A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Identification of Alternative Splicing and Polyadenylation in RNA-seq Data
In This Article
Summary
Alternative splicing (AS) and alternative polyadenylation (APA) expand the diversity of transcript isoforms and their products. Here, we describe bioinformatic protocols to analyze bulk RNA-seq and 3' end sequencing assays to detect and visualize AS and APA varying across experimental conditions.
Abstract
As well as the typical analysis of RNA-Seq to measure differential gene expression (DGE) across experimental/biological conditions, RNA-seq data can also be utilized to explore other complex regulatory mechanisms at the exon level. Alternative splicing and polyadenylation play a crucial role in the functional diversity of a gene by generating different isoforms to regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level, and limiting analyses to the whole gene level can miss this important regulatory layer. Here, we demonstrate detailed step by step analyses for identification and visualization of differential exon and polyadenylation site usage across conditions, using Bioconductor and other packages and functions, including DEXSeq, diffSplice from the Limma package, and rMATS.
Introduction
RNA-seq has been widely used over the years typically for estimating differential gene expression and gene discovery1. In addition, it can also be utilized to estimate varying exon level usage due to gene expressing different isoforms, hence contributing to a better understanding of gene regulation at the post-transcriptional level. The majority of eukaryotic genes generate different isoforms by alternative splicing (AS) to increase the diversity of mRNA expression. AS events can be divided into different patterns: skipping of complete exons (SE) where a ("cassette") exon is completely removed out of the transcript along with its flanking introns; alternative (donor) 5' splice site selection (A5SS) and alternative 3' (acceptor) splice site selection (A3SS) when two or more splice sites are present on either end of an exon; retention of introns (RI) when an intron is retained within the mature mRNA transcript and mutual exclusion of exon usage (MXE) where only one of the two available exons can be retained at a time2,3. Alternative polyadenylation (APA) also plays an important role in regulating gene expression using alternative poly (A) sites to generate multiple mRNA isoforms from a single transcript4. Most polyadenylation sites (pAs) are located in the 3' untranslated region (3' UTRs), generating mRNA isoforms with diverse 3' UTR lengths. As the 3' UTR is the central hub for recognizing regulatory elements, different 3' UTR lengths can affect mRNA localization, stability and translation5. There are a class of 3' end sequencing assays optimized to detect APA that differ in the details of the protocol6. The pipeline described here is designed for PolyA-seq, but can be adapted for other protocols as described.
In this study, we present a pipeline of differential exon analysis methods7,8 (Figure 1), which can be divided into two broad categories: exon-based (DEXSeq9, diffSplice10) and event-based (replicate Multivariate Analysis of Transcript Splicing (rMATS)11). The exon-based methods compare the fold change across conditions of individual exons, against a measure of overall gene fold change to call differentially expressed exon usage, and from that compute a gene-level measure of AS activity. Event-based methods use exon-intron-spanning junction reads to detect and classify specific splicing events such as exon skipping or retention of introns, and distinguish these AS types in the output3. Thus, these methods provide complementary views for a complete analysis of AS12,13. We selected DEXSeq (based on the DESeq214 DGE package) and diffSplice (based on the Limma10 DGE package) for the study as they are amongst the most widely used packages for differential splicing analysis. rMATS was chosen as a popular method for event-based analysis. Another popular event-based method is MISO (Mixture of Isoforms)1. For APA we adapt the exon-based approach.
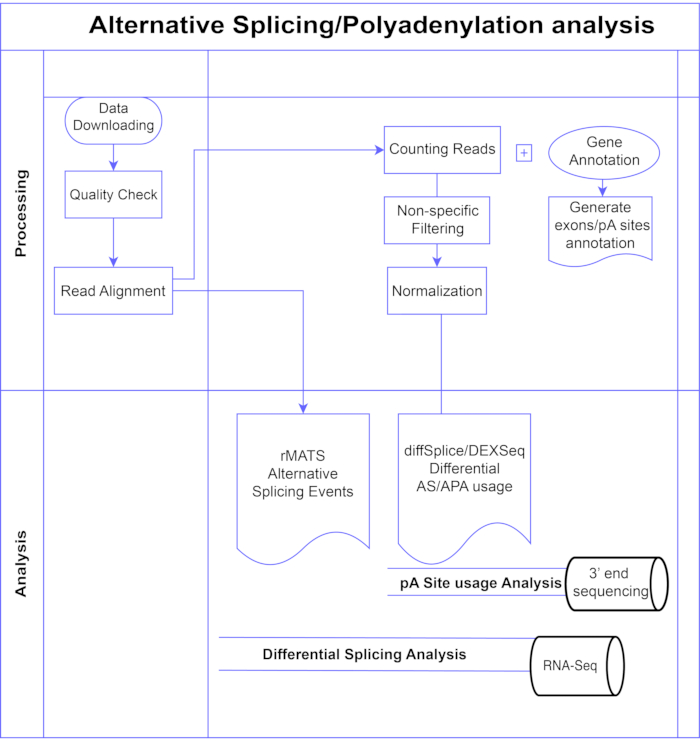
Figure 1. Analysis pipeline. Flowchart of the steps used in the analysis. Steps include: obtaining the data, performing quality checks and read alignment followed by counting reads using annotations for known exons, introns and pA sites, filtering to remove low counts and normalization. PolyA-seq data was analysed for alternative pA sites using diffSplice/DEXSeq methods, bulk RNA-Seq was analysed for alternative splicing at the exon level with diffSplice/DEXseq methods, and AS events analysed with rMATS. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
The RNA-seq data used in this survey was acquired from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) (GSE138691)15. We used mouse RNA-seq data from this study with two condition groups: wild-type (WT) and Muscleblind-like type 1 knockout (Mbnl1 KO) with three replicates each. To demonstrate differential polyadenylation site usage analysis, we obtained mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs) PolyA-seq data (GEO Accession GSE60487)16. The data has four condition groups: Wild-type (WT), Muscleblind-like type1/type 2 double knockout (Mbnl1/2 DKO), Mbnl 1/2 DKO with Mbnl3 knockdown (KD) and Mbnl1/2 DKO with Mbnl3 control (Ctrl). Each condition group consists of two replicates.
| GEO Accession | SRA Run number | Sample name | Condition | Replicate | Tissue | Sequencing | Read length | |
| RNA-Seq | GSM4116218 | SRR10261601 | Mbnl1KO_Thymus_1 | Mbnl1 knockout | Rep 1 | Thymus | Paired-end | 100 bp |
| GSM4116219 | SRR10261602 | Mbnl1KO_Thymus_2 | Mbnl1 knockout | Rep 2 | Thymus | Paired-end | 100 bp | |
| GSM4116220 | SRR10261603 | Mbnl1KO_Thymus_3 | Mbnl1 knockout | Rep 3 | Thymus | Paired-end | 100 bp | |
| GSM4116221 | SRR10261604 | WT_Thymus_1 | Wild type | Rep 1 | Thymus | Paired-end | 100 bp | |
| GSM4116222 | SRR10261605 | WT_Thymus_2 | Wild type | Rep 2 | Thymus | Paired-end | 100 bp | |
| GSM4116223 | SRR10261606 | WT_Thymus_3 | Wild type | Rep 3 | Thymus | Paired-end | 100 bp | |
| 3P-Seq | GSM1480973 | SRR1553129 | WT_1 | Wild type (WT) | Rep 1 | Mouse embryonic Fibroblasts (MEFs) | Single-end | 40 bp |
| GSM1480974 | SRR1553130 | WT_2 | Wild type (WT) | Rep 2 | Mouse embryonic Fibroblasts (MEFs) | Single-end | 40 bp | |
| GSM1480975 | SRR1553131 | DKO_1 | Mbnl 1/2 double knockout (DKO) | Rep 1 | Mouse embryonic Fibroblasts (MEFs) | Single-end | 40 bp | |
| GSM1480976 | SRR1553132 | DKO_2 | Mbnl 1/2 double knockout (DKO) | Rep 2 | Mouse embryonic Fibroblasts (MEFs) | Single-end | 40 bp | |
| GSM1480977 | SRR1553133 | DKOsiRNA_1 | Mbnl 1/2 double knockout with Mbnl 3 siRNA (KD) | Rep 1 | Mouse embryonic Fibroblasts (MEFs) | Single-end | 40 bp | |
| GSM1480978 | SRR1553134 | DKOsiRNA_2 | Mbnl 1/2 double knockout with Mbnl 3 siRNA (KD) | Rep 2 | Mouse embryonic Fibroblasts (MEFs) | Single-end | 36 bp | |
| GSM1480979 | SRR1553135 | DKONTsiRNA_1 | Mbnl 1/2 double knockout with non-targeting siRNA (Ctrl) | Rep 1 | Mouse embryonic Fibroblasts (MEFs) | Single-end | 40 bp | |
| GSM1480980 | SRR1553136 | DKONTsiRNA_2 | Mbnl 1/2 double knockout with non-targeting siRNA (Ctrl) | Rep 2 | Mouse embryonic Fibroblasts (MEFs) | Single-end | 40 bp |
Table 1. Summary of RNA-Seq and PolyA-seq datasets used for the analysis.
Protocol
1. Installation of tools and R packages used in the analysis
- Conda is a popular and flexible package manager that allows convenient installation of packages with their dependencies across all platforms. Use 'Anaconda' (conda package manager) to install 'conda' which can be used to install the tools/packages required for the analysis.
- Download 'Anaconda' according to the system requirements from https://www.anaconda.com/products/individual#Downloads and install it by following the prompts in graphical installer. Install all required packages using ‘conda’ by typing the following at the Linux command-line.
conda install -c daler sratoolkit
conda install -c conda-forge parallel
conda install -c bioconda star bowtie fastqc rmats rmats2sashimiplot samtools fasterq-dump cutadapt bedtools deeptools - To download all the R packages used in the protocol, type the following code in the R console (started on the Linux command-line by typing 'R') or Rstudio console.
bioc_packages<- c("DEXSeq", "Rsubread", "EnhancedVolcano", "edgeR", "limma", "maser","GenomicRanges")
packages<- c("magrittr", "rtracklayer", "tidyverse", "openxlsx", "BiocManager")
#Install if not already installed
installed_packages<-packages%in% rownames(installed.packages())
installed_bioc_packages<-bioc_packages%in% rownames(installed.packages())
if(any(installed_packages==FALSE)) {
install.packages(packages[!installed_packages],dependencies=TRUE)
BiocManager::install(packages[!installed_bioc_packages], dependencies=TRUE)
}
NOTE: In this computational protocol, commands will be given as either R Notebook files (files with extension ".Rmd"), R code files (files with extension ".R"), or Linux Bash shell scripts (files with extension ".sh"). R Notebook (Rmd) files should be opened in RStudio using File|Open File…, and individual code chunks (which may be R commands or Bash shell commands) then run interactively by clicking the green arrow at the upper right. R code files can be run by opening in RStudio, or on the Linux command-line by prefacing with "Rscript", e.g. Rscript example.R. Shell scripts are run on the Linux command-line by prefacing the script with the "sh" command e.g. sh example.sh.
2. Alternative splicing (AS) analysis using RNA-seq
- Data downloading and pre-processing
NOTE: The code snippets annotated below are available in the supplementary code file "AS_analysis_RNASeq.Rmd", to follow the individual steps interactively, and are also provided as a bash script to be run in batch on the Linux command-line (sh downloading_data_preprocessing.sh).- Downloading the raw data.
- Download the raw data from Sequence Read Archive (SRA) using the 'prefetch' command from SRA toolkit (v2.10.8)17. Give the SRA Accession IDs in sequence in the following command to download them in parallel using GNU parallel utility18. To download SRA files of accession ids from SRR10261601 to SRR10261606 in parallel, use the following on the Linux command-line.
seq 10261601 10261606 | parallel prefetch SRR{} - Extract the fastq files from the archive using 'fastq-dump' function from SRA toolkit. Use GNU parallel and give the names of all SRA files together.
parallel -j 3 fastq-dump --gzip --skip-technical --read-filter pass --dumpbase --split-e --clip --origfmt {} ::: <name of sra files together> - Download the reference genome and annotations for Mouse (Genome assembly GRCm39) from www.ensembl.org using the following at the Linux command-line.
wget -nv -O annotation.gtf.gz http://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-103/gtf/mus_musculus/Mus_musculus.GRCm39.103.gtf.gz \ && gunzip -f annotation.gtf.gz
wget -nv -O genome.fa.gz http://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-103/fasta/mus_musculus/dna/Mus_musculus.GRCm39.dna.primary_assembly.fa.gz \ && gunzip -f genome.fa.gz
GTF=$(readlink -f annotation.gtf)
GENOME=$(readlink -f genome.fa)
- Download the raw data from Sequence Read Archive (SRA) using the 'prefetch' command from SRA toolkit (v2.10.8)17. Give the SRA Accession IDs in sequence in the following command to download them in parallel using GNU parallel utility18. To download SRA files of accession ids from SRR10261601 to SRR10261606 in parallel, use the following on the Linux command-line.
- Pre-processing and mapping reads to the genome assembly
- Quality Control. Assess the quality of raw reads with FASTQC (FASTQ Quality Check v0.11.9)19. Create an output folder and run fastqc with parallel on multiple input fasta files. This step will generate a quality report for each sample. Examine the reports to ensure the quality of reads is acceptable before doing further analysis. (Refer to the user manual for understanding the reports at https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/)
mkdir fastqc_out
parallel "fastqc {} -o fastqc_out" ::: $RAW_DATA/*.fastq.gz
NOTE: If necessary, perform adapter trimming with 'cutadapt'20 or 'trimmomatic'21 to remove sequencing into flanking adapters, which varies based on RNA fragment size and read length. In this analysis we skipped this step as the fraction of reads affected was minimal. - Read alignment. The next step in pre-processing includes mapping the reads to the reference genome. Firstly, build the index for the reference genome using the 'genomeGenerate' function of STAR22 and then align the raw reads to the reference (alternatively prebuilt indexes are available from the STAR website and can be used directly for alignment). Run the following commands at the Linux command-line.
#Build STAR index
GDIR=STAR_indices
mkdir $GDIR
STAR --runMode genomeGenerate --genomeFastaFiles $GENOME --sjdbGTFfile $GTF --runThreadN 8 --genomeDir $GDIR
ODIR=results/mapping
mkdir -p $ODIR
#Align reads to the genome
for fq1 in $RAW_DATA/*R1.fastq.gz;
do
fq2=$(echo $fq1| sed 's/1.fastq.gz/2.fastq.gz/g');
OUTPUT=$(basename ${fq1}| sed 's/R1.fastq.gz//g');
STAR --genomeDir $GDIR \
--runThreadN 12 \
--readFilesCommand zcat \
--readFilesIn ${fq1}${fq2}\
--outFileNamePrefix $ODIR\/${OUTPUT} \
--outSAMtype BAM SortedByCoordinate \
--outSAMunmapped Within \
--outSAMattributes Standard
Done
NOTE: The STAR aligner will generate and sort BAM (Binary Alignment Map) files for each sample after read alignment. Bam files must be sorted before proceeding to further steps.
- Quality Control. Assess the quality of raw reads with FASTQC (FASTQ Quality Check v0.11.9)19. Create an output folder and run fastqc with parallel on multiple input fasta files. This step will generate a quality report for each sample. Examine the reports to ensure the quality of reads is acceptable before doing further analysis. (Refer to the user manual for understanding the reports at https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/)
- Downloading the raw data.
- Preparing Exon annotations.
- Run the supplementary code file "prepare_mm_exon_annotation.R" with the downloaded annotation in GTF (Gene transfer format) format to prepare the annotations. To run, type the following at the Linux command-line.
Rscript prepare_mm_exon_annotation.R annotation.gtf
NOTE: The GTF file contains multiple exon entries for different isoforms. This file is used to "collapse" the multiple transcript IDs for each exon. It is an important step to define exon counting bins.
- Run the supplementary code file "prepare_mm_exon_annotation.R" with the downloaded annotation in GTF (Gene transfer format) format to prepare the annotations. To run, type the following at the Linux command-line.
- Counting Reads. The next step is to count the number of reads mapped to different transcripts/exons. See Supplementary file: "AS_analysis_RNASeq.Rmd".
- Load required libraries:
packages<- c("Rsubread","tidyverse", "magrittr", "EnhancedVolcano", "edgeR","openxlsx")
invisible(lapply(packages, library, character.only=TRUE)) - Load the processed annotation file obtained from previous step (2.2).
load("mm_exon_anno.RData") - Read all bam files obtained in step 2.2.2 as input for ‘featureCounts’ to count reads. Read the folder containing bam files by first listing each file from the directory that ends with .bam. Use 'featureCounts' from the Rsubread package which takes bam files and processed GTF annotation (reference) as input to generate a matrix of counts associated with each feature with rows representing exons(features) and columns representing samples.
countData <- dir("bams", pattern=".bam$", full.names=T) %>%
featureCounts(annot.ext=anno,
isGTFAnnotationFile=FALSE,
minMQS=0,useMetaFeatures=FALSE,
allowMultiOverlap=TRUE,
largestOverlap=TRUE,
countMultiMappingReads=FALSE,
primaryOnly=TRUE,
isPairedEnd=TRUE,
nthreads=12) - Next, perform non-specific filtering to remove lowly expressed exons (“non-specific” indicates that the experimental condition information is not used in the filtering, to avoid selection biases). Transform the data from raw scale to counts per million (cpm) using the cpm function from 'edgeR' package23 and keep exons with counts greater than a settable threshold (for this dataset one cpm is used) in at least three samples. Also remove genes with only one exon.
# Non-specific filtering: Remove the exons with low counts
isexpr<- rownames(countData$counts)[rowSums(cpm(countData$counts)>1) >=3]
countData$counts<-countData$counts[rownames(countData$counts) %in%isexpr, ]
anno<-anno%>% filter(GeneID%in% rownames(countData$counts))
# Remove genes with only 1 site and NA in geneIDs
dn<-anno%>%group_by(GeneID)%>%summarise(nsites=n())%>% filter(nsites>1&!is.na(GeneID))
anno<-anno%>% filter(GeneID%in%dn$GeneID)
countData$counts<-countData$counts[rownames(countData$counts) %in%anno$GeneID, ]
NOTE: Check the required parameters for featureCounts when using different data, for example, for single-end reads, set 'isPairedEnd = FALSE'. Refer to RSubread user-guide to choose the options for your data, and see the Discussion section below.
- Load required libraries:
- Differential splicing and exon usage analysis. We describe two alternatives for this step: DEXSeq and DiffSplice. Either can be used and give similar results. For consistency, select DEXSeq if you prefer a DESeq2 package for DGE and use DiffSplice for a Limma-based DGE analysis. See Supplementary file: "AS_analysis_RNASeq.Rmd".
- Using DEXSeq package for differential exon analysis.
- Load library and create a sample table to define the experimental design.
library(DEXSeq)
sampleTable<-data.frame(row.names= c("Mbnl1KO_Thymus_1", "Mbnl1KO_Thymus_2", "Mbnl1KO_Thymus_3", "WT_Thymus_1", "WT_Thymus_2", "WT_Thymus_3"), condition= rep(c("Mbnl1_KO", "WT"),c(3,3)), libType= rep(c("paired-end")))
NOTE: The row names should be consistent with the bam file names used by featureCounts to count the reads. sampleTable consists of details of each sample which includes: library-type and condition. This is required to define the contrasts or test group for detecting differential usage. - Prepare the exon information file. Exon information in the form of GRanges (genomic ranges) objects (https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/GenomicRanges.html) is required as an input to create the DEXSeq object in the next step. Match the gene Ids with the read counts to create exoninfo object.
exoninfo<-anno[anno$GeneID%in% rownames(countData$counts),]
exoninfo<-GRanges(seqnames=anno$Chr,
ranges=IRanges(start=anno$Start, end=anno$End, width=anno$Width),strand=Rle(anno$Strand))
mcols(exoninfo)$TranscriptIDs<-anno$TranscriptIDs
mcols(exoninfo)$Ticker<-anno$Ticker
mcols(exoninfo)$ExonID<-anno$ExonID
mcols(exoninfo)$n<-anno$n
mcols(exoninfo)$GeneID<-anno$GeneID
transcripts_l= strsplit(exoninfo$TranscriptIDs, "\\,")
save(countData, sampleTable, exoninfo, transcripts_l, file="AS_countdata.RData") - Create DEXSeq object using DEXSeqDataSet function. The DEXSeq object collects together read counts, exon feature information, and sample information. Use the read counts generated in step 3 and the exon information obtained from the previous step to create the DEXSeq object from the count matrix. The sampleData argument takes a data frame input defining the samples (and their attributes: library type and condition), 'design' uses sampleData to generate a design matrix for the differential testing using model formula notation. Note that a significant interaction term, condition:exon, indicates that the fraction of reads over a gene falling on a particular exon depends on the experimental condition i.e. there is AS. See DEXSeq documentation for a full description of setting the model formula for more complex experimental designs. For feature information, exon ids, corresponding gene and transcripts are required.
dxd<-DEXSeqDataSet(countData$counts,sampleData=sampleTable, design=~sample+exon+condition:exon,featureID=exoninfo$ExonID,groupID=exoninfo$GeneID,featureRanges=exoninfo, transcripts=transcripts_l) - Normalization and dispersion estimation. Next, perform normalization between samples and estimate the variance of the data, due to both Poisson count noise from the discrete nature of RNA-seq and biological variability, using the following commands.
dxd %<>% estimateSizeFactors %>% estimateDispersions %T>% plotDispEsts - Test for differential usage. After the estimation of variation, test for differential exon usage for each gene and generate the results.
dxd%<>%testForDEU%>%estimateExonFoldChanges(fitExpToVar=
"condition")#Estimate fold changes
dxr=DEXSeqResults(dxd) - Visualize splicing events for selected genes using the following command.
plotDEXSeq(dxr,"Wnk1", displayTranscripts=TRUE, splicing=TRUE,legend
=TRUE,cex.axis=1.2,cex=1.3,lwd=2)
Examine the R Notebook file "AS_analysis_RNASeq.Rmd" to generate additional plots for genes of interest and to generate volcano plots at different thresholds.
- Load library and create a sample table to define the experimental design.
- Using diffSplice from Limma to identify differential splicing. Follow the R Notebook file "AS_analysis_RNASeq.Rmd". Ensure steps 2.1-2.3 have been followed to prepare input files before proceeding further.
- Load libraries
library(limma)
library(edgeR) - Non-specific filtering. Extract the matrix of read counts obtained in 2.3. Create a list of features using 'DGEList' function from edgeR package, where rows represent genes and columns represent samples.
mycounts=countData$counts
#Change the rownames of the countdata to exon Ids instead of genes for unique rownames.
rownames(mycounts) = exoninfo$ExonID
dge<-DGEList(counts=mycounts)
#Filtering
isexpr<- rowSums(cpm(dge)>1) >=3
dge<-dge[isexpr,,keep.lib.sizes=FALSE]
#Extract the exon annotations for only transcripts meeting non-specific filter
exoninfo=anno%>% filter(ExonID%in% rownames(dge$counts))
#Convert the exoninfo into GRanges object
exoninfo1<-GRanges(seqnames=exoninfo$Chr,
ranges=IRanges(start=exoninfo$Start, end=exoninfo$End, width=exoninfo$Width),strand=Rle(exoninfo$Strand))
mcols(exoninfo1)$TranscriptIDs<-exoninfo$TranscriptIDs
mcols(exoninfo1)$Ticker<-exoninfo$Ticker
mcols(exoninfo1)$ExonID<-exoninfo$ExonID
mcols(exoninfo1)$n<-exoninfo$n
mcols(exoninfo1)$GeneID<-exoninfo$GeneID
transcripts_l= strsplit(exoninfo1$TranscriptIDs, "\\,")
NOTE: As a non-specific filtering step, counts are filtered by cpm < 1 in x out of n samples, where x is the minimum number of replicates in any condition. n = 6 and x = 3 for this example data. - Normalize the counts across samples, with 'calcNormFactors' function from 'edgeR' package using Trimmed Mean of M values (TMM normalization method)24 It will compute scaling factors to adjust library sizes.
dge<-calcNormFactors(dge) - Use sampleTable as generated in step 2.4.1.1 and create the design matrix. The design matrix characterizes the design. See the Limma User Guide (https://www.bioconductor.org/packages/devel/bioc/vignettes/limma/inst/doc/usersguide.pdf) chapters 8 & 9 for details on design matrices for more advanced experimental designs.
Treat<- factor(sampleTable$condition)
design<- model.matrix(~0+Treat)
colnames(design) <- levels(Treat) - Fit a linear model per exon. Run 'voom' function of 'limma' package to process RNA-seq data to estimate variance and generate precision weights to correct for Poisson count noise, and transform the exon-level counts to log2-counts per million (logCPM). Then run linear modelling using 'lmfit' function to fit linear models to the expression data for each exon. Compute empirical Bayes statistics for fitted model using 'eBayes' function to detect differential exon expression. Next, define a contrast matrix for the experimental comparisons of interest. Use 'contrasts.fit' to obtain coefficients and standard errors for each pair of comparison.
v<-voom(dge,design,plot=FALSE)
fit<-lmFit(v,design)
fit<-eBayes(fit)
colnames(fit)
cont.matrix<-makeContrasts(
Mbnl1_KO_WT=Mbnl1_KO-WT,
levels=design)
fit2<-contrasts.fit(fit,cont.matrix) - Differential splicing analysis. Run 'diffSplice' on the fitted model to test the differences in exon usage of genes between wild-type and knockout and explore the top ranked results using 'topSplice' function: test="t" gives a ranking of AS exons, test="simes" gives a ranking of genes.
ex<-diffSplice(fit2,geneid=exoninfo$GeneID,exonid=exoninfo$ExonID)
ts<-topSplice(ex,n=Inf,FDR=0.1, test="t", sort.by="logFC")
tg<-topSplice(ex,n=Inf,FDR=0.1, test="simes") - Visualization. Plot the results with the 'plotSplice' function, giving gene of interest in the geneid argument. Save the top results sorted by log Fold change into an object and generate a volcano plot to exhibit the exons.
plotSplice(ex,geneid="Wnk1", FDR=0.1)
#Volcano plot
EnhancedVolcano(ts,lab=ts$ExonID,selectLab= head((ts$ExonID),2000), xlab= bquote(~Log[2]~'fold change'), x='logFC', y='P.Value', title='Volcano Plot', subtitle='Mbnl1_KO vs WT (Limma_diffSplice)', FCcutoff=2, labSize=4,legendPosition="right", caption= bquote(~Log[2]~"Fold change cutoff, 2; FDR 10%"))
- Load libraries
- Using rMATS
- Ensure the latest version of rMATS v4.1.1 (also known as rMATS turbo due to the reduced processing time and less requirements of memory) is installed either using conda or github (https://github.com/Xinglab/rmats-turbo/releases/download/v4.1.1/rmats_turbo_v4_1_1.tar.gz) in the working directory. Follow the section 4.3 in "AS_analysis_RNASeq.Rmd".
- Go to the folder containing bam files obtained after mapping and prepare text files, as required by rMATS, for the two conditions by copying the name of bam files (along with the path) separated by ','. Following commands should be run at the Linux command-line:
mkdir rMATS_analysis
cd bams/
ls -pd "$PWD"/*| grep "WT"| tr '\n'','> Wt.txt
ls -pd "$PWD"/*| grep "Mb"| tr '\n'','> KO.txt
mv *.txt ../rMATS_analysis - Run rmats.py with the two input files generated in the previous step, along with the GTF file obtained in 2.1.1.3. This will generate an output folder 'rmats_out' containing text files describing statistics (p-values and Inclusion levels) for each splicing event separately.
python rmats-turbo/rmats.py --b1 KO.txt --b2 Wt.txt --gtf annotation.gtf -t paired --readLength 50 --nthread 8 --od rmats_out/ --tmp rmats_tmp --task pos
NOTE: The reference annotation in the form of a GTF file is also required. Check the parameters if the data is single-end, and change the -t option accordingly. - Exploring rMATS results. Use Bioconductor package 'maser'25 to explore the rMATS results. Load the Junction and exon counts (JCEC) text files into 'maser' object and filter the result based on coverage by including at least five average reads per splicing event.
library(maser)
mbnl1<-maser("/rmats_out/", c("WT","Mbnl1_KO"), ftype="JCEC")
#Filtering out events by coverage
mbnl1_filt<-filterByCoverage(mbnl1,avg_reads=5) - Visualizing rMATS results. Select the significant splicing events at False Discovery Rate (FDR) 10% and minimum 10% change in Percent Spliced In (deltaPSI) using 'topEvents' function from 'maser' package. Next, check the gene events for individual genes of interest (sample gene-Wnk1) and plot PSI values for each splicing event of that gene. Generate a volcano plot by specifying the event type.
#Top splicing events at 10% FDR
mbnl1_top<-topEvents(mbnl1_filt,fdr=0.1, deltaPSI=0.1)
mbnl1_top
#Check the gene events for a particular gene
mbnl1_wnk1<-geneEvents(mbnl1_filt,geneS="Wnk1", fdr=0.1, deltaPSI=0.1)
maser::display(mbnl1_wnk1,"SE")
plotGenePSI(mbnl1_wnk1,type="SE", show_replicates
=TRUE)
volcano(mbnl1_filt,fdr=0.1, deltaPSI=0.1,type="SE")
+xlab("deltaPSI")+ylab("Log10 Adj. Pvalue")+ggtitle("Volcano Plot of exon skipping events") - Generate Sashimi plots for the splicing events result obtained with rMATS in the form of text files using 'rmats2shahimiplot' package. Run the python script at the Linux command-line.
python ./src/rmats2sashimiplot/rmats2sashimiplot.py --b1 ../bams/WT_Thymus_1.bam,../bams/WT_Thymus_2.bam,../bams/WT_Thymus_3.bam --b2 ../bams/Mbnl1KO_Thymus_1.bam,../bams/Mbnl1KO_Thymus_2.bam,../bams/Mbnl1KO_Thymus_3.bam -t SE -e ../rMATS_analysis/rmats_out/SE.MATS.JC.txt --l1 WT --l2 Mbnl1_KO --exon_s 1 --intron_s 5 -o ../rMATS_analysis/rmats2shasmi_output
NOTE: This process can be time-consuming as it will generate the Sashimi plot for all the results in the events file. Choose the top results (gene names and exons) as displayed by the topEvents function from 'maser' and visualize the corresponding Sashimi plot.
- Using DEXSeq package for differential exon analysis.
3. Alternative polyadenylation (APA) analysis using 3' end sequencing
- Data downloading and pre-processing
NOTE: Refer to the supplementary R Notebook file "APA_analysis_3PSeq_notebook.Rmd" for the complete commands for data downloading and pre-processing steps, or run the supplementary bash file "APA_data_downloading_preprocessing.sh" on the Linux command-line.- Download data from SRA with the Accession Ids (1553129 to 1553136).
- Trim adapters and reverse complement to obtain the sense strand sequence.
NOTE: This step is specific to the PolyA-seq assay used. - Map reads to mouse genome assembly using bowtie aligner26.
- Preparing pA sites annotations.
NOTE: The processing of the pA site annotation file is performed firstly using supplementary R Notebook file "APA_analysis_3PSeq_notebook.Rmd" (2.1 - 2.6), and then using bash file "APA_annotation_preparation.sh".- Download pA sites annotation from the PolyASite 2.0 database6.
- Select pA site annotations to retain 3'-untranslated region (UTR) pA sites, which are annotated as Terminal Exon (TE) or 1000 nt downstream of an annotated terminal exon (DS) for downstream analysis.
- Obtain pA site peaks. Anchor at each pA cleavage site, and visualize the average read coverage using bedtools and deeptools27,28. The results showed that the peaks of the mapped reads were mainly dispersed within ~60 bp upstream of the cleavage sites (figure 5 and supplementary figure 5). Therefore, the coordinates of pA sites were extended from the annotation file to 60 bp upstream of their cleavage sites. Depending on the specific 3' end sequencing protocol used, this step will need to be optimized for assays other than PolyA-seq.
- Counting reads
- Prepare the pA sites annotation file.
anno<- read.table(file= "flanking60added.pA_annotation.bed",
stringsAsFactors=FALSE, check.names=FALSE, header=FALSE, sep="")
colnames(anno) <- c("chrom", "chromStart", "chromEnd", "name", "score", "strand", "rep", "annotation", "gene_name", "gene_id")
anno<- dplyr::select(anno,name,chrom, chromStart,chromEnd, strand,gene_id,gene_name,rep)
colnames(anno) <- c("GeneID", "Chr", "Start", "End", "Strand", "Ensembl", "Symbol", "repID") - Apply 'featureCounts' to acquire raw counts. Save the count table as the RData file "APA_countData.Rdata" for APA analysis using different tools.
countData<- dir("bamfiles", pattern="sorted.bam$", full.names=TRUE) %>%
# Read all bam files as input for featureCounts
featureCounts(annot.ext=anno, isGTFAnnotationFile= FALSE,minMQS=0,useMetaFeatures= TRUE,allowMultiOverlap=TRUE, largestOverlap= TRUE,strandSpecific=1, countMultiMappingReads =TRUE,primaryOnly= TRUE,isPairedEnd= FALSE,nthreads=12)%T>%
save(file="APA_countData.Rdata")
NOTE: Be conscious to change any of the parameters listed in the 'featureCounts' function. Modify the 'strandSpecific' parameter to ensure it is consistent with the sequencing direction of the 3' end sequencing assay used (empirically, visualizing the data in a genome browser over genes on plus and minus strands will clarify this). - Apply non-specific filtering of countData. Filtering can significantly improve the statistical robustness in differential pA site usage tests. First, we removed those genes with only one pA site, on which differentially pA site usage cannot be defined. Second, we apply non-specific filtering based on coverage: counts are filtered by cpm less than 1 in x out of n samples, where x is the minimum number of replicates in any condition. N = 8 and x = 2 for this example data.
load(file= "APA_countData.Rdata")# Skip this step if already loaded
# Non-specific filtering: Remove the pA sites not differentially expressed in the samples
countData<-countData$counts%>%as.data.frame%>% .[rowSums(edgeR::cpm(.)>1) >=2, ]
anno%<>% .[.$GeneID%in% rownames(countData), ]
# Remove genes with only 1 site and NA in geneIDs
dnsites<-anno%>%group_by(Symbol)%>%summarise(nsites=n())%>% filter(nsites>1&!is.na(Symbol))
anno<-anno%>% filter(Symbol%in%dnsites$Symbol)
countData<-countData[rownames(countData) %in%anno$GeneID, ]
- Prepare the pA sites annotation file.
- Differential polyadenylation site usage analysis using DEXSeq and diffSplice pipelines.
- Using DEXSeq package
NOTE: As a contrast matrix cannot be defined for the DEXSeq pipeline, the differential APA analysis of each two experimental conditions has to be performed separately. The differential APA analysis of the condition WT and the condition DKO is performed as an example to explain the procedure. Refer to the supplementary file "APA_analysis_3PSeq_notebook.Rmd" for the step-by-step workflow of this section and the differential APA analysis of other contrasts.- Load library and create a sample table to define the experimental design.
c("DEXSeq", "GenomicRanges") %>% lapply(library, character.only=TRUE) %>%invisible
sampleTable1<- data.frame(row.names= c("WT_1","WT_2","DKO_1","DKO_2"),
condition= c(rep("WT", 2), rep("DKO", 2)),
libType= rep("single-end", 4)) - Prepare the pA sites information file using Bioconductor package GRanges.
# Prepare the GRanges object for DEXSeqDataSet object construction
PASinfo <- GRanges(seqnames = anno$Chr,
ranges = IRanges(start = anno$Start, end = anno$End),strand = Rle(anno$Strand))
mcols(PASinfo)$PASID<-anno$repID
mcols(PASinfo)$GeneEns<-anno$Ensembl
mcols(PASinfo)$GeneID<-anno$Symbol
# Prepare the new feature IDs, replace the strand information with letters to match the current pA site clusterID
new.featureID <- anno$Strand %>% as.character %>% replace(. %in% "+", "F") %>% replace(. %in% "-", "R") %>% paste0(as.character(anno$repID), .) - Use the read counts generated in step 3.3 and the pA site information obtained from the previous step to create the DEXSeq object.
# Select the read counts of the condition WT and DKO
countData1<- dplyr::select(countData, SRR1553129.sorted.bam, SRR1553130.sorted.bam, SRR1553131.sorted.bam, SRR1553132.sorted.bam)
# Rename the columns of countData using sample names in sampleTable
colnames(countData1) <- rownames(sampleTable1)
dxd1<-DEXSeqDataSet(countData=countData1,
sampleData=sampleTable1,
design=~sample+exon+condition:exon,
featureID=new.featureID,
groupID=anno$Symbol,
featureRanges=PASinfo) - Define the contrast pair through defining the levels of conditions in DEXSeq object.
dxd1$condition<- factor(dxd1$condition, levels= c("WT", "DKO"))
# The contrast pair will be "DKO - WT" - Normalization and dispersion estimation. Similar to RNA-seq data, for 3' end sequencing data perform normalization between samples (column-wise median of ratios for each sample) using the 'estimateSizeFactors' function, and estimate the variation of the data using with the 'estimateDispersions' function, then visualize the dispersion estimation result using the 'plotDispEsts' function.
dxd1 %<>% estimateSizeFactors %>% estimateDispersions %T>% plotDispEsts - Differential pA site usage testing for each gene using the function 'testForDEU', then estimate the fold change of pA site usage using the function 'estimateExonFoldChanges'. Check the results using the function 'DEXSeqResults' and set 'FDR < 10%' as the criterion for significantly differential pA sites.
dxd1 %<>% testForDEU %>% estimateExonFoldChanges(fitExpToVar = "condition")
dxr1 <- DEXSeqResults(dxd1)
dxr1
mcols(dxr1)$description
table(dxr1$padj<0.1) # Check the number of differential pA sites (FDR < 0.1)
table(tapply(dxr1$padj<0.1, dxr1$groupID, any)) # Check the number of gene overlapped with differential pA site - Visualization of the differential pA site usage results using differential APA plots generated by the function 'plotDEXSeq' and volcano plot by the function 'EnhancedVolcano'.
# Select the top 100 significant differential pA sites ranked by FDR
topdiff.PAS<- dxr1%>%as.data.frame%>%rownames_to_column%>%arrange(padj)%$%groupID[1:100]
# Apply plotDEXSeq for the visualization of differential polyA usage
plotDEXSeq(dxr1,"S100a7a", legend=TRUE, expression=FALSE,splicing=TRUE, cex.axis=1.2, cex=1.3,lwd=2)
# Apply perGeneQValue to check the top genes with differential polyA site usage
dxr1%<>% .[!is.na(.$padj), ]
dgene<- data.frame(perGeneQValue= perGeneQValue (dxr1)) %>%rownames_to_column("groupID")
dePAS_sig1<-dxr1%>% data.frame() %>%
dplyr::select(-matches("dispersion|stat|countData|genomicData"))%>%
inner_join(dgene)%>%arrange(perGeneQValue)%>%distinct()%>%
filter(padj<0.1)
# Apply EnhancedVolcano package to visualise differential polyA site usage
"EnhancedVolcano"%>% lapply(library, character.only=TRUE) %>%invisible
EnhancedVolcano(dePAS_sig1, lab=dePAS_sig1$groupID, x='log2fold_DKO_WT',
y='pvalue',title='Volcano Plot',subtitle='DKO vs WT',
FCcutoff=1,labSize=4, legendPosition="right",
caption= bquote(~Log[2]~"Fold change cutoff, 1; FDR 10%"))
- Load library and create a sample table to define the experimental design.
- Using diffSplice package. Refer to the supplementary R Notebook file "APA_analysis_3PSeq_notebook.Rmd" for the step-by-step workflow of this section.
- Define contrasts of interest for differential pA usage analysis.
NOTE: This step should be performed after the construction and processing of the DGEList object, which is included in the R Notebook file "APA_analysis_3PSeq_notebook.Rmd".
contrast.matrix<-makeContrasts(DKO_vs_WT=DKO-
WT,Ctrl_vs_DKO=Ctrl-DKO,
KD_vs_Ctrl=KD-Ctrl,KD_vs_DKO=KD-DKO,levels=design)
fit2<-fit%>%contrasts.fit(contrast.matrix)%>%eBayes
summary(decideTests(fit2))
ex<-diffSplice(fit2,geneid=anno$Symbol,exonid=new.featureID)
topSplice(ex) #Check the top significant results with topSplice - Visualize the result of contrasts of interest (here "DKO - WT") using differential APA plots by the function 'plotSplice' and volcano plots with the function 'EnhancedVolcano'. Refer to the R Notebook file "APA_analysis_3PSeq_notebook.Rmd" 4.2.7 - 4.2.9 for the visualization of other contrast pairs.
sig1<-topSplice(ex,n=Inf,FDR=0.1,coef=1, test="t", sort.by="logFC")
sig1.genes<-topSplice(ex,n=Inf,FDR=0.1,coef=1, test="simes")
plotSplice(ex, coef=1,geneid="S100a7a", FDR = 0.1)
plotSplice(ex,coef=1,geneid="Tpm1", FDR = 0.1)
plotSplice(ex,coef=1,geneid="Smc6", FDR = 0.1)
EnhancedVolcano(sig1, lab=sig1$GeneID,xlab= bquote(~Log[2]~'fold change'),
x='logFC', y='P.Value', title='Volcano Plot', subtitle='DKO vs WT',
FCcutoff=1, labSize=6, legendPosition="right")
- Define contrasts of interest for differential pA usage analysis.
- Using DEXSeq package
Results
After running the above step-by-step workflow, the AS and APA analysis outputs and representative results are in the form of tables and data plots, generated as follows.
AS:
The main output of the AS analysis (Supplementary Table 1 for diffSplice; Table 2 for DEXSeq) is a list of exons showing differential usage across conditions, and a list of genes showing significant overall splicing activity of one or more of its constituent exo...
Discussion
In this study, we evaluated exon-based and event-based approaches to detect AS and APA in bulk RNA-Seq and 3' end sequencing data. The exon-based AS approaches produce both a list of differentially expressed exons and a gene-level ranking ordered by the statistical significance of overall gene-level differential splicing activity (Tables 1-2, 4-5). For the diffSplice package, differential usage is determined by fitting weighted linear models at an exon-level to estimate the differential log fold-chan...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by an Australian Research Council (ARC) Future Fellowship (FT16010043) and ANU Futures Scheme.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Not relevent for computational study |
References
- Katz, Y., Wang, E. T., Airoldi, E. M., Burge, C. B. Analysis and design of RNA sequencing experiments for identifying isoform regulation. Nature Methods. 7 (12), 1009-1015 (2010).
- Wang, Y., et al. Mechanism of alternative splicing and its regulation. Biomedical Reports. 3 (2), 152-158 (2015).
- Mehmood, A., et al. Systematic evaluation of differential splicing tools for RNA-seq studies. Briefings in Bioinformatics. 21 (6), 2052-2065 (2020).
- Movassat, M., et al. Coupling between alternative polyadenylation and alternative splicing is limited to terminal introns. RNA Biology. 13 (7), 646-655 (2016).
- Tian, B., Manley, J. L. Alternative polyadenylation of mRNA precursors. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 18 (1), 18-30 (2017).
- Herrmann, C. J., et al. PolyASite 2.0: a consolidated atlas of polyadenylation sites from 3' end sequencing. Nucleic Acids Research. 48 (1), 174-179 (2020).
- Liu, R., Loraine, A. E., Dickerson, J. A. Comparisons of computational methods for differential alternative splicing detection using RNA-seq in plant systems. BMC Bioinformatics. 15 (1), 364 (2014).
- Conesa, A., et al. A survey of best practices for RNA-seq data analysis. Genome Biology. 17 (1), 13 (2016).
- Anders, S., Reyes, A., Huber, W. Detecting differential usage of exons from RNA-seq data. Genome Research. 22 (10), 2008-2017 (2012).
- Ritchie, M. E., et al. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Research. 43 (7), 47 (2014).
- Shen, S., et al. rMATS: Robust and flexible detection of differential alternative splicing from replicate RNA-Seq data. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 111 (51), 5593-5601 (2014).
- Mehmood, A., et al. Systematic evaluation of differential splicing tools for RNA-seq studies. Briefings in bioinformatics. 21 (6), 2052-2065 (2020).
- Kanitz, A., et al. Comparative assessment of methods for the computational inference of transcript isoform abundance from RNA-seq data. Genome biology. 16 (1), 1-26 (2015).
- Love, M. I., Huber, W., Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biology. 15 (12), 550 (2014).
- Sznajder, L. J., et al. Loss of MBNL1 induces RNA misprocessing in the thymus and peripheral blood. Nature Communications. 11, 1-11 (2020).
- Batra, R., et al. Loss of MBNL leads to disruption of developmentally regulated alternative polyadenylation in RNA-mediated disease. Molecular Cell. 56 (2), 311-322 (2014).
- Leinonen, R., Sugawara, H., Shumway, M., et al. The sequence read archive. Nucleic acids research. 39, 19-21 (2010).
- Tange, O. . GNU parallel-the command-line power tool. 36, 42-47 (2011).
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet journal. 17 (1), 10-12 (2011).
- Bolger, A. M., Lohse, M., Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics. 30 (15), 2114-2120 (2014).
- Dobin, A., et al. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics. 29 (1), 15-21 (2013).
- Robinson, M. D., McCarthy, D. J., Smyth, G. K. edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26 (1), 139-140 (2010).
- Robinson, M. D., Oshlack, A. A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biology. 11 (3), 25 (2010).
- Veiga, D. F. T. maser: Mapping Alternative Splicing Events to pRoteins. R package version 1.4.0. , (2019).
- Langmead, B., Trapnell, C., Pop, M., Salzberg, S. L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biology. 10 (13), 25 (2009).
- Quinlan, A. R., Hall, I. M. BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics. 26 (6), 841-842 (2010).
- Ramírez, F., Dündar, F., Diehl, S., Grüning, B. A., Manke, T. deepTools: a flexible platform for exploring deep-sequencing data. Nucleic acids research. 42 (1), 187-191 (2014).
- Merino, G. A., Conesa, A., Fernández, E. A. A benchmarking of workflows for detecting differential splicing and differential expression at isoform level in human RNA-seq studies. Briefings in bioinformatics. 20 (2), 471-481 (2019).
- Chhangawala, S., Rudy, G., Mason, C. E., Rosenfeld, J. A. The impact of read length on quantification of differentially expressed genes and splice junction detection. Genome biology. 16 (1), 1-10 (2015).
- Conesa, A., et al. A survey of best practices for RNA-seq data analysis. Genome Biol. 17, 13 (2016).
- Trapnell, C., et al. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc. 7 (3), 562-578 (2012).
- Li, B., Dewey, C. N. RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics. 12, 323 (2011).
- Bray, N. L., Pimentel, H., Melsted, P., Pachter, L. Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat Biotechnol. 34 (5), 525-527 (2016).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved