessment of nutraceutical compounds and novel nutraceutical formulations in a liver-steatosis-based model. Lipids in Health and Disease. 17 (1), 24 (2018).
- Pachikian, B. D., et al. Implication of trans-11, trans-13 conjugated linoleic acid in the development of hepatic steatosis. PLoS One. 13 (2), 0192447 (2018).
- Ferreira, T., Rasband, W. Analyze. ImageJ User Guide. , 132-135 (2012).
- Geng, Y., Wu, Z., Buist-Homan, M., Blokzijl, H., Moshage, H. Hesperetin protects against palmitate-induced cellular toxicity via induction of GRP78 in hepatocytes. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. , 404 (2020).
- Geng, Y., et al. Protective effect of metformin against palmitate-induced hepatic cell death. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - Molecular Basis of Disease. 1866 (3), 165621 (2020).
- Sarnyai, F., et al. Effect of cis- and trans-monounsaturated fatty acids on palmitate toxicity and on palmitate-induced accumulation of ceramides and diglycerides. International Journal of Molecular Science. 21 (7), 2626 (2020).
- Chen, J. W., et al. Tetrahydrocurcumin ameliorates free fatty acid-induced hepatic steatosis and improves insulin resistance in HepG2 cells. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis. 26 (3), 1075-1085 (2018).
- Burhans, M. S., et al. Hepatic oleate regulates adipose tissue lipogenesis and fatty acid oxidation. Journal of Lipid Research. 56 (2), 304-318 (2015).
- Abenavoli, L., Milanovic, M., Milic, N., Luzza, F., Giuffre, A. M. Olive oil antioxidants and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Reviews in Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 13 (8), 739-749 (2019).
- Nagarajan, S. R., et al. Lipid and glucose metabolism in hepatocyte cell lines and primary mouse hepatocytes: A comprehensive resource for in vitro studies of hepatic metabolism. American Journal of Physiology - Endocrinology and Metabolism. 316 (4), 578-589 (2019).
- Hodson, L., Skeaff, C. M., Fielding, B. A. Fatty acid composition of adipose tissue and blood in humans and its use as a biomarker of dietary intake. Progress in Lipid Research. 47 (5), 348-380 (2008).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved