Spinal Cord Transection In Xenopus laevis Tadpoles
In This Article
Summary
Xenopus laevis tadpole spinal cord transection is a relevant injury method to study spinal cord injury and regeneration by making a transverse cut that completely severs the spinal cord at the thoracic level.
Abstract
Spinal cord injury (SCI) is a permanent affliction, which affects the central nervous system (CNS) motor and sensory nerves, resulting in paralysis beneath the injury site. To date, there is no functional recovery therapy for SCI, and there is a lack of clarity regarding the many complexes and dynamic events occurring after SCI. Many non-mammalian organisms can regenerate after severe SCI, such as teleost fishes, urodele amphibians, and larval stages of anuran amphibians, including Xenopus laevis tadpoles. These are bona fide model organisms to study and understand the response to SCI and the mechanisms underlying successful regenerative processes. This type of research can lead to the identification of potential targets for SCI therapeutic intervention. This article describes how to perform Xenopus laevis tadpole spinal cord transection, including husbandry, surgery, postsurgery care, and functional test evaluation. This injury method can be applied for elucidating the different steps of spinal cord regeneration by studying the cellular, molecular, and genetic mechanisms, as well as histological and functional evolution after SCI and during spinal cord regeneration.
Introduction
Spinal cord injury (SCI) is an affliction that affects approximately 250,000-500,000 people worldwide every year1. In addition to this high prevalence, SCI affects sensory and motor nerves, generating paralysis beneath the injury site and disconnection of some internal organs from the control of the CNS. The spinal cord, a part of the CNS, cannot regenerate, and due to the complexity of the affliction and the lack of complete understanding of all the involved processes, there are still no efficient therapies allowing functional recovery.
Non-mammalian organisms, such as teleost fishes, urodele amphibians, and larval stages of anuran amphibians, which can regenerate the spinal cord after severe SCI2,3,4, are excellent model organisms for studying the processes that govern a successful regenerative event and understanding the failure of mammalian regeneration. This understanding is of great interest as it could provide original insights to develop new therapeutic targets and possible therapies for SCI.
The anuran frog, Xenopus laevis, is an excellent model organism to study SCI. It has excellent regenerative capacities during the tadpole stages, which are progressively lost during metamorphosis, allowing experimentation in the regenerative and nonregenerative stages3,5. The established injury method for studying SCI in Xenopus laevis tadpoles consists of tail amputation, where the entire tail is removed, including tissues such as muscle, notochord, and spinal cord6. This approach has been instrumental in the understanding of general mechanisms of regenerative processes4,7,8,9,10.
As tail amputation involves multiple tissues in addition to the spinal cord, which is different from what happens after human SCI, a more relevant injury paradigm is needed for the study of SCI. We have relied on studies used in the past11 for generating comprehensive descriptions of injury paradigms5,12,13,14 and different methods for the study of SCI12,13,14,15,16,17,18. After spinal cord transection, the caudal portion of the spinal cord can be isolated for RNA and protein expression and high-throughput analyses14,19,20,21. Additionally, intracelomic injections of drugs and small molecules, as well as electroporation of cDNA, RNA, or morpholinos, before or after spinal cord transection, allow the study of the effects of these molecules in the prevention or treatment of SCI or of specific events occurring after SCI and spinal cord regeneration13,14. Further, injury evolution and the regenerative processes can be studied at different timings after injury using biochemical, molecular, histological, and functional approaches12,13,14,17,19,20,21,22,23.
Finally, all the aforementioned techniques can be used in non-regenerative stages, highlighting one of the most important advantages of using Xenopus laevis as a model organism to study SCI, the comparative studies of regenerative and non-regenerative mechanisms in the same species13,19,20,21,22. This paper presents a protocol for Xenopus laevis tadpole spinal cord transection, starting with the staging and selection of regenerative Nieuwkoop and Faber (NF) stage 50 tadpoles. This is followed by the description of the procedures for spinal cord surgery to produce sham and transected animals, postsurgical care, and finally the analysis of functional recovery by the measurement of free tadpole swimming distance.
Protocol
This protocol provides enough information to successfully perform spinal cord transection. Of note, there are excellent detailed protocols of these techniques published elsewhere14, which can complement the one presented here. All animal procedures have been approved by the Committee on Bioethics and Biosafety from the Faculty of Biological Sciences, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile.
1. Natural mating of frogs
- Three to five days prior to mating, subcutaneously preinject male and female frogs with 50 units of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). Use the "iron claw" technique for restraining the frogs; as the frogs are slippery, use a net to surround the frog if necessary. Insert the tip of a 26 G x ½" needle posterior to the lateral line, pushing it dorsally to a depth of 1 cm, between the skin and the muscle.
- Before mating, inject the male with 300 units and the female with 700 units of hCG.
- For mating to occur, place the male and the female in 2 L of 0.1x Barth solution immediately after chilling the solution at 4 °C for 15 min to resemble spring conditions and leave overnight at 18 °C.
- Sixteen hours later, carefully collect the embryos with the help of a plastic Pasteur pipette, with the tip cut off, and place them in 10 cm diameter Petri dishes. Remove the embryonic jelly coat by incubating the embryos with 25 mL of 2% cysteine in distilled water (pH 7.8; ensure the solution covers the embryos) for 5 min with slight agitation. Wash 3 times with distilled water and 3 times with 0.1x Barth solution (8.9 mM NaCl; 102 µM KCl; 238.1 µM NaHCO3; 1 mM 4-(2- hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazine ethanesulfonic acid (HEPES); 81.14 µM MgSO4; 33.88 µM Ca(NO3)2; 40.81 µM CaCl2, pH 7.6).
- Select healthy embryos that have a brownish color and symmetrically dividing blastomeres. Place the embryos in 10 cm diameter Petri dishes with 50 mL of 0.1x Barth solution at a density of no more than 100 embryos per dish.
2. Husbandry
- During the first week, maintain the embryos at 18 °C until they get off the vitelline sac. During this time, change the Barth solution every day, and remove whitish dead embryos and tadpoles presenting any visible anatomical alteration or tadpoles without any swimming movement.
- After the first week, transfer tadpoles to chlorine-free water in plastic tanks at a density of 10 animals per liter. Grow tadpoles at 20-21 °C with a 12-h light/12-h dark cycle, with oxygen stones available in each tank to aerate the water and fed once a day with 0.5 mg per animal. Replace water once a week and check for accumulated waste and dead animals daily24.
3. Staging
- Three to four weeks after fertilization, place the animals in a Petri dish; then, one by one, check the morphology and appearance of forelimbs and hindlimbs. If necessary, anesthetize the animals by placing the animals in a Petri dish with 50 mL of 0.02% tricaine mesylate in 0.1x Barth solution for better manipulation. After no more than 2 min, place the animals in 0.1x Barth solution for recovery from the anesthesia.
- Look for the following anatomical characteristics of stage 50 animals25: forelimbs that are just appearing and are spherical (Figure 1); hindlimbs that are protruding and are spherical (Figure 1).
NOTE: Animals from stages 49 to 51 can be used for this procedure (Figure 1); for more information about stages, refer to Nieuwkoop and Faber's Normal Table of Xenopus laevis25.
4. Surgery: spinal cord transection and sham-operated animals
- Anesthetize stage 50 tadpoles by placing them in a Petri dish with 50 mL of 0.02% tricaine mesylate in 0.1x Barth solution for 2 min.
- With the help of a tablespoon and forceps, place the tadpole, dorsal side-up, on a wet piece of gauze in the upper half of a glass Petri dish.
- Perform an incision of the skin and dorsal muscles at the mid-thoracic level (Figure 2A, B) using microdissection spring scissors.
- For control sham animals, ensure that the incision size is only ~0.2 mm (Figure 2C); do not damage the spinal cord (Figure 2D,D´).
- For transected animals, perform a second incision of ~0.2 mm (Figure 2C) to fully transect the spinal cord (Figure 2E,E´).
5. Postsurgery care
- After surgery, transfer the tadpoles to a tank containing 0.5 L of 0.1x Barth solution with 1x Penicillin-streptomycin, at a density of 10-12 animals per tank. Maintain the transected and control sham animals in separate tanks.
NOTE: Tadpoles will recover from the anesthesia in a couple of minutes. - Maintain the tadpoles with aeration at a temperature of 20-21 °C.
- Change the Barth solution with antibiotics every other day until the end of the experiment.
- Start feeding the animals one day after surgery, once per day.
- Eliminate dead animals.
6. Swimming assay
- Obtain a box with LED illumination from the inside, covered with a transparent polystyrene sheet, which allows the light to pass through.
- Install a camera over the LED box.
- Place a 15 cm diameter Petri dish on top of the box, filled with 100 mL of 0.1x Barth solution.
- One day post transection, place a tadpole in the Petri dish and leave for a 5 min adaptation period.
- After adaptation, start video-tracking the free-swimming behavior using the referenced software (see the Table of Materials) for 5 min.
- After the video is completed, transfer the tadpole back to its tank.
- Repeat the video tracking 5, 10, 15, and 20 days post transection (Figure 3).
7. Bioethical considerations
NOTE: The mortality of animals after sham surgery and transection is 13% and 30%, respectively. Additionally, a minimum of 15-20 animals per group is necessary for statistical analysis. Therefore, start with 23 sham and 26 transected animals.
- Anesthetize the animals with 0.02% tricaine mesylate for 2 min to assure reduction in neuronal and motor activity and pain before surgery.
- After surgery, check the animals for recovery from anesthesia. Additionally, feed and check the animals daily.
- After finishing the swimming assay, sacrifice the animals with an overdose of tricaine mesylate (1% tricaine mesylate prepared in 30 mM sodium bicarbonate solution).
Representative Results
The protocol described herein allows the study of spinal cord regeneration in Xenopus laevis. The effects of specific pharmacological treatments and the contribution of specific gene expression in spinal cord regeneration can be evaluated by measuring their effects on swimming recovery. The total swimming distance is plotted against the days after injury to compare control and treated animals at a specific time point or over a specified period. The recovery of motor function through time is exemplified in Figure 3, showing the swimming distance at 5, 10, 15, and 20 days post transection. At 5 days post transection, animals swam an average of 0.7 m in 5 min, showing a reduced swimming capacity. This capacity increased with the passing days, as an average of 2.1 and 3.1 m/5 min was observed after 10 and 15 days post transection, respectively, and complete recovery of swimming capacities was observed at 20 days post transection, with an average of 5.7 m/5 min.
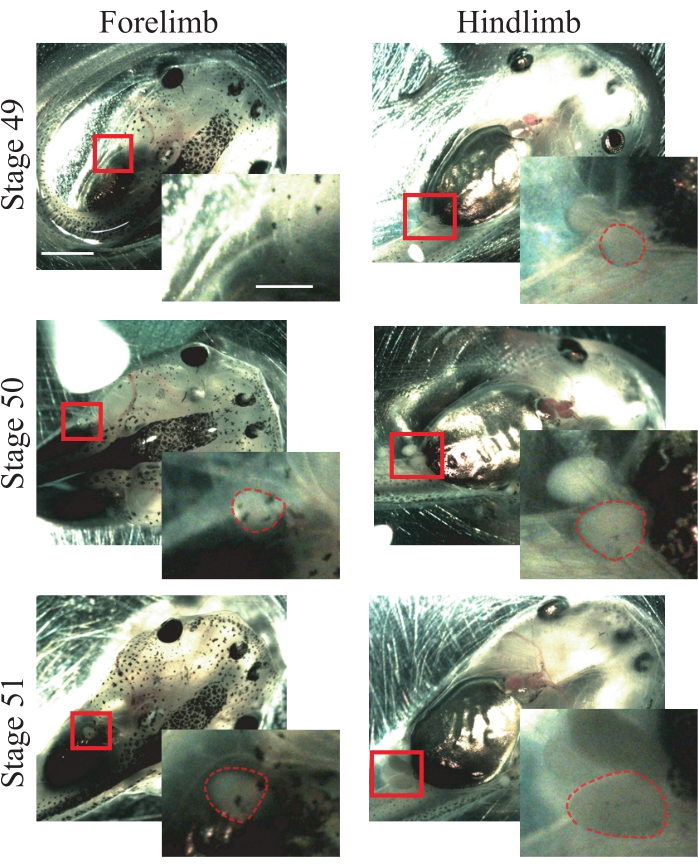
Figure 1: Xenopus tadpole staging. Representative images of stages 49-51, showing fore- and hindlimbs for animal staging reference. Scale bars = 2 mm. Magnifications of the boxed region are shown in the lower-right of each image.Scale bars = 1 mm. In stage 49, forelimbs are not observed, while hindlimbs are just appearing, showing a spherical shape. Stage 50 presents forelimbs that are just appearing, showing a spherical shape and hindlimbs protruding with a spherical shape. In stage 51, forelimbs present a protruding spherical shape and hindlimbs a protruding elongated shape. Dashed outlines show fore- and hindlimbs. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
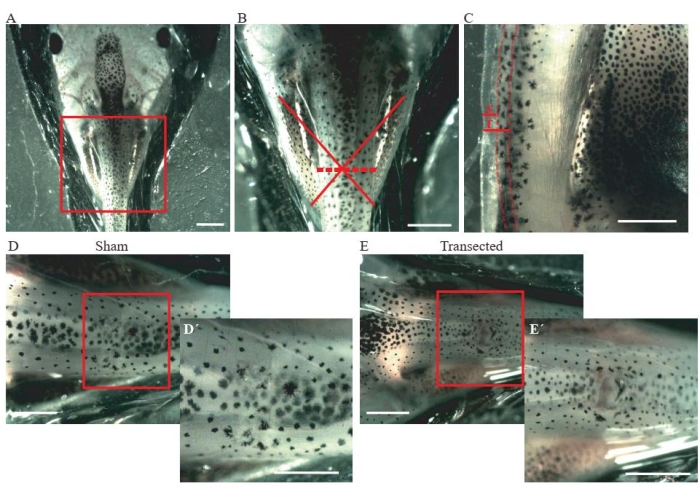
Figure 2: Spinal cord transection. (A) Representative image showing the correct positioning of the animal, dorsal side up, for performing the surgery. Scale bar = 2 mm. (B) Magnification of A shows the location and extent of injury. The red cross shows the exact location of the injury site at the thoracic level of the spinal cord, and the dashed line shows the extent of the injury. Scale bar = 1 mm. (C) Representative image showing a lateral view of the thoracic level of the spinal cord. The extension of the sham incision and transection are shown. Dashed lines delineate the limits of the spinal cord. Scale bar = 1 mm. (D) Representative image showing a sham animal with an intact spinal cord. Scale bars = 1 mm. (E) Representative image showing a transected animal with an interrupted spinal cord. Scale bars = 1 mm. Magnifications of the boxed region are shown in the lower-right of each image (D´ and E´).Scale bars = 1 mm. Abbreviations: S = sham incision; T = transection. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
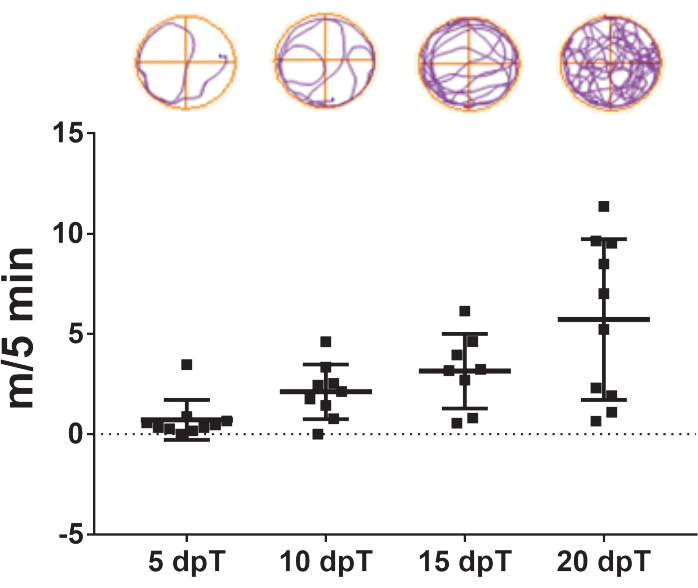
Figure 3: Swimming function recovery over time. Representative dot plot of the swimming distance covered by transected animals in 5 min at 5, 10, 15, and 20 days post transection. Samples of swimming trajectories are shown on top. Data presented as mean ± SEM from 10 tadpoles. Abbreviations: dpT = days post transection; SEM = standard error of the mean. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Discussion
The protocol described herein is an excellent method to perform SCI and evaluate functional recovery. For reproducibility, it is essential to grow healthy tadpoles and choose animals that are similar in size. Lack of proper feeding generates nutrient stress, which results in poor regenerative capacities26; therefore, special attention should be paid to tadpole feeding. As tadpoles reach stage 50 after 3-4 weeks, they can be reared at higher temperatures to accelerate the growth process, 18-25 °C being optimal27. Water quality is important, as animals are sensitive to water conditions and chemical products. The optimal water conditions include using carbon filtered, chlorine-free water with the following parameters: pH (6.5-7.5), chloride (<0.02 mg/L), conductivity of water (1.0 mS/cm ± 0.1 units), copper (<0.3 mg/L); carbonate hardness (KH: 5-10 dKH); general hardness (GH: 6-16 dGH); nitrate (NO3: <20 mg/L); and nitrite (NO2: <0.1 mg/L)14,27,28. Additionally, to avoid contamination, plastic tanks should be cleaned once a week for rearing animals or every other day after surgery by washing thoroughly with chloride-free water and a sponge; detergent must be avoided.
For a better survival rate after surgery, tadpoles must not be exposed to anesthesia for long periods (no longer than 2 min). Moreover, it is recommended to anesthetize one tadpole at a time. As the animals need to stay hydrated, keep the animals immersed in solution all the time before and after surgery, and pour the solution with a spoon on top of the tadpole before beginning the surgery. Ensure that the damage is extensive enough to cover the whole spinal cord but not too extensive as it can induce poor functional recovery or death. If the notochord is damaged, the animal will be bent, and the functional recovery will be affected. If the damage extends beyond the notochord, the probability of death increases14. During the swimming assay, recording is considered correct if the software identifies each animal with a blue shadow; otherwise, the recording should be repeated. It is important to avoid movement and air or light changes during the recording process to prevent recording mistakes.
There are still many open questions about the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying spinal cord damage and regeneration. The protocol described in this work can be used to study the contribution of different cellular events, gene expression, and treatments on functional recovery, determined by measuring swimming capacities. Additionally, many other techniques can be applied to the operated animals. The spinal cord can be isolated to perform protein and/or mRNA extraction14 to study protein and gene expression profiles after damage and treatment19,20. This surgery has also been the basis for studying the spinal cord cellular response22 and the behavior of neural stem progenitor cells12,13,22 after spinal cord injury. Signaling cascades involved in spinal cord regeneration have also been studied using the spinal cord damage paradigm described herein23. In summary, the protocol described here is an excellent model to study spinal cord injury and regeneration and has been used for many studies that have contributed to the existing knowledge about the subject.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by research grants from: PG Slater: FONDECYT N° 3190820; J. Larraín: FONDECYT N° 1180429, CARE Chile UC-Centro de Envejecimiento y Regeneración (PFB 12/2007).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Air pump | Regent CALM | RC-006 | For oxygen diffuser stones function |
| ANY-maze software | Stoelting | Swimming behavior test | |
| Ca(NO3)2·4H2O | Sigma-Aldrich | 237124 | |
| CaCl2·2H2O | Sigma-Aldrich | 223506 | |
| Camera | Stoelting | 60528 | Swimming behavior test |
| Computer | Swimming behavior test (minimum recommended specifications: PC, Windows 7, Intel Core i3, 2 GB RAM, 10-GB drive disk, 1 available USB port, 1,366 × 768 monitor) | ||
| Cysteine | Sigma-Aldrich | C7352 | |
| Dissecting stereomicroscope | Nikon | SMZ745T | Surgery / staging |
| Glass Petri dishes | 100 x 20 mm | ||
| HEPES | Gibco | 11344-041 | |
| Human chorionic gonadotropin | It can be found in different formats in the pharmacy | ||
| KCl | Merck Millipore | 104936 | |
| LED light box | custom made | wood box: 55-cm length, 34-cm width, 9-cm height, LED lights, transparent polystyrene sheet) | |
| MgSO4·7H2O | Merck Millipore | 105886 | |
| Microdissection scissors for transection | Fine Science Tools | 15003-08 | Spring Scissors for surgery |
| MS-222 | Sigma-Aldrich | E10521 | Anesthetic; tricaine mesylate |
| NaCl | Merck Millipore | 106404 | |
| NaHCO3 | Sigma-Aldrich | S6014 | |
| Nasco Frog Brittle for Tadpole Xenopus | Nasco | SB09480(LM)MX | Food for Xenopus tadpoles stage 44 to 60 |
| Oxygen diffuser stones | Pentair | AA1 | Mantainance of animals |
| Pair of forceps | Fine Science Tools | Dumont n° 5 SF forceps | For surgery |
| Penicillin | Sigma-Aldrich | P7794 | |
| pH meter | |||
| Plastic Pasteur pipette | Sigma-Aldrich | Z331740 | For collecting embryos after mating |
| Plastic Petri dishes | Sigma-Aldrich | P5981 | 150 x 15 mm |
| Plastic tank/box with lid | 4.5 liter capacity; 20 cm × 17 cm × 15 cm or similar | ||
| Sterilized gauze | |||
| Streptomycin | Sigma-Aldrich | S1277 | |
| Tablespoon | |||
| Xenopus laevis specialized strains and lines | National Xenopus Resource European Xenopus Resource Centre Xenopus laevis Research Resource Centre | http://www.mbl.edu/xenopus https://xenopusresource.org/ https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/microbiology-immunology/xenopus-laevis.aspx | |
| Xenopus laevis wild type | Xenopus 1 Xenopus Express | https://xenopus1.com http://www.xenopus.com |
References
- International perspectives on spinal cord injury. World Health Organization Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/I/item/international-perspectives-on-spinal-cord-injury (2013)
- Quiroz, J. F. D., Echeverri, K. Spinal cord regeneration: Where fish, frogs and salamanders lead the way, can we follow. Biochemical Journal. 451 (3), 353-364 (2013).
- Lee-Liu, D., Méndez-Olivos, E. E., Muñoz, R., Larraín, J. The African clawed frog Xenopus laevis: A model organism to study regeneration of the central nervous system. Neuroscience Letters. 652, 82-93 (2017).
- Phipps, L. S., Marshall, L., Dorey, K., Amaya, E. Model systems for regeneration: Xenopus. Development. 147 (6), (2020).
- Lee-Liu, D., Edwards-Faret, G., Tapia, V. S., Larraín, J. Spinal cord regeneration: Lessons for mammals from non-mammalian vertebrates. Genesis. 51 (8), 529-544 (2013).
- Beck, C. W., Christen, B., Slack, J. M. W. Molecular pathways needed for regeneration of spinal cord and muscle in a vertebrate. Developmental Cell. 5 (3), 429-439 (2003).
- Love, N. R., et al. Genome-wide analysis of gene expression during Xenopus tropicalis tadpole tail regeneration. BMC Developmental Biology. 11, 70 (2011).
- Love, N. R., et al. Amputation-induced reactive oxygen species are required for successful Xenopus tadpole tail regeneration. Nature Cell Biology. 15 (2), 222-228 (2013).
- Gargiolo, C., Slack, J. M. W. Cell lineage tracing during Xenopus tail regeneration. Development. 131 (11), 2669-2679 (2004).
- Lin, G., Chen, Y., Slack, J. M. W. Regeneration of neural crest derivatives in the Xenopus tadpole tail. BMC Developmental Biology. 7, 56 (2007).
- Filoni, S., Bosco, L., Cioni, C. Reconstitution of the spinal cord after ablation in larval Xenopus laevistle. Acta Embryologiae et Morphologiae Experimentalis. 5 (2), 109-129 (1984).
- Gaete, M., et al. Spinal cord regeneration in Xenopus tadpoles proceeds through activation of Sox2-positive cells. Neural Development. 7, 13 (2012).
- Muñoz, R., et al. Regeneration of Xenopus laevis spinal cord requires Sox2/3 expressing cells. Developmental Biology. 408 (2), 229-243 (2015).
- Edwards-Faret, G., et al. Spinal cord regeneration in Xenopus laevis. Nature Protocols. 12 (2), 372-389 (2017).
- Méndez-Olivos, E. E., Larraín, J. Cell transplantation as a method to investigate spinal cord regeneration in regenerative and nonregenerative xenopus stages. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. 2018 (12), 943-947 (2018).
- Méndez-Olivos, E. E., Muñoz, R., Larraín, J. Spinal cord cells from pre-metamorphic stages differentiate into neurons and promote axon growth and regeneration after transplantation into the injured spinal cord of non-regenerative Xenopus laevis froglets. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience. 11, 398 (2017).
- de Vidts, S., Méndez-Olivos, E., Palacios, M., Larraın, J., Mery, D. Characterization of spinal cord damage based on automatic video analysis of froglet swimming. Biology Open. 8 (12), 2-11 (2019).
- Slater, P. G., Palacios, M., Larraín, J. Xenopus, a model to study wound healing and regeneration: Experimental approaches. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. 2021 (8), 100966 (2021).
- Lee-Liu, D., et al. Genome-wide expression profile of the response to spinal cord injury in Xenopus laevis reveals extensive differences between regenerative and non-regenerative stages. Neural Development. 9, 12 (2014).
- Lee-Liu, D., Sun, L., Dovichi, N. J., Larraín, J. Quantitative proteomics after spinal cord injury (SCI) in a regenerative and a nonregenerative stage in the frog Xenopus laevis. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics. 17 (4), 592-606 (2018).
- Peñailillo, J., et al. Analysis of the early response to spinal cord injury identi fi ed a key role for mTORC1 signaling in the activation of neural stem progenitor cells. NPJ Regenerative Medicine. 6 (1), 68 (2021).
- Edwards-Faret, G., et al. Cellular response to spinal cord injury in regenerative and non-regenerative stages in Xenopus laevis. Neural Development. 16 (1), 2 (2021).
- Tapia, V. S., Herrera-Rojas, M., Larrain, J. JAK-STAT pathway activation in response to spinal cord injury in regenerative and non-regenerative stages of Xenopus laevis. Regeneration. 4 (1), 21-35 (2017).
- Ishibashi, S., Amaya, E. How to grow Xenopus laevis tadpole stages to adult. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. 2021 (3), (2021).
- Nieuwkoop, P. D., Faber, J. . Normal table of Xenopus laevis (Daudin).: A systematical and chronological survey of the development from the fertilized egg till the end of metamorphosis. , (1994).
- Williams, M. C., Patel, J. H., Kakebeen, A. D., Wills, A. E. Nutrient availability contributes to a graded refractory period for regeneration in Xenopus tropicalis. Developmental Biology. 473, 59-70 (2021).
- Vleminckx, K. . Xenopus: Methods and protocols. , (2018).
- Sive, H. L., Grainger, R. M., Harland, R. M. . Early development of Xenopus laevis: A laboratory manual. , (2000).
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2024 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved