A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Electrophysiological Recording from Colonic Afferent Nerves in an Ex Vivo Rat Colon
In This Article
Overview
This video demonstrates a method to record the activity of colonic afferent nerves in an ex-vivo rat colon, cannulated at both ends and infused with saline to increase intraluminal pressure. As pressure increases, the nerve signal rises, indicating its stimulation.
Protocol
All procedures involving animal models have been reviewed by the local institutional animal care committee and the JoVE veterinary review board.
1. Preparation of Perfusion Solution and Test Compounds
- Prepare 5 L of Krebs solution: 113 mM sodium chloride, NaCl, 5.9 mM potassium chloride, KCl, 1.2 mM Di-hydrogen sodium phosphate, NaH2PO4, 1.2 mM magnesium sulfate, MgSO4, 25 mM sodium bicarbonate, NaHCO3, 1.2 mM calcium chloride, CaCl2, and 11.5 mM glucose. Saturate the solution with a 95% O2 + 5% CO2 gas mixture. Pre-cool ~500 mL of oxygenated Krebs in the fridge.
- Prepare aliquots of stock test compounds (1 mM capsaicin in ethanol and 10 mM 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) in saline) as needed. Dilute the stock in Krebs (for bath application) and in saline (for intraluminal administration) to the final concentration just prior to use.
2. Preparation of the Recording Electrode
- Pull the recording electrode from standard glass tubes without inner filaments (1.5 mm outer diameter) using a conventional electrode puller. Adjust the puller settings for heat and pull so that the shank of the pulled electrodes is between 20 and 25 mm.
3. Tissue Collection
- Anaesthetize the rat deeply using sodium pentobarbital (80 mg/kg, i.p.).
- While ensuring sterility, expose the abdominal cavity by performing a midline incision on the abdominal wall using a scalpel. Pull the mesentery and other tissues aside to expose the colorectum.
- Place the animal under the dissecting microscope. Through careful dissection, locate the left pelvic ganglion (PG) and identify the pelvic nerves (PN) and the lumbar splanchnic nerves (LSN) joining it. Cut these nerves a few millimeters away from the PG.
NOTE: The PG lies close to the colorectal junction. Typically, 3 - 4 PN from the lumbosacral spinal cord and an LSN project to the PG (Figure 1). - Cut the symphysis bone to expose the rectum. Remove the tissues (i.e., urinary bladder, etc.) above the colorectum; be careful to leave the PG intact.
- Sacrifice the rat by the intravenous injection of an overdose of pentobarbital. Transect the colon about 3 cm above the PG and remove the colorectum from the animal using forceps.
- Transfer the colorectum to a Petri dish filled with pre-cooled Krebs solution. Remove the feces by gently flushing the colon. Remove the remnant urinary bladder and other tissues carefully, without compromising the PG.
4. Dissection of the Colonic Afferent Nerves
- Place the colon into a recording chamber (20 mL) and perfuse the tissue continuously with carbogenated Krebs solution. Set the perfusion rate at 15 mL/min.
- Cannulate the colorectum at both the oral and anal ends. Start the intraluminal infusion of the colon with saline at a rate of 10 mL/h in the oral to anal direction.
- Locate the major PG under the dissecting microscope. Use insect pins to expose the ganglion. With careful dissection, find a fine branch of nerve emanating from the ganglion and running towards the colon (Figure 1). Cut the nerve close to the ganglion.
NOTE: Figure 1 illustrates a recording from a nerve branch distal to the PG. The nerve presumably contains a mixture of pelvic and lumbar splanchnic afferent fibers. Alternatively, a recording can be made from the PN and/or the LSN proximal to the PG. - Turn on the heating bath and warm the Krebs solution to keep the chamber temperature at 34 ± 0.5 °C.
5. Preparation of the Suction Electrode
- Take a pre-pulled glass pipette (step 2) and inspect it under the dissecting microscope. Break the tip of the electrode with a pair of forceps so that it is of a size compatible with the diameter of the nerve to be recorded.
- Bevel the tip by placing it close to a lighter flare.
6. Electrophysiological Recording
- Connect the beveled electrode to the electrode holder. Connect a 10-mL syringe to the side port on the holder to apply negative or positive pressure to the electrode.
- Connect the holder to the headstage of the bioamplifier and mount the headstage onto a manipulator.
- Move the electrode to the tissue bath and fill the electrode with the Krebs solution by applying gentle suction until it contacts the silver wire of the holder. Place the electrode tip close to the cut end of the nerve and apply negative pressure to suck the nerve into the electrode. Apply more negative pressure so that ~1 mm of the nerve is pulled into the electrode and forms a tight seal.
- Turn on the bioamplifier and set the filter to 300 - 3,000 Hz. Monitor the signal on the oscilloscope and record the nerve signal (20-kHz sampling rate) and the intraluminal pressure signal (100-Hz sampling rate) using a computer with spike data processing software.
7. Testing the Colonic Afferent Sensitivity
- Apply ramp distension of the colon by closing the three-way tap on the outlet cannula while continuously infusing intraluminally. Monitor the intraluminal pressure until it reaches 60 mmHg, at which time open the three-way tap on the draining cannula.
النتائج
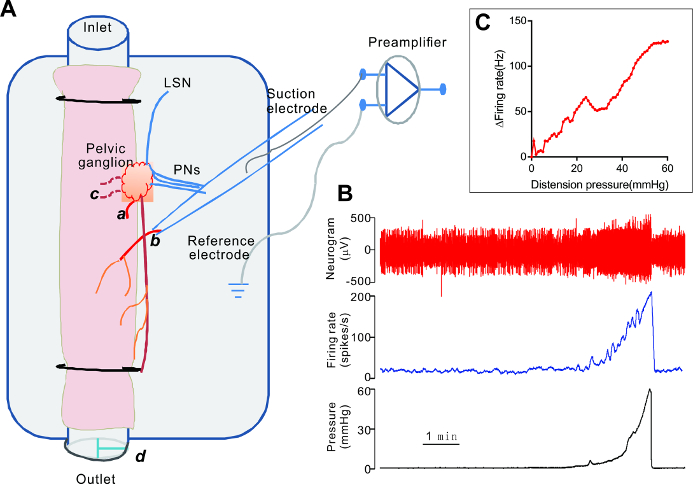
Figure 1. Electrophysiological Recording of Rat Colonic Afferent Nerves In Vitro. A. A schematic illustration of the ex vivo "tube" colon preparation of the rat. The colorectum, with the attached PG, is superfused in the recording chamber and is cannulated at both ends. Intraluminal infusion is achieved using a syringe pump and moves in the oral to anal direction. Disten...
Disclosures
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Sodium Pentobarbital | Shanghai Westang Bio-Tech | B558 | |
| Capsaicin | Sigma | M2028 | |
| Electrode puller | MicroData Instrument Inc | PMP107 | |
| Neurolog System (Bioamplifier) | Digitimer, Ltd | Neurolog System | |
| A/D converter | Cambridge Electronic Design | Micro1401 | |
| Data processing software | Cambridge Electronic Design | Spike2 version 6 | |
| Silver wire | World Precision Instruments | EP12 | |
| Glass tubes | World Precision Instruments | 1B150-4 | |
| Electrode holder | World Precision Instruments | MEH3SBW | |
| Heating bath | Grant | GR150 | |
| Dissecting microscope | Leica | Zoom2000 | |
| Dissecting microscope | World Precision Instruments | PZMIII-BS | |
| Cigarette lighter | any | NA | |
| Surgical tools | World Precision Instruments | NA | |
| Insect pins | home-made from 0.1 mm stainless steel wire | NA | |
| Three way manipulator | World Precision Instruments | KITF-R | |
| Rats | Any | NA | Any strain/sex can be used. |
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Source: Meng, Y. et al., In Vitro Characterization of the Electrophysiological Properties of Colonic Afferent Fibers in Rats. J. Vis. Exp. (2017)
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved