13.7 : Wilcoxon Signed-Ranks Test for Matched Pairs
The Wilcoxon signed-rank test for matched pairs evaluates the null hypothesis by combining the ranks of differences with their signs. It essentially tests whether the median of the differences in a population of matched pairs is zero. Since the test incorporates more information than the sign test, it generally yields more trustable conclusions. This test also does not require the data to follow a normal distribution, but two conditions must be met for it to be applicable: (1) the data must consist of matched pairs; and (2) the distribution of the differences between these pairs should be approximately symmetric.
The difference, d, for each data pair is calculated by subtracting the second value from the first. In the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, the signs of these differences are initially ignored, and their absolute values are ranked in ascending order, and ranks are then assigned to each difference. After that, the original signs are reapplied to the ranks, creating signed ranks. The sum of the positive and negative signed ranks is calculated separately. With this, the sample size, n, is the number of pairs with non-zero differences, which determines the test statistic used.
- If n is less than equal to 30, the test statistic, T, is taken as the smallest of the two sums obtained;
- If n is higher than 30, the test statistic, Z, is calculated using the formula: 14160_Equation_PT_1
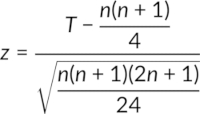
In both cases, the critical z-value is also up from its table. If the test statistic, T, is less than the critical value, z, the null hypothesis is rejected.
来自章节 13:

Now Playing
13.7 : Wilcoxon Signed-Ranks Test for Matched Pairs
Nonparametric Statistics
84 Views

13.1 : Introduction to Nonparametric Statistics
Nonparametric Statistics
658 Views

13.2 : Ranks
Nonparametric Statistics
225 Views

13.3 : Introduction to the Sign Test
Nonparametric Statistics
667 Views

13.4 : Sign Test for Matched Pairs
Nonparametric Statistics
96 Views

13.5 : Sign Test for Nominal Data
Nonparametric Statistics
69 Views

13.6 : Sign Test for Median of Single Population
Nonparametric Statistics
86 Views

13.8 : Wilcoxon Signed-Ranks Test for Median of Single Population
Nonparametric Statistics
93 Views

13.9 : Wilcoxon Rank-Sum Test
Nonparametric Statistics
147 Views

13.10 : Bootstrapping
Nonparametric Statistics
580 Views

13.11 : The Anderson-Darling Test
Nonparametric Statistics
654 Views

13.12 : Spearman's Rank Correlation Test
Nonparametric Statistics
668 Views

13.13 : Kendall's Tau Test
Nonparametric Statistics
585 Views

13.14 : Kruskal-Wallis Test
Nonparametric Statistics
551 Views

13.15 : Wald-Wolfowitz Runs Test I
Nonparametric Statistics
599 Views
See More
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。