A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Standardization of a Cytometric Bead Assay Based on Egg-Yolk Antibodies
In This Article
Summary
This protocol describes a methodology for the preparation of latex beads for assays using IgY antibodies for antigen detection.
Abstract
Immunoassays are important tests for the detection of numerous molecular targets. Among the methods currently available, the cytometric bead assay has gained prominence in recent decades. Each microsphere that is read by the equipment represents an analysis event of the interaction capacity between the molecules under test. Thousands of these events are read in a single assay, thus ensuring high assay accuracy and reproducibility. This methodology can also be used in the validation of new inputs, such as IgY antibodies, for the diagnosis of diseases. These antibodies are obtained through immunizing chickens with the antigen of interest and then extracting the immunoglobulin from the yolk of the animals' eggs; therefore, this is a painless and highly productive method for obtaining the antibodies. In addition to a methodology for the high-precision validation of the antibody recognition capacity of this assay, this paper also presents a method for extracting these antibodies, determining the best coupling conditions for the antibodies and latex beads, and determining the sensitivity of the test.
Introduction
Among the immunoassay techniques aimed at diagnosing diseases, the cytometric bead assay has emerged as a highly sensitive and reliable approach, since it allows for the analysis of thousands of particles in a single assay1. This technique, in addition to having high productivity and allowing the use of smaller volumes of samples, also presents great flexibility, since it allows for the detection of several molecules, such as cytokines, adhesion molecules, antibody isotypes, and proteins2,3.
Different particles are used for the development of these assays, among them latex beads, which are an effective and low-cost input. These can present modifications on their surface, such as the presence of functional groups or proteins that allow the covalent or non-covalent coupling of certain molecules3,4,5.
These immunoassays use components such as antigens and antibodies to perform the detection of disease markers and commonly require antibodies from mammals such as mice, rabbits, and goats. This creates problems related to ethical issues, since the immunization of mammals generally requires many animals to obtain a good yield, as well as the frequent performance of procedures that lead to the suffering of the animals6,7. An alternative to this is the use of IgY antibodies isolated from the egg yolks of immunized chickens, since high concentrations of the specific antibodies against the inoculated antigens can be found in the yolks; the production of a chicken is equivalent to the production of 4.3 rabbits over the course of a year6,7.
Thus, the objective of this protocol is to provide a method for evaluating IgY antibodies obtained from chicken egg yolks using flow cytometry with latex beads. For this, we propose a standardization method for a cytometric bead immunoassay in sandwich format using latex beads. As a model, we used IgY antibodies directed to the Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein II antigen (IgY-PfHRP2). We describe a method for extracting the antibodies, discuss the critical steps for defining the coupling concentration of these to the latex beads, and present an evaluation of the limit of detection of the antigen. The high accuracy of flow cytometry, coupled with the low cost of latex beads, make this technique applicable for the analysis of immunoassay tools, such as antibodies and antigens. This method can be used for the detection of diverse targets.
Protocol
NOTE: See the Table of Materials for details related to all the materials, reagents, and instruments used in this protocol.
1. Extraction of IgY from egg yolks
- Hygienization of the eggs
- Immerse the eggs (freshly laid or until 4 days post-laid, from the Gallus gallus Dekalb White lineage) in a 0.2% diluted solution of sodium hypochlorite, rinse quickly under running water, and wipe gently for later or immediate use.
NOTE: If not used immediately, keep at 4 °C for up to 15 days.
- Immerse the eggs (freshly laid or until 4 days post-laid, from the Gallus gallus Dekalb White lineage) in a 0.2% diluted solution of sodium hypochlorite, rinse quickly under running water, and wipe gently for later or immediate use.
- Separation of the yolks
- Break the egg carefully, and separate the yolk from the white with the help of a yolk separator.
- Remove the excess white with the help of filter paper. Pierce the yolk, and collect its interior into a 50 mL conical tube. Store the yolk at −20 °C for at least 24 h prior to use.
NOTE: During these experiments (data not shown), it was observed that the use of yolks that had not been frozen previously hindered the isolation of immunoglobulins from the lipid portion of the yolks.
- Acidification of the yolks
- Thaw the stored yolk and dilute it at a 1:10 ratio in 1 mM PBS. Adjust the pH of the solution to 5 with 1 N HCl, and incubate the solution at 4 °C for 6-24 h.
- Centrifuge the solution at 3,000 × g for 40 min, recover the supernatant, and filter it using a 0.7 mm cellulose filter.
- Precipitation of lipids with caprylic acid
- Readjust the pH of the supernatants to 5, and add the caprylic acid (≥98% initial concentration) to a final concentration of 8.7% under constant stirring for 30 min at 4 °C.
NOTE: The volume of the supernatant may vary depending on the lipid mass precipitated in step 1.3.2. Thus, for example, 3.107 mL of caprylic acid should be added to 35 mL of the supernatant obtained after filtration. - Centrifuge the samples for 15 min at 18,600 × g, and separate the supernatant from the precipitated material.
- Readjust the pH of the solution to 7.4 using 1 M NaOH, quantify the antibodies using the Bradford assay8, and store the antibodies at −20 °C until the time of use.
NOTE: The antibodies were obtained at a concentration of 1 µg/µL, which was verified by means of a 12% SDS-PAGE gel.
- Readjust the pH of the supernatants to 5, and add the caprylic acid (≥98% initial concentration) to a final concentration of 8.7% under constant stirring for 30 min at 4 °C.
2. Saturation curve of IgY antibodies to latex beads
- Coupling of the beads to the IgY antibodies
- Add 21 µL of 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (EDC, initial concentration of 367 mM) and 21 µL of N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS, initial concentration of 50 mM) to 21 µL of latex beads (4% w/v), and adjust to a final volume of 2.1 mL with filtered 10 mM PBS.
NOTE: The pH range of the PBS solution should be between 7.2 and 7.4, since in this work, a negative change in the coupling and other steps was observed when using a solution outside this range. - Incubate at 22 °C with rapid shaking for 3 h.
- Add 4 µg, 2 µg, 1 µg, 0.5 µg, 0.25 µg, 0.125 µg, and 0 µg of the previously extracted capture antibody IgY-PfHRP2 (see step 1.4.3) to different microtubes containing 100 µL of the solution described in step 2.1.1 (0.04% final bead concentration), and incubate under the same conditions as described in step 2.1.2 for 16 h.
- Centrifuge the samples at 857 × g at 15 °C for 5 min, discard the supernatants, and wash the latex beads twice with 500 µL of filtered 10 mM PBS (0.008% final bead concentration) using centrifugation and resuspension cycles.
NOTE: Do not exceed 857 × g, as in this work, it was observed that beyond this speed the beads undergo deformations that negatively alter the test result.
- Add 21 µL of 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (EDC, initial concentration of 367 mM) and 21 µL of N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS, initial concentration of 50 mM) to 21 µL of latex beads (4% w/v), and adjust to a final volume of 2.1 mL with filtered 10 mM PBS.
- Blocking the beads
- Resuspend the samples in 1 mL of blocking buffer (0.004% final bead concentration) (filtered 10 mM PBS + bovine serum albumin, BSA, 5%), and incubate under the same conditions as described in step 2.1.2 for 2 h.
- After blocking, wash as described in step 2.1.4, and resuspend in 10 mM PBS buffer.
- Incubation with anti-chicken secondary antibodies labeled with Alexa Fluor 488
- Add 100 µL of fluorescent anti-chicken antibody (2 mg/mL) diluted to 1:2,000 in 10 mM PBS + 0.5% BSA to each microtube, as described in step 2.1.3.
- Incubate the samples as described in step 2.1.2, this time in the dark, for 30 min.
- Wash the beads as in step 2.1.4, and resuspend with 250 µL of (0.016% final bead concentration) filtered 10 mM PBS. Perform the flow cytometer reading as described in section 5.
NOTE: From the fluorescence percentage data obtained, observe the initial point of plateau formation (1 µg, as observed in this study). We recommend using the plateau's second point (2 µg, as observed here) for the next steps (Figure 1).
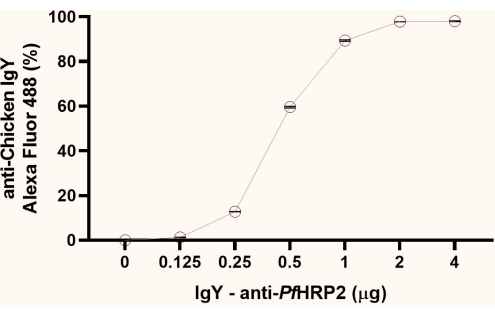
Figure 1: Graph of the flow cytometry analysis to determine the saturation point of the IgY-PfHRP2 antibody coupling to the latex beads. The x-axis represents the antibody concentration, and the Y-axis represents the percentage fluorescence obtained. Kruskal-Wallis test, p < 0.0033. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
3. Flow cytometry assay based on latex beads for antigen detection
- After determining the saturation point of the IgY antibodies to the latex beads, perform the bead activation process again, according to step 2.1.1.
- Couple the beads at the observed saturation concentration (as described in step 2.1.3), and incubate according to step 2.1.2.
NOTE: In the assays performed using the IgY-PfHRP2 antibody, the saturation condition was 2 µg for every 1 µL of latex beads.
- Couple the beads at the observed saturation concentration (as described in step 2.1.3), and incubate according to step 2.1.2.
- Block and wash the beads according to step 2.2.
- Incubation with the antigen
- To determine the limit of detection, distribute the equivalent of 100 µL of the blocked bead preparation into tubes containing different amounts of the recombinant protein PfHRP2 (1 µg/mL) (rPfHRP2, 10 µg, 1 µg, 0.1 µg, 0.01 µg, 0.001 µg, 0.0001 µg, and 0 µg) diluted in 10 mM PBS + 0.5% BSA in triplicate.
NOTE: This recombinant protein was developed in the work of Sousa et al.9. - Incubate the bead solutions with rPfHRP2 protein as described in step 2.1.2 for 1 h.
- Perform washings as described in step 2.1.4, and discard the supernatant after centrifugation.
- To determine the limit of detection, distribute the equivalent of 100 µL of the blocked bead preparation into tubes containing different amounts of the recombinant protein PfHRP2 (1 µg/mL) (rPfHRP2, 10 µg, 1 µg, 0.1 µg, 0.01 µg, 0.001 µg, 0.0001 µg, and 0 µg) diluted in 10 mM PBS + 0.5% BSA in triplicate.
- Incubation with the primary antibody
- Add 2 µg of mouse IgG antibody against the rPfHRP2 protein diluted in 10 mM PBS + 0.5% BSA to a final volume of 100 µL in each sample. Incubate the samples as described in step 2.1.2, and discard the supernatant after the last centrifugation.
NOTE: This antibody was developed in the work of Sousa et al.9.
- Add 2 µg of mouse IgG antibody against the rPfHRP2 protein diluted in 10 mM PBS + 0.5% BSA to a final volume of 100 µL in each sample. Incubate the samples as described in step 2.1.2, and discard the supernatant after the last centrifugation.
- Incubation with the secondary antibody
- Add 100 µL of fluorescent anti-mouse antibody (2 mg/mL) diluted to 1:2,000 in 10 mM PBS + 0.5% BSA to each sample. Incubate as described in step 2.1.2, and resuspend in 250 µL (0.016% final bead concentration) of filtered 10 mM PBS. Perform the reading according to section 5.
4. Flow cytometer reading of the samples
- Cytometry setting: Alignment of the optical parameters of the cytometer coupled to a computer
- Turn on the computer and flow cytometer, and wait a few minutes for the equipment to connect to the computer.
- Click on the cytometry software installed on the computer and log in to it. From the software workspace, select Cytometer | Startup | Clean mode | SIT fluids.
NOTE: Air bubbles and obstructions should be removed during the cytometer initiation process prior to sample acquisition.
- Quality control
- Use the quality control reagent to check the voltages of the photomultiplier tubes and assess the cytometer's sensitivity.
- Place the cytometer setup reagent and tracking beads in a 12 mm x 75 mm capped polystyrene tube.
- Gently mix the tube by vortexing.
- Preparation of the suspension beads
- For defining the baseline, add 0.5 mL of diluent (10 mM filtered PBS, pH 7) and three drops of beads to the 12 mm x 75 mm capped polystyrene tube. Vortex the tube gently before use.
- In the cytometer software workspace, select Cytometer | CST, and wait for the cytometer to disconnect from the cytometer software interface and connect to the CS&T interface. Observe the following message on the cytometer software Status Bar at the bottom of the screen: Disconnected Cytometer.
- Use the 12 mm x 75 mm capped polystyrene tube containing the quality control reagent and attach it to the flow cytometer probe.
- Verification of the cytometer configuration
- In the System Summary window, verify that the cytometer configuration is appropriate for the experiment.
- Setup for a performance check
- Select the setup beads' ID corresponding to the lot of CS&T research beads.
- Performance check
- Attach the tube to the flow cytometer probe, and click on the Setup Control window. Select Check Performance, and click on Run.
- Once the performance check is complete, wait for a dialog box to open. Do one of the following:
- To view the Cytometer Performance report, click on View Report.
- To complete the performance check and return to the setup view of the workspace, click on Finish.
- Observe the final result of the morphometric and fluorescence sensitivity analysis that appears in System Summary | Cytometer Performance Result with the status PASSED.
- Remove the tube from the cytometer. Check the cytometer performance results displayed in the System Summary window.
5. Sample analysis using flow cytometry
- Log in to cytometer software.
- From the cytometer software workspace, select Cytometer | Clean mode | SIT fluids.
- Adjust to the software workspace.
- Define the gating strategy based on the negative control particles' morphometric and fluorescence characteristics (beads without fluorescence).
- To determine the cell morphometry, choose Dot Plot Plot Graphic for the analysis of FSC-A parameters using SSC-A (Supplemental Figure 1A).
- Determine single cells by SSC using Dot Plot Plot Graphic for the analysis of SSC-H in the y-axis and SSC-W in the x-axis (Supplemental Figure 1B), and determine single cells by FSC using Dot Plot Plot Graphic for the analysis of FSC-H in the y-axis and FSC-W in the x-axis (Supplemental Figure 1C).
- For the fluorescence analyses, choose FL1 Dot Plot Plots using FCS-A. Use a 12 mm x 75 mm stoppered polystyrene tube containing unlabeled samples and samples previously labeled with single-color Alexa Fluor 488 (Supplemental Figure 1D, E).
- Acquire the sample in flow cytometry.
- Use a 12 mm x 75 mm stoppered polystyrene tube containing the previously labeled samples. Mix the tube contents carefully, attach the tube to the flow cytometer probe, and left-click on Acquire.
- To set the power of the lasers, click on Parameters, and in the options below, adjust the voltage of the FSC to 182 V and the voltage of the SSC to 236 V. To set the threshold, click on Cytometer | Threshold, and in the options below, adjust the FSC to 500 V.
- Set the analysis gate to characterize particles by size and complexity, as well as to perform single-cell analysis.
- To remove autofluorescence, analyze the dye-free sample containing only the latex beads, and adjust the voltages of the detector: in the options below, adjust the voltage of the FL1 (FITC) to 332 V.
- Set the fluorescence analysis gate in quadrangular format from the negative point shown in the dot plot graph.
- After the morphometric and fluorescent analyses have been adjusted, configure the device for 50,000 events: under Acquisition, click on Record.
Results
Figure 2 provides a graphical representation of the extraction process of IgY antibodies via acidification, followed by separation using caprylic acid (Figure 2).
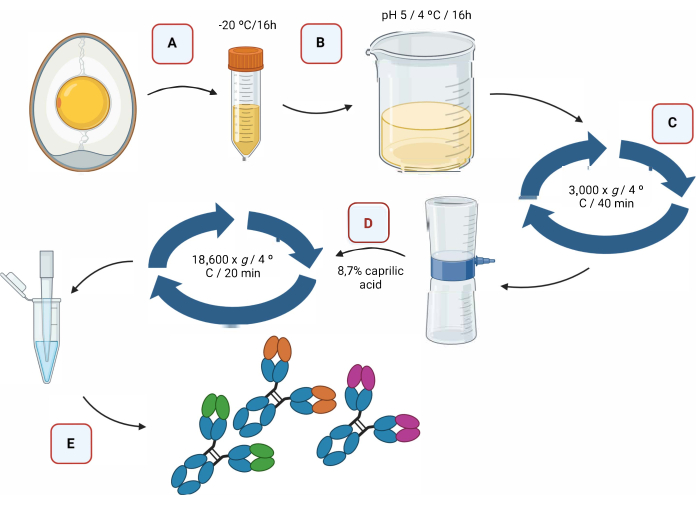
Figure 2: Schematic representation of the extraction step of IgY antibodies and separation...
Discussion
The method of precipitation of the IgY antibody by pH reduction followed by lipid separation using caprylic acid is efficient in isolating total antibodies without any loss in functionality. The method proposed here is simpler and cheaper than that reported by Redwan et al.11, which also used precipitation by acidification and caprylic acid but with a more complex and laborious protocol. This method also presents advantages over commonly used methodologies for IgY isolation from egg yolks, such as...
Disclosures
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the FIOCRUZ ("Programa de excelência em pesquisa básica e aplicada em saúde dos laboratórios do Instituto Leônidas e Maria Deane - ILMD/Fiocruz Amazônia-PROEP-LABS/ILMD FIOCRUZ AMAZÔNIA"), the Post-graduate Program in Biotechnology (PPGBIOTEC at the Universidade Federal do Amazonas - UFAM), the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível (CAPES), and the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Amazonas (FAPEAM) for providing the scholarships. Figure 2 and Figure 4 were created with biorender.com.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Anti-Chicken IgY (H+L), highly cross-adsorbed, CF 488A antibody produced in donkey | Sigma-Aldrich | SAB4600031 | |
| Anti-mouse IgG (H+L), F(ab′)2 | Sigma-Aldrich | SAB4600388 | |
| BD FACSCanto II | BD Biosciences | BF-FACSC2 | |
| BD FACSDiva CS&T research beads (CS&T research beads) | BD Biosciences | 655050 | |
| BD FACSDiva software 7.0 | BD Biosciences | 655677 | |
| Bio-Rad Protein Assay Dye Reagent Concentrate | Bio-Rad | #5000006 | |
| Bovine serum albumin | Sigma-Aldrich | A4503 | |
| Caprilic acid | Sigma-Aldrich | O3907 | |
| Centrifuge 5702 R | Eppendorf | Z606936 | |
| Chloride 37% acid molecular grade | NEON | 02618 NEON | |
| CML latex, 4% w/v | Invitrogen | C37253 | |
| Megafuge 8R | Thermo Scientific | TS-HM8R | |
| N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide Hydrochloride Powder (EDC) | Sigma-Aldrich | E7750-1G | |
| N-Hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) | Sigma-Aldrich | 130672-25G | |
| Phosphate buffered saline | Sigma-Aldrich | 1003335620 | |
| Sodium hydroxide | Acs Cientifica | P.10.0594.024.00.27 | |
| Sodium hypochlorite | Acs Cientifica | R09211000 | |
| Thermo Mixer Heat/Cool | KASVI | K80-120R |
References
- Salzer, U., Sack, U., Fuchs, I. Flow cytometry in the diagnosis and follow up of human primary immunodeficiencies. Electronic Journal of the International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory. 30 (4), 407 (2019).
- de Figueiredo, A. M., Glória, J. C., Chaves, Y. O., Neves, W. L. L., Mariúba, L. A. M. Diagnostic applications of microsphere-based flow cytometry: A review. Experimental Biology and Medicine. 247 (20), 1852-1861 (2022).
- Morgan, E., et al. Cytometric bead array: A multiplexed assay platform with applications in various areas of biology. Clinical Immunology. 110 (3), 252-266 (2004).
- Graham, H., Chandler, D. J., Dunbar, S. A. The genesis and evolution of bead-based multiplexing. Methods. 158, 2-11 (2019).
- Kellar, K. Multiplexed microsphere-based flow cytometric assays. Experimental Hematology. 30 (11), 1227-1237 (2002).
- Schade, R., et al. Chicken egg yolk antibodies (IgY-technology): A review of progress in production and use in research and human and veterinary medicine. ATLA Alternatives to Laboratory Animals. 33 (2), 129-154 (2005).
- Xu, Y., et al. Application of chicken egg yolk immunoglobulins in the control of terrestrial and aquatic animal diseases: A review. Biotechnology Advances. 29 (6), 860-868 (2011).
- Bradford, M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry. 72 (1-2), 248-254 (1976).
- Sousa, L. P., et al. A novel polyclonal antibody-based sandwich ELISA for detection of Plasmodium vivax developed from two lactate dehydrogenase protein segments. BMC Infectious Diseases. 14 (1), 49 (2014).
- Klimentzou, P., et al. Development and immunochemical evaluation of antibodies Y for the poorly immunogenic polypeptide prothymosin alpha. Peptides. 27 (1), 183-193 (2006).
- Redwan, E. M., Aljadawi, A. A., Uversky, V. N. Simple and efficient protocol for immunoglobulin Y purification from chicken egg yolk. Poultry Science. 100 (3), 100956 (2021).
- Lee, H. Y., Abeyrathne, E. D. N. S., Choi, I., Suh, J. W., Ahn, D. U. K. Sequential separation of immunoglobulin Y and phosvitin from chicken egg yolk without using organic solvents. Poultry Science. 93 (10), 2668-2677 (2014).
- Pauly, D., Chacana, P., Calzado, E., Brembs, B., Schade, R. IgY Technology: Extraction of chicken antibodies from egg yolk by polyethylene glycol (PEG) precipitation. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (51), e3084 (2011).
- Chang, H. M., Lu, T. C., Chen, C. C., Tu, Y. Y., Hwang, J. Y. Isolation of immunoglobulin from egg yolk by anionic polysaccharides. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 48 (4), 995-999 (2000).
- Ko, K. Y., Ahn, D. U. Preparation of immunoglobulin Y from egg yolk using ammonium sulfate precipitation and ion exchange chromatography. Poultry Science. 86 (2), 400-407 (2007).
- Polson, A. Isolation of IgY from the yolks of eggs by a chloroform polyethylene glycol procedure. Immunological Communications. 19 (3), 253-258 (1990).
- Simonova, M. A., et al. xMAP-based analysis of three most prevalent staphylococcal toxins in Staphylococcus aureus cultures. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 406 (25), 6447-6452 (2014).
- Sharma, P., et al. A multiplex assay for detection of staphylococcal and streptococcal exotoxins. PLoS One. 10 (8), e0135986 (2015).
- Merbah, M., et al. Standardization of a cytometric p24-capture bead-assay for the detection of main HIV-subtypes. Journal of Virological Methods. 230, 45-52 (2016).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved