A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Abstract
Medicine
Hochauflösende Respirometrie zur Beurteilung der Mitochondrienfunktion in menschlichen Spermien
ERRATUM NOTICE
Important: There has been an erratum issued for this article. Read more …Abstract
Die Samenqualität wird oft durch eine routinemäßige Samenanalyse untersucht, die beschreibend und oft nicht schlüssig ist. Männliche Unfruchtbarkeit ist mit einer veränderten mitochondrialen Aktivität der Spermien verbunden, so dass die Messung der mitochondrialen Funktion der Spermien ein Indikator für die Spermienqualität ist. Die hochauflösende Respirometrie ist eine Methode zur Messung des Sauerstoffverbrauchs von Zellen oder Geweben in einem geschlossenen Kammersystem. Diese Technik kann zur Messung der Atmung in menschlichen Spermien eingesetzt werden und liefert Informationen über die Qualität und Integrität der Spermienmitochondrien. Die hochauflösende Respirometrie ermöglicht es den Zellen, sich frei zu bewegen, was bei Spermien a priori von Vorteil ist. Diese Technik kann mit intakten oder permeabilisierten Spermien angewendet werden und ermöglicht die Untersuchung der intakten Mitochondrienfunktion der Spermien und der Aktivität einzelner Atmungskettenkomplexe. Das hochauflösende Oxygraph-Gerät verwendet Sensoren zur Messung der Sauerstoffkonzentration in Verbindung mit einer empfindlichen Software zur Berechnung des Sauerstoffverbrauchs. Die Daten werden verwendet, um Atmungsindizes auf der Grundlage der Sauerstoffverbrauchsverhältnisse zu berechnen. Folglich sind die Indizes die Anteile von zwei Sauerstoffverbrauchsraten und werden intern auf die Zellzahl oder Proteinmasse normiert. Die Atmungsindizes sind ein Indikator für die mitochondriale Funktion und Dysfunktion der Spermien.
Erratum
Erratum: High-Resolution Respirometry to Assess Mitochondrial Function in Human SpermatozoaAn erratum was issued for: High-Resolution Respirometry to Assess Mitochondrial Function in Human Spermatozoa. The Protocol and Representative Result sections were updated.
Step 2.4.12 of the Protocol was updated from:
Finally, inject 1 µL of 5 mM antimycin A (2.5 µM final concentration). This is a complex II inhibitor to discriminate between the mitochondrial and residual oxygen consumption (non-mitochondrial respiration). For the analysis of complex I, add 1 µL of 1 mM rotenone (0.5 µM final concentration), an inhibitor of this complex, instead of AA. Measure the oxygen consumption until the signal decreases and stabilizes.
to:
Finally, inject 1 µL of 5 mM antimycin A (2.5 µM final concentration). This is a complex III inhibitor to discriminate between the mitochondrial and residual oxygen consumption (non-mitochondrial respiration). For the analysis of complex I, add 1 µL of 1 mM rotenone (0.5 µM final concentration), an inhibitor of this complex, instead of AA. Measure the oxygen consumption until the signal decreases and stabilizes.
Figure 3 in the Representative Results section was updated from:
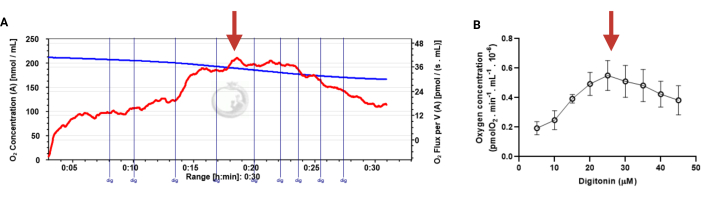
Figure 3: Determination of the optimal concentration of digitonin for the permeabilization of human sperm cells. The respiration rates were measured at 37 °C in MRM medium with glutamate, malate, and adenosine diphosphate. (A) Representative respiratory trace. The blue line is the O2 concentration, and the red line represents the O2 flow per volume correlated. (B) Mitochondria respiration rate means ± standard error, n = 4. The red arrow represents the optimal concentration. Abbreviation: dig = digitonin. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
to:
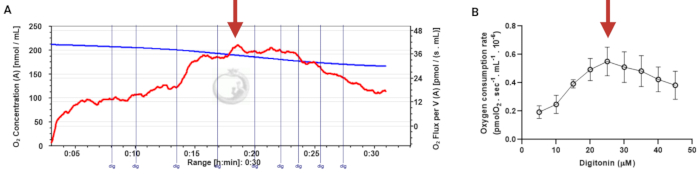
Figure 3: Determination of the optimal concentration of digitonin for the permeabilization of human sperm cells. The respiration rates were measured at 37 °C in MRM medium with glutamate, malate, and adenosine diphosphate. (A) Representative respiratory trace. The blue line is the O2 concentration, and the red line represents the O2 flow per volume correlated. (B) Mitochondria respiration rate means ± standard error, n = 4. The red arrow represents the optimal concentration. Abbreviation: dig = digitonin. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Explore More Videos
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2024 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved