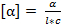Polarimeter
Overview
Source: Vy M. Dong and Diane Le, Department of Chemistry, University of California, Irvine, CA
This experiment will demonstrate the use of a polarimeter, which is an instrument used to determine the optical rotation of a sample. Optical rotation is the degree to which a sample will rotate polarized light. Optically active samples will rotate the plane of light clockwise (dextrorotatory), designated as d or (+), or counterclockwise (levorotatory), designated as l or (−).
Procedure
1. Preparing the Polarimeter
- Turn on instrument and let it warm up for 10 min.
- Make sure instrument is set to "optical rotation" mode.
- Prepare a blank sample in the polarimeter cell (1.5 mL total sample volume, 1 dm in length) containing only CHCl3. Make sure there are no air bubbles present.
- Place the blank cell in the holder and press "zero."
2. Preparation of Analyte Sample
- Prepare a stock solution of 10
Results
Representative results for the measurement and calculation of specific rotation for Procedures 1-4.