7.1 : Work
Work is done when energy is transferred from one object to another. In other words, work is when a force acts on something that undergoes a displacement from one position to another. Forces can vary as a function of position, and displacements can be along various paths between two points. The increment of work (dW) done by a force acting through an infinitesimal displacement can be defined as the dot product of force (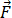 ) and displacement (
) and displacement (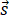 )vectors.
)vectors.
The dot product can be expressed in terms of the magnitudes of the vectors and the cosine of the angle between them, as it is easier to define the dot product in words as an expression of magnitudes and angles. It can also be expressed in terms of various components, as introduced in the vectors lesson.
From vector properties, it does not matter if you take the component of the force parallel to the displacement, or the component of the displacement parallel to the force—the result is the same either way. The units of work are units of force multiplied by units of length; this is Newtons multiplied by meters (N·m) in the SI system. In the English system, the unit of force is the pound (lb), and the unit of distance is the foot (ft), so the unit of work is the foot-pound (ft·lb).
The work done by a force that is constant in magnitude and direction is the simplest to calculate. In general, forces can vary in magnitude and direction at points in space, and the paths between two points can be curved. The infinitesimal work done by a variable force can be expressed in terms of the components of the force and the displacement along the path. In these cases, the components of the force are functions of position along the path, and the displacements depend on the equations of the path. However, the physical concept of work is straightforward: calculate the work for tiny displacements and add them up.
This text is adapted from Openstax, University Physics Volume 1, Section 7.1: Work.
来自章节 7:

Now Playing
7.1 : Work
Work and Kinetic Energy
20.9K Views

7.2 : 正、负和零功
Work and Kinetic Energy
18.2K Views

7.3 : 能源
Work and Kinetic Energy
12.9K Views

7.4 : 势能类型
Work and Kinetic Energy
6.5K Views

7.5 : 动能的类型
Work and Kinetic Energy
6.7K Views

7.6 : 动能 - I
Work and Kinetic Energy
10.0K Views

7.7 : 动能 - II
Work and Kinetic Energy
5.9K Views

7.8 : 功-能量定理
Work and Kinetic Energy
22.0K Views

7.9 : 可变力的功和能量
Work and Kinetic Energy
3.4K Views

7.10 : 沿曲线运动的功-能量定理
Work and Kinetic Energy
2.5K Views

7.11 : 在斜面上完成的功
Work and Kinetic Energy
2.8K Views

7.12 : 多方力量完成的工作
Work and Kinetic Energy
3.9K Views

7.13 : 重力完成的工作
Work and Kinetic Energy
6.6K Views

7.14 : 权力
Work and Kinetic Energy
11.1K Views

7.15 : 恒定力消耗的功率
Work and Kinetic Energy
7.2K Views
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。