Bu içeriği görüntülemek için JoVE aboneliği gereklidir. Oturum açın veya ücretsiz deneme sürümünü başlatın.
Electroencephalography-Based Recording Technique to Record the Epileptiform Activity
Overview
This video describes the technique for recording the epileptiform activity of rhinal cortex-hippocampus organotypic slices ex vivo using electrophysiology or EEG set-up. This helps to study the dynamics and progression of epileptogenesis and screen potential therapeutic targets to treat epilepsy.
Protokol
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board.
1. Preparation of rhinal cortex-hippocampus slices
NOTE: The preparation of rhinal cortex-hippocampus slices uses P6-7 Sprague-Dawley rats.
- Culture setup and medium preparation
- On the day before the culture, prepare the required media and place them at 4 °C.
- Prepare dissection medium: 25 mM glucose in Gey's Balanced Salt Solution (GBSS).
- Prepare culture medium: 50% Opti-MEM, 25% HBSS, 25% Horse Serum (HS), 25 mM glucose, 30 µg/mL Gentamycin.
- Prepare maintenance medium: Neurobasal-A (NBA), 2% B27, 1 mM L-glutamine, 30 µg/mL Gentamycin, HS (15%, 10%, 5%, and 0%).
- Brain harvesting
- Just before starting the culture, add 1.1 mL of culture medium to each well of the 6-well plate with a P1000 pipette and place it at 37 °C.
- Place all the equipment (dissection microscope, tissue chopper, dissecting lamp, dissecting tools, electrodes, plates, inserts, and filter papers) inside the biological safety cabinet and sterilize under UV light for 15 minutes.
- Adjust slice thickness to 350 µm.
- Withdraw the GBSS from the fridge. Add 5 mL of GBSS to six Petri dishes. Six Petri dishes will be required per animal.
- Euthanize the rat pup. Perform decapitation by using a sharp scissor at the base of the brainstem of the animal.
- Wash the animal head three times in cold GBSS and take it inside the safety cabinet.
- Tissue isolation and preparation of slices
- Firmly insert sharp forceps into the eye sockets to hold the head.
- Using a thin scissor cut the skin/scalp along the midline starting from the vertebral foramen towards the frontal lobes and put it aside.
- Cut in the same way the skull and along the cerebral transverse fissure (space between brain and cerebellum). With curved long forceps, move it apart.
- Discard the olfactory bulbs with a spatula. Remove the brain from the head and place it in ice-cold GBSS with the dorsal surface faced up (Figure 1A).
- Insert the fine forceps into the cerebellum and go along the midline with the spatula opening each hemisphere very carefully (Figure 1B).
- With short curve forceps, carefully remove the excess tissue that covers the hippocampi, without touching the hippocampal structure. Then with a spatula, cut below each hippocampus (Figure 1C).
- Pick up one hemisphere and place it, with hippocampus facing up, onto a filter paper. Repeat the procedure with the other hemisphere and place it parallel to the first one, in the filter paper. Put the filter paper on the tissue chopper, with the hemispheres perpendicular to the blade, and cut the hemispheres in 350 μm slices (Figure 1D).
- Place the sliced tissue into a Petri dish with cold GBSS (Figure 1E).
- Carefully separate the slices using the round tip electrodes (Figure 1F). Keep only the slices with a structurally intact rhinal cortex and hippocampus. DG and CA areas should be perfectly defined, as well as the entorhinal and perirhinal cortex (Figure 1G).
- Place each slice onto the insert (Figure 1H-I), with a spatula and a round-tip electrode. Remove excess dissection medium around each slice with a P20 pipette (Figure 1J). Four rhinal cortex-hippocampus slices can be cultured in a single insert (Figure 1K).
- Culture maintenance
- Change the medium every other day.
- Warm up the medium at 37 °C.
- Take the plates from the incubator. Pick up each insert by holding the plastic edge with forceps (Figure 1L).
- Use a free hand to aspirate the medium from the well. Place the insert back into the well and add 1 mL, with a P1000 pipette, of fresh warmed medium (Figure 1M). Repeat for all the inserts. Make sure no air bubbles are trapped between the membrane and the medium.
NOTE: Epileptic-like slices undergo a gradual and controlled deprivation of serum in the medium. From 9 Days In Vitro (DIV) on, slices are maintained in NBA without HS.
2. Electrophysiological recordings
NOTE: Electrophysiological recordings were performed in rhinal cortex-hippocampus organotypic slices at 7, 14, and 21 DIV in an interface-type chamber. Recordings were obtained with an amplifier, digitized, and analyzed with software. All recordings were band-pass filtered (eight-pole Bessel filter at 60 Hz and Gaussian filter at 600 Hz).
- Setup preparation
- Prepare 50 mL of NBA medium with 1 mL of B27 and 250 μL of L-Glutamine. Warm up at 37 °C.
- Set the electrophysiology setup in a closed circuit. Verify if the flow rate is 2 mL/min.
- Open the carbox (5% CO2/95% O2) valve and check the water level in the system.
- Put the filter paper in the interface recording chamber to drain excess medium and the lens cleaning paper beneath the frame to supply medium to the slice.
- Turn on the temperature controller, the amplifiers, and the micromanipulator.
- Let the temperature in the interface chamber stabilize at 37 °C before starting the recordings.
- Prepare artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF: 124 mM NaCl, 3mM KCl, 1.2 mM NaH2PO4, 25 mM NaHCO3, 10 mM glucose, 2 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgSO4 with pH 7.4) and use it to fill the glass electrode with a syringe. Place it in the receiving electrode.
- Recordings of spontaneous activity
- Once the temperature is stable, remove the plate from the incubator and cut one slice from the insert with a highly sharp blade. Place it in a 60 mm plate with a drop of medium. Take it to the interface recording chamber.
- Place the slice in the interface chamber with the hippocampus to the bottom right. Place the receiving electrode in the CA3 pyramidal cell layer.
- Proceed to the continuous acquisition protocol and record for 30 min.
Sonuçlar
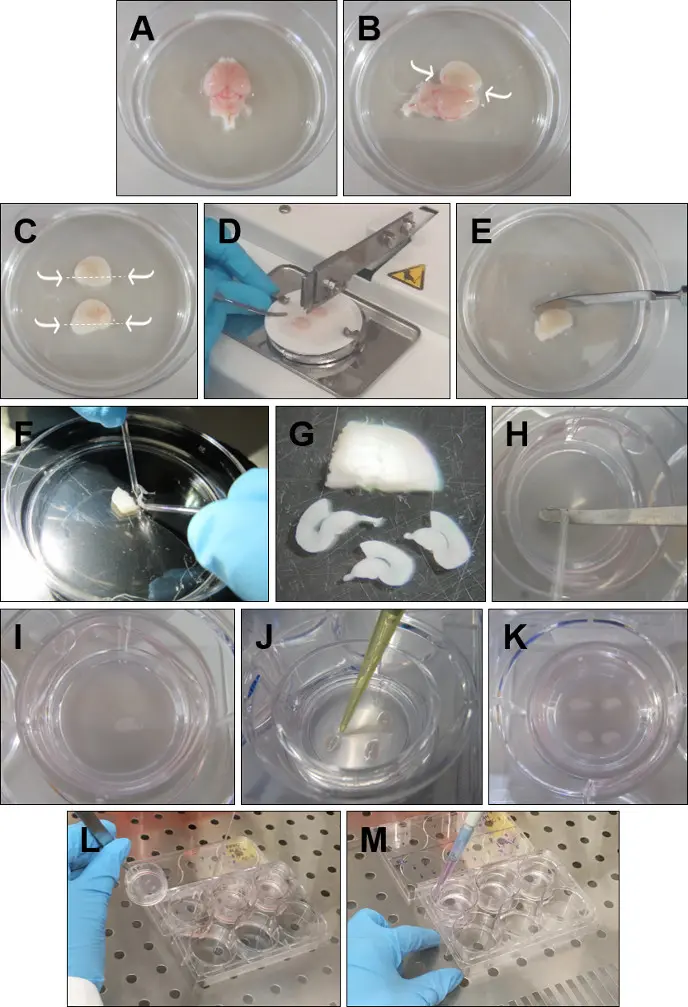
Figure 1: Detailed procedure for the preparation of rhinal cortex-hippocampus organotypic slices. (A) Remove the brain from the head and place it in ice-cold GBSS with the dorsal surface faced up. (B) Insert the forceps into the cerebellum. Open the brain through the midline and remove the excess tissue over the hippocampus. (C) With a spatu...
Açıklamalar
Malzemeler
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF) | Homemade | ||
| B-27™ Supplement (50X), serum free | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 17504-044 | |
| Blades for scalpel handle | Fine Science Tools | 10011-00 | |
| Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) | NZYTech | MB04602 | 5% BSA is used to dilute the primary antibodies. Add 0.5g BSA in 10 mL PBS. |
| Brain/Tissue Slice Chamber System | Warner Instruments | ||
| Cell culture inserts, 30 mm, hydrophilic PTFE | Millipore SAS | PICM03050 | |
| Conventional incubator | Thermo Scientific Heraeus | BB15, Function Line | Set to 37 °C and 5% CO2 |
| Gey’s Balanced Salt Solution (GBSS) | Biological Industries | 01-919-1A | |
| Glass Electrodes | Science Products | GB150F-10 | Round tips homemade |
| Interface chamber | Warner Instruments | BSC-HT Haas Top | |
| Iris Spatula Curved | Fine Science Tools | 10092-12 | |
| Lens Cleaning Paper | TIFFEN | ||
| L-Glutamine solution 200 mM (Q) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 25030-024 | |
| Tissue Chopper | The Mickle Laboratory Engineering CO. LTD. | MTC/2 | Set to 350 μm |
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Source: Carvalho, M. et al., A Model of Epileptogenesis in Rhinal Cortex-Hippocampus Organotypic Slice Cultures. J. Vis. Exp. (2021).
JoVE Hakkında
Telif Hakkı © 2020 MyJove Corporation. Tüm hakları saklıdır