14.16 : Kepler's Second Law of Planetary Motion
In the early 17th century, German astronomer and mathematician Johannes Kepler postulated three laws for the motion of planets in the solar system. His first law states that all planets orbit the Sun in an elliptical orbit, with the Sun at one of the ellipse's foci. Therefore, the distance of a planet from the Sun varies throughout its revolution around the Sun.
While in an elliptical orbit, the total energy of the planet is conserved. Therefore, the planet slows down when it is at apogee and speeds up when it is at perigee. These conclusions led Kepler to state his second law, that the radius vector of the planet sweeps out in equal areas in equal time. This means that if a planet takes the same time to travel from A to A1, and then from B to B1, then the areas AF1A1 and BF1B1 are equal, as shown in Figure 1.
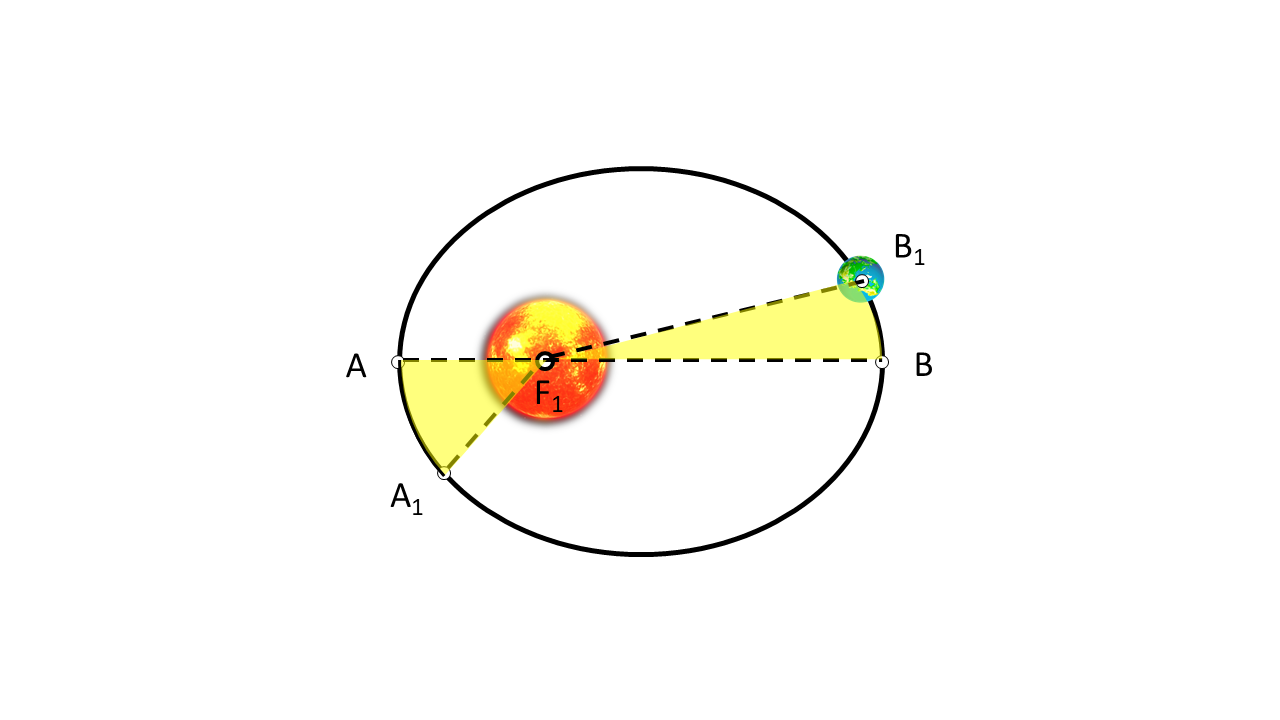
Since the area is constant in a given time interval, the planet's sector velocity remains constant. Since the sector velocity is proportional to the planet's angular momentum, KeplerâÃÂÃÂs second law implies that the angular momentum of a planet in an elliptical orbit is conserved.
This text is adapted from Openstax, University Physics Volume 1, Section 13.5 KeplerâÃÂÃÂs Laws of Motion.
From Chapter 14:

Now Playing
14.16 : Kepler's Second Law of Planetary Motion
Gravitation
4.1K Views

14.1 : جاذبية
Gravitation
6.1K Views

14.2 : قانون نيوتن للجاذبية
Gravitation
12.3K Views

14.3 : الجاذبية بين الكتل المتماثلة كرويا
Gravitation
818 Views

14.4 : الجاذبية بين الأجسام الكروية
Gravitation
8.2K Views

14.5 : إحداثيات الكتلة المنخفضة: مشكلة معزولة ثنائية الجسم
Gravitation
1.2K Views

14.6 : التسارع بسبب الجاذبية على الأرض
Gravitation
10.4K Views

14.7 : التسارع بسبب الجاذبية على الكواكب الأخرى
Gravitation
4.0K Views

14.8 : الوزن الظاهري ودوران الأرض
Gravitation
3.5K Views

14.9 : التباين في التسارع بسبب الجاذبية بالقرب من سطح الأرض
Gravitation
2.3K Views

14.10 : الطاقة الكامنة بسبب الجاذبية
Gravitation
5.4K Views

14.11 : مبدأ التراكب ومجال الجاذبية
Gravitation
1.3K Views

14.12 : سرعة الهروب
Gravitation
5.5K Views

14.13 : المدارات الدائرية والسرعة الحرجة للأقمار الصناعية
Gravitation
2.8K Views

14.14 : طاقة القمر الصناعي في مدار دائري
Gravitation
2.2K Views
See More
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved