Primordial Germ Cell Cryopreservation and Revival of Drosophila Strains
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
A long-term preservation method for Drosophila strains as an alternative to the frequent transfer of adult flies to fresh food vials is highly desirable. This protocol describes the cryopreservation of Drosophila primordial germ cells and strain revival via their transplantation to agametic host embryos.
Abstract
Drosophila strains must be maintained by the frequent transfer of adult flies to new vials. This carries a danger of mutational deterioration and phenotypic changes. Development of an alternative method for long-term preservation without such changes is therefore imperative. Despite previous successful attempts, cryopreservation of Drosophila embryos is still not of practical use because of low reproducibility. Here, we describe a protocol for primordial germ cell (PGC) cryopreservation and strain revival via transplantation of cryopreserved PGCs into agametic Drosophila melanogaster (D. melanogaster) host embryos. PGCs are highly permeable to cryoprotective agents (CPAs), and developmental and morphological variation among strains is less problematic than in embryo cryopreservation. In this method, PGCs are collected from approximately 30 donor embryos, loaded into a needle after CPA treatment, and then cryopreserved in liquid nitrogen. To produce donor-derived gametes, the cryopreserved PGCs in a needle are thawed and then deposited into approximately 15 agametic host embryos. A frequency of at least 15% fertile flies was achieved with this protocol, and the number of progeny per fertile couple was always more than enough to revive the original strain (the average progeny number being 77.2 ± 7.1), indicating the ability of cryopreserved PGCs to become germline stem cells. The average number of fertile flies per needle was 1.1 ± 0.2, and 9 out of 26 needles produced two or more fertile progeny. It was found that 11 needles are enough to produce 6 or more progeny, in which at least one female and one male are likely included. The agametic host makes it possible to revive the strain quickly by simply crossing newly emerged female and male flies. In addition, PGCs have the potential to be used in genetic engineering applications, such as genome editing.
Introduction
The maintenance of Drosophila strains by the transfer of adult flies to new food vials inevitably results in the accumulation of mutations and epigenetic changes over time. Development of an alternative method for long-term maintenance of Drosophila strains without such changes is imperative, especially for reference strains in which the whole genome has to be maintained. Several successful attempts to cryopreserve Drosophila embryos or ovaries have been described1,2,3. Unfortunately, they are still not of practical use because of low reproducibility. Indeed, early-stage embryos have a low survival rate after cryopreservation because of their high yolk content, which impedes cryoprotective agent (CPA) permeation and diffusion2,3. CPA permeability is also severely limited by the waxy layers of late-stage embryos. It is difficult and time-consuming to find a strain-specific time period in which embryos have a high survival rate and a thinner wax layer. Recently, Zhan et al.4 improved methods for embryo permeabilization, CPA loading, and vitrification and successfully cryopreserved embryos of multiple strains. However, the methods are not easy to apply because the viability of embryos after permeabilization tends to be poor. Therefore, further improvement and development of alternative approaches are still needed. Methods involving the cryopreservation of primordial germ cells (PGCs) are an alternative approach for the long-term maintenance of Drosophila strains.
PGC (also called pole cell) transplantation has been used to generate germline chimeras, especially females, to study processes such as maternal effects of zygotic lethal mutations and sex determination of germ cells5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12. PGCs are much smaller than embryos and are likely to be highly permeable to most cryoprotectants. Furthermore, developmental and morphological variation among strains is less problematic, and an agametic host enables quick restoration of whole genomes. We recently developed a new method of PGC cryopreservation13, which prevents the otherwise inevitable genetic and epigenetic changes in Drosophila strains. Here, we present the detailed protocol.
This cryopreservation method requires specific expertise in PGC handling and instrumentation. While a step-by-step approach may be an efficient solution for those who are unfamiliar with it, it may be unsuitable for small laboratories due to instrumentation requirements. This PGC cryopreservation protocol can be more easily adapted for use with different Drosophila species and different insect species than embryo cryopreservation protocols because of smaller developmental and morphological differences. PGCs can also potentially be used in genetic engineering applications, such as genome editing14,15,16. In summary, this method can be used in stock centers and other laboratories to maintain fly and other insect strains for prolonged periods of time without changes.
Protocol
1. Equipment preparation
- Micromanipulator system: Assemble a micromanipulator system to collect and transplant cells (Figure 1A).
- PGC-collection glass slides (Figure 2A)
- To prepare heptane glue, cut approximately 30 cm long double-sided tape and soak it overnight in 7 mL of technical (regular)-grade heptane solution.
- Draw two parallel reference lines for embryo alignment on the back of a glass slide.
- Spread drops of the above heptane glue on the glass slide (on the side without the lines) using a Pasteur pipette. Air-dry the surface of the slide until it becomes white.
- Repeat the addition and spreading of heptane-glue drops and dry the slide again.
NOTE: The glue prevents liquid solutions from spreading over the flat surface and makes it easier to load aqueous solutions into a needle. - To make embryo-pool frames, stick three layers of 0.2 mm-thick standard vinyl tape, such as electrical tape, on a cutting board. Cut the tape into 1.5 cm-wide rectangles. Then, cut away all three layers of tape, leaving a 2 to 3 mm frame.
NOTE: An embryo-pool frame is affixed after aligning embryos, to form a pool for embryos.
- Transplantation needles
NOTE: All commercially available needles at the time of this study were too narrow or too broad for PGC cryopreservation.- Make a needle using a glass capillary and a puller. We use a NARISHIGE PN-31 puller with the heater level at 85.0-98.4, the magnet main level at 57.8, and the magnet sub-level at 45.0.
- To make a needle with an approximate wall thickness of 1 µm and a tip of approximately 200 µm in length with an inner diameter of 10-12 µm, polish the needle tip in the following three-step process (Figure 3). First, grind down the needle tip at an angle of 30° at a speed of 780 rpm until the tip has an inner diameter of 10-12 µm. This first grinding step takes approximately 1 h.
NOTE: To avoid breaking the needle tip, first rotate the grindstone and then gently move the needle down onto the grindstone. - Draw a line on the top of the needle to track the desired angle. Rotate the needle counterclockwise at 90° and polish it again at a speed of 180 rpm. This takes approximately 5 min.
- Rotate the needle clockwise 45° and polish it at a speed of 180 rpm for one second.
- Place a collection glass slide with a drop of chromic acid mixture (CAUTION: toxic) onto the microscope stage. Attach the needle to the capillary holder (Figure 1D) at a 10°-13° angle relative to the slide surface, carefully move the needle down, and immerse the tip in the chromic acid mixture.
- By pulling and pushing the plunger (Figure 1B), mechanically load and discharge the solution from the needle several times to remove glass debris in the needle. Be sure to clean the outer wall as well.
- Wash the inside and outside of the needle two times with distilled water to remove the chromic acid completely.
2. Collection and cryopreservation of PGCs
- Collecting embryos
- Transfer an appropriate number of flies of the donor strain of interest (approximately 450 for each sex for the embryo-collection cup) into an embryo-collection cup with an embryo-collection plate (Figure 1E) and incubate them at 25 °C. We usually use 3- to 5-day-old parental flies that are reared under less crowded conditions at room temperature (23-25 °C).
- Perform two 30-min pre-collections and discard any eggs laid. Because females can retain fertilized eggs that develop in the oviduct, this step is required to synchronize egg laying in step 2.1.3 (Figure 4).
- After the two pre-collections, collect embryos for 50 min and then incubate the collected embryos in a humidified chamber at 25 °C to allow the embryos to develop to the blastoderm stage (early stage 517). The incubation time is usually 100 min but can be extended up to 120 min, depending on the strain (Figure 4).
NOTE: A humidified chamber is made by placing a moist paper towel at the bottom of a plastic box and spraying it with a mist of water before use. In early stage-5 embryos, PGC formation is complete, but somatic cellularization is not. The exact stage of an embryo is determined under a compound microscope in step 2.4.
- Dechorionating embryos
- Deposit a drop of distilled water on a stainless-steel mesh strainer (150 mesh, 109 µm opening, 60 µm wire diameter; Figure 1F). Using forceps, collect embryos from the embryo-collection plate and put them in the water droplet.
- Press tissue paper against the strainer from underneath to absorb the water. Add droplets of fresh 5% (as Cl) sodium hypochlorite solution to the embryos and continuously tap the strainer for 10 s.
- Wash the embryos by directly splashing them with distilled water and press tissue paper against the strainer from underneath to absorb the water. Repeat this step 3x.
- Aligning dechorionated embryos
- Under a stereo microscope, use forceps to transfer embryos. Align the dechorionated embryos in two rows on a PGC-collection glass slide along the two reference lines (Figure 2A). The embryos are oriented with their anterior to the right (the side to be manipulated) and ventral side up.
NOTE: This step should be finished in 20 min, during which we usually align approximately 40 embryos. - Affix an embryo-pool frame around the embryos on the PGC-collection glass slide. Drop 1 µL of CPA solution (1x Ephrussi-Beadle Ringer solution, EBR, containing 20% ethylene glycol and 1 M sucrose; 1x EBR: 130 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, and 10 mM Hepes at pH 6.9) at two separate spots in the area enclosed by the frame and fill the pool with silicone oil to prevent the embryos from drying out (Figure 2A).
NOTE: To prepare the CPA solution, completely dissolve 10.26 g of sucrose in approximately 20 mL of distilled H2O containing 3 mL of 10 x EBR solution. Add 6 mL of ethylene glycol and then add distilled H2O up to 30 mL. After thorough mixing, filter the solution through a 0.22 mm disposable membrane.
- Under a stereo microscope, use forceps to transfer embryos. Align the dechorionated embryos in two rows on a PGC-collection glass slide along the two reference lines (Figure 2A). The embryos are oriented with their anterior to the right (the side to be manipulated) and ventral side up.
- Collecting PGCs
- Place the PGC-collection glass slide of step 2.3.2 onto the stage of a microscope equipped with a micromanipulator system. Attach the needle to the capillary holder and bring the first embryo in the left row and the needle tip into the same focal plane. Load silicone oil into the needle for 2-3 s.
- Begin PGC collection from embryos in the left row. Using a 20x objective lens, gently move the needle tip to the surface of the anterior end of the embryo and penetrate the embryo toward the posterior end, not by moving the needle but by moving the microscope stage.
- When the needle tip reaches the posterior end, retract the needle slightly and completely discharge any yolk in the needle just inside the somatic cell layer.
- While keeping the pressure in the needle constant, move the needle tip to the PGCs just inside the posterior pole and gently, but without taking much time, load the PGCs.
- Pull the needle out of the embryo quickly and discharge yolk and other contaminants from the needle into the silicone oil pool, keeping the PGCs in the needle. Then, load clean silicone oil from the pool.
- Repeat steps 2.4.2 to 2.4.5 for the other embryos in the left row. Before collecting PGCs from a new embryo, deposit as much of the silicone oil loaded in step 2.4.5 inside the somatic cell layer as possible while keeping loaded PGCs in the needle. This ensures that newly loaded PGCs are adjacent to the previously collected PGCs without any intervening material between them.
- After completing PGC collection from embryos in the left row, separate PGCs from the yolk and other contaminants as much as possible. To achieve this, deposit all PGCs in the needle onto the surface of an embryo and remove any yolk or other contaminants to another neighboring embryo.
- Next, collect PGCs from embryos in the right row. Combine the PGCs collected from the right and left rows.
- Applying cryoprotective agent (CPA) to PGCs
- After washing the needle with CPA in one drop, load fresh CPA in another drop into the needle and add CPA to the PGCs deposited on the embryo. The volume of CPA should be equivalent to that of the PGCs.
- Remove as much CPA as possible from the cluster of PGCs 1-2 s after the addition of CPA. PGCs shrink slightly and become square in shape immediately after CPA addition.
- Empty the needle and then load silicone oil for 5 s or longer. Load all the collected PGCs and then load silicone oil once again for 5 s or longer. PGCs are now sandwiched between two layers of silicone oil (Figure 2B).
NOTE: It is important to remove as much yolk, CPA, and other contaminants as possible.
- Cryopreserving PGCs
- Open the three-way stopcock (Figure 1C) and then detach the needle from the micromanipulator. Blot the oil off the surface of the needle with soft tissue paper. Do not directly touch the tip of the needle with the tissue.
- Attach the needle to a needle holder and lock it in position at the base using vinyl tape (Figure 1H). Affix a label to the holder tube.
- Flash freeze the holder with the needle pointing downwards by submerging it in liquid nitrogen. Do not release the holder until the liquid stops fizzing out of the rack.
- Store the holder in a liquid nitrogen storage tank in the liquid phase area, not the vapor phase area.
3. Thawing and transplanting PGCs
- Collecting, dechorionating, and aligning embryos from agametic host flies
- Collect and dechorionate embryos from agametic host flies following step 2.
- Align the stage 5 agametic host embryos on a transplantation glass slide. However, this time, orient the posterior to the right (the side to be manipulated) and ventral to the top (Figure 5). Line up approximately 30 embryos in two rows in 20 min.
- While aligning embryos, operate a humidifier for 2-10 min if the room humidity requires it (Table 1). The ideal humidity is 30% to 40%, but this can vary depending on thermal conditions.
- Thawing and transplanting PGCs in host embryos
- To quickly thaw cryopreserved PGCs, slip the holder containing the needle into room temperature 1x EBR solution with the needle pointing downwards and keep it submerged for 10 s.
- Place the transplantation glass slide on the stage of a microscope. Attach the freeze-thawed needle to the capillary holder and bring the first embryo in the left row and the needle tip into the same focal plane.
- Using a 20x objective lens, gently move the needle tip to the surface of the posterior end of the embryo.
- Gently prod the outside of each embryo and make sure that they slowly return to their original shape. The prodding will confirm that the inner pressure of the embryo is not too high or too low.
- Gently move the needle and penetrate an embryo from the posterior pole.
- Gently deposit approximately 10-20 PGCs just inside the posterior pole, precisely between the vitelline membrane and the somatic cell layer of the embryo. Avoid depositing them in the somatic cell layer. If the perivitelline fluid leaks out of the embryo, suck the leaked fluid into the needle and remove it.
- Retract the needle from the embryo. Repeat steps 3.2.5 and 3.2.6 for subsequent embryos.
4. Incubating embryos and restoring donor strains
- Remove any embryos that do not receive transplanted PGCs and incubate the remaining embryos in a humidified chamber (Figure 1G) at 25 °C.
- At 24 h or more after transplantation and as soon as possible after hatching, use forceps to pick up and transfer hatched larvae to standard Drosophila food vials and incubate at 25 °C.
- To revive the strain, cross newly emerged females and males (Figure 6).
NOTE: Agametic hosts make it possible to restore the entire genome at once without crossing to balancer-chromosome strains. The co-existence of agametic males in a vial will not matter because females, even if mated with them, do not show long-term post-mating responses, including decreased receptivity to remating18,19.
Representative Results
The efficiency of cryopreserved PGC transplantation has been reported by Asaoka et al.13 and is given in Table 2 for transplantation of PGCs cryopreserved for 1 day or longer in liquid nitrogen. The hatching rate was 168/208 transplanted embryos (80.8%), and the embryo-to-adult viability was 87/208 (41.8%). The frequency of fertile flies was 28/87 (32.2%). This frequency did not differ between PGCs cryopreserved for 8 to 30 days and for those cryopreserved for 31-150 days (20/57 vs. 8/30, G' = 0.63, p >0.1, d.f. = 1). The average number of progeny per couple was 77.2 ± 7.1 (n = 18, 28-122), indicating the ability of cryopreserved PGCs to become germline stem cells. Of the 26 needles, 10 produced no fertile progeny, 7 needles produced 1 fertile progeny, 7 needles produced 2 fertile progeny, and 2 needles produced 3 or 4 fertile progeny. The average number of fertile flies per needle was 1.1 ± 0.2. Based on this data, with 95% confidence, 11 needles are enough to produce 6 or more progeny, in which at least one female and one male are likely included.
In the above experiments, we used embryos expressing ovo-A mRNA in PGCs (nanos>ovo-A, OvoA_OE embryos) as an agametic host. Out of 669 F1 females and 720 F1 males produced from transplanted nanos>ovo-A couples, there was no escaper that was derived from the host PGCs. Several oskar (osk) mutants are also temperature sensitive agametic20,21. Because an osk mutant with high homozygous viability and the agametic phenotype is no longer available, we recreated the osk[8] missense mutant20 by CRISPR/Cas9-assisted genome editing. These flies were completely agametic (0 escapers out of 230 females and 192 males) at 25 °C, but a few escapers emerged at 23 °C (1 of 248 females and 1 of 290 males). nanos>ovo-A are thus recommended as agametic host embryos. Both UASp-ovo-A and nanos-Gal4 stocks13 will be available soon from the KYOTO Drosophila Stock Center.
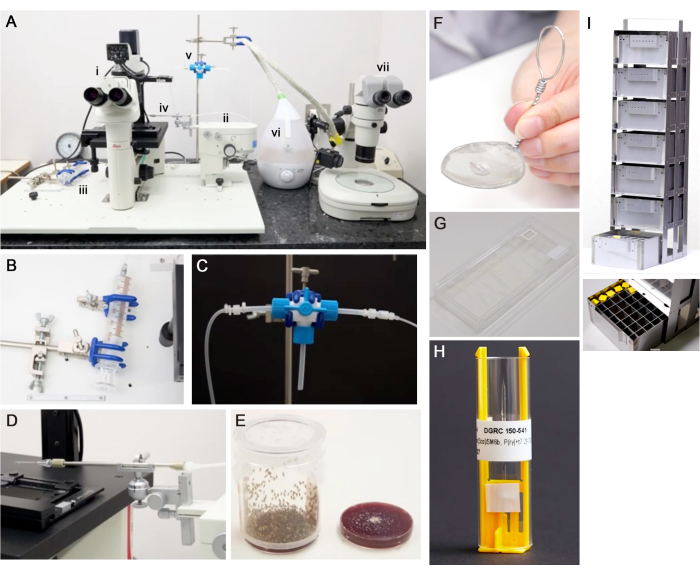

Figure 1: Equipment required. (A) A micromanipulator system to collect and transplant cells. i) inverted microscope, ii) mechanical micromanipulator, iii) syringe, iv) capillary holder, v) three-way stopcock, vi) humidifier, and vii) stereo microscope. (B) A syringe. (C) A three-way stopcock and silicone tubes connect a syringe and a capillary holder. (D) A needle and a capillary holder are attached to a micromanipulator. (E) An embryo-collection cup with an embryo-collection plate (6 cm diameter, 7.7 cm high). (F) A stainless-steel mesh strainer. (G) A container used as a moist chamber with a glass slide. To maintain humidity, place wet paper on the bottom and close the lid. (H) A needle holder with a needle for cryopreservation. (I) A storage rack for cryopreservation and a box with needles. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
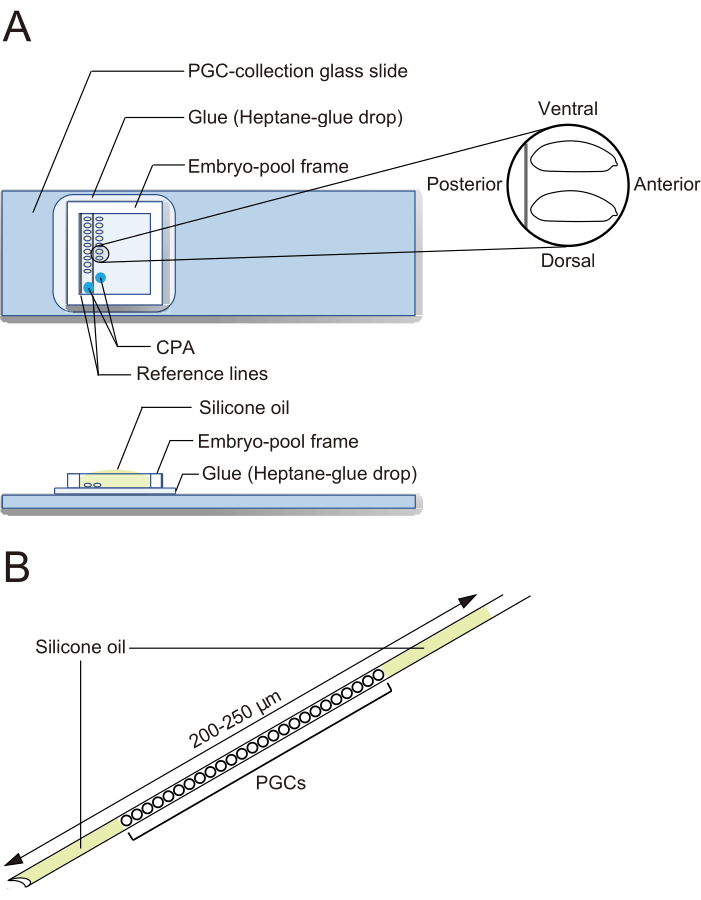
Figure 2: A PGC-collection glass slide and a cryopreservation needle. (A) A primordial germ cell (PGC)-collection glass slide coated with glue. Dechorionated embryos are aligned in two rows and oriented with their anterior to the right (the side to be manipulated) and ventral side up. An embryo-pool frame is affixed, two drops of cryoprotective agents (CPA) solution are deposited, and the pool is filled with silicone oil. (B) A needle should contain as small an amount of yolk and other contaminants as possible. PGCs are sandwiched between two layers of silicone oil when cryopreserved in liquid nitrogen. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
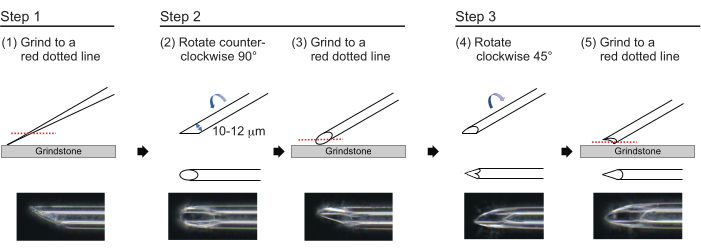
Figure 3: Making the needle. Three-step tip-polishing method to make a needle with an appropriate hole size and a sharp tip. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
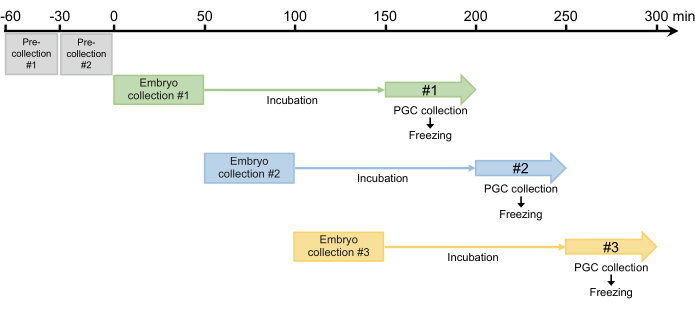
Figure 4: Embryo collection scheme. After two pre-collections, we usually collect three or four times per day. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
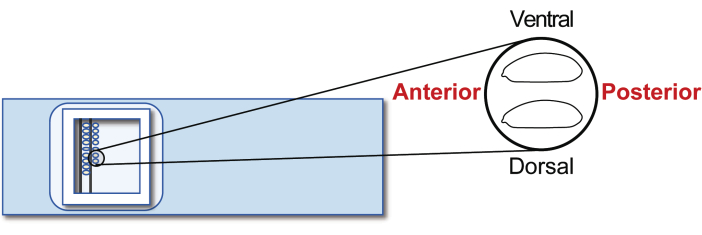
Figure 5: Host embryo alignment. Alignment of host embryos on a glass slide. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
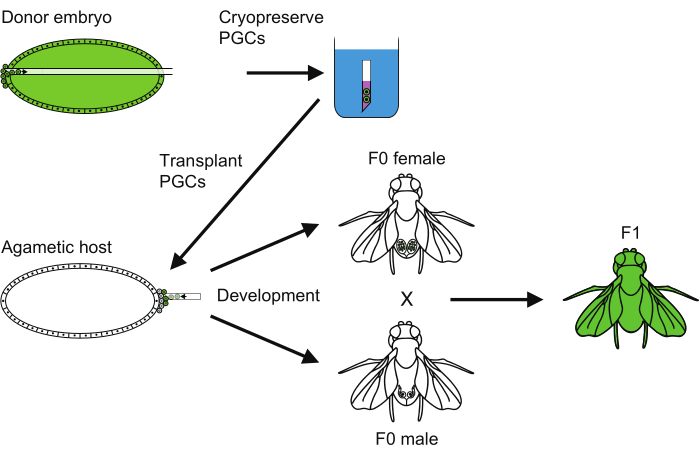
Figure 6: An overview of the PGC cryopreservation method. An overview of all the steps followed to carry out the primordial germ cell (PGC) cryopreservation. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
| Room humidity | |||
| < 30% | ~ 30% | > 30% | |
| Align host embryos (~20 min) | Use a humidifer for 2 - 10 min | Use a humidifer intermittently for 1 min | Do not use a humidifer |
| Thaw donor PGCs | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| Air dry PGCs | Omit this step | Omit this step | 5 min |
| Apply silicone oil | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| Transplant PGCs | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| All these steps should be finshed in 50 min. | |||
Table 1: Drying of embryos during embryo alignment and PGC thawing.
| Donor strain | Cryopreservation period | Number of transplanted embryos (A) | Number of hatched larvae (B) (hatchability, B/A) | Number of eclosed adults (C) (egg-to-adult viability, C/A) | Number of fertile adults (D) (frequency of fertile flies, D/C) |
| M17 | 8 - 30 days | 134 | 108 (80.6%) | 57 (42.5%) | 20 (35.1%) |
| M17 | 31 - 150 days | 74 | 60 (81.1%) | 30 (40.5%) | 8 (26.7%) |
| M17: yw; TM6B, P{Dfd-GMR-nvYFP}4, Sb[1] Tb[1] ca[1]/ Pri[1] | |||||
Table 2: Efficiency of cryopreserved PGC transplantation. This table is modified from13. All data are from agametic hosts.
Discussion
A critical factor for success in PGC cryopreservation and revival is to use good embryos. Young females (e.g., 3- to 5-day-old) should be used for embryo collection. Both donor and host embryos are assessed by microscopic inspection, and only those at the blastoderm stage (stage 5) are used12. For PGC collection, we usually align approximately 40 donor embryos in a 20 min period and collect PGCs from approximately 30 embryos at early stage 5; older and defective embryos are not used. After cryopreservation and thawing, PGCs should maintain their shape; PGCs rupture in unsuccessful preservation. Host embryos should also be at stage 5 and have a moderate inner pressure; embryos should slowly return to their original shape after gentle prodding. Overly and insufficiently dried embryos will not develop normally after transplantation. Because heterosexual transplantation of PGCs fails to produce gametes in Drosophila5,10, transplantation of PGCs from multiple donor embryos into host embryos is more likely to yield fertile adults. To this end, we usually collect PGCs from approximately 30 embryos per needle.
As cryoprotectants, we tried ethylene glycol, dimethyl sulfoxide, and glycerol together with sucrose at various concentrations. We determined EBR containing 20% ethylene glycol and 1 M sucrose to be the best13; however, the use of different cryoprotectants may improve PGC preservation22.
This cryopreservation method requires specialized skills in PGC handling, and approximately 6 weeks of training is needed to comfortably collect and transplant PGCs. To assess and improve skill proficiency, this may be broken into six training steps: 1) aligning embryos on a glass slide, 2) controlling a manipulator, 3) transplanting PGCs from an embryo into another embryo without cryopreservation, 4) transplanting PGCs from 10 or more embryos into 5 to 10 embryos, 5) transplanting PGCs after applying CPA, and 6) transplanting PGCs after freeze-thawing. Each step may take 1 week. The short-term goals at step 3 are a hatching rate of 40%, embryo-to-adult viability of 10%-20%, and a frequency of fertile flies of 20%.
PGC cryopreservation requires costly instrumentation and highly skilled personnel. Therefore, this method may not be adopted by many laboratories. However, the current PGC method has several important aspects. First, PGCs are much smaller than embryos and are very permeable to cryoprotectants. In contrast, cryoprotectant permeability is severely limited by the waxy layers of Drosophila embryos, which is the most serious problem in embryo cryopreservation. Indeed, previous studies have made great efforts to find a time window in which embryos have a high survival rate and a thinner wax layer. The second is concerned with developmental and morphological variation among strains. PGCs are collected from early stage-5 embryos (2 h 30 min-3 h 20 min after egg laying), while embryo cryopreservation is performed on stage-16 embryos (14-22 h after egg laying). The embryos are, therefore, much older and show much larger strain variation in the optimal time window for cryopreservation compared with PGC cryopreservation. Indeed, the frequency of hosts producing donor-derived progeny did not vary among five strains studied by Asaoka et al.13, although the hosts were not agametic. Moreover, PGCs have the potential to be used in genetic engineering applications, such as genome editing14,15,16.
Acknowledgements
We thank the KYOTO Drosophila Stock Center for fly strains. We also thank Ms. Wanda Miyata for English language editing of the manuscript and Dr. Jeremy Allen from Edanz (https://jp.edanz.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript. This work was supported by grants (JP16km0210072, JP17km0210146, JP18km0210146) from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) to T.T.-S.-K., grants (JP16km0210073, JP17km0210147, JP18km0210145) from AMED to S.K., a grant (JP20km0210172) from AMED to T.T.-S.-K. and S.K., a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (JP19K06780) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) to T.T.-S.-K., and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas (JP18H05552) from JSPS to S.K.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Acetic acid | FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation | 017-00256 | For embryo collection |
| Agar powder | FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation | 010-08725 | For embryo collection |
| Calcium chloride | FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation | 038-24985 | For EBR solution |
| Capillary | Sutter Instrument | B100-75-10-PT | BOROSILICATE GLASS; O.D: 1.0mm, I.D: 0.75mm , length: 10cm, 225Pcs |
| Capillary holder | Eppendorf | 5196 081.005 | Capillary holder 4; for micromanipulation |
| Chromic acid mixture | FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation | 037-05415 | For needle washing |
| CPA solution | 1x EBR containing 20% ethylene glycol and 1M sucrose | ||
| Double-sided tape | 3M | Scotch w-12 | For glue extracting |
| Ephrussi–Beadle Ringer solution (EBR) | 130 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 2 mM CaCl2, and 10 mM Hepes at pH 6.9 | ||
| Ethanol (99.5) | FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation | 057-00451 | For embryo collection |
| Ethylene glycol | FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation | 054-00983 | For CPA solution |
| Falcon 50 mm x 9 mm bacteriological petri dish | Corning Inc. | 351006 | For embryo collection |
| Forceps | Vigor | Type5 Titan | For embryo handling |
| Grape juice | Asahi Soft Drinks Co., LTD. | Welch's Grape 100 | For embryo collection |
| Grape juice agar plate | 50% grape juice, 2% agar, 1% ethanol, 1% acetic acid | ||
| Heptane | FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation | 084-08105 | For glue extracting |
| Humidifier | APIX INTERNATIONAL CO., LTD. | FSWD2201-WH | For embryo preparation |
| Inverted microscope | Leica Microsystems GmbH | Leica DM IL LED | For micromanipulation |
| Luer-lock glass syringe | Tokyo Garasu Kikai Co., Ltd. | 0550 14 71 08 | Coat a plunger with silicon oil (FL-100-450CS);for micromanipulation |
| Mechanical micromanipulator | Leica Microsystems GmbH | For micromanipulation | |
| Micro slide glass | Matsunami Glass Ind., Ltd. | S-2441 | For embryo aligning |
| Microgrinder | NARISHIGE Group | Custom order | EG-401-S combined EG-401 and MF2 (with ocular lens MF2-LE15 ); for needle preparation |
| Microscope camera | Leica Microsystems GmbH | Leica MC170 HD | For micromanipulation |
| Needle holder | Merck KGaA | Eppendorf TransferTip (ES) | For cryopreservation |
| Potassium chloride | Nacalai Tesque, Inc. | 28514-75 | For EBR solution |
| Puller | NARISHIGE Group | PN-31 | For needle preparation; the heater level is set to 85.0-98.4, the magnet main level to 57.8, and the magnet sub level to 45.0. |
| PVC adhesive tape for electric insulation | Nitto Denko Corporation | J2515 | For embryo-pool frame |
| Silicon oil | Shin-Etsu Chemical, Co, Ltd. | FL-100-450CS | For embryo handling |
| Sodium chloride | Nacalai Tesque, Inc. | 31320-05 | For EBR solution |
| Sodium hypochlorite solution | FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation | 197-02206 | Undiluted and freshly prepared; for embryo breaching |
| Sucrose | Nacalai Tesque, Inc. | 30404-45 | For CPA solution |
References
- Brüschweiler, W., Gehring, W. A method for freezing living ovaries of Drosophila melanogaster larvae and its application to the storage of mutant stocks. Experientia. 29, 134-135 (1973).
- Steponkus, P. L., et al. Cryopreservation of Drosophila melanogaster embryos. Nature. 345, 170-172 (1990).
- Mazur, P., Cole, K. W., Hall, J. W., Schreuders, P. D., Mahowald, A. P. Cryobiological preservation of Drosophila embryos. Science. 258 (5090), 1932-1935 (1992).
- Zhan, L., Li, M. G., Hays, T., Bischof, J. Cryopreservation method for Drosophila melanogaster embryos. Nat Comm. 12, 2412 (2021).
- Van Deusen, E. B. Sex determination in germ line chimeras of Drosophila melanogaster. Development. 37 (1), 173-185 (1977).
- Breen, T. R., Duncan, I. M. Maternal expression of genes that regulate the bithorax complex of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 118, 442-456 (1986).
- Schupbach, T., Wieschaus, E. Germline autonomy of maternal-effect mutations altering the embryonic body pattern of Drosophila. Dev Biol. 113, 443-448 (1986).
- Irish, V., Lehmann, R., Akam, M. The Drosophila posterior-group gene nanos functions by repressing hunchback activity. Nature. 338, 646-648 (1989).
- Hülskamp, M., Schröder, C., Pfeifle, C., Jäckle, H., Tautz, D. Posterior segmentation of the Drosophila embryo in the absence of a maternal posterior organizer gene. Nature. 338, 629-632 (1989).
- Steinmann-Zwicky, M., Schmid, H., Nöthiger, R. Cell-autonomous and inductive signals can determine the sex of the germ line of Drosophila by regulating the gene Sxl. Cell. 57 (1), 157-166 (1989).
- Stein, D., Roth, S., Vogelsang, E., Nüsslein-Volhard, C. The polarity of the dorsoventral axis in the drosophila embryo is defined by an extracellular signal. Cell. 65 (5), 725-735 (1991).
- Kobayashi, S., Yamada, M., Asaoka, M., Kitamura, T. Essential role of the posterior morphogen nanos for germline development in Drosophila. Nature. 380, 708-711 (1996).
- Asaoka, M., et al. Offspring production from cryopreserved primordial germ cells in Drosophila. Comm Biol. 4 (1), 1159 (2021).
- Blitz, I. L., Fish, M. B., Cho, K. W. Y. Leapfrogging: primordial germ cell transplantation permits recovery of CRISPR/Cas9-induced mutations in essential genes. Development. 143 (15), 2868-2875 (2016).
- Koslová, A., et al. Precise CRISPR/Cas9 editing of the NHE1 gene renders chickens resistant to the J subgroup of avian leukosis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 117 (4), 2108-2112 (2020).
- Zhang, F. Efficient generation of zebrafish maternal-zygotic mutants through transplantation of ectopically induced and Cas9/gRNA targeted primordial germ cells. J Genet Genom. 47 (1), 37-47 (2020).
- Campos-Ortega, J. A., Hartenstein, V. Stages of Drosophila Embryogenesis. The Embryonic Development of Drosophila. , (1997).
- Manning, A. A sperm factor affecting the receptivity of Drosophila melanogaster females. Nature. 194, 252-253 (1962).
- Kubli, E. Sex-peptides: seminal peptides of the Drosophila male. Cell Mol Life Sci. 60, 1689-1704 (2003).
- Lehmann, R., Nüsslein-Volhard, C. Abdominal segmentation, pole cell formation, and embryonic polarity require the localized activity of oskar, a maternal gene in drosophila. Cell. 47 (1), 141-152 (1986).
- Kiger, A. A., Gigliotti, S., Fuller, M. T. Developmental genetics of the essential Drosophila Nucleoporin nup154: allelic differences due to an outward-directed promoter in the P-element 3′ end. Genetics. 153 (2), 799-812 (1999).
- Rienzi, L. F., et al. Perspectives in gamete and embryo cryopreservation. Semin Reprod Med. 36 (5), 253-264 (2018).
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved