Quantifying Food Intake in Caenorhabditis elegans by Measuring Bacterial Clearance
In This Article
Summary
This protocol describes an assay to quantify Caenorhabditis elegans feeding rate based on measuring the clearance of bacteria in liquid culture.
Abstract
Feeding is an essential biological process for an organism's growth, reproduction, and survival. This assay aims to measure the food intake of Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans), an important parameter when studying the genetics of aging or metabolism. In most species, feeding is determined by measuring the difference between the amount of food provided and the amount left after a given time interval. The method presented here uses the same strategy to determine the feeding of C. elegans. It measures the amount of bacteria, the food source of C. elegans, cleared within 72 h. This method uses 96-well microtiter plates and has allowed the screening of hundreds of drugs for their ability to modulate food intake at a speed and depth not possible in other animal models. The strength of this assay is that it allows to measure feeding and lifespan simultaneously and directly measures the disappearance of food and, thus, is based on the same principles used for other organisms, facilitating species-to-species comparison.
Introduction
Caenorhabditis elegans has been extensively used in aging research. It has been a powerful model to study the genetics underlying metabolism-mediated longevity induced by dietary restriction, reduced mitochondrial activity, or reduced insulin signaling.1,2,3,4,5,6,7. However, measuring feeding in the context of longevity has been proven difficult for C. elegans due to the small size of the animal3,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15.
Feeding is a fundamental biological behavior required for survival, and its tight regulation lies at the core of maintaining metabolic health, reproduction, and aging. Feeding behavior is controlled by multiple signaling pathways in both the nervous system and periphery and, thus, can only be studied in vivo16,17,18,19. Feeding represents the first of three pillars: (i) energy intake, (ii) energy storage, and (iii) energy expenditure that govern an organism's energy homeostasis. Feeding in C. elegans has been chiefly investigated by measuring the pharyngeal pumping, as defined by the rate of contractions of the pharynx. This approach has provided crucial insights into C. elegans' feeding behavior3,4,8,12,13,20,21; however, pharyngeal pumping, especially measured over short intervals of minutes, is not necessarily correlated with food intake.
Food intake is not only determined by the pharyngeal pumping rate but also by parameters such as duration and frequency of feeding bouts and the density of food bacteria. An animal may have a very high pharyngeal pumping, but the length of its feeding bouts may be shorter, offsetting the increased rate. Another confounding factor is the efficiency by which pumping may or may not ingest and grind up bacteria. An extreme example of uncoupling food intake from pharyngeal pumping is the addition of serotonin without any food (bacteria) present. In the presence of exogenous serotonin, animals pump at a high rate, but without bacteria present, the high pumping rate does not lead to food intake2,6,13,22,23.
The bacterial clearance method presented here measures the food intake of worm populations in individual wells as the decline of bacterial concentrations over time (Figure 1). This approach is similar to those used in other species where the disappearance of food represents a measure of food intake10,11,24,25,26,27,28. In the original publication, we validated this method of measuring food intake by feeding C. elegans with 15N isotope-labeled bacteria11. Subsequent measures by mass spectrometry showed that measuring the disappearance of bacteria correlated strongly with the occurrence of isotope labeling, revealing the actual uptake of the bacteria into the animal11. Thus, we are confident that the bacterial clearance assay represents food intake in most circumstances. The assay's purpose is not to replace the pharyngeal pumping assay but to add to the toolbox of assays to study feeding and metabolism in C. elegans and how it relates to aging and longevity.
Protocol
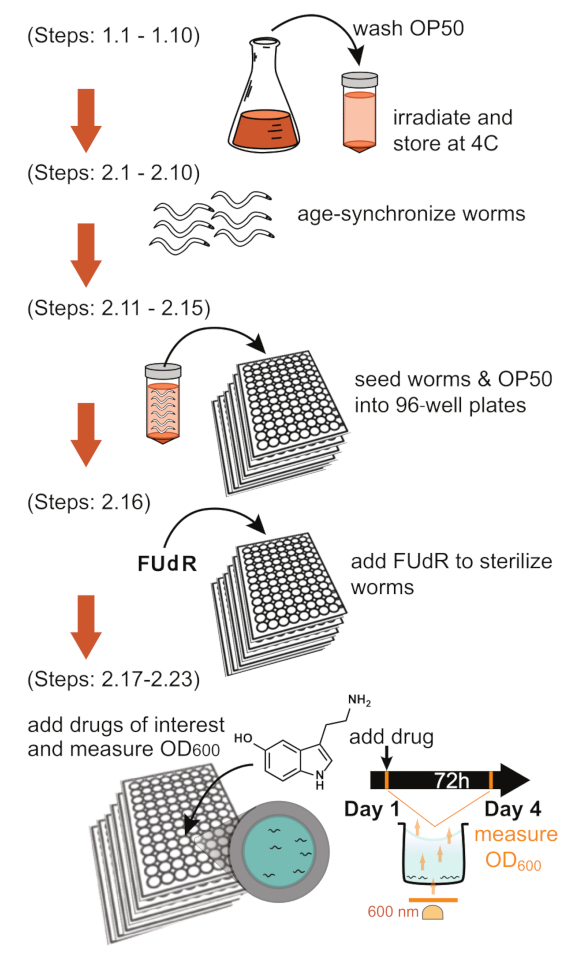
Figure 1: Schematic of the bacterial clearance assay. Graphical outline of the main sections of the protocol (Top-to-bottom): Preparing bacteria, synchronizing the worm population, seeding in 96-well plates, sterilizing worms, adding drugs, measuring OD600 on day 1 and day 4. A detailed description of these specific steps is indicated to the left of each depiction. Abbreviations: OD = optical density; FUdR = fluorodeoxyuridine. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
1. Bacteria preparation
NOTE: This section details the preparation of the feeding bacteria used in this assay. The specific E. coli strain used in the assay is called OP50. OP50 is the most widely used strain to feed C. elegans. The OP50 strain used is Carbenicillin/Ampicillin-resistant, which prevents cross-contamination of the worm culture with other bacteria9.
- Prepare the OP50 4-5 days in advance, and x-ray irradiate a day prior to usage. Ensure that all materials encountering OP50 are sterile29,30.
- Day -8: Wednesday (week 1):
- Prepare the preinoculum by inoculating 5 mL of LB with 100 µg/mL Ampicillin and 0.1 µg/mL Amphotericin B, and a single OP50 colony and incubate for approximately 6 h at 37 °C in a bacterial shaker. Inoculate early to allow sufficient growth for the culture to become cloudy.
- Once the culture is cloudy, dilute the preinoculum culture of OP50 by 1:2,000 in 250 mL of TB containing 100 µg/mL Ampicillin. Incubate the culture overnight in a bacterial shaker for 17-19 h at 37 °C.
NOTE: The culture should not be allowed to grow longer than 19 h.
- Day -7: Thursday (week 1)
- After the 17-19 h incubation, transfer the OP50 liquid culture into a sterile centrifugation tube and centrifuge for 15 min at 3,100 × g in a tabletop centrifuge at 4 °C.
- Discard the supernatant, resuspend the OP50 pellet with sterile water, and re-centrifuge. Repeat this wash 2x.
- After the second wash, discard the supernatant, resuspend the OP50 pellet in sterile water to a volume of 50 mL and transfer it to a preweighed 50 mL conical tube. Pellet the OP50 by centrifugation for 20 min at 3,100 × g in a tabletop centrifuge at 4 °C.
- After the third wash, carefully remove all the remaining supernatant, ensuring no water remains in the tube. Calculate the weight of the pellet by subtracting the weight of the empty centrifugation tube from the weight of the centrifugation tube with the pellet.
NOTE: Pellet weights typically range from 3-3.5 g. - Thoroughly resuspend the OP50 pellet in the S-complete buffer to a concentration of 100 mg/ mL, ensuring no clumps are present.
- Ensure that the concentration of OP50 at 100 mg/mL corresponds to 2 × 1010 bacteria/mL. If the relationship between the optical density and the number of bacteria per mL is known, determine the bacterial concentration per mL spectrophotometrically. If necessary, use S-complete buffer to adjust the concentration of the OP50 feeding solution to 2 × 1010 bacteria/mL.
- Test the OP50 on an agar plate to determine if it has been contaminated.
- Store the OP50 suspended in S-complete buffer at 4 °C.
- Day -3: Monday (week 2)
- Kill the bacteria via X-ray irradiation to prevent bacterial growth during the assay.
2. Synchronous worm culture preparation
NOTE: This section discusses the preparation of a synchronous worm population. All materials that come into contact with the worm populations are sterile. All plates are kept at 20 °C unless otherwise noted.
- Day -6: Friday (week 1), 4:00 p.m.
- Transfer the animals to a fresh plate.
- Take an NGM plate on which most of the worm population consists of starved L1 larvae.
NOTE: A mixed population will also produce results. Using L1 worms that have been starved for a long time may affect the feeding behavior in the current or future generations, as starvation can leave epigenetic marks for at least three generations. - Wash the worms off with no more than 1 mL of sterile water. Aliquot ~300 µL of the washed-off worm population onto NGM plates seeded with concentrated OP50 (~300 mg/mL). Allow the plates to dry under either a plate drier or a Bunsen burner. Incubate the plates at 20°C until much of the population contains gravid adults (Monday).
NOTE: This time frame is optimized for a wild-type N2 worm population and may vary from strain to strain. Worms with development delays should be taken into account and be chunked earlier and/or seeded earlier so that all strains tested will reach adulthood simultaneously.
- Take an NGM plate on which most of the worm population consists of starved L1 larvae.
- Transfer the animals to a fresh plate.
- Day -3: Monday (week 2) 10:00 a.m.
- Establishing a synchronous population
CAUTION! Bleach is corrosive to skin and eyes. Handling it requires gloves and safety glasses.- Collect worms by washing them off the plate with up to 10 mL of sterile water. Transfer this worm/water solution into a 15 mL conical tube.
- Wash the worms by gravity sink on the bench top for approximately 4 min (conversely, wash by centrifugation for 2 min in a tabletop centrifuge at 310 × g.
- Discard the supernatant through aspiration using a small tip and add up to 15 mL of sterile water. Repeat 3x.
- Remove the supernatant and add 5 mL of a freshly prepared bleach/NaOH solution (1.8 mL of household bleach, 0.5 mL of 10 N NaOH, 7.7 mL of dH2O).
- Incubate for 5 min at room temperature or until the worms break open. Vortex gently every minute for at least 10 s. Monitor the progress under the dissecting microscope.
NOTE: The time necessary to break open the worms may vary from strain to strain. Leaving the worms in the bleach solution for too long may result in nonviable eggs. - Add M9 buffer to neutralize the reaction once all the adults break open or dissolve (final volume to be 15 mL) and centrifuge for 2 min at 1,300 × g.
- Wash the eggs 3x with 13 mL of M9 buffer.
- Wash the eggs once with 10 mL of S-complete buffer by centrifuging for 2 min at 1,300 × g.
- Aspirate the supernatant, add 10 mL of S-complete, and transfer the suspension to a fresh 15 mL conical tube. Gently rotate the tube at room temperature overnight on a nutator or similar device.
- Optional: If adult carcasses are present after final centrifugation in S-complete buffer, filter the worm solution through a 40 µm cell strainer.
- Establishing a synchronous population
- Day -2: Tuesday (week 2), 1:00 p.m.
- Seeding the animals into plates
- Using a dissecting scope, check if the worms have hatched. Determine the concentration of worms in the S-complete buffer by counting the worm population in 10 µL drops using a dissecting scope; count 5-10 drops for each sample. If the concentration of worms in each 10 µL drop exceeds 30 worms per drop, dilute the total stock with S-complete to a lower worm density per drop to facilitate counting.
- Seed the liquid worm mixture into each well of a 96-well plate at a volume of 120 µL as follows (final concentrations): 60 worms/mL in S-complete, 50 µg/mL Carbenicillin, 0.1 µg/mL Amphotericin, and 6 mg/mL of OP50 prepared in section 1.
NOTE: The total volume to be prepared depends on the number of plates (~12 mL per 96-well plate). There should be 6-12 worms in each well. Alternatively, a large particle flow cytometry, such as the COPAS FP by Union Biometrica, can be used to precisely sort 10 worms into each well (See crowding effect section). - Also include a no-worms liquid mixture: 50 µg/mL of Carbenicillin, 0.1 µg/mL Amphotericin, and 6 mg/mL of OP50 prepared in section 1.
- Put 120 µL of the no-worms mixture into row H of the 96-well plate, which is used to determine the selflysis values, as mentioned earlier. Put 120 µL per well of the mixture with worms in rows A-G.
NOTE: Ensure the worms are kept in suspension during pipetting (see Figure 2A, B). We use clear 96-well plates with a flat bottom. Our plate layout divides the plate to produce 4 or 6 conditions in which each pair of columns will be a different drug treatment or worm strain, and the bottom row will serve as a "no worm" control (Figure 2A, B). - To avoid contamination and evaporation, seal the plate with a tape sealer. Incubate the plates for approximately 65 h at 20 °C until the animals become L4 worms.
- Seeding the animals into plates
- Day 0: Thursday (week 2) before noon.
- Sterilization of the worm population through the addition of Fluorodeoxyuridine (FUdR).
- Add 30 µL of a 0.6 mM FUdR stock solution to sterilize the animals in each well. Reseal the plate using tape sealers and shake the plates for 20 min on a microtiter plate shaker at 800 rpm. Return plates to the 20 °C incubator.
NOTE: In this step, the final OP50 concentration is reduced from 6 mg/mL to 5 mg/mL (1 × 109 bacteria/mL), and each well has a final volume of 150 µL. It is crucial to add FUdR to the L4 stage before the animals reach adulthood.
- Add 30 µL of a 0.6 mM FUdR stock solution to sterilize the animals in each well. Reseal the plate using tape sealers and shake the plates for 20 min on a microtiter plate shaker at 800 rpm. Return plates to the 20 °C incubator.
- Sterilization of the worm population through the addition of Fluorodeoxyuridine (FUdR).
- Day 1: Friday (week 2)
- Add drugs to the culture.
- By 9:00 a.m., confirm that most animals are gravid and each well contains several eggs. If necessary, add any drugs to the desired concentration (see the discussion).
- After adding the drug, seal the plates with tape sealer and shake the plates for 20 min at 800 rpm on a plate shaker.
NOTE: The shaking ensures that all bacterial clumps are dissolved without touching the sealer. Both bacterial clumps or liquid on the sealer will distort the OD600 reading. If liquid drops are on the sealer, briefly spin it for 10-20 s at 310 × g. Shake again on the shaker for 5 min and measure. - After 20 min of shaking on the microtiter plate shaker, remove the lid and the seal and measure the OD600 in a plate reader; this is the Day 1 OD600 measurement. Seal and return plates to a 20 °C incubator.
NOTE: Because bacteria settle quickly, the reading should occur within 10 min after shaking the plates. - Use an inverted microscope to check the population of worms for signs of contamination or toxicity if a drug has been added. Return the plates to the 20 °C incubator.
- Add drugs to the culture.
- Day 4: Monday (week 3)
- Take the Day 4 OD600 reading.
- Repeat the reading procedure from Day 1 (step 2.5.1.3) to get the Day 4 OD600 value. Before the OD600 measurement, shake the plates for 20 min at 800 rpm on the microtiter plate shaker.
- On an inverted microscope, with ideally a 2x objective, count the population of worms in each well and record it in a spreadsheet. Return the plates to the 20 °C incubator after counting.
NOTE: See a sample of our scoring sheet provided in Supplemental Material. - After the Day 4 reading, the food intake measurements are complete. If required, keep these plates for lifespan analysis.
NOTE: This protocol is compatible with Solis and Petrascheck31.
- Take the Day 4 OD600 reading.
3. Analysis of food intake data
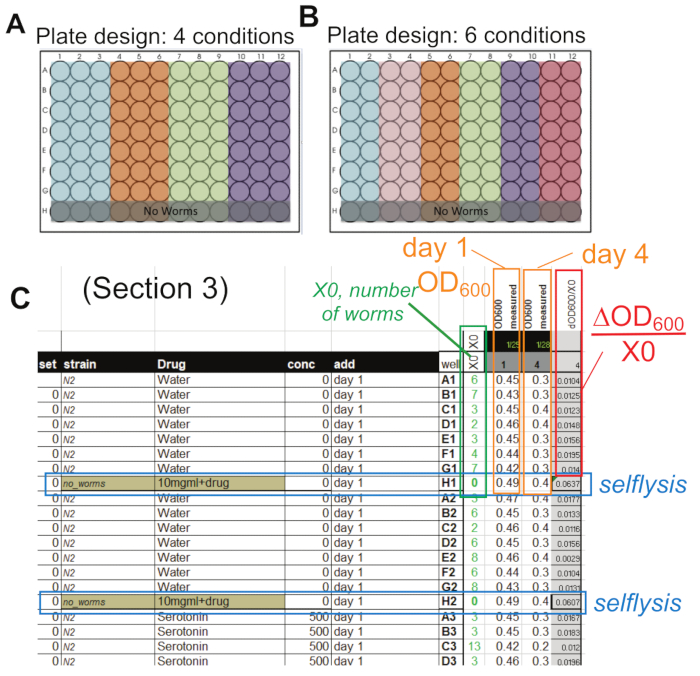
Figure 2: Design and analysis. (A, B) Possible plate designs for 4 and 6 conditions with the "no worm" control wells in row H. These wells are necessary to determine the selflysis rate. In each plate, always include an N2 untreated control population as a reference. (C) Sample data collected in the provided spreadsheet with the number of worms (green box), the two OD600 measures on days 1 and 4 (orange boxes), the selflysis values (blue box), and the evaluation using formula (2) ((OD600 -selflysis)/X0) in the red box. The specific example shown here uses the plate design shown in (B). Abbreviations: OD = optical density; X0 = number of worms per well. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
NOTE: This section describes how the food intake data from section 2 of this protocol are analyzed. The first values to be calculated are the selflysis control values. Bacteria lyse over time in liquid, even in the absence of worms. This selflysis value can also be affected by many chemicals and needs to be controlled as it is relatively large compared to a worm's food intake. As described in step 2.3.1.4 and shown in the plate layout in Figure 2A, B, row H contains the same solution, excluding the worms. In our plate setup shown in Figure 2B, there are 14 wells per condition with two respective selflysis control wells (row H, "no worms").
- Calculate the selflysis control values for the no-worms control wells in each condition using equation ( 1). For each replicate group of wells, ensure there are at least two no-worm control wells, as mentioned in step 2.3.1.4. Use the mean from all the no-worms control wells for the selflysis value for a replicate group.
Selfysis = mean(OD600 Day 1 - OD600 Day 4) (1)
NOTE: For the plate setup shown in Figure 2B, we would calculate six selflysis values, one for each of the six groups, by calculating the mean of the two selflysis control wells in row H. - Calculate the food intake per worm using equation
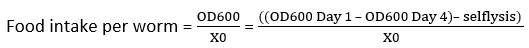 (2).
(2).
NOTE: Formula used in the spreadsheet (red box, Figure 2C) with X0 being the number of worms per well. - After the food intake per worm is determined for each well, calculate the averages and standard deviation for the entire condition.
NOTE: For the plate setup shown in Figure 2B, 14 replicate wells per condition are sufficient for statistical comparisons. - Normalize each condition to its respective N2 untreated control population. Indicate the change in feeding as a fold change or percentage of N2 feeding.
NOTE: Normalization is done because the absolute values of OD600/X0 from equation (2) can vary between experiments conducted on different days.
Results
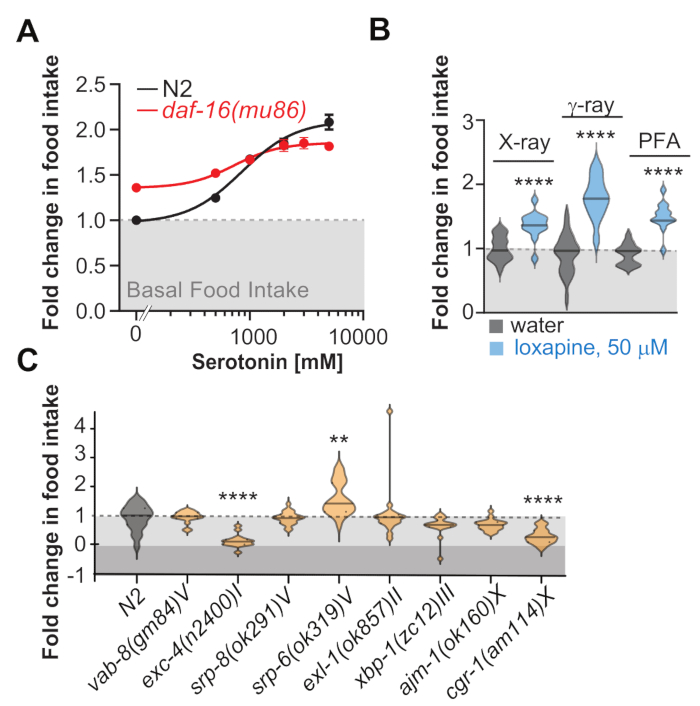
Figure 3: Representative data. (A) The graph shows dose-response curves of fold change in food intake as a function of serotonin concentration. All data show unstimulated basal food intake normalized to N2 basal feeding. Note that the daf-16(mu86) animals eat more than the wild type N2 when no serotonin was added but show a blunted range in their ability to control feeding. (B) Graph shows a violin plot of fold change in food intake of worms treated with 50 μM of the antipsychotic Loxapine but fed bacteria killed by either X-rays, γ-rays, or paraformaldehyde (C) Graph shows a violin plot of fold change in food intake of different mutants with their genotypes indicated in the x-axis. These data suggest that exc-4 and cgr-1 mutants eat less while srp-6 mutants eat more. Asterisks represent ** p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 as determined by ANOVA and Brown-Forsythe-Welch, post-hoc corrected to account for multiple hypotheses testing. Error Bars show ±S.E.M. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Figure 1 highlights the overall workflow of this protocol. It illustrates the entire process, from making the bacteria to acquiring the OD600 reading on day 1 and day 4. In addition, the infographic references the specific steps of the methods being used. Figure 2A, B shows two possible experimental plate layouts, including "no-worms" control wells in row H, necessary for calculating the selflysis rates described in the discussion section. In our lab's experience, it is necessary for one of the conditions to be untreated N2 control to account for the variability of bacterial intake of worms observed between experiments (see discussion: Planning [N2 reference population]).
Figure 2C is an example of the spreadsheet used to analyze the data generated in this protocol. It highlights the worm count in green, selflysis in blue, day 1 OD600 and day 4 OD600 in orange, and the food intake per worm in red. In addition, each well is tracked for the strain, drug, concentration, date of experiment, and other treatments added. Further information on the specific equations used can be found in protocol section 3. Overall, these spreadsheets (template provided as Supplemental Materials) provide efficient data collection and analysis of this protocol.
Figure 3A shows representative results for a dose-response curve of how serotonin modulates feeding in N2 and daf-16 mutants using this protocol. In this experiment, the fold change from basal food intake (first dot in the curve) was calculated across five increasing doses of serotonin. As these results highlight, the N2 strain is able to overeat in a dose-dependent manner. However, for the daf-16(mu86) mutant, although basal feeding is higher than N2, the mutant cannot respond to serotonin in the same dose-dependent manner as the N2 strain. This protocol allows us to determine the feeding behavior between two strains where the concentration of serotonin was the variable factor to generate dose-response curves. Figure 3B shows the food intake of worms treated with the antipsychotic Loxapine but fed with bacteria killed by either X-rays, γ-rays, or paraformaldehyde. Note that these experiments were not conducted in parallel and that the differences are not representative of the different methods to kill the bacteria but are due to inter-experimental variability. Figure 3C shows the food intake of a series of genetic strains, with two strains showing a decrease and one strain showing an increase in feeding behavior relative to N2. This application of the protocol enables the testing of one drug at one concentration across different genetic backgrounds. It is suited to identify genetic backgrounds that show a different food intake response than wild-type N2 controls when given the same drug. It can be paired with our lifespan protocol to quickly screen food intake and lifespan in the same plate setup31.
Supplemental Material: Spreadsheet templates shown in Figure 2C. Please click here to download these materials.
Discussion
The protocol presented measures bacterial clearance as a readout for C. elegans food intake in 96-well microtiter plates. The dose-response curves in the representative results section show that the assay quantitatively measures food intake, a notion that was independently confirmed using isotope-labeled bacteria11. Using this assay, we successfully tested FDA-approved drugs such as antipsychotics with known human metabolic side effects and showed that these drugs increased feeding in C. elegans10,26. The assay is useful to study the genetics or pharmacology of feeding and adds a new tool for C. elegans research to study metabolism. This assay provides a low-cost method to study feeding in a scalable and time-friendly manner, which is not possible in most other organisms. Our work on FDA-approved drugs shows that many side effects seen in human patients are also observed in C. elegans, revealing evolutionary conservation24,26,32.
The assay is limited by the concentration of bacteria that can be measured within the linear range of the OD600 measurement. As a result, the number of worms and the range of bacterial concentrations that can be assayed are limited. Too many worms will affect OD600 by consuming the bacteria too quickly, hence "eating" the bacterial concentration out of the linear OD600. In our experience, variability in bacterial preparation is the critical parameter that causes results to vary from one experiment to another. We have unsuccessfully tried to freeze large batches of bacteria or to use lyophilized bacteria. In these cases, either the selflysis rate became too high, or the bacteria were of a quality that slowed down C. elegans development. However, our tests have not been exhaustive, and this problem may be solvable.
In general, the selflysis rate of the bacteria is the most challenging to control, and it can cause considerable variability. We found that some drugs can increase the selflysis rate to levels that the assay could not reliably determine food intake. Because the selflysis rate increases over time in the assay, we have not measured food intake beyond day 5 of adulthood. By that age, the bacteria are ~10 days in culture. To measure food intake past day 5 of adulthood, the old bacteria must be washed off and replaced with fresh ones.
The presented assay is an extension of our 96-well microtiter plates-based lifespan assay31. This combination enables measuring lifespan and food intake in the same population. While the bacterial clearance assay presented here does not allow the determination of food intake over the whole life of C. elegans due to bacterial selflysis, it provides solid data for the first four days of adulthood, the time with the highest food intake. Especially for small molecule drug discovery, controlling for food intake is essential. In summary, we anticipate that the assay presented will be useful to the C. elegans community and expand the toolset to study metabolism or control it in the context of aging and lifespan studies.
Planning:
Before planning to measure food intake, a few considerations must be made.
Killing the bacteria:
We kill bacteria by irradiation with X-rays in a 50 mL conical tube (900 Gray for 4 h set at 160.0 kV and 25.0 mA). We use the RS2000 by Rad Source for the irradiation. Depending on the equipment, the specific time and radiation dose may vary from facility to facility. The complete killing of the bacteria needs to be determined by plating the bacteria after irradiation to detect survivors by growth. It is essential to kill all the bacteria to prevent growth during the assay, as this will cause an underestimation of feeding or even negative feeding values. Importantly, the bacteria must be killed so that C. elegans will still eat them. In our experience, there are three ways to kill large quantities of bacteria reliably: (i) Irradiation by X-rays,(ii) by γ-rays, and (iii) the addition of formaldehyde29,30. The selflysis rates between these three methods are comparable, with an 8% coefficient of variation between the selflysis rates for the experiments shown in Figure 3B. Methods that did not reliably work in our hands were UV irradiation, antibiotic cocktails, heat inactivation, and sodium azide. These methods either fail to completely kill the bacteria (UV and antibiotics), produce bacteria that C. elegans does not eat (heat), or change food intake (sodium azide).
Number of replicates:
In our experience, the fold changes in feeding are generally small compared to the observed variation. Thus, measuring changes in food intake requires several replicate wells. Figure 2A,B show 96-well plates designed for four or six different conditions, with 21 or 14 replicate wells and two selflysis control wells without worms. Given the large variability and the relatively small changes to be expected, 0.5-2.5 fold-changes in feeding tend to be the lower and upper limits. We recommend 14 to 21 replicate wells for each condition and at least two selflysis control wells, described next. These replicates are enough to generate quantitative dose-response curves for drugs that change feeding11,26.
Selflysis controls:
OD600 measures the number of particles in a solution, mostly independent of particle size. However, dead bacteria will lyse, losing their particle nature. We call this selflysis, which happens independently in the presence of worms and lowers the OD600 measurements without the worms eating. Selflysis happens during the assay and needs to be independently measured in at least two wells per condition. These wells receive the same treatment as the others within the same condition, except they do not contain any worms. We found that many drugs can also alter the selflysis rate. Thus, each condition needs independent selflysis control wells with their respective concentration. Figure 2 shows a plate setup for four or six conditions with all the selflysis control wells at the bottom of the plate in row H.
N2 reference population:
We also noted that the absolute amount of bacteria consumed can fluctuate between experiments, most likely related to the quality of the bacteria. Despite our best efforts to prepare them exactly the same way each time, there are fluctuations. For example, bacteria can be harvested while in a dividing state during the logarithmic growth phase and, therefore, be much larger in size than bacteria harvested in the stationary phase. Hence, these simple differences in bacterial size can lead to changes in the number of bacteria consumed and different OD600 values since the OD600 measurements do not distinguish between sizes. For this reason, we always include one population of untreated N2 control animals that serve as a reference value, either set to 1 or 100%, to determine if the experimental groups eat more or less than the N2 control. This practice allows comparisons between experiments, even if the OD600 values vary.
Time intervals:
Using OD600 values to measure food intake requires the bacterial concentration to decline measurably. Because the culture volume is much larger than the worms, they must eat a significant amount of bacteria to make a detectable difference. Staying in the linear range for OD600 values requires the bacterial concentration to stay between ~1 mg/mL and 10 mg/mL so that a considerable amount of bacteria must disappear to detect it. Worms eat the most from late L4 to day 4 of adulthood because of egg production. Thus, this interval is ideal. Shorter intervals like 24 h can be measured11, but that is considerably more difficult and needs ~40 wells per condition. Another option to measure the food intake of larvae is to double the number of animals per well. However, the problem with this approach is that too many worms will start to affect the OD600 readings when they grow up.
Stock solutions for drugs to be tested:
If drugs such as serotonin are tested for their ability to modulate feeding, consider the following when preparing stock solutions. We generally prepare a 50x stock for water-soluble drugs and add 3 µL to each well (1:50), but other stock concentrations (100x, 300x) also work. However, if the drugs are diluted in solvents other than water (e.g., DMSO), the final concentration should not exceed 0.5%. Solvents quickly become harmful to C. elegans. Thus, stock solutions of drugs dissolved in organic solvents such as DMSO must be 300x or higher.
Scoring live and dead worms:
The determination of live and dead animals is based on the worm's movement. Strong light, especially blue light, is used because it causes the animals to move. Furthermore, scoring the number of animals per well will reveal if there are excess deaths. Excess deaths can occur with toxic substances or high concentrations (>0.5%) of several solvents, including DMSO. Generally, there should be less than 1:100 (1%) dead animals. Plates can be shaken for 30 s at 800 rpm on the microtiter plate shaker if the food has settled and the population becomes hard to count. Ignore wells with males or more than 16 worms (see problems).
Potential problems:
Inadequate shaking:
In a liquid medium, bacteria can easily clump together and settle at the bottom of the wells. In our experience, shaking for less than 20 min may fail to break up bacterial clumps and resuspend them, causing inaccurate OD600 measurements. OD600 measurements in the presence of bacterial clumps will underestimate the bacterial concentration. Excessive shaker settings may cause the liquid to be stuck to the sealer. Once the sealer is removed for the OD600 reading, the liquid stuck to the sealer will result in a lower OD600 reading. If there is liquid on the sealer, quickly spin the plate at a low speed (500-1,000 rpm) and shake again for 5 min. Further, make sure, as stated for the readings on Day 1 and Day 4, to read within 10 min of shaking the plates to avoid the bacteria from settling down.
Different absolute food intake values between experiments:
Despite our best efforts to standardize the bacterial preparations, they often differ in ways that affect food intake in worms. For example, due to their dividing state, bacteria differ in size based on whether it was harvested in the logarithmic growth or stationary phase, with the logarithmic bacteria being larger. Due to OD600 measurements not distinguishing between sizes, the differences in bacterial size due to the phase in which the bacteria was harvested may lead to the apparent differences observed in the basal food intake between bacterial preparations. The best way to compare between experiments is to always include an untreated N2 control population and normalize the results to this N2 population.
Crowding effects:
The bacterial concentration in this protocol is enough to keep the OD600 in the linear range for 2-16 worms per well for ~72 h. Depending on the drug of interest, a well containing more than 16 worms may deplete the bacterial concentration before the second measurement. We also found that wells with one animal tend to be unreliable. The lysis factor outweighs what a single worm eats. Hence, minor errors in determining the lysis factor disproportionally affect wells with fewer worms.
We recommend excluding wells from statistical analyses if one of the conditions below is met. There are males in the well (we have no data comparing food intake between males and hermaphrodites); there are less than 2 worms in the well or more than 16 worms in the well; worms are dead upon the second reading; or if there are progeny in the wells because the FUdR failed. FUdR is heat-sensitive and gets inactivated even by temperatures as low as 37 °C. Always defrost FUdR in room-temperature water.
Negative food intake values:
The food intake values are occasionally negative, suggesting more food on Day 4 than on Day 1. Negative food intake values may indicate one of the following factors: a high selflysis rate, possibly caused by a drug added acting on the bacteria, or negative food intake values, which may suggest that the well is contaminated and something other than worms is growing. Selflysis rates also increase as the bacteria get older; therefore, we recommend using bacteria no longer than a week old. A drug that precipitates over time has been added, affecting the OD600 value. Insufficient shaking on Day 1 may lead to a lower OD600 reading due to bacterial clumps. The worms underwent hypoxic stress. This occurs when the surface-to-air ratio is not enough to allow oxygen exchange. Use the specific 96-well plate in materials and do not exceed 150 µL (120 µL + 30 µL of FUdR) per well. The distance between the surface of the well and the bottom where the worms live determines the oxygen concentration.
Limitations:
This assay is limited to liquid culture. Feeding behaviors observed in solid plates, such as moving on and off food lawns, cannot be assessed with the assay.
Disclosures
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Acknowledgements
We want to thank Xiaolan Ye, as this protocol was developed as a result of an observation she originally made. We thank all the past and present members of the Petrascheck Lab for their help with the development and optimization of this protocol. This work was funded by R21 AG080376 (to M.P.). Some strains were provided by the CGC, which is funded by the NIH Office of Research Infrastructure Programs (P40 OD010440).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Amphotericin B | RPI | A40030-0.1 | solvent: EtOH |
| Ampicillin | Fisher Scientific | BP176025 | solvent: water |
| Bacto Peptone | BD Biosciences | 211677 | use to make NGM plates |
| Carbenicillin | Fisher Scientific | 46-100-RG | solvent: water |
| Cell strainer | Fisher Scientific | 22363547 | 40 µm to remove adults |
| Cholesterol | MP Biomedicals | 02101380-CF | 5 mg/mL stock |
| Difco, Agar, Bacteriological | BD Biosciences | 214510 | use to make NGM plates |
| Fluorodeoxyuridine | Sigma Aldrich | F0503 | to sterilize worms on L4 |
| Luria Broth | RPI | L24045-1000.0 | open capsule, mix with 1 L of water, autoclave |
| M9 Buffer | Laboratory Prepared | Store in sterile conditions at room temperature To prepare 1 L: 15 g Na2HPO4*12H2O (FW: 358) 3 g KH2PO4 (FW: 136) 5 g NaCl (FW: 58), 0.25 g MgSO4*7H2O (FW: 246) autoclave | |
| Microplate Sealer | Fisher Scientific | 236707 | |
| OP50 | Caenorhabditis Genetics Center | ||
| Plate 96-well | Falcon | 351172 | |
| Plate reader | Tecan | 30016056 | use 600 nm filter lens |
| Potassium Citrate, 1 M , pH 6 | Laboratory Prepared | Store in sterile conditions at room temperature To prepare 1 L: 268.8 g Potassium citrate tribasic monohydrate (FW: 324) 26.3 g citric acid monohydrate (FW: 210) 900 mL of dH2O pH to 6 using 5 M KOH autoclave | |
| Potassium Phosphate, 1 M , pH 6 | Laboratory Prepared | Store in sterile conditions at room temperature To prepare 1 L: 136 g KH2PO4 (FW: 136) 900 mL dH2O pH to 6 using 5 M KOH autoclave | |
| S-Basal | Laboratory Prepared | Store in sterile conditions at room temperature To prepare 1 L: 5.9 g NaCl (FW: 58) 50 mL 1 M potassium phosphate (pH 6) add 900 mL dH2O autoclave, cool to 55 °C | |
| S-Complete | Laboratory Prepared | Store in sterile conditions at room temperature To prepare 1 L: Add to 1 L of S-basal (cooled to 55 °C or RT) 10 mL of 1 M potassium citrate pH 6, 10 mL of trace metal solutions 3 mL of 1 M CaCl2 3 mL of 1 M MgSO4 | |
| Serotonin hydrochloride | Thermo Scientific | AAB2126309 | used at 5 mM |
| Sodium Chloride | Sigma Aldrich | S7653-5KG | to make buffers and NGM plates |
| Terrific Broth | Thermo Scientific | J75856-A1 | 12.5 g in 250 mL of water, autoclave |
| Titer plate Shaker | Thermo Scientific | 88880023 | shaken at 800 rpm, depends on shaker |
| Trace Metals Solution | Laboratory Prepared | Store in sterile conditions at room temperature To prepare 1 L: 1.86 g Na2EDTA (FW: 372.24) 0.69 g FeSO4*7H2O (FW: 278) 0.20 g MnCl2*4H2O (FW: 198) 0.29 g ZnSO4*7H2O (FW: 287) 0.016 g CuSO4 (FW: 158) autoclave wrap in aluminum foil to keep in the dark | |
References
- Taormina, G., Mirisola, M. G. Calorie restriction in mammals and simple model organisms. Biomed Res Int. 2014, 308690 (2014).
- Cunningham, K. A., et al. Amp-activated kinase links serotonergic signaling to glutamate release for regulation of feeding behavior in C. elegans. Cell Metab. 16 (1), 113-121 (2012).
- You, Y. J., Kim, J., Raizen, D. M., Avery, L. Insulin, cgmp, and tgf-beta signals regulate food intake and quiescence in C. elegans: A model for satiety. Cell Metab. 7 (3), 249-257 (2008).
- Dorman, J. B., Albinder, B., Shroyer, T., Kenyon, C. The age-1 and daf-2 genes function in a common pathway to control the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 141 (4), 1399-1406 (1995).
- Apfeld, J., Kenyon, C. Cell nonautonomy of C. elegans daf-2 function in the regulation of diapause and life span. Cell. 95 (2), 199-210 (1998).
- Srinivasan, S. Neuroendocrine control of lipid metabolism: Lessons from C. elegans. J Neurogenet. 34 (3-4), 482-488 (2020).
- Calculli, G., et al. Systemic regulation of mitochondria by germline proteostasis prevents protein aggregation in the soma of. elegans. Sci Adv. 7 (26), eabg3012 (2021).
- Avery, L. The genetics of feeding in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 133 (4), 897-917 (1993).
- Wu, Z., et al. Dietary restriction extends lifespan through metabolic regulation of innate immunity. Cell Metab. 29 (5), 1192-1205.e8 (2019).
- Chen, A. L., et al. Pharmacological convergence reveals a lipid pathway that regulates C. elegans lifespan. Nat Chem Biol. 15 (5), 453-462 (2019).
- Gomez-Amaro, R. L., et al. Measuring food intake and nutrient absorption in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 200 (2), 443-454 (2015).
- Mckay, J. P., Raizen, D. M., Gottschalk, A., Schafer, W. R., Avery, L. Eat-2 and eat-18 are required for nicotinic neurotransmission in the Caenorhabditis elegans pharynx. Genetics. 166 (1), 161-169 (2004).
- Hobson, R. J., et al. Ser-7, a Caenorhabditis elegans 5-ht7-like receptor, is essential for the 5-ht stimulation of pharyngeal pumping and egg laying. Genetics. 172 (1), 159-169 (2006).
- Deshpande, S. A., et al. Quantifying Drosophila food intake: Comparative analysis of current methodology. Nat Methods. 11 (5), 535-540 (2014).
- Webster, C. M., et al. Genome-wide rnai screen for fat regulatory genes in C. elegans identifies a proteostasis-ampk axis critical for starvation survival. Cell Rep. 20 (3), 627-640 (2017).
- Reis Rodrigues, P., et al. Synthetic ligands of cannabinoid receptors affect dauer formation in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. G3 (Bethesda). 6 (6), 1695-1705 (2016).
- Levichev, A., et al. The conserved endocannabinoid anandamide modulates olfactory sensitivity to induce hedonic feeding in C. elegans. Curr Biol. 33 (9), 1625-1639.e4 (2023).
- Wang, D., et al. Genetic behavioral screen identifies an orphan anti-opioid system. Science. 365 (6459), 1267-1273 (2019).
- Cheong, M. C., Artyukhin, A. B., You, Y. J., Avery, L. An opioid-like system regulating feeding behavior in C. elegans. Elife. 4, e06683 (2015).
- Lakowski, B., Hekimi, S. The genetics of caloric restriction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 95 (22), 13091-13096 (1998).
- Huang, C., Xiong, C., Kornfeld, K. Measurements of age-related changes of physiological processes that predict lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 101 (21), 8084-8089 (2004).
- Witham, E., et al. C. elegans body cavity neurons are homeostatic sensors that integrate fluctuations in oxygen availability and internal nutrient reserves. Cell Rep. 14 (7), 1641-1654 (2016).
- Hussey, R., et al. Oxygen-sensing neurons reciprocally regulate peripheral lipid metabolism via neuropeptide signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Genet. 14 (3), e1007305 (2018).
- Zapata, R. C., et al. Adipocytes control food intake and weight regain via vacuolar-type h(+) atpase. Nat Commun. 13 (1), 5092 (2022).
- Clay, K. J., Yang, Y., Clark, C., Petrascheck, M. Proteostasis is differentially modulated by inhibition of translation initiation or elongation. Elife. 12, e76465 (2023).
- Perez-Gomez, A., et al. A phenotypic caenorhabditis elegans screen identifies a selective suppressor of antipsychotic-induced hyperphagia. Nat Commun. 9 (1), 5272 (2018).
- Zapata, R. C., Zhang, D., Chaudry, B., Osborn, O. Self-administration of drugs in mouse models of feeding and obesity. J Vis Exp. (172), 62775 (2021).
- Zapata, R. C., et al. Targeting clic1 for the treatment of obesity: A novel therapeutic strategy to reduce food intake and body weight. Mol Metab. 76, 101794 (2023).
- Stuhr, N. L., Curran, S. P. Bacterial diets differentially alter lifespan and healthspan trajectories in C. elegans. Commun Biol. 3 (1), 653 (2020).
- Stuhr, N. L., Curran, S. P. Different methods of killing bacteria diets differentially influence Caenorhabditis elegans physiology. MicroPubl Biol. 2023, (2023).
- Solis, G. M., Petrascheck, M. Measuring caenorhabditis elegans life span in 96 well microtiter plates. J Vis Exp. (49), (2011).
- Wofford, M. R., King, D. S., Harrell, T. K. Drug-induced metabolic syndrome. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 8 (2), 114-119 (2006).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved