A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Studies of Chaperone-Cochaperone Interactions using Homogenous Bead-Based Assay
In This Article
Summary
This protocol presents a technique for probing protein-protein interactions using glutathione-linked donor beads with GST-fused TPR-motif co-chaperones and acceptor beads coupled with an Hsp90-derived peptide. We have used this technique to screen small molecules to disrupt Hsp90-FKBP51 or Hsp90-FKBP52 interactions and identified potent and selective Hsp90-FKBP51 interaction inhibitors.
Abstract
Targeting the heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90)-cochaperone interactions provides the possibility to specifically regulate Hsp90-dependent intracellular processes. The conserved MEEVD pentapeptide at the C-terminus of Hsp90 is responsible for the interaction with the tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) motif of co-chaperones. FK506-binding protein (FKBP) 51 and FKBP52 are two similar TPR-motif co-chaperones involved in steroid hormone-dependent diseases with different functions. Therefore, identifying molecules specifically blocking interactions between Hsp90 and FKBP51 or FKBP52 provides a promising therapeutic potential for several human diseases. Here, we describe the protocol for an amplified luminescent proximity homogenous assay to probe interactions between Hsp90 and its partner co-chaperones FKBP51 and FKBP52. First, we have purified the TPR motif-containing proteins FKBP51 and FKBP52 in glutathione S-transferase (GST)-tagged form. Using the glutathione-linked donor beads with GST-fused TPR-motif proteins and the acceptor beads coupled with a 10-mer C-terminal peptide of Hsp90, we have probed protein-protein interactions in a homogeneous environment. We have used this assay to screen small molecules to disrupt Hsp90-FKBP51 or Hsp90-FKBP52 interactions and identified potent and selective Hsp90-FKBP51 interaction inhibitors.
Introduction
Molecular chaperones contribute to protein homeostasis, including protein folding, transport, and degradation. They regulate several cellular processes and are linked to numerous diseases such as cancer and neurodegenerative diseases1. Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is one of the most important chaperones whose function is dependent on conformational changes driven by ATP hydrolysis and binding with client proteins mediated by its co-chaperones2. Despite an obvious potential of Hsp90 as the therapeutic target, fine-tuning its function represents a big challenge. There are several Hsp90 inhibitors targeting the N-terminal ATP binding region, which have been evaluated in clinical trials, but none of them has been approved for marketing3. Due to the lack of a well-defined ligand-binding pocket4, targeting the C-terminal region of Hsp90 has had limited success4. Recently, disruption of Hsp90-cochaperone interactions by small molecules has been investigated as an alternative strategy5. Targeting the Hsp90-cochaperone interactions would not elicit general cell stress response and provides the possibility to specifically regulate various intracellular processes. The conserved MEEVD pentapeptide at the C-terminus of Hsp90 is responsible for the interaction with the tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) motif of co-chaperones6. Of the 736 TPR motif-containing proteins annotated in the human protein database, ~20 different proteins interact with Hsp90 via this peptide7. Molecules competing for MEEVD peptide-binding would disrupt the interactions between Hsp90 and co-chaperones containing a TPR domain. The peptide binding site has similar tertiary structure but the overall homology between different TPR motif domains is relatively low7, providing an opportunity to identify molecules specifically capable of blocking interactions between Hsp90 and particular TPR-motif co-chaperones. Among these TPR-motif co-chaperones, FK506-binding protein (FKBP) 51 and FKBP52 are regulators of steroid hormone receptor (SHR) signaling and involved in several steroid hormone-dependent diseases including cancer, stress-related diseases, metabolic diseases, and Alzheimer's disease8. Although FKBP51 and FKBP52 share > 80% sequence similarity, their functions differ: FKBP52 is a positive regulator of SHR activity, while FKBP51 is a negative regulator in most cases8. Therefore, identifying molecules, specifically blocking interactions between Hsp90 and FKBP51 or FKBP52, provides a promising therapeutic potential for related diseases.
Amplified Luminescent Proximity Homogenous Assay (AlphaScreen) was first developed in 1994 by Ullman EF et al.9. Now it is widely used to detect different types of biological interactions, such as peptide10, protein11, DNA12, RNA13, and sugar14. In this technique, there are two kinds of beads (diameter 200 nm), one is the donor bead and the other is the acceptor bead. The biomolecules are immobilized onto these beads; their biological interactions bring donor and acceptor beads into proximity. At 680 nm, a photosensitizer in the donor bead illuminates and converts oxygen to singlet oxygen. Because the singlet oxygen has a short lifetime, it can only diffuse up to 200 nm. If the acceptor bead is in proximity, its thioxene derivative reacts with the singlet oxygen generating chemiluminescence at 370 nm. This energy further activates fluorophores in the same acceptor bead to emit light at 520-620 nm15. If the biological interactions are disrupted, the acceptor bead and donor bead cannot reach proximity, resulting in the singlet oxygen decay and low produced signal.
Here we describe a protocol using this technique for screening small molecules inhibiting interactions between Hsp90 and TPR co-chaperones, especially FKBP51 and FKBP52.The 10 amino acid long peptides corresponding to Hsp90 extreme C-terminus are attached to acceptor beads. Purified GST-tagged TPR co-chaperones interact with glutathione-linked donor beads. When the interaction between Hsp90-derived peptides and TPR-motif co-chaperones brings the beads together, an amplified signal is produced (Figure 1A). If the screened small molecules can inhibit the interactions between Hsp90 and TPR-motif co-chaperones, this amplified signal will be decreased (Figure 1B). Their IC50 can be calculated by quantitative measurement. This protocol can be extended to any chaperone - TPR-motif co-chaperone interactions of interest and is of great importance in the development of novel molecules, specifically blocking the interaction between Hsp90 and FKBP51 or FKBP52.

Figure 1: The basic principle of this assay. (A) Purified GST-FKBP51 interacts with glutathione-linked donor beads. The 10 amino acid long peptides corresponding to the extreme C-terminus of Hsp90 are attached to acceptor beads. The interaction between Hsp90-derived peptides and TPR domain of FKBP51 brings the donor and acceptor beads into proximity. At 680 nm, a photosensitizer in the donor bead illuminates and converts oxygen to singlet oxygen. The thioxene derivative on the acceptor bead reacts with the singlet oxygen and generates chemiluminescence at 370 nm. This energy further activates fluorophores in the same acceptor bead to emit light at 520-620 nm. (B) When small molecules inhibit the interactions between Hsp90 and FKBP51, the donor and acceptor beads cannot reach proximity. Then the singlet oxygen with short lifetime decays, and no detectable signal is produced. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Protocol
NOTE: An overview of this protocol is shown in Figure 2.
1. Expression and purification of GST-FKBP51 and GST-FKBP52 (Figure 2A)
- Plasmids
NOTE: Obtain cDNA clones for human FKBP51 (clone id: 5723416) and for human FKBP52 (clone id: 7474554) from IMAGE consortium.- Amplify the human FKBP51 DNA by PCR with primers (forward; 5`GGATCCATGACTACTGATGAAGGT-3`, reverse; 5`-CTCGAGCTATGCTTCTGTCTCCAC-3`) containing BamHI and XhoI overhangs and clone into pGEX6-1 vector at BamHI / XhoI restriction sites.
- Amplify the human FKBP52 DNA by PCR with primers (forward; 5`-GAATTCATGACAGCCGAGGAGATG-3`, reverse; 5`-CTCGAGCTATGCTTCTGTCTCCAC-3`) containing EcoRI and XhoI overhangs and clone into pGEX6-2 vector at EcoRI / XhoI restriction sites.
NOTE: PCR reaction set up and conditions are shown in Table 1 and Table 2. - Verify the inserted sequence and transform the plasmids into the chemically competent E. coli according to the manufacture protocol.
- Protein expression and purification
- Add 25 g of Luria broth (LB) base in 1 L of distilled water to make the LB solution. Autoclave it at 121 °C for 15 min. After cooling, add 50 µg/mL ampicillin.
- Take a colony of bacteria expressing GST-FKBP51 or GST-FKBP52 and mix with 500 µL of LB solution in a 1.5 mL tube. Vortex.
- Add the mixture of "1.2.2" into 1 L of LB solution in the Erlenmeyer flask covered with an aluminum foil. Incubate the Erlenmeyer flask in the shaker overnight at 37 °C.
- Induce protein expression by adding 1 mM isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG) to the Erlenmeyer flask and continue the incubation for a further 2 h.
- To get cell pellets, centrifuge at 5,000 x g for 15 min. Remove the supernatant.
NOTE: The cell pellets can be stored at -20 °C. - Resuspend the cell pellets in 40 mL of PBS and sonicate 3 x 20 s on ice. Add 1 mM PMSF, 1 mM EDTA, and protease inhibitor cocktail (1 tablet) to prevent proteolysis.
- Centrifuge the suspension for 30 min 50,000 x g to remove cell debris and apply the supernatant onto 5 mL GST-trap column.
- After washing the column with 30 mL PBS, elute GST-FKBP51 and GST-FKBP52 with 5 mL of 10 mM glutathione in PBS.
- Concentrate proteins on 15 mL 10.000 MWCO centrifugation unit. To remove free glutathione, pass concentrates through PD-10 column equilibrated with 0.5x PBS and again concentrate on the filter centrifuge device.
- Collect protein-containing fractions. Verify the proteins in SDS-PAGE and adjust protein concentrations to 1 mg/mL.
NOTE: Typical protein yield is 2-5 mg/L culture. The protein can be stored at -20 °C.
2. Coupling of Hsp90 C-terminal peptide to the acceptor beads (Figure 2B)
- Hsp90 peptide preparation
- Synthesize ten amino acid peptide NH2-EDASRMEEVD-COOH corresponding to amino acids 714-724 of human Hsp90 beta isoform (UniProt ID: P08238) by a peptide synthesis service.
- Dilute the Hsp90 peptide in PBS to 1 mg/mL concentration.
- Acceptor beads preparation
- Dilute the unconjugated acceptor beads in PBS to 1 mg/mL concentration and transfer to a 1.5 mL tube.
- Perform the washing by centrifugation at 16,000 x g for 15 min. Carefully remove the supernatant.
- Conjugation
- Set the ratio between beads and peptide as 10:1. In the 1.5 mL tube containing 1 mg of acceptor bead pellet (prepared as described above), add 1 mL of PBS (pH 7.4), 0.1 mg of diluted peptide, 1.25 µL of Tween-20, 10 µL of a 400 mM solution of sodium cyanoborohydride (NaBH3CN) in water.
CAUTION: NaBH3CN is toxic; use a fume hood and gloves. NaBH3CN solution should be freshly prepared. - Incubate for 24 h at 37 °C with end-over-end agitation (10-20 rpm) on a rotary shaker.
- Set the ratio between beads and peptide as 10:1. In the 1.5 mL tube containing 1 mg of acceptor bead pellet (prepared as described above), add 1 mL of PBS (pH 7.4), 0.1 mg of diluted peptide, 1.25 µL of Tween-20, 10 µL of a 400 mM solution of sodium cyanoborohydride (NaBH3CN) in water.
- Reaction quenching and beads washing
- Add 20 µL of 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) solution to the reaction to block unreacted sites. Incubate for 1 h at 37 °C.
- Centrifuge at 16,000 x g (or maximum speed) for 15 min at 4 °C. Remove the supernatant and resuspend the bead pellet in 1 mL of Tris-HCl solution (100 mM, pH 8.0).
- Repeat the washing step three times.
- After the last centrifugation, resuspend the beads at 1 mg/mL in storage buffer (1 mL of 0.5 × PBS with 0.01% sodium azide as a preservative). Store the conjugated acceptor bead solution at 4 °C light protected.
CAUTION: Sodium azide is toxic; use a fume hood and gloves.
3. The assay probing the interaction between GST-FKBP51 or GST-FKBP52 and Hsp90 C-terminal peptide, and inhibition with small molecular mass compounds (Figure 2C)
- GST-tagged proteins interacting with glutathione donor beads
- Set up the reactions in 384-well plates.
- Prepare the solution containing 10 µg/mL of the glutathione donor beads in 0.5x PBS, pH 7.4.
NOTE: After prolonged storage, beads settle down and need to be vortexed. - Add GST-FKBP51 or GST-FKBP52 to a final concentration of 10 µg/mL.
- Incubate in the dark at 25 °C for 10 min.
NOTE: At this step, GST-tagged proteins will interact with glutathione attached to the beads. For each well, 22.5 µL of this mixture will be used. The concentration of the binding partners must be determined empirically. Titrate GST-FKBP51 and GST-FKBP52 and choose the concentration that gives the best signal.
- Compound addition
- Make serial dilutions of test compounds in DMSO.
NOTE: The concentrations used are typically 10, 30, 100, 300, 1,000, and 3,000 µM. - Add 0.25 µL of DMSO (negative control) or Hsp90 C-terminal peptide (positive control, 30 µM) or compounds in DMSO to the corner of each well of the plate. Use triplicates for every compound concentration.
- Add 22.5 µL of the solution containing glutathione donor beads with GST-tagged proteins to each well.
- Shake the plate gently with hand but thoroughly. Incubate in the dark at 25 °C for 15 min.
NOTE: During this time, compounds will interact with the TPR domain at the Hsp90 C-terminal peptide binding site.
- Make serial dilutions of test compounds in DMSO.
- Acceptor beads addition
- Dilute the acceptor beads with attached Hsp90 C-terminal peptide to 100 µg/mL in 0.5x PBS.
- Add 2.25 µL of diluted acceptor beads to each well.
- Mix gently but thoroughly. Incubate in the dark at 25 °C for 15 min.
NOTE: At this step, donor and acceptor beads are brought into proximity by the protein-peptide interactions. The final volume of the reaction mixture is 25 µL. Therefore, the final concentrations of compounds are ranging from 0.1 to 30 µM.
- Plate reading
NOTE: Read the plate using a plate reader set in the relevant mode.- Turn on the instrument and open the software
- Choose the relevant protocol.
- Click Edit plate map and select the well being used in the plate for measurement.
- Click Next to continue and Run the selected protocol.
- After measurement, click Show Results to view results.
- Export the data.
4. Data analysis
- Z' factor and signal-to-background (S/B) ratio
- Calculate the Z' factor and S/B ratio for the assay using the following equation:
Z'=1-(3σpos+3σneg)/│µpos-µneg│16
S/B=µneg/µpos
where, σ and µ represent the standard deviations and means of the positive (Hsp90 C-terminal peptide, 30 µM) and negative (DMSO) controls, respectively. A Z' factor > 0.5 will ensure that the assay is robust enough for screening. To monitor the assay sensitivity, the S/B ratio has also been calculated.
- Calculate the Z' factor and S/B ratio for the assay using the following equation:
- Dose-response curve and IC 50
NOTE: Use nonlinear regression analysis to fit the data of Hsp90-cochaperones PPI inhibitors by software.- Create an XY data table in the Welcome dialog and select X Numbers, and Y Enter 3 (if triplicates) replicate values in side-by-side columns.
- Normalize the signal data of samples to the negative control group. Import concentration values to the X column and the signal values to the Y column.
- Click Analyze and choose Transform concentration (X) under Transform | Normalize. Choose Transform to Logarithms.
NOTE: This will transform the concentration to a log scale. If your starting concentration is zero, set it to a very small number that is effectively zero (e.g., 0.1 nM) not to lose those values since the logarithm of zero is not defined. - Click Analyze and choose Nonlinear regression (curve fit) under XY analyses, open the Dose-Response-Inhibition and choose Log(inhibitor) vs. response -- Variable slope.
- Click OK to view the Results (containing IC50 value) and Graphs.
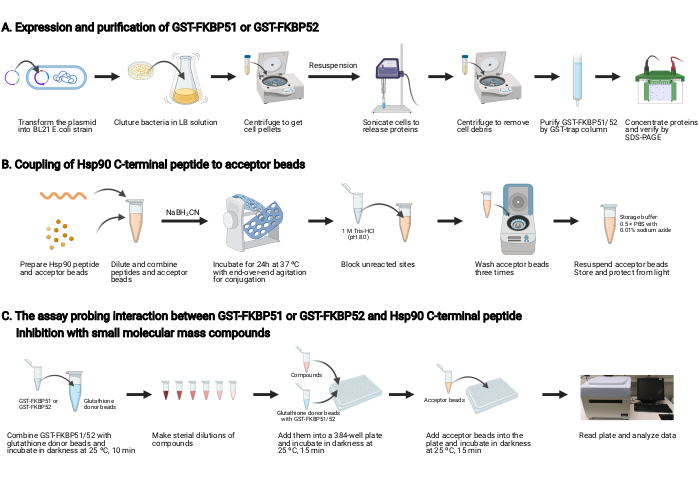
Figure 2: Schematic of this protocol. (A) Expression and purification of GST-FKBP51 and GST-FKBP52. (B) Coupling of Hsp90 C-terminal peptide to the acceptor beads. (C) The assay probing the interaction between GST-FKBP51 or GST-FKBP52 and Hsp90 C-terminal peptide. Inhibition with small molecular mass compounds. Created with BioRender.com Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Results
In our assay, Z' factor and S/B ratio are 0.82 and 13.35, respectively (Figure 3A), demonstrating that our assay is robust and reliable for high-throughput screening. We then used it to screen small molecular mass compounds. Figure 3B presents dose-dependent inhibition of chaperone-cochaperone interactions with a selected small molecule (D10). The dose-response curves for D10 are generated by nonlinear regression analysis, based on which the values of IC
Discussion
Here we describe a protocol using the assay for screening small molecules inhibiting interactions between Hsp90 and TPR-motif co-chaperones, especially FKBP51 and FKBP52. Its high Z' score (>0.8) demonstrates the robustness and reliability for a high-throughput format. Results can be obtained within one hour, and small amounts of beads, protein and compounds are required. Moreover, this protocol could easily be extended to any Hsp90/Hsp70 - TPR-motif co-chaperone interactions of interest. Several TPR-motif co-chaperon...
Disclosures
Authors report no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from Swedish Research Council (2018-02843), Brain Foundation (Fo 2019-0140), Foundation for Geriatric Diseases at Karolinska Institutet, Gunvor and Josef Anérs Foundation, Magnus Bergvalls Foundation, Gun and Bertil Stohnes Foundation, Tore Nilssons Foundation for medical research, Margaretha af Ugglas foundation and the Foundation for Old Servants.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 384-well plates | Perkin Elmer | 6008350 | Assay volume 25 ml |
| Amicon 10.000 MWCO centrifugation unit | Millipore | UFC901008 | Concentrate protein |
| Ampicillin | Sigma | A0166 | Antibiotics |
| Bacteria shaker Unimax 1010 | Heidolph | Culture bacteria | |
| cDNA clones for human FKBP51 | Source BioScience | clone id: 5723416 | pCMV-SPORT6 vector |
| cDNA clones for human FKBP52 | Source BioScience | clone id: 7474554 | pCMV-SPORT6 vector |
| Chemically Competent E. coli | Invitrogen | C602003 | One Shot BL21 Star (DE3) |
| Data analysis software | GraphPad Prism | 9.0.0 | Analysis data and make figures |
| Data analysis software | Excel | Analysis data | |
| DMSO | Supelco | 1.02952.1000 | Dilute compounds |
| DPBS | Gibco | 14190-144 | Prepare solution |
| EDTA | Calbiochem | 344504 | Prevent proteolysis during sonication |
| Glutathione | Sigma | G-4251 | Elute GST-tagged proteins |
| Glutathione donor beads | Perkin Elmer | 6765300 | Donor bead |
| GST-trap column | Cytiva (GE Healthcare) | 17528201 | Purify GST-tagged proteins |
| Isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside | Thermo Fisher Scientific | R0392 | Induce protein expression |
| LB Broth (Miller) | Sigma | L3522 | Microbial growth medium |
| PCR instrument | BIO-RAD | S1000 Thermal Cycler | Amplification/PCR |
| PD-10 column | Cytiva (GE Healthcare) | 17085101 | Solution exchange |
| pGEX-6P-1 vector | Cytiva (GE Healthcare) | 28954648 | Plasmid |
| pGEX-6P-2 vector | Cytiva (GE Healthcare) | 28954650 | Plasmid |
| Plate reader | Perkin Elmer | EnSpire 2300 Multilabel Reader | Read alpha plate |
| Plate reader software | Perkin Elmer | EnSpire Manager | Plate reader software |
| Plate reader software protocol | Perkin Elmer | Alpha 384-well Low volume | Use this protocol to read plate |
| PMSF | Sigma | P7626 | Prevent proteolysis during sonication |
| protease inhibitor cocktail | Sigma | S8830 | Prevent proteolysis during sonication |
| Sodium azide | Sigma | S2002 | As a preservative |
| Sodium cyanoborohydride (NaBH3CN) | Sigma | 156159 | Activates matrix for coupling |
| Ten amino acid peptide NH2-EDASRMEEVD-COOH corresponding to amino acids 714-724 of human Hsp90 beta isoform | Peptide 2.0 inc | Synthesize Hsp90 C-terminal peptide | |
| Test-Tube Rotator | LABINCO | Make end-over-end agitation | |
| Tris-HCl | Sigma | 10708976001 | Block unreacted sites of acceptor beads |
| Tween-20 | Sigma | P1379 | Prevent beads aggregation |
| Ultra centrifuge Avanti J-20 XP | Beckman Coulter | Centrifuge to get bacteria cell pellets | |
| Ultrasonic cell disruptor | Microson | Sonicate cells to release protein | |
| Unconjugated acceptor beads | Perkin Elmer | 6762003 | Acceptor beads |
| XCell SureLock Mini-Cell and XCell II Blot Module | Invitrogen | EI0002 | SDS-PAGE |
References
- Muchowski, P. J., Wacker, J. L. Modulation of neurodegeneration by molecular chaperones. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 6 (1), 11-22 (2005).
- Eckl, J. M., Richter, K. Functions of the Hsp90 chaperone system: lifting client proteins to new heights. International Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 4 (4), 157-165 (2013).
- Yuno, A. Clinical evaluation and biomarker profiling of Hsp90 inhibitors. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1709, 426-441 (2018).
- Dutta Gupta, S., Bommaka, M. K., Banerjee, A. Inhibiting protein-protein interactions of Hsp90 as a novel approach for targeting cancer. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 178, 48-63 (2019).
- Pavlov, P. F., Hutter-Paier, B., Havas, D., Windisch, M., Winblad, B. Development of GMP-1 a molecular chaperone network modulator protecting mitochondrial function and its assessment in fly and mice models of Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. 22 (7), 3464-3474 (2018).
- Young, J. C., Obermann, W. M., Hartl, F. U. Specific binding of tetratricopeptide repeat proteins to the C-terminal 12-kDa domain of hsp90. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 273 (29), 18007-18010 (1998).
- Scheufler, C., et al. Structure of TPR domain-peptide complexes: critical elements in the assembly of the Hsp70-Hsp90 multichaperone machine. Cell. 101 (2), 199-210 (2000).
- Storer, C. L., Dickey, C. A., Galigniana, M. D., Rein, T., Cox, M. B. FKBP51 and FKBP52 in signaling and disease. Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism. 22 (12), 481-490 (2011).
- Ullman, E. F., et al. Luminescent oxygen channeling immunoassay: measurement of particle binding kinetics by chemiluminescence. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 91 (12), 5426-5430 (1994).
- Wigle, T. J., et al. Screening for inhibitors of low-affinity epigenetic peptide-protein interactions: an AlphaScreen-based assay for antagonists of methyl-lysine binding proteins. Journal of Biomolecular Screening. 15 (1), 62-71 (2010).
- Guenat, S., et al. Homogeneous and nonradioactive high-throughput screening platform for the characterization of kinase inhibitors in cell lysates. Journal of Biomolecular Screening. 11 (8), 1015-1026 (2006).
- Sabatucci, A., et al. A new methodological approach for in vitro determination of the role of DNA methylation on transcription factor binding using AlphaScreen(R) analysis: Focus on CREB1 binding at hBDNF promoter IV. Journal of Neuroscience Methods. 341, 108720 (2020).
- Mills, N. L., Shelat, A. A., Guy, R. K. Assay Optimization and Screening of RNA-Protein Interactions by AlphaScreen. Journal of Biomolecular Screening. 12 (7), 946-955 (2007).
- Huang, X., et al. A competitive alphascreen assay for detection of hyaluronan. Glycobiology. 28 (3), 137-147 (2018).
- Principles of alphascreen amplified luinescent proximmity homogenous assay. PerkinElmer Life Sciences Available from: https://www.perkinelmer.com/lab-solutions/resources/docs/APP_AlphaScreen_Principles.pdf (2021)
- Zhang, J. H., Chung, T. D., Oldenburg, K. R. A Simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays. Journal of Biomolecular Screening. 4 (2), 67-73 (1999).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ISSN 2578-2037
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved
We use cookies to enhance your experience on our website.
By continuing to use our website or clicking “Continue”, you are agreeing to accept our cookies.