Male Rectal Exam
Source: Joseph Donroe, MD, Internal Medicine and Pediatrics, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
While its usefulness in cancer screening is debated, the male rectal examination remains an important part of the physical exam. The exam is indicated in selected patients with lower urinary tract symptoms, urinary and/or fecal incontinence or retention, back pain, anorectal symptoms, abdominal complaints, trauma patients, unexplained anemia, weight loss, or bone pain. There are no absolute contraindications to the rectal exam; however, relative contraindications include patient unwillingness to undergo the exam, severe rectal pain, recent anorectal surgery or trauma, and neutropenia.
When performing the rectal exam, the examiner should conceptualize the relevant anatomy. The external anal sphincter is the most distal part of the anal canal, which extends three to four centimeters before transitioning into the rectum. The prostate gland lies anterior to the rectum, just beyond the anal canal. The posterior surface of the prostate, including its apex, base, lateral lobes, and median sulcus, can be palpated through the rectal wall (Figure 1). The normal consistency of the prostate is similar to the thenar eminence when the hand is in a tight fist. The thumb knuckle is representative of what a hard nodule may feel like. The normal size of the prostate increases with age and is approximately 4.0 cm by 3.5 cm, or 20-30 g, in a young man.
The steps of the male rectal exam, including preparation, positioning, neurologic assessment, external inspection and palpation, examination of the prostate and rectum, and evaluation of the stool, are detailed in this video.
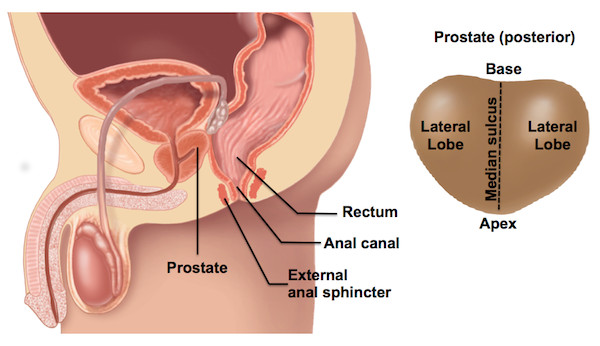
Figure 1. Male rectal anatomy (left) and regions of prostate gland posterior surface (right).
1. Preparation
- Prepare the Patient
- Inform the patient of the exam about to be performed and the reason for it. Recognize that some men may feel uncomfortable at the idea of having the exam performed. If it seems that the patient feels uncomfortable with the exam, take a moment to explore the reasons why. Discussing the exam in a-matter-of-fact way tends to lessen a patient's anxiety.
- As with all sensitive examinations, it is important to be mindful of the language used during the ex
The male rectal exam remains an important part of the physical exam, particularly for patients with abdominal, genitourinary, or gastrointestinal concerns. It is a sensitive procedure and requires careful attention to verbal and body language to ensure patient comfort. This video reviewed the indications and contraindications for the exam, relevant anatomy, as well the steps involved in performing the examination. Abnormalities that may be encountered at each step are found in Table 1. Physician comfort
Skip to...
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2024 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved