Generation of a Bovine Primary Enteroid-Derived Two-Dimensional Monolayer Culture System for Applications in Translational Biomedical Research
In This Article
Summary
Enteroids are emerging as a novel model for studying tissue physiology and pathophysiology, drug development, and regenerative medicine. Here, we describe a bovine primary cell 2D enteroid-derived culture system that permits co-culture with relevant tissue cell types. This model offers a translational advantage for gastrointestinal research modeling.
Abstract
Organoid cell culture systems can recapitulate the complexity observed in tissues, making them useful in studying host-pathogen interactions, evaluating drug efficacy and toxicity, and tissue bioengineering. However, applying these models for the described reasons may be limited because of the three-dimensional (3D) nature of these models. For example, using 3D enteroid culture systems to study digestive diseases is challenging due to the inaccessibility of the intestinal lumen and its secreted substances. Indeed, stimulation of 3D organoids with pathogens requires either luminal microinjection, mechanical disruption of the 3D structure, or generation of apical-out enteroids. Moreover, these organoids cannot be co-cultured with immune and stromal cells, limiting in-depth mechanistic analysis into pathophysiological dynamics. To circumvent this, we optimized a bovine primary cell two-dimensional (2D) enteroid-derived monolayer culture system, allowing co-culture with other relevant cell types. Ileal crypts isolated from healthy adult cattle were cultured to generate 3D organoids that were cryopreserved for future use. A 2D monolayer was created using revived 3D enteroids that were passaged and disrupted to yield single cells, which were seeded on basement membrane extract-coated transwell cell culture inserts, thereby exposing their apical surface. The intestinal monolayer polarity, cellular differentiation, and barrier function were characterized using immunofluorescence microscopy and measuring transepithelial electrical resistance. Stimulation of the apical surface of the monolayer revealed the expected functionality of the monolayer, as demonstrated by cytokine secretion from both apical and basal compartments. The described 2D enteroid-derived monolayer model holds great promise in investigating host-pathogen interactions and intestinal physiology, drug development, and regenerative medicine.
Introduction
Animal models in research play a crucial role in enhancing our understanding of disease pathophysiology and the dynamics of the host immune response during infection and support the development of novel preventative and therapeutic strategies1,2,3,4. These models support research discovery and advancement in animals and are key to the progress of human health research. For decades, rodent models have underpinned advances in immune mechanisms and fundamental biology research for human diseases3,5,6,7. While rodent models are critical in screening and early development research, large animal models offer a more relevant comparison in researching human diseases in both early discovery and later development studies, including therapeutic efficacy and safety testing1,3,4,5. Livestock offers clear advantages compared to rodent models for more efficient translation for human applications for some diseases, including cryptosporidiosis, salmonellosis, tuberculosis, respiratory syncytial virus, and brucellosis1,7,8. Indeed, these diseases and others develop spontaneously in cattle, which share several analogous disease pathogenesis and immune processes to humans, and as an outbred population, cattle mimic the genetic and environmental heterogeneity influencing human immune responses5,8,9,10. The benefits of bovine models for infectious disease research can be maximized by first employing a sophisticated culture system and then implementing in vivo studies stepwise. The initial use of a highly complex bovine-derived culture system can considerably reduce the number of live animal studies while improving the chances of successful translational and applied research. Culture models should recapitulate the disease processes at an organ level for optimal predictive validity, retaining the native tissue microenvironment spatially and functionally.
The mucosal immune response is a multifaceted system comprised of a highly efficient barrier formed by gastrointestinal enterocytes and diverse populations of immune cells located below the mucosal surface11. This highly complex system is critical during infection in maintaining GI homeostasis and initiating immune defenses against enteric pathogens11. Communication between enterocytes and underlying innate immune cells initiates the development of protective immune responses against pathogenic microorganisms. As such, culture systems that are comparative in their level of complexity are necessary for an optimal investigation into host-enteric pathogen interactions and are highly effective in understanding enteric physiology and drug discovery and development12,13. Organoids are a robust culture system that resembles the architecture and function of the tissue of origin14,15. The multicellularity of these models permits investigation into the role of diverse cell populations and the cellular interactions involved in enteric health and disease12,14. However, human-derived organoid models in research are currently limited by the difficulty of obtaining a sufficient quantity and consistent quality of human intestinal epithelial cells and limited cell viability in culture. Immortalized cell lines can be used to obtain high yields of homologous cultures in these models consistently; however, transformed cells inherently lack the diversity and functional complexity of non-transformed epithelial cells16,17. The advantages of using cultures derived from bovine tissue as a model for investigating gastrointestinal diseases and physiology include the ease with which tissue samples can be consistently obtained from healthy donors, improved cell viability, and greater cellular diversity achievable only with non-immortalized tissue. Comparative tissue transcriptomics and characterization of intestinal organoids reveal similarities in conserved orthologous genes and cellular potentials between humans and cattle18. Therefore, a bovine organoid-derived culture system may be advantageous in investigating human intestinal diseases, with findings easily translatable to human medicine.
The protocol described herein details an effective platform to evaluate host responses to enteric pathogens or compounds and intestinal physiology using a bovine enteroid-derived 2D primary cell culture system. Unlike 3D organoids, 2D culture systems generated on transwell inserts permit a dual culture of intestinal cells with immune or stromal cells, allowing study into the tissue-level dynamics. With applications in biomedical research, pharmaceutical development, and efficacy testing, this physiologically relevant model can benefit the health and advancement of both cattle and people alike.
Protocol
All protocols were performed in compliance with institutional and national guidelines and regulations for animal welfare.
1. Reagent preparation
NOTE: The stock and final concentrations of the reagents used in this study are listed in Table 1.
- Prepare sample collection buffer: Mix 1 L of ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing penicillin (100 U/mL), streptomycin (100 µg/mL), gentamicin (25 µg/mL), and caspofungin (2.5 µg/mL). Store stock solution at 4 °C.
- Prepare Dissociation Reagent #1: Mix 18.55 mL of sample collection buffer (as described in step 1.1), 1.422 mL of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA, 0.422 M/pH 7.4), 20 µL of 1 M 1,4-Dithiothreitol (DTT) solution, 4 µL of Y-27632 solution (5000x/50 mM). Store the solution at 4 °C.
- Prepare Dissociation Reagent #2: Mix 18.57 mL of collection buffer (as described in step 1.1), 1.422 mL of EDTA (0.422 M/pH 7.4), 4 µL of Y-27632 solution (5000x/50 mM). Store the solution at 37 °C.
- Prepare enteroid growth media stock: Mix 9.875 mL of organoid growth medium plus supplement, 100 µL of penicillin (100 U/mL), streptomycin (100 µg/mL), 5 µL of gentamicin (25 µg/mL), and 20 µL of caspofungin (2.5 µg/mL). Store the solution at 4 °C.
- Prepare enteroid differentiation media stock: Mix 10 mL of organoid differentiation medium plus supplement, 100 µL of penicillin (100 U/mL), streptomycin (100 µg/mL), 5 µL of gentamicin (25 µg/mL), and 20 µL of caspofungin (2.5 µg/mL). Store solution at -20 °C.
- Prepare wash media: Mix 48.45 mL of DMEM/ F-12 1.1 medium (with L-glutamine, without HEPES), 1 mL of B-27 supplement without vitamin A (50x stock), 500 µL of penicillin (100 U/mL), streptomycin (100 µg/mL), 25 µL of gentamicin (50 mg/mL stock), and 25 µL of caspofungin (5 mg/mL stock). Store the solution at 4 °C.
- Prepare coating buffer: Mix 25 mL of DMEM: F12 complete media without inhibitors and 25 mg of bovine serum albumin (BSA). Store the solution at 4 °C.
2. Isolation of intestinal crypts from whole tissue (Figure 1)
NOTE: Bovine small intestinal enteroids were generated from ileal tissue obtained from healthy adult Holstein steers (>2 years of age) from a local beef processing plant. One donor was used for this series of experiments.
- Preparation of intestinal tissue samples
- Place the harvested ~10 inch (25 cm) intestinal tissue samples in ~400 mL of ice-cold collection buffer (PBS+ antibiotics/antimycotics) and on ice for transport to the laboratory.
- Using surgical scissors (e.g., mayo scissors) and forceps (e.g., adson forceps), remove the excess fat and mesentery from the intestinal tissue sample.
- Cut the tissue into two equal pieces.
- Open the tissue longitudinally with surgical scissors and rinse the tissue in sterile PBS.
- Gently remove the mucus layer of the intestinal sample using the side of a sterile glass microscope slide and rinse the tissue with fresh PBS.
NOTE: This step helps to remove the villi and helps increase the purity of the crypt fractions in subsequent steps. - For each 5-inch (13 cm) piece, cut the tissue into two 2.5 inches (6.5 cm) and then cut each piece into 4 approximately equal small pieces to facilitate tissue dissociation.
- Dissociation of intestinal tissue
- Prepare a 20 mL volume of the tissue Dissociation Reagent #1 in a sterile 50 mL conical tube and deposit the small tissue samples into the conical tube until the volume displacement moves the meniscus from the 20 mL mark to the 35 mL mark on the conical tube.
- Repeat the above step for the remaining small intestine tissue sample pieces.
- Seal the conical tubes with parafilm and manually shake the conical tube 10 times.
NOTE: Throughout the protocol, manual shaking should be done in a deliberate but gentle manner. - Place the conical tubes horizontally on ice in a container on an orbital shaking platform.
- Shake the conical tubes on ice in the container for 30 min at 80 revolutions per minute (rpm). Every 10 min, manually shake the conical tube.
- Prepare a 20 mL volume of pre-warmed (37 °C) tissue Dissociation Reagent #2 (formulated as above, but without DTT) in a 50 mL conical tube. Deposit the tissue samples from the conical tubes containing the Dissociation Reagent #1 into the conical tubes containing the Dissociation Reagent #2.
- Seal the conical tubes with parafilm and manually shake the conical tubes 10 times.
- Place the conical tubes into a pre-warmed (37 °C) shaking water bath, tilted at an approximately 60 °C angle, and shake at 150 rpm for 10 min, with manual shaking after 5 min and again after the total 10 min incubation.
- Isolation of crypt fragments
- Label 10 sterile conical tubes #1 - #10. Add 20 mL of sterile ice-cold PBS to each labeled conical tube.
- Transfer the tissue pieces from the conical tubes containing the dissociation reagent #2 into a new sterile 50 mL conical tube containing ice-cold PBS #1.
- Manually shake the conical tubes 10 times.
- Seal the conical tubes with parafilm and place them horizontally on ice. Shake conical tubes on an orbital shaker for 10 min at 80 rpm. After 10 min, manually shake conical tube #1 10 times. This is considered Wash #1.
- Gently transfer tissue samples using a pair of surgical forceps to conical tube #2.
- Repeat steps 2.3.2 - 2.3.4, this is considered Wash #2.
- Repeat washes until wash #10.
- The supernatants from each wash contain the crypts that will be used for enteroid generation. Keep the tubes containing the supernatants at 4 °C until all 10 washes are complete.
- After the 10th wash is complete and the tissue section discarded, centrifuge the supernatants of conical tubes #6-#10 at 400 x g for 2 min at 4 °C to pellet the isolated crypts.
NOTE: Washes 6-10 contain the cleanest fractions of intact crypts with limited debris and single cells. As such, it is recommended that only these fractions are used for enteroid generation, and the earlier washes (#2-#5) are discarded) - Discard the supernatant and add 4 mL of fresh, ice-cold PBS to crypts without resuspending (this helps to keep the fragments intact until microscopy).
- Assess the purity of the dissociated crypts for each conical tubes #6-#10 by microscopy.
- Add 50 µL of PBS to a 384-well plate.
- Add 10 µL of crypt suspension to the PBS and use a 40x magnification objective lens to determine the crypt purity, integrity, and count.
NOTE: Drawing a cross on the bottom of the plate well makes counting easier.
3. Ex vivo generation and passage of bovine ileal enteroids (Figure 2)
NOTE: The crypts from the conical tubes with the most pure, intact intestinal crypts will be used for downstream assays. For all steps that involve crypts and enteroids, pipette tips, cell scrapers, and tubes must be pre-coated with the coating buffer, and bubbles should be avoided to prevent the loss of crypts. Unless otherwise stated, a 1000 µL pipet tip should be used to prevent breaking up crypt fragments.
- Generating enteroids from crypt fragments
- Combine the purest crypt fractions (usually #6-#10) into one conical tube.
- Centrifuge the conical tube containing the crypts at 400 x g for 2 min at 4 °C.
- Discard the supernatant by aspirating it with a pipette and resuspend the crypt pellet in Wash Media.
- Centrifuge as in step 3.1.2. Decant the supernatant and add 2 mL of Wash Media to the crypt pellet.
- Count the number of crypts as described in step 2.3.11.1.
- Centrifuge as in step 3.1.2 to pellet the crypts, discard supernatant, and resuspend in ice-cold 100% reduced growth factor basement membrane extracellular matrix (BME) to achieve a concentration of approximately 400 crypts/100 µL.
NOTE: it is important to properly thaw BME at 4 °C as changes in temperature alter its consistency. The BME can be prevented from solidifying prematurely using a cooling block and pre-chilled pipet tips.- Using another basement membrane matrix formulation may require dilution of the BME when creating domes. Refer to the manufacturer instructions specific to the BME being used.
- Pipet up and down to thoroughly suspend the crypts in the BME.
- Make crypt-BME domes by slowly pipetting 50 µL of crypt-BME suspension onto a 6-well tissue culture plate on a warming plate set to 37 °C with up to 8 domes/well.
NOTE: The 6-well plate must be pre-warmed in an incubator at 37 °C overnight prior to the plating of domes. - Keep the 6-well plate on the warming plate for 1 min before carefully moving the plate to a 37 °C, 5% CO2 incubator.
- After 2 min, flip the 6-well plate so the lid is facing down and incubate for an additional 30 min to allow the domes to polymerize.
- After 30 min, carefully add 3 mL of room temperature (RT) Enteroid Growth Media supplemented with 10 µM SB202190, 0.5 µM LY2157299, and 10 µM Y-27632 to the wells containing domes.
- Incubate at 37 °C, 5% CO2.
- Remove media and replace with fresh Enteroid Growth media supplemented with inhibitors every 2-3 days.
- Passaging of enteroids
- After 7-10 days, ensure that the crypts have formed 3D enteroids with many budding structures, as in Figure 2E, and are ready to be passaged.
- Discard the media from the wells containing domes.
- For every 4 domes per well, add 1 mL of ice-cold Non-Enzymatic Cell Dissociation Solution supplemented with 10 µM Y-27632 to each well containing domes.
- Using a pre-coated cell scraper, gently detach the dome from the tissue culture plate.
- Collect enteroids in a 15 mL conical tube and triturate by pipetting up and down 10 times.
- Incubate the conical tube containing the fragmented enteroids at RT on an orbital shaker at 80 rpm for 10 min.
- Add 10 mL of ice-cold Wash Media with 10 µM Y -27632 to the enteroids.
- Centrifuge the conical tube at 300 x g for 5 min at RT.
- Discard the supernatant and resuspend the pellet in 10 mL of fresh Wash Media and transfer to a new 15 mL conical tube.
- Centrifuge the conical tube at 300 x g for 5 min at RT.
- Discard the supernatant and resuspend the pellet in 1 mL of Enteroid Growth Media in 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube.
- Centrifuge the microcentrifuge tube at 300 x g for 5 min at RT and discard the supernatant.
- Resuspend the enteroid pellet in ice-cold 100% BME and follow steps 3.1.6-3.1.13.
- Repassage enteroids every 7 days. Expansion times may vary due to the density, viability, and extent of budding. Multiple budding structures creating large enteroid structures are indicative of the enteroids needing to be passaged.
- Cryopreservation of enteroids
- For cryopreservation, Ensure that the enteroids are passaged no more than five times in culture.
NOTE: This has not been tested experimentally and is based on the authors' observation that later passages have reduced viability and yield variable results. - To harvest the enteroids, use the dissociation buffer as described in steps 3.2.2-3.2.9.
NOTE: Mechanically dissociate the enteroids using a 5 mL pipet. - Count the number of enteroid fragments as described in step 2.3.11.1.
- Centrifuge the conical tube at 300 x g for 5 min at RT.
- Discard the supernatant and resuspend the enteroid fragments in cryopreservation media supplemented with 10 µM Y-27632 to achieve a concentration of ~2000 enteroid fragments/mL and aliquot 1 mL into pre-labeled cryovials.
- Place the cryovials in a controlled freezing container and store at -80 °C overnight.
- Transfer the cryovials to vapor-phase liquid nitrogen for long-term storage.
- For cryopreservation, Ensure that the enteroids are passaged no more than five times in culture.
- Resuscitation of intestinal crypts fragments
- Place a 6- well plate overnight inside the incubator.
- Pre-coat a 5 mL tube with 5 mL of coating media.
- Remove the cryovials from liquid nitrogen storage.
- Immediately, once thawed, transfer crypts from the cryovial to the pre-coated 5 mL tube. Rinse out the cryovial with Wash Media and add to the 5 mL tube. Avoid bubbles.
- Bring the volume up to 5 mL with Wash Media and centrifuge at 400 x g for 5 min at 4 °C .
- During the centrifugation, pre-coat a 1.5 mL tube with coating media.
- After centrifugation, pour off the supernatant, resuspend the pellet in the media remaining in the tube, and transfer to the pre-coated 1.5 mL tube. Wash the 5 mL tube with Wash Media and transfer it to a 1.5 mL tube. Centrifuge at 400 x g for 5 min at 4 °C.
- Bring the volume up to 1.5 mL with Enteroid Growth Media.
- Centrifuge as above (step 3.4.7), and carefully aspirate.
- Take BME from 4 °C and place on ice/ice block.
- Resuspend the enteroid pellet in ice-cold 100% BME and follow steps 3.1.6- 3.1.12.
- Change the media every 2-3 days.
4. Generation and assessment of 2D monolayers from 3D enteroids
NOTE: As above, for all steps that involve crypts and enteroids, pipette tips, cell scrapers, and tubes should be pre-coated with the Coating Buffer, and bubbles should be avoided to prevent the loss of crypts.
- Preparation of transwell inserts for 2D monolayer formation
- Place inserts into a 24-well tissue culture adapter plate and pre-coat the apical side of 1 µm PET 24-well cell culture inserts with 100 µL of 1:15 dilution of BME in Enteroid Growth Media. Always coat an extra insert that will be used as a control when taking barrier integrity measurements.
- Place the coated insert in a 24-well tissue culture adapter plate in the incubator.
NOTE: A specific adapter or companion tissue culture plate must be used with the transwell inserts. - Incubate the culture inserts at 37 °C, 5% CO2 for 1 h to allow polymerization.
NOTE: BME-coated transwells can be sealed with parafilm and stored at 4 °C for up to 1 week if not used immediately. - At the end of the incubation, aspirate the 3D enteroid culture medium.
- Dissociation of 3D enteroids
- Generate 2D enteroid monolayers from cryopreserved enteroid fragments that were resuscitated, plated, and cultured as described above in section 3.1 to form 3D enteroids. Passage the thawed enteroids at least twice, with the last passage cultured for a minimum of 5 days before processing to generate 2D monolayer cultures.
- Harvest the enteroids by adding ice-cold Wash Media supplemented with 10 µM Y-27632 to enteroid domes (use approximately 1 mL of dissociation buffer for 4 domes)
- Detach the domes with a cell scraper and collect them into a 15 mL conical tube.
- Triturate 30 times using a 1 mL pipette tip to generate enteroid fragments.
- Triturate 40 times with a 200 µL pipette tip to further break up the enteroid fragments.
- Bring the volume of the 15 mL conical tube with enteroid fragments to 10 mL with ice-cold Wash Media.
- Centrifuge the conical tube at 300 x g for 5 min at RT.
- Aspirate the supernatant, including the BME layer, taking care not to disturb the enteroid pellet.
NOTE: The BME layer will appear as a cloudy gelatinous layer just above the pellet. - For every 4 domes, resuspend the pellet in 1 mL of pre-warmed TrypLE express enzyme supplemented with 10 µM of Y-27632.
- Add enteroid-TrypLE mixture to a 24-well plate and incubate at 37 °C, 5% CO2 for 10 min.
- After 10 min, pipet the enteroid-TrypLE mixture 40 times using a 1 mL pipette to further fragment the enteroids.
- Then, pipet fragments 40 times with a 200 µL pipette to break the fragments into single cells.
- Using a 3 mL or 5 mL syringe with a sterile 22-G needle attached, aspirate and dispense the cell suspension 4 times to achieve single cell suspension.
- Monitor cell dissociation by microscopy as described in step 2.3.11.1, until 80% of the enteroids are broken down into single cells.
- Collect cell suspension into a 15 mL conical tube and quench enzymatic reaction by adding 4x volume of Wash Media supplemented with 10% FBS.
- Filter the enteroids through a pre-coated 40 µm cell strainer twice into a 50 mL conical tube.
- Pellet the single cells by centrifuging the conical tube at 300 x g for 5 min.
- 2D monolayer seeding on transwell inserts.
- Decant the supernatant and resuspend the pellet in a small volume (~600 µL) of organoid growth media supplemented with 20% fetal bovine serum (FBS) at RT.
- Determine enteroid cell density and viability using the Trypan Blue dye exclusion method, hemacytometer, or automated cell counter. An average viability of 75% is expected.
- Carefully remove the excess coating solution applied in step 1.3 from the cell culture insert just prior to seeding the cells.
- Seed the single cells at 1 x 105 cells in a volume of 200 µL per insert on the apical surface of a pre-coated cell culture insert.
- Add 700 µL of complete media supplemented with 20% FBS to the basolateral side of the cell culture insert.
- Maneuver the plate 10 times in the shape of the number 8 to allow the cells to spread evenly over the insert.
- Keep the plate on the plate warmer for 10 min in the biosafety cabinet.
- Incubate the plate at 37 °C and 5% CO2.
- After 48 h, replace media on the apical and basal compartments with fresh Enteroid Growth Media supplemented with 20% FBS and inhibitors.
- On the third day, remove the media from the apical and basolateral compartments, carefully wash the insert with 1x PBS, and replace it with Enteroid Differentiation media supplemented with inhibitors only.
- Change the media in both compartments every 2-3 days.
- Quantitative measurement of epithelial barrier integrity and monolayer confluency
NOTE: Barrier integrity can be assessed by using an epithelial voltohmmeter to measure transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER).- Remove the transwell culture plate from the incubator and allow it to equilibrate at RT for a few minutes in the biosafety cabinet.
- Make sure the STX2 electrodes have been pre-conditioned and voltohmmeter calibrated to 1000Ω per the manufacturer's instructions.
- Insert the long stick of the probe into the basolateral compartment and the short end into the apical compartment of the transwell epithelial cell culture. Take care not to disrupt the monolayer or damage the insert.
- Once stable, record 3 TEER measurements per transwell insert, including the insert without cells. Take an average of the measurements for each insert.
- Calculate the corrected TEER value by subtracting the average measurement of the blank well from the average measurements of the experimental wells and then multiplying it by the surface area of the insert to determine the resistance of the epithelial barrier (TEER [Ω.cm2] = [Rcell layer - Rblank] × Area).
Representative Results
The first step in generating 2D enteroid-derived monolayers is to prepare the section of intestinal tissue harvested (Figure 1A) for tissue dissociation. This is done by removing the attached fat and the mesentery from the tissue (Figure 1B), followed by cutting the tissue longitudinally to expose the lumen surface so that the mucus layer of the intestine can be removed by gentle scraping using a glass slide. The harvested intestinal section is then cut into progressively smaller tissue sections (Figure 1C) to increase the ease of dissociation. Crypts are then dissociated from the underlying sub-mucosal tissue using a series of washes consisting of chelation buffers (Figure 1D,E) and PBS. The isolated intestinal crypts (Figure 1F) are then embedded in basement membrane matrix domes (Figure 2A) and cultured for several days to generate 3D enteroids. From a 10-inch section of bovine ileum, approximately 900,000 crypts can be isolated and used for enteroid formation. After just a few hours in culture, the plated crypts begin to elongate and develop into enterospheres (Figure 2B). After 2 days, a well-defined lumen can be observed (Figure 2C), with budding structures noted as early as day 4 in culture (Figure 2D). By day 7, mature enteroids have developed (Figure 2E). The immunofluorescence staining of 7-day-old 3D enteroid demonstrates the presence of different cell lineages. Confocal microscopy of enteroids demonstrates localization of DAPI nuclear stain, E-cadherin protein at the adherens junction, Chromogranin-A (Chr-A) staining showing the presence of enteroendocrine cells, Lysozyme (LYZ) demonstrating Paneth cells, and Cytokeratin-18 (CK-18) representing enterocyte cells in Figure 3. After 7-10 days in culture, the enteroids should be passaged to allow for further expansion and prevent overcrowding. The optimal time to passage enteroids was determined to be 7-10 days after initial primary crypt isolation and is ultimately dependent upon the health and growth rate of enteroids in culture. The optimal seeding density to achieve the desired enteroid morphology and viability, as depicted in Figure 2E, is 400 crypts per dome. Enteroids can easily be cryopreserved, and the thawed enteroid fragments fully recover for experimental use after two passages post-thaw. Notably, at least two passages of the primary crypt culture are recommended before cryopreservation.
In order to produce a 2D enteroid-derived monolayer, the 3D enteroids are harvested and over a series of steps, are mechanically triturated in the presence of a dissociation solution (Figure 4A) into single cells. These single cells can then be seeded on a transwell insert that has been pre-coated with a basement membrane matrix-culture media solution. On average, four transwells can be seeded from four 3D enteroid domes. The number of 3D enteroids processed is thus dependent upon the number of transwells needed for the experiment. Plating single cells at a seeding density of 1 x 105 and initially culturing them in the presence of 20% FBS (Figure 4B-D) can generate a confluent monolayer in less than 1 week. The progressive confluence of the 2D monolayer in culture can be monitored over time using light microscopy (Figure 4E,F). Transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) measurements can confirm confluency and characterize the epithelial barrier integrity over time and in response to experimental stimulation (Figure 5A). On average, after seven days in culture, a roughly 100% confluent monolayer will have a corresponding TEER value of ~1500 Ω·cm2. A longitudinal assessment of 2D enteroid monolayer TEER values demonstrates a steady increase in TEER values over seven days, reaching a maximum average value of 1546 Ω·cm2 before declining with the lowest value of 11.5 Ω·cm2 obtained on day twelve (Figure 5B). Immunofluorescent labeling of differentiated monolayers indicates that intact, organized, polarized intestinal epithelial sheets are formed using this protocol (Figure 6). Confocal microscopy of the stained 2D monolayer demonstrates localization of DAPI nuclear stain, E-cadherin, and F-actin staining (Figure 6A-D). Fluorescence microscopy of the 2D monolayer shows hallmarks of differentiated intestinal epithelial cells with Chromogranin-A (Chr-A) staining showing the presence of enteroendocrine cells, Lysozyme (LYZ) demonstrating Paneth cells, and Cytokeratin-18 (CK-18) indicating enterocyte cell lineages (Figure 6E-L). Z-stack modeling shows the expected polarization of the 2D monolayer culture with characteristic deposition of F-actin that is found in the microvilli covering the apical aspect of the differentiated enterocytes and E-cadherin, a protein located at the adherens junctions interspaced between epithelial cells (Figure 6M).
The functionality of the monolayer can be assessed by apical stimulation with various components, including Toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands or pathogens, followed by cytokine quantification of cell cultures supernatants harvested from the apical and basal compartments. Indeed, when the apical aspect of the monolayer is stimulated for 24 h with the TLR 1/2 agonist Pam3csk4 on day 4 of culture, increased cytokine production in both compartments is observed compared to the untreated monolayers (Figure 7A,B).
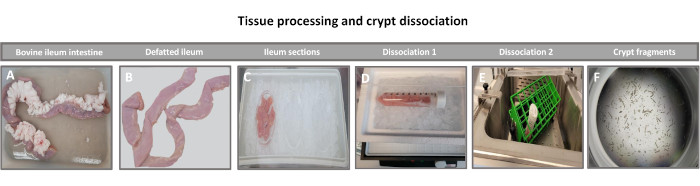
Figure 1: Bovine intestinal crypt isolation from healthy adult cattle. Images illustrating the tissue processing of (A) whole adult cattle ileum, (B) defatted ileum, (C) ileum sectioned into 2.5-inch (6.3 cm) pieces in PBS on ice, (D) ileal tissue sections in dissociation buffer #1 at 4 °C, and (E) in dissociation buffer 2 in a shaking water bath at 37 °C, and (F) isolated ileal crypt fragments. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
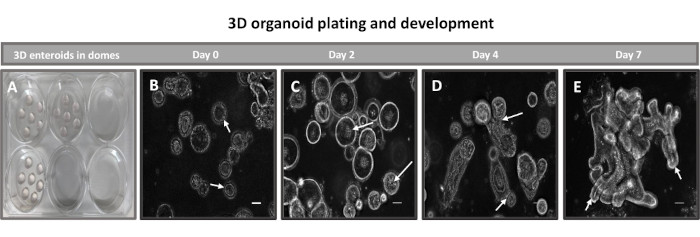
Figure 2: Bovine primary 3D ileal enteroid development in basement membrane matrix. Representative images of (A) 3D enteroid domes created in a 6-well tissue culture plate and (B-E) 3D enteroid development from days 0, 2, 4, and 7 in culture. Scale bar = 50 µm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
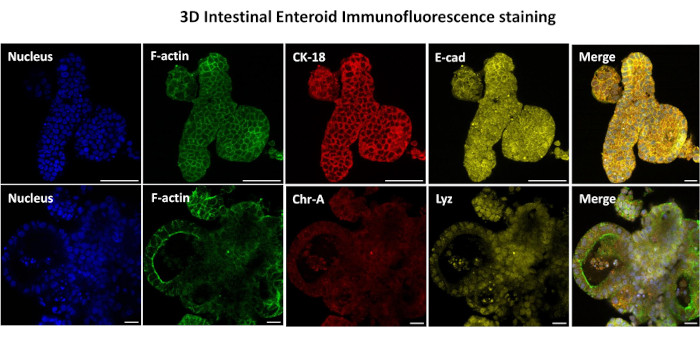
Figure 3: Three-dimensional intestinal enteroids show epithelial cell lineage staining. Representative images of 3D enteroids after 7 days in culture demonstrate the presence of nuclear stain, F-actin, cytokeratin-18 (CK-18), Chromogranin-A (Chr-A), Ecadherin (E-cad), Lysozyme (Lyz) and overlay of images (Merge). Scale bar 50 µm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
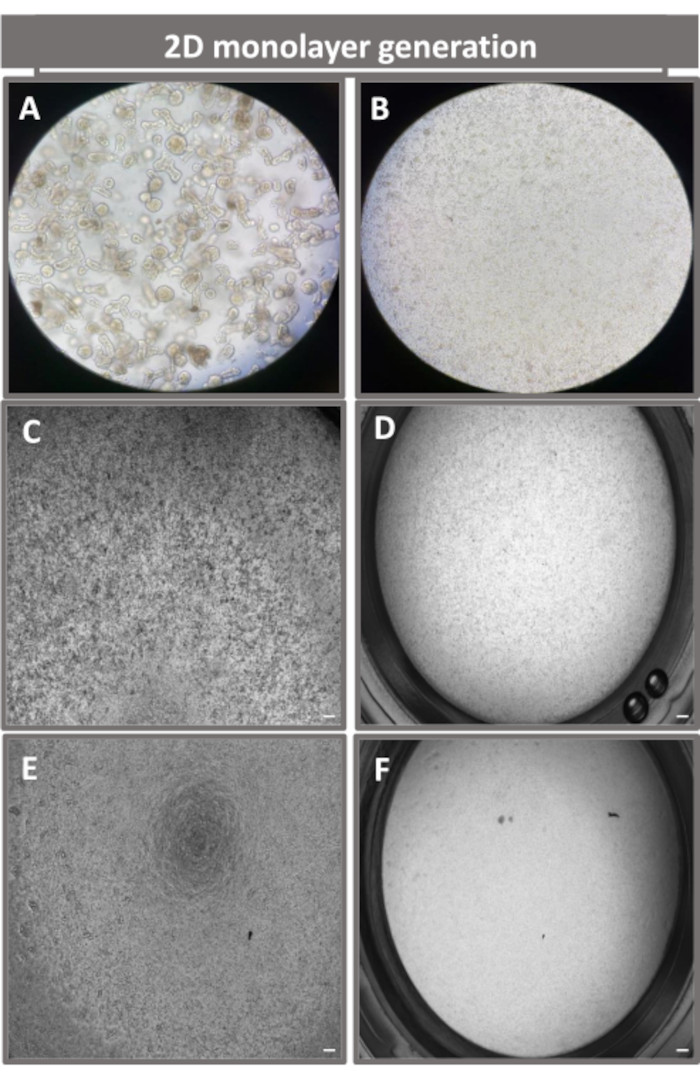
Figure 4: Establishment of 2D enteroid-derived monolayer from ileal enteroids. Representative images of (A) 3D enteroid fragments in dissociation solution in preparation for monolayer seeding, single cells plated on a transwell insert at a seeding density of 1 x 105 imaged on day 0 using (B) light, (C) phase contrast, and (D) bright field microscopy, and monolayer development on transwell inserts imaged on day five using (E) phase contrast and (F) bright field microscopy. 40x magnification and scale bar = 50 µm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
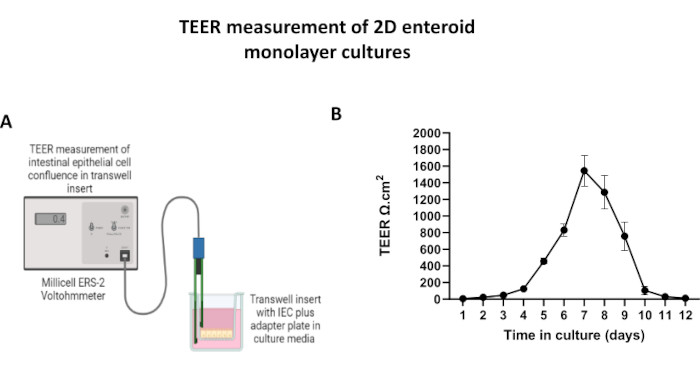
Figure 5: Transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) measurements of the 2D enteroid-derived monolayer on transwell inserts. (A) Schematic diagram of how TEER measurements of the 2D intestinal epithelial cell (IEC) monolayer are obtained using the STX2 chopstick electrodes of a voltohmmeter, (B) Longitudinal monitoring of 2D monolayer TEER measurements over 12 days in cell culture. Each data point represents an average TEER value and standard error of mean (SEM) obtained from two technical replicates. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
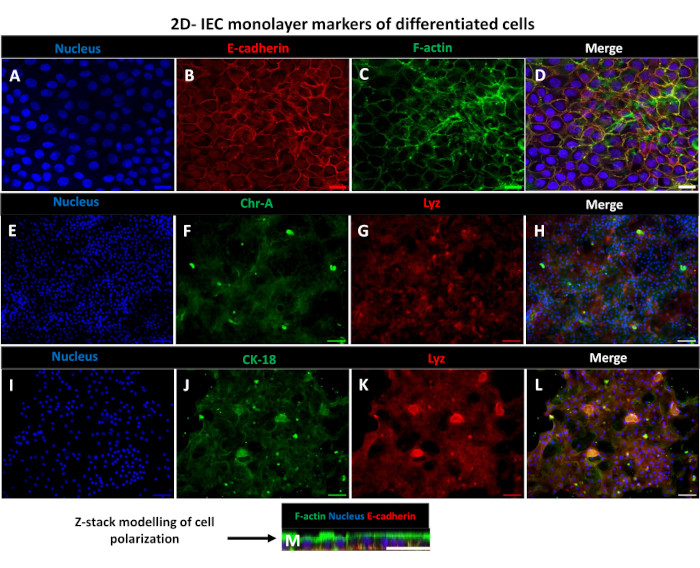
Figure 6:Differentiated 2D enteroid-derived monolayers on transwell inserts develop into polarized intestinal epithelial sheets. (A-M) Representative immunofluorescent images of a 2D enteroid-derived monolayer on transwell insert after 5 days in culture showing the (A) nucleus (blue), (B) E-cadherin (Red), (C) F-actin (green) and (D) overlay of the 3 images (merge), (E,I) Nuclear stain, (F) Chromogranin-A, (J) Cytokeratin-18, (G,K) Lysozyme, and (H,L) Merge of images. (M) Z-stack modeling showing the distribution of the same epithelial cell marker proteins of the 2D monolayer sheet. Images were obtained from 2 biological replicates. Scale bar = 50 µm. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
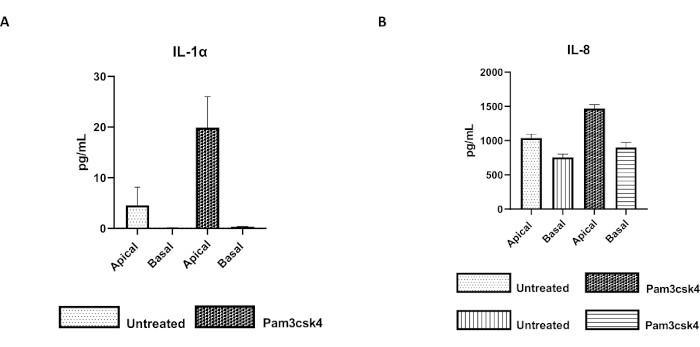
Figure 7: Bovine primary 2D enteroid-derived monolayers on transwell inserts are functionally active. Apical and basal cell culture supernatant cytokine secretion of (A) IL-1α, and (B) IL-8 by 2D monolayers on transwell inserts after 5 days in culture that were untreated or stimulated with Pam3csk4 for 24 h. Data are representative of average cytokine levels and SEM from monolayers derived from frozen stocks of crypts from one animal and three independent experiments. Cytokines were quantified using the bead-based multiplex assay (Table of Materials) according to the manufacturer's instructions and analyzed on a compact multiplexing unit (Table of Materials) and immunoassay curve fitting software (Table of Materials). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Table 1: The stock and final concentrations of the reagents. Please click here to download the table.
Discussion
The protocol presented here describes a physiologically relevant model for investigating intestinal physiology and enteric disorders. Several research groups have described the generation of bovine enteroid cultures, including 2D monolayers16,19,20,21,22,23,24. While monolayer generation is not overtly technically challenging, several-minute steps are critical in developing successful cultures consistently. As such, the reproducibility of 2D monolayers using the briefly described methods in the published literature can be challenging for a researcher novice to the field of organoids to undertake. The protocol described herein is adapted from these protocols and those published in other species, providing a step-by-step guide to monolayer generation on transwell inserts that is highly reproducible.
The protocol outlined herein can easily be modified to fit the specific goals of the experimental design or the availability of reagents. Indeed, following this protocol, successful cultures can be achieved by seeding monolayers at a lower cell density (e.g., 2.5 x 104) or in the absence of FBS, as described by other publications24. However, altering these parameters may require an increased culture to establish a confluent monolayer. As such, if other factors integral to the study design, including co-culture with immune cells, dictate a specific time course for the experiment, the seeding density can be altered as needed. While other basement membrane formulations can be substituted in place of the one used in this protocol to generate 3D enteroids and 2D monolayers, these will require some optimization to determine the optimal basement membrane-to-media ratio.
The application of transwell inserts in the described methodology has many benefits over monolayer growth on conventional plasticware and 3D enteroid cultures. Compared to standard tissue culture plates, using transwells for monolayer cultures promotes cellular differentiation and organization in a way that retains semblance to intestinal crypts14,25. The intestinal epithelial barrier is vital in preventing the translocation of toxins and microorganisms into the body while simultaneously facilitating nutrient absorption. As such, it is critical to understand how the barrier integrity of the intestine functions in healthy and is altered during intestinal disorders or in response to compounds. Unlike 3D enteroid cultures, objective assessment of intestinal barrier integrity is possible when combining monolayers on transwells and measuring TEER, as demonstrated herein14,25. Generating 2D monolayers on transwells also permits dual culture with pertinent cell types such as immune or stromal cells. This allows critically important crosstalk between intestinal cells and cells of the tissue microenvironment to be characterized, which cannot be achieved with 3D cultures. Exposure of the apical surface of the monolayer not only permits experimental exposure to pathogens and compounds and collection of luminal products but also affords studies into other aspects of intestinal physiology and disease, including the investigation into intestinal microbiota and molecular absorption or transport physiology13. Independent control over the apical and basal intestinal surfaces is a distinct advantage over 3D enteroid models.
Through several trial experiments, we identified key steps that contributed to the protocol's success. While whole intestinal tissue samples can be refrigerated overnight and processed the following day, the tissue dissociation and isolation of crypt fragment steps must be performed promptly to prevent the disintegration of the isolated crypt fractions. After completing the PBS washes, centrifuging the crypts in Wash Media can help prevent crypt breakdown, as detailed in step 2.3.10. When passaging the enteroids or harvesting them for monolayer formation, it is essential to separate the enteroids from the BME domes. The Wash Media must be ice cold to aid in dissolving the BME. In contrast, using pre-warmed TrypLE and filtering the cell suspension twice can help form the single cells needed for monolayer generation. Finally, manually maneuvering the plate in the shape of the number 8 can help evenly disperse the single cells over the transwell insert.
An important limitation of this protocol is that the 2D monolayers were produced from enteroid stocks generated from a mature Holstein steer (>2 years of age). The maturing gastrointestinal tract in calves may necessitate minor modifications to the described protocol to yield optimal results. Breed-specific differences in the intestinal physiology of cattle breeds have been described in the literature26. While it is unknown if these differences could impact enteroid and subsequent monolayer generation, we suspect any differences would result in only minor changes to our protocol. Additionally, the 2D culture model has some inherent disadvantages. Compared to 3D enteroid models, 2D cultures may lack some aspects of the intestinal tissue architecture and cellular diversity and create restrictions and challenges associated with the propagation of 2D culture13. Still, studies demonstrate that some monolayers can emulate expected crypt organization27, and some of these limitations may even be overcome by establishing 2D cultures with an air-liquid interface. Nevertheless, the limitations of this model should be fully considered to determine if its application is suitable for the experimental question being asked.
This protocol describes an optimized culture system that models the bovine gastrointestinal tract using enteroids derived from the bovine ileum to form monolayers on transwell inserts. With a wide array of applications from infectious disease research to drug discovery and regenerative medicine, this high-throughput culture system could lead to the unprecedented development of preventative and therapeutic strategies that could be mutually beneficial to animal and human health.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the use of the Cellular and Molecular Core Facility at Midwestern University. This research was supported by the research program of the U.S. Department of Agriculture, National Institute of Food and Agriculture (Animal Health and Production and Animal Products: Animal Health and Disease, 1025812). The findings and conclusions in this publication have not been formally disseminated by the U. S. Department of Agriculture and should not be construed to represent any agency determination or policy.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 0.2 mL pipette tip | MidSci | PR-200RK-S | |
| 1 µm PET 24-well cell culture inserts | Corning | 353104 | |
| 1000 mL pipette tip | MidSci | PR-1250RK-S | |
| 22 G needle | Becton, Dickinson and Company | 305156 | |
| 24-well culture vessel | Corning | 353504 | |
| 40 μm cell strainer | Corning | 431750 | |
| 50 mL centrifuge tube | Fisher scientific | 14-955-240 | |
| 5-mL pipet tip | Fisher scientific | 30075307 | |
| 5 mL syringe | Becton, Dickinson and Company | 309647 | |
| 5 mL tube | Eppendorf | 30119401 | |
| Anti-Cytokeratin -18 (C-04) | Abcam | AB668-1001 | |
| B-27 supplement without vitamin A | Gibco | 12-587-010 | |
| Belysa software | Luminex | 40-122 | Immunoassay curve fitting software |
| Bovine serum albumin (BSA) | Fisher bioreagents | BP9704-100 | |
| Caspofungin acetate | Selleckchem | S3073 | |
| Cell lifter | Fisher Scientific | 08-100-241 | |
| Chromogranin-A (E-5) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | SC-271738 | |
| Coverslips | Fisher scientific | 12-540-C | |
| Cryovials | Neptune scientific | 3471.X | |
| Cultrex Ultimatrix RGF BME | R&D Systems | BME001-05 | |
| DAPI | MilliporeSigma | D9542-5MG | |
| Dissecting scissors | VWR | 82027-588 | |
| Dithiothreitol (DTT) solution | Thermo Scientific | FERR0861 | |
| DMEM/ F-12 1.1 medium (with L-glutamine, without HEPES) | Cytiva | SH30271.01 | |
| E-cadherin | Cell Signaling Technology | #3195 | |
| Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid | Fisher Scientific | BP2482500 | |
| FBS | Corning | MT35070CV | |
| Gentamicin | Gibco | 15710064 | |
| Glass microscope slide | Fisher scientific | 12-550-07 | |
| Goat anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 488 | Invitrogen | A11001 | |
| Goat anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 647 | Invitrogen | A21235 | |
| Goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 555 | Invitrogen | A21428 | |
| Hemacytometer | Bio-Rad | 1450015 | |
| IntestiCult organoid Differentiation medium (Human) | StemCell Technologies | 100-0214 | |
| IntestiCult organoid growth medium (Human) | StemCell Technologies | 0-6010 | |
| Keyence BZ-X700 | Keyence | BZ-X700 | |
| LY2157299 (Galunisertib) | Selleckchem | S2230 | |
| MAGPIX system | Luminex | Magpix system | Compact multiplexing unit |
| Microscope | Keyence | BZ-X700 | |
| MILLIPLEX Bovine Cytokine/Chemokine Magnetic Bead Panel | MilliporeSigma | BCYT1-33K | Bead-based multiplex assay |
| Mr. Frosty container | Nalgene | 5100-0001 | |
| Non-Enzymatic Cell Dissociation Solution | ATCC | 30-2103 | |
| NutriFreeze D10 Cryopreservation Media | Biological Industries | 05-713-1B | |
| Orbital shaking platform | Thermo Fisher | 88880021 | |
| Pam3Csk4 | invivogen | tlrl-pms | |
| Parafilm sealing film | dot scientific inc. | #HS234526C | |
| Paraformaldehyde 16% solution | Electron Microscopy Sciences | 15710 | |
| Phalloidin-FITC | R&D Systems | 5782/12U | |
| Phosphate buffered saline | Fisher Scientific | BP399-20 | |
| Prolong Glass Antifade | Invitrogen | P36982 | |
| Rabbit anti-human Lyzozyme (EC3.2.1.17) | Agilent technologies | A009902-2 | |
| SB202190 (FHPI) | Selleckchem | S1077 | |
| Shaking water bath | Thermo Fisher | MaxQ 7000 | |
| Sodium Azide | VWR | BDH7465-2 | |
| Streptomycin | Teknova | S6525 | |
| Trypan Blue dye | Gibco | 15250-061 | |
| TrypLE express enzyme | Life technologies | 12604013 | |
| Tween 20 | Fisher Scientific | BP337 | |
| Voltohmmeter | MilliporeSigma | Millicell ERS-2 | |
| Y-27632 | Selleckchem | S1049 |
References
- Gerdts, V., et al. Large animal models for vaccine development and testing. ILAR Journal. 56 (1), 53-62 (2015).
- Reza Khorramizadeh, M., Saadat, F. Animal models for human disease. Animal Biotechnology. Chapter 8, 153-171 (2020).
- Meyerholz, D. K., Beck, A. P., Singh, B. Innovative use of animal models to advance scientific research. Cell and Tissue Research. 380 (2), 205-206 (2020).
- Hamernik, D. L. Farm animals are important biomedical models. Animal Frontiers. 9 (3), (2019).
- Ribitsch, I., et al. Large animal models in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering: To do or not to do. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology. 8, 972 (2020).
- Wagar, L. E., DiFazio, R. M., Davis, M. M. Advanced model systems and tools for basic and translational human immunology. Genome Medicine. 10 (1), 73 (2018).
- Ziegler, A., Gonzalez, L., Blikslager, A. Large animal models: The key to translational discovery in digestive disease research. Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2 (6), 716-724 (2016).
- Roth, J. A., Tuggle, C. K. Livestock models in translational medicine. ILAR Journal. 56 (1), 1-6 (2015).
- Schultz, R. D., Dunne, H. W., Heist, C. E. Ontogeny of the bovine immune response. Infection and Immunity. 7 (6), 981-991 (1973).
- Potter, A. A., et al. Large animal models for vaccine development and testing. ILAR Journal. 56 (1), 53-62 (2015).
- Ahluwalia, B., Magnusson, M. K., Öhman, L. Mucosal immune system of the gastrointestinal tract: maintaining balance between the good and the bad. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology. 52 (11), 1185-1193 (2017).
- Roodsant, T., et al. A human 2D primary organoid-derived epithelial monolayer model to Study host-pathogen interaction in the small intestine. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. 10, 272 (2020).
- Liu, Y., Chen, Y. G. 2D- and 3D-based intestinal stem cell cultures for personalized medicine. Cells. 7 (12), 225 (2018).
- Duque-Correa, M. A., Maizels, R. M., Grencis, R. K., Berriman, M. Organoids - New models for host-helminth interactions. Trends in Parasitology. 36 (2), 170-181 (2020).
- Kar, S. K., et al. Organoids: a promising new in vitro platform in livestock and veterinary research. Veterinary Research. 52 (1), 43 (2021).
- Hamilton, C. A., et al. Development of in vitro enteroids derived from bovine small intestinal crypts. Veterinary Research. 49 (1), 54 (2018).
- Beaumont, M., et al. Intestinal organoids in farm animals. Veterinary Research. 52 (1), 33 (2021).
- Lee, B. R., et al. Robust three-dimensional (3D) expansion of bovine intestinal organoids: An in vitro model as a potential alternative to an in vivo system. Animals (Basel). 11 (7), 2115 (2021).
- Töpfer, E., et al. Bovine colon organoids: From 3D bioprinting to cryopreserved multi-well screening platforms. Toxicology in Vitro. 61, 104606 (2019).
- Powell, R. H., Behnke, M. S. WRN conditioned media is sufficient for in vitro propagation of intestinal organoids from large farm and small companion animals. Biology Open. 6 (5), 698-705 (2017).
- Derricott, H., et al. Developing a 3D intestinal epithelium model for livestock species. Cell and Tissue Research. 375 (2), 409-424 (2019).
- Rusu, D., Loret, S., Peulen, O., Mainil, J., Dandrifosse, G. Immunochemical, biomolecular and biochemical characterization of bovine epithelial intestinal primocultures. BMC Cell Biology. 6, 42 (2005).
- Dibb-Fuller, M. P., Best, A., Stagg, D. A., Cooley, W. A., Woodward, M. J. An in-vitro model for studying the interaction of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and other enteropathogens with bovine primary cell cultures. Journal of Medical Microbiology. 50 (9), 759-769 (2001).
- Sutton, K. M., Orr, B., Hope, J., Jensen, S. R., Vervelde, L. Establishment of bovine 3D enteroid-derived 2D monolayers. Veterinary Research. 53 (1), 15 (2022).
- Barrila, J., et al. Modeling host-pathogen interactions in the context of the microenvironment: Three-dimensional cell culture comes of age. Infection and Immunity. 86 (11), e00282-e00318 (2018).
- Carvalho, P. H. V., Pinto, A. C. J., Millen, D. D., Felix, T. L. Effect of cattle breed and basal diet on digestibility, rumen bacterial communities, and eating and rumination activity. Journal of Animal Science. 98 (5), skaa114 (2020).
- Thorne, C. A., et al. Enteroid monolayers reveal an autonomous WNT and BMP circuit controlling intestinal epithelial growth and organization. Developmental Cell. 44 (5), 624-633 (2018).
Explore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2024 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved