Method Article
中空纤维生物反应器的
摘要
在培养细胞的功能行为可以通过在更体内样的三维培养环境16-21培养得到改善。该原稿描述了一种中空纤维生物反应器系统的用于体内式的哺乳动物组织培养的设置和操作。
摘要
Tissue culture has been used for over 100 years to study cells and responses ex vivo. The convention of this technique is the growth of anchorage dependent cells on the 2-dimensional surface of tissue culture plastic. More recently, there is a growing body of data demonstrating more in vivo-like behaviors of cells grown in 3-dimensional culture systems. This manuscript describes in detail the set-up and operation of a hollow fiber bioreactor system for the in vivo-like culture of mammalian cells. The hollow fiber bioreactor system delivers media to the cells in a manner akin to the delivery of blood through the capillary networks in vivo. The system is designed to fit onto the shelf of a standard CO2 incubator and is simple enough to be set-up by any competent cell biologist with a good understanding of aseptic technique. The systems utility is demonstrated by culturing the hepatocarcinoma cell line HepG2/C3A for 7 days. Further to this and in line with other published reports on the functionality of cells grown in 3-dimensional culture systems the cells are shown to possess increased albumin production (an important hepatic function) when compared to standard 2-dimensional tissue culture.
引言
组织培养是用于已经被用于超过100年1,2-细胞的生长和/或维持已建立的技术。研究细胞和响应体外的便利具有深远允许实验,否则将极具挑战性的,如果不是不可能的优点,例如遗传工程细胞系的产生,并在高通量筛选测定法3中使用报道细胞的。最近的组织培养,已经引起了组织工程领域, 在体外模型的生成和再生医学。与这些应用中,在动态的三维(3D)培养系统兴趣显著增长。
三维培养的方法(这里定义为3D培养基材和/或引入定向动态流动的)更好概括的体内细胞环境的体系结构,用于实现重要更多的生理样的功能。提取,生长,分化和移植细胞修复病变和损伤组织的目标的能力是研究领域有病人的利益和商业机会,潜力巨大。例如使用用于治疗烧伤的自体角质形成细胞(见4),并用于治疗中风的使用基于细胞的疗法(见5)。同样,市场对体外模型涵盖药物发现到药物分层应用。在组织培养中的约定是粘附或锚定依赖性细胞类型的组织培养烧瓶中的2维(2D)表面上的生长。虽然目前公认的在研究设置的金标准,近期组织工程应用的兴趣强调,当前2D组培环境不足以在电池生产6所需要的规模。
对于贴壁细胞类型scaffold被需要,这将取决于最终用途,在这两种化学成分和机械性能的方面。一些系统采用的支架作为由从高内相乳液模板形成高度多孔的基质的多孔板插入件(参见7)或电纺纤维(见第8)规定从常规的2D培养技术的最小的适应。细胞可以接种到不同成分的微载体和搅拌槽内的输送养分和信号分子长大,并通过动态以及混合环境9带走废物(大众交通)。然而,这些系统都在它们的体内样环境限制,并且进一步改进可以与问候作出按比例放大的成本。中空纤维生物反应器(HFBs)是由固定在与通常接种在通过纤维内腔递送的多孔纤维和介质的外部单元的模块的纤维的三维培养系统(1审查0)( 图1)。 HFBs提供与纤维模仿毛细血管以及从与动态媒体递送相关联的剪切应力屏蔽的细胞,同时使规定剪切经由流体流动通过侧口如果需要的话可以应用于细胞的体内样的环境。这将创建具有优越的物质传输中高细胞密度可以达到11一个多功能的文化体系。的HFB系统非常适合于维持锚地依赖性细胞类型,并已用于培养多种细胞,包括朗格汉斯12,小鼠β-TC-3胰岛细胞系12,原代人肝细胞13人骨的大 鼠胰岛骨髓单核细胞14的Madin Darby犬肾细胞(MDCK)15和Caco-2细胞16仅举几。
除了传质和放大的系统的优点,细胞生长在3D炎告培养系统往往更体内样形态,更响应于实验线索。例如大鼠原代肝细胞显示更立方形形态,增加活力,细胞色素P450酶的活性更大的诱导和敏感性增加扑热息痛毒性相比,在2D培养17生长的细胞中的市售聚苯乙烯脚手架生长时。使用肝癌细胞系HepG2也已显示出增加白蛋白生产18,并显示在体内的更样响应于甲氨蝶呤相比2D培养细胞19相同的支架。原代人肝证明延迟去分化,较高细胞色素P450酶活性的和用于在灌注培养系统20测试的4/5的化合物增加的间隙。人神经干细胞衍生的神经元和神经胶质细胞中的市售聚苯乙烯支架培养显示出兼具高(动作电位)和低frequeNCY(局部场电位)自发活动,而没有神经元的活动在2D培养细胞21进行检测。 Caco-2细胞相比通过增加的碱性磷酸酶,γ谷氨和P-糖蛋白的活性和F-肌动蛋白和卵occludens-1蛋白16高表达测量的2D培养中HFB证明增强的分化。尽管优点,细胞在比二维组织培养瓶表面的其它系统的常规培养仍然没有在许多实验室实施,虽然出版物引用的3D细胞培养物的数量在不断增长(在过去的10年增加8倍。源:考研"结果按年份"工具,"3D文化")的侦测。
该原稿描述HFB系统的用于哺乳动物细胞培养物中的设置和操作条件,并演示了在培养人肝癌细胞系HepG2 / C3A其效用。该方法的目的是要培养的细胞更在体内样的文化,保留足够的简单系统,使它适合那些谁是新的三维培养系统。后面在应用程序中使用HFBs理描述在这里,这是改善肝模型的可预测性是它在理论上是可能的HFB环境22内模仿肝窦。这不是目前与其他文化系统是可行的。
研究方案
1.纤维
- 制造由倒相旋铸纤维(纺)。该方法的细节可以在23,24找到。
注意:对于这个工作纤维在内部使用非生物可降解的专有的聚合物制造的NMP作为溶剂和H 2 O作为非溶剂。其它合适的聚合物的细节可以在讨论中找到。在这里所描述的系统中使用的纤维是1.05毫米外径用600-700微米管腔直径。纤维是多孔与孔径测量2.28微米±1.5微米(平均值±标准偏差)。这被设计为从在纤维内腔介质馈送分离细胞,复制其他组织的肝血窦或脉管。纤维也可以从膜的供应商如Pall公司购买。
2.模块制造
注意:在此研究中使用的模块从1mm厚的硼硅玻璃带2侧端口作出( 图2A)。这里所描述的模块中的纤维具有4.95 平方厘米其大致半一个6孔板的孔中的等效的外表面面积。
- 第一次使用前SILICONIZE模块由内表面与Sigmacote( 表1)涂敷,并允许在通风橱中干燥。高压釜(121℃,1个大气压,20分钟),以增加治疗的寿命。
- 使用手术刀切75毫米长纤维和插入三种纤维到每个模块留下〜7毫米多余长度在各端( 图3A)。
- 地方〜0.5毫升硅胶胶水( 表1)进入称重船。使用P200的枪头拿起硅氧烷少量和工作胶水到模块的端部周围的纤维,以形成一个3-5毫米插头( 图3B)。晾干时间> 3小时。
- 使用手术刀切与玻璃模块端部( 图3C)硅氧烷齐平。
- 紧裹聚四氟乙烯(PTFE)的少量(〜4层)周围一侧端口胶带。
3.系统设置和消毒
注:泵管和模块用纤维不高压灭菌并用70%乙醇灭菌。作者建议校准要使用与泵的泵管。下面的步骤是在层流罩下进行。
- 高压灭菌器(如2.1节)中的所有组件高压灭菌之前设置。
- 建立
- 将10mL 70%乙醇到容器瓶和设置储液瓶,Q系列帽,进料管,泵和泵管( 表1)如在图4中。
- 松散放置在聚四氟乙烯贴侧端口端盖。滑动的L / S16模块连接器的端部在模块端部和自由侧端口。连接的L / S13油管最靠近封端侧端口的模块连接器( 表1)的40mm的部分, 如图2B所示 。
- 该模块连接到泵管,确保能够定向模块,使该上限侧端口是最接近泵。
- 连接渗透物管线和滞留线到模块连接器和左/储液瓶的Y形连接器的S14中( 表1)。确保的建立类似于原理图在图4中。
- 消毒
- 通过在800微升/小时(每根光纤267微升/小时)有足够的时间来治疗时间> 30分钟unautoclaved组件模块泵乙醇(如果使用其他方法消毒调整时间,见25)。
- 洗
- 洗乙醇淘汰制,先关掉水泵和排水管材。首先,从分离的模块适配器管泵管。持模块高处排空乙醇出纤维和滞留线,返回到储液瓶。从模块排日卸下侧面端口端盖从模块本身,而且渗透物线e乙醇。重新装上侧口端盖。扭转在泵的介质的流动以排出泵管和乙醇进料管线。关闭水泵,并重新安装泵管到模块适配器。
- 从盖拧开乙醇瓶并用含有10ml细胞生长培养基(如EMEM,GMEM,DMEM或RPMI)无血清瓶替换。在800微升泵通过系统的介质/小时直到滞留线充满介质。夹紧滞留行来强制媒体的渗透过纤维洗模块。洗〜2小时。
4.播种
注:媒体和在这个协议中使用应该是那些为所需的细胞类型建立的补充。请参考文献中,欧洲细胞培养的(ECACC)和美国典型培养物保藏中心(ATCC)以获得进一步的信息。在此之前,方法的细胞应该是maintaINED根据用于所需的细胞类型建立的协议。对这项工作的人肝癌细胞系HepG2 / C3A亚克隆分别根据分销商的建议(ATCC)维护。
注意:下面给出还播种协议用于现有预培养用细胞培养基将模块细胞生长。应该更广泛的预培养需要那么这应该之前通过从系统排出洗涤介质,用生长培养基代替,并通过几个小时模块渗透此播种模块进行。查看系统中的替代媒体细节部分7.5.2.1。
- 根据用于所需的细胞类型建立的协议通过胰蛋白酶消化制备单细胞悬浮液。对于T75文化的一般协议如下:
注:细胞的数目在播种步骤使用应该是你所需的细胞类型凭经验确定。这里所描述的生物反应器在35倍的更高的CEL接种比在二维组织培养塑料为7天的培养中使用的LS密度(细胞/厘米2)。- 通过加入10ml磷酸盐缓冲盐水(PBS),吸洗细胞,然后添加3毫升0.05%胰蛋白酶乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)(足以覆盖细胞),并在37℃,5%的CO 2孵育5分钟。
- 在7ml生长培养基收获细胞补充有10%胎牛血清(FBS),以中和胰蛋白酶。拌匀,加入10微升至血细胞计数器的室和计数细胞。
- 离心在200×g离心5分钟以沉淀细胞。
- 吸在生长培养基在4×10 6 / ml的上清液和重悬细胞所必需的期望的细胞类型的补充。
- 关掉泵和漏进料管和模块如在3.4.1。
- 从模块的连接器分离的模块和连接模块端盖( 表1)在70%乙醇预消毒,留下一侧端口自由
- 用18G的针和1ml注射器,注意避免气泡形成和不损坏纤维转移〜500微升细胞悬浮液(2×10 6个细胞)(4.1.4)的模块。
- 使用端盖帽侧端口。孵育细胞在37℃,5%CO 2的2-4小时与180°,每5分钟的模块的手动转动。可替代地,模块可以连接到管旋转用间歇混合设定( 表1)。
- 以下播种,附加的端帽将注射口( 表1)在70%乙醇预消毒,并附加该到聚四氟乙烯录音侧端口。除去另一侧端口端盖并用27克针和1ml注射器注入空气进入附注入口慢慢排空细胞。
- 与端盖更换注射端口。慢慢填充使用自由侧端口和一个1ml注射器18G的针媒体的模块。雷莫已经模块端盖和使用该模块的连接器的模块连接到管上。
- 更换清洗媒体瓶含有下列7.5.2.1中详述的方法50毫升生长介质和补充之一。通过该系统,在800微升/小时的泵的生长介质。
5.扩散
注意:在这里描述的研究系统中使用的纤维是设定在约80微升/小时渗透,用800微升/小时的进料速率。
- 使用该纤维中生长的7天期间的细胞在加湿培养箱设定为37℃,5%的CO 2。
注:在生长阶段营养物和代谢物的监测可以提供关于增殖有用的信息,代谢摄取和在媒体细胞和营养物和代谢物水平的输出。例如使用葡萄糖和乳酸的生产。套件可从可从媒体的定量分析这些因素的不同供应商(见表1对于那些在本研究中使用)。喷射口可以加入渗透和滞留物管道并经由27克针头和注射器取样媒体和媒体可从媒体贮存瓶进行采样。这给出了输入和两个输出流养分和代谢信息。取样应在层流罩下进行。通过举办针对端口> 30秒的乙醇浸泡蓝色卷采样前消毒注射口。
6.切除
注:纤维可从模块在一个实验进行分析的结束被切除。
- 拔下并沥干HFB。
- 插入手术刀/微刀( 表1)刀片的玻璃和硅之间。转动模块以便切掉从玻璃的硅酮。在模块的两端重复此过程。
- 用刀片从一端钩出来的硅胶塞,轻轻一拉。确保纤维随之而来。
7.细胞分析
- 手机号码
注意:对于在本研究中7天的生长周期内的任何时间点都适合在此计算中使用用作增长率基本上不超过改变此时间取得的细胞密度的C3A细胞。- 切除(第6节)后浸纤维到PBS洗并把它们切成含有0.5 ml的三EDTA(TE)缓冲液1.5 ml的管中。在受试者这两个冻融循环-80℃冷冻机中。使用的PicoGreen测定DNA含量和通过该值进行比较,以与所需细胞类型26制成的标准曲线确定的细胞数。
- 细胞增殖率
- 使用在两个不同的时间点计算出计算细胞数的比生长速率μ(式1),此处Ln(X1)是在第一时间点和LN(X2)的细胞数的自然对数是细胞的自然对数在第二个时间点数目。
μ=(LN(X2)-Ln(X1))/时间(小时)(1)
从这个计算群体倍增时间(DT)(等式2)其中μ是比生长速率。
DT一LN2 /μ(2)
- 使用在两个不同的时间点计算出计算细胞数的比生长速率μ(式1),此处Ln(X1)是在第一时间点和LN(X2)的细胞数的自然对数是细胞的自然对数在第二个时间点数目。
- 细胞活力
- 切除(第6节)后浸纤维到PBS洗并把它们切成含有500微升0.05%胰蛋白酶乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)1.5 ml的管中。孵育在37℃下10分钟。
- 混合并加入10微升细胞悬液,以10微升台盼蓝。负载10微升到血球计和计数的死(蓝色)和活细胞的数目。
- 成像
- 切除后浸纤维到PBS洗并用剪刀将它们切割成较小的长度成24孔板。添加400μl的4%多聚甲醛(在PBS中),并在室温孵育20分钟。
- 由微升打开和关闭400吹打用PBS洗涤。重复THIS步进新鲜PBS。
- 添加400μl的4',在PBS中稀释至约6二脒基-2-苯基吲哚(DAPI)。 100毫微克/毫升,并在室温孵育20分钟。避光。
- 用PBS洗涤两次(如7.3.2),一次用H 2 O.添加荧光安装介质,立即覆盖纤维和图像采集干样品之前的数据(DAPI EX / EM;四百六十一分之三百五十九纳米)。
- 拍摄图像在不同的焦平面,并使用"集中堆放"软件( 例如 ,堆栈聚焦插件ImageJ的,下同),使显示领域的一个极大的扩展深度的合成图像。作为纤维不平坦这是必需的。
- 下载ImageJ的(http://imageJ.nih.gov/ij/)和"栈聚焦"插件(http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/plugins/stack-focuser.html)。
- 在ImageJ的打开图像被堆叠。然后在"图像"菜单进入"堆栈" - "图像至栈"。在"插件"菜单进入"堆栈调焦"。指定n×n个内核的n。试错与'n'个可以产生具有小的"噪音"的图像是必需的。 11&77之间的值往往运行良好。
- 白蛋白分泌
注意:这是一个肝细胞功能测试,而不是细胞功能的通用测试。- 种子细胞(HepG2细胞/ C3A)到2D组织培养塑料在10,667 / cm 2,并且生长6天。在第4节和成长6天的种子HFBs。
- 以下这个增殖期间改变培养基(EMEM + 10%FBS,1×谷氨酰胺及1×青霉素/链霉素)的组织培养塑料和HFB到补充有1X谷氨酰胺和1x青霉素/链霉素24小时无血清Williams E无媒体:
- 排水以下载于3.4.1的步骤管道和HFB模块。拧开储液瓶和含威廉姆斯e媒体一瓶替换此。通过HFB 8该泵00微升/小时。
- 继24小时,采取媒体样本。根据制造商的说明( 表1)通过ELISA定量分泌白蛋白。稀释培养基样品1在40 10至1在使用前,以使该标准曲线的范围内白蛋白的浓度。
结果
细胞种植是关键的一步。细胞粘附在3D设置的纤维的能力比看到的二维组织培养塑料相当少。这可能是由于细胞与基板之间的减小的接触时间。在HFB细胞播种期间的静态阶段告吹模块。这些都是在时间大大缩短相比,在2D中使用的一个连续的静态相。细胞具有使在此时的衬底连接。另外,由于纤维的弯曲性质是没有平坦面为细胞休息和使连接像有在二维培养。虽然这可以通过纤维的化学配混使用我们知道这不被用于本研究中所用的聚合物的情况下(未示出数据)。增加播种时间和细胞接种密度导致细胞的聚集体,在以较快的r处的静态阶段通过模块落形成吃比单细胞,并进一步降低了细胞和衬底之间的接触时间。增加时间也导致了媒体的泛黄,因为这里的细胞的高密度,并且在该步骤中没有媒体交换。使用中的〜15%第4节细胞播种率所述的条件用的HepG2 / C3A细胞( 图5A)一致地实现。虽然这可被认为是低级分有足够的细胞以产生天( 图5B和6)的一个问题,填充井纤维;继七天增殖期的HFB细胞密度达到将至3×10 5 / 平方厘米。这是用于利用许多测定肝细胞,并可以被认为是达到汇合合适的密度。
相比,在二维的细胞培养( 图5C)来实现时,在HFB取得的扩散速率慢。这是联合国很可能是由于在该系统的动态流动细胞的损失在媒体细胞计数低(平均±SEM:20343细胞±每24小时3,674细胞于汇合,这是细胞总数的4%),这当渗透速率被接通到400微升/小时不增加(数据未显示)。也不太可能是由于在存活力的降低和细胞的后续损耗( 见图5D及以下)。它可能是由以下事实此细胞系克隆从HepG2细胞衍生的并在其显示细胞增殖的接触抑制的能力来选择进行说明,至少部分。在HFB将细胞在6倍接种二维细胞,其可能会导致较慢的扩散速率的密度。
生存能力仍然与各地参展> 90%细胞HFB高。虽然有在出口端在存活率略有下降相比入口此没有被发现是显著(叔检验p = 0.22)。
葡萄糖消耗和乳酸生产的监测已被用于调谐系统中的媒体进料速率和媒体的体积。用800微升/小时,毫升葡萄糖和乳酸水平维持不变的上方和下方(分别)为50,总介质卷那些标准组织培养塑料培养观察。
白蛋白分泌是由肝细胞进行的一个关键肝功能。它被分泌到那里它在运输和稳态几个角色的血清。白蛋白分泌通过在HFB生长的细胞比在( 图7)上生长2D细胞15倍。这表明细胞在HFB官能和至少在白蛋白分泌的情况下,这种功能在HFB升高。
JPG"/>
图 1. HFB 的体内 样的环境。将细胞接种到多孔纤维的外侧。介质通过纤维内腔递送,模仿毛细血管。 (A)中的纤维的纵截面(不按比例)。 (B)跨3纤维反应器的部分。 请点击此处查看该图的放大版本。
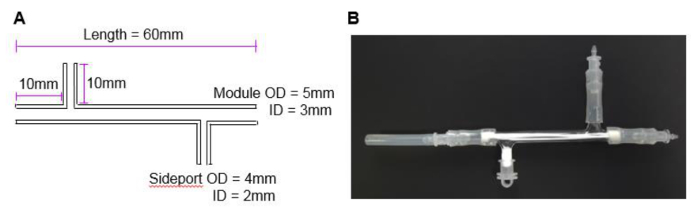
图2. HFB模块:(A)在本研究中使用的模块的尺寸。尺寸被选择,以适应3纤维和满足当前研究项目的需求。不同的尺寸可以制造和各个系统和纤维量身定做。 (B)的第m的照片附带端盖和模块连接odule。 请点击此处查看该图的放大版本。
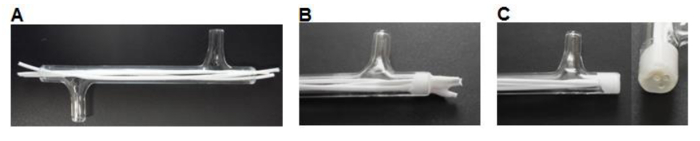
图3.模块制造。(A)中的纤维被切割成一定尺寸,并插入该模块。 (B)的纤维被粘合成模块,使其干燥。 (C)两端切割与玻璃冲洗。 请点击此处查看该图的放大版本。
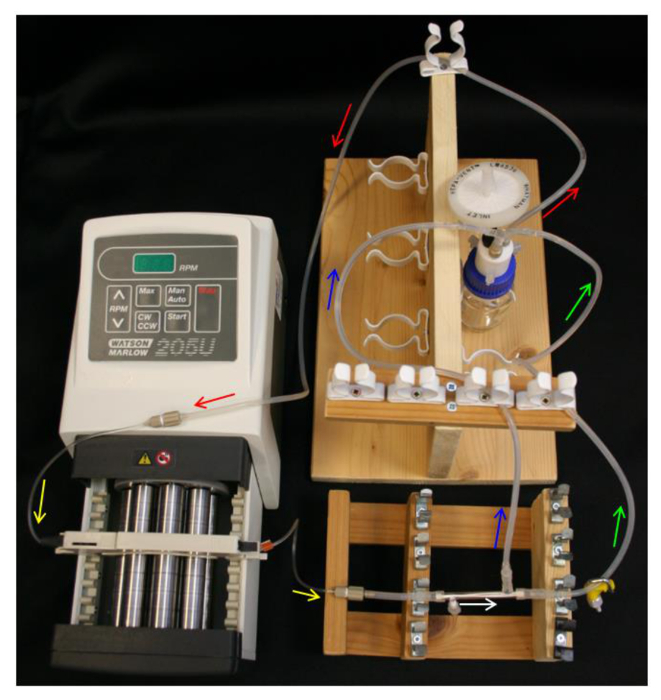
图4. HFB系统设置。箭头指示媒体流的方向。红色=进料管。黄色=泵涂是。白色= HFB模块。绿色=截留管钳。蓝色=渗透管。 请点击此处查看该图的放大版本。
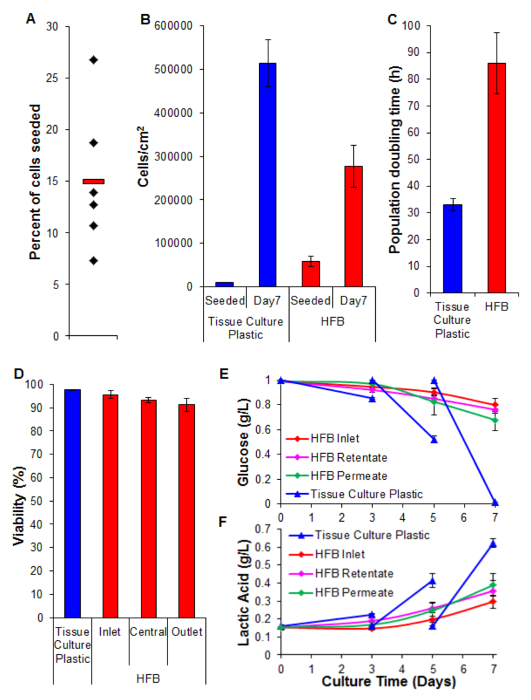
图5.播种,增殖活力和生化分析( 一 )种子细胞的百分比。黑色菱形代表个人HFBs。红色条是平均值。 (B)细胞密度在播种和7天的增殖期。 2D细胞数通过胰蛋白酶消化,并使用血球计计数测定。使用PicoGreen检测结果和从C3A细胞26产生的标准曲线测定的HFB细胞数目。 N = 5-6。酒吧= SEM。 ( 三 )人口倍增时间。 N = 5-7。酒吧= SEM。 ( 四 )由生存能力确定的色氨酸一个蓝排除在7天的增殖的结束。入口,中部和出口代表HFB内的区域。 N = 3-5。酒吧= SEM。 (E&F),葡萄糖消耗和乳酸生产。水平在储液瓶(入口)以及滞留监视和渗透出口以及司仪到组织培养塑料常规培养(培养基在第3天及5改变)。 N = 3-5。酒吧= SEM。 请点击此处查看该图的放大版本。
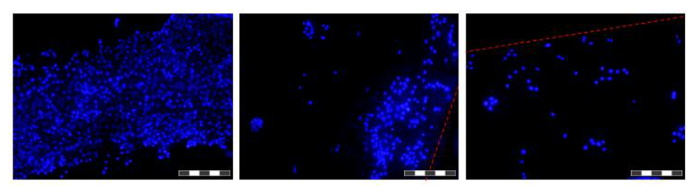
图6.图像在HFB生长在纤维细胞。细胞接种,并生长48小时切下的纤维之前,在PBS中洗涤,固定在4%多聚甲醛,在PBS中,用DAPI染色的细胞核洗涤。每个图像是12的复合"集中堆放"IMA为了GES来增加所产生的图像的景深。较高和较低的细胞密度的区域被在这个时间点沿纤维发现,被示出。其中,本纤维的边界来表示有一个红色的虚线。图像是在一个倒置荧光显微镜。图片= 10X目标。酒吧= 200微米。 请点击此处查看该图的放大版本。
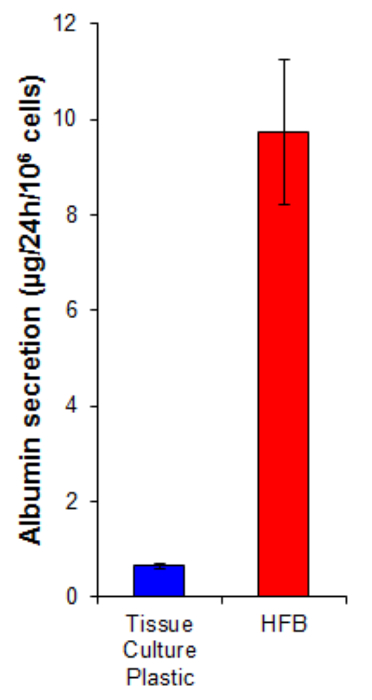
图7.白蛋白分泌。将细胞以10,667 /厘米2,并在HFB如第4节细胞增殖6天描述接种到组织培养塑料。在此之后增殖期的组织培养塑料和HFB培养基改变为补充谷氨酰胺和青霉素/ streptomyci无血清·威廉姆斯e媒体n,用于24小时。媒体取样并白蛋白通过ELISA根据生产商的说明( 表1)定量。 N = 5-6。酒吧= SEM。 请点击此处查看该图的放大版本。
| 部分 | 设备名称 | 公司 | 猫。没有。 | 笔记 | 图片 |
| 2 | 玻璃HFB模块 | Soham科学 | --- | 自定义项。 | |
| 2.1 | Sigmacote® | Sigma-Aldrich公司 | SL2 | ||
| 2.3 | Silicoset 151 | Intertronics | ACCSS151 | 水磨石一点涂胶。 | |
| 2.5 | 四氟带 | Sigma-Aldrich公司 | Z104388 | ||
| 3.2.1 | 储液瓶 | 费舍尔 | 11972619 | ||
| Q系列帽 | 室壁运动 | 00932Q-3V | PTFE适配器和装配螺母的螺纹。附加到Q系列帽。随机附送的PTFE管1mm的适配器下的8.5广告区间和3mm的适配器下4cm的部分。 |  | |
| 适配器,男性为1.0毫米内径 | 室壁运动 | 008NB10-KD5L | |||
| 适配器,男,3.0 mm内径 | 室壁运动 | 008NB30-KD5L | |||
| 接头螺母 | 室壁运动 | U-350 | |||
| 氯丁橡胶管 | 费舍尔 | 10366344 | 附上HEPA过滤器,以氯丁橡胶管6厘米,并附这对"接头螺母"。附加的L / S14管道的2倍30毫米节到Y连接器的顶两个倒钩和L / S16管3cm的部分的底部。连接这3 mm内径适配器的倒钩。 (第3.2.1节) |  | |
| HEPA泄 | 费舍尔 | 11374634 | |||
| Y型连接器,带刺 | 科尔帕默 | OU-06295-10 | |||
| L / S16硅胶管 | 科尔帕默 | OU-96410-16 | |||
| L / S14硅胶管 | 科尔帕默 | WZ-96410-14 | |||
| L / S13硅胶管 | 科尔帕默 | OU-96410-13 | 80厘米到1.0毫米倒钩的适配器连接的Q系列帽到泵桶 ING =进料管。 | ||
| WM 205U / CA泵 | 费舍尔 | 1248-6300 | |||
| WM泵管,PVC,蓝橙为0.25mm口径 | 费舍尔 | 12416310 | 聚四氟乙烯阳适配器的螺纹和连接凹入式适配器。在倒钩的一个工作泵管。重复此设置在管的另一端。 (第3.2.1节) |  | |
| 适配器,男性为1.0毫米内径 | 室壁运动 | 008NB10-KD5L | |||
| 适配器,女性为1.0毫米内径 | 室壁运动 | 008NB10-KD2L | |||
| 3.2.2 | 女露儿帽 | 科尔帕默 | WZ-45508-64 | 方口端盖。 | blefig4.jpg"/>  |
| L / S13硅胶管 | 科尔帕默 | OU-96410-13 | 40毫米部到泵管连接到模块连接器。 | ||
| L / S16硅胶管 | 科尔帕默 | OU-96410-16 | 3X升30毫米/ S16配备3倍减速=模块连接器。 (第3.2.2节) | ||
| 刺减速1/8"×1/16" | 科尔帕默 | 30616-43 | |||
| 3.2.4 | L / S13硅胶管 | 科尔帕默 | OU-96410-13 | 55厘米部分滞留物连接到L上的Q系列帽的Y连接器的/ S14。 |  |
| L / S13硅胶管 | 科尔帕默 | OU-96410-13 | 45厘米部到渗透连接到L上的Q系列帽的Y连接器的/ S14。 | ||
| 带刺的直工会 | 科尔帕默 | WZ-30612-43 | 连接到L / S13将与该Y形连接器的L / S14连接的结束。 | ||
| 3.4.2 | 钳 | VWR | 229-0609 | ||
| 4.3 | 4毫米硅胶管 | 费舍尔 | FB68858 | 折叠管40mm的部分,并用扎带=模块端盖固定。 (第4.3节) |  |
| 扎带 | 费舍尔 | 12326377 | |||
| 4.4 | MACSmix管旋转 | 美天旎生物技术 | 130-090-753 | 适应可能需要ATTAC小时的模块。 | |
| 4.5 | 勒尔进样口 | 蓟科学 | IB-10820 | 连接端帽到注射端口。 (第4.5节) | |
| 女露儿帽 | 科尔帕默 | WZ-45508-64 | |||
| 五 | L-乳酸试剂盒 | Megazyme的 | K-LATE | ||
| 五 | D-葡萄糖试剂盒 | Megazyme的 | K-GLUC | ||
| 6.2 | 手术刀/微刀 | InterFocus | 10315-12 | ||
| 7.4.3 | 白蛋白ELISA | BETHYL实验室 | E80-129 |
表1. HFB设置的组件。 有关每个组件的文本段在第1列中给出。
讨论
该原稿描述了一种中空纤维生物反应器(HFB)系统,用于哺乳动物细胞培养的设置和操作,它的效用是表现在增殖的肝细胞系HepG2 / C3A。该系统的设计,以适应到一个标准培养箱及其组式的货架足以任何主管细胞生物学家熟悉无菌技术进行简单。
在这里描述的研究系统中使用的纤维是在房子由相位反转自旋使用非生物可降解的专有聚合物浇铸(纺丝制造)。有可能通过从各种适于细胞培养,包括可生物降解的和不可生物降解的,例如材料纺丝使纤维;聚己内酯(PCL)27,聚-L-丙交酯酸(PLLA)28,聚(乳酸-共-乙醇酸)(PLGA)29,聚砜(PSU)12和聚醚醚酮(PEEK)13。每个人都有不同的属性次应该基于系统的需要来选择。检查与在杀菌工序中使用的乙醇所采用光纤的兼容性。 PLGA是已知用乙醇迫使一种替代治疗,如抗生素/抗 真菌溶液25增塑。
这里使用的玻璃模块的尺寸是基于目前的研究的需要选择。不同的大小可通过任何有信誉的玻璃吹制公司进行。在模块尺寸的考虑是细胞的数目,这是与在模块中的纤维和可能的流速的数量。在更多的细胞有所述模块的较高的流率将需要以维持良好的培养条件在生物反应器的流出端英寸这将达到一些点,一些试验和错误可能会在模块渗透监测的媒体条件要求的限制。数学建模可以提供一些见解所需模块扪sions和流速22。
这里使用的设备的尺寸被设计为装配到培养箱货架。管道的长度由同时还允许部件的足够的运动,以允许设置和操作的连接器之间,以达到所需要的长度所决定的。如果需要的时间当然采样,例如在模块中的媒体状况监测渗透然后喷射口可以加入渗余物和渗透物线,以促进此。
一种用于任何细胞培养系统的先决条件是保持细胞存活并在大多数情况下生长。在研究证明体内样表型的更多,在3D培养系统中生长的细胞的光似乎也很重要,以提供密切模仿由细胞所遇到的体内环境的环境。最后这一点往往被忽视的2D细胞培养赞成这种文化系统提供了方便。 ŧ他通过纤维内腔递送营养物质到细胞HFB 体内毛细管网络模拟物。废物产品也从系统的动态流中去除。这产生用于细胞培养和一个密切模仿由肝细胞看到的在体内环境中的体内样系统,使得该系统更好的选择相比2D组织培养塑料用于培养这些细胞。这由以下事实证实了细胞分泌15倍相比,生长在二维组织培养塑料白蛋白的量,一个重要的肝功能,在HFB培养系统。
虽然HFB系统适合于大多数,如果不是全部贴壁依赖细胞类型,这里的例子为肝细胞,因为有一个真正的需要,以便能够培养官能,更体内样用于在药物开发使用肝细胞由制药工业并在体外支持生物人工肝设备的肝衰竭患者。需要更多的功能单元延伸超出这些例子中,特别是作为再生医学的领域进入的平移工作阶段。更在体内样的文化环境的优势不可小觑。
披露声明
MJE is a founder and director of Cellesce Ltd which aims to provide bioprocessing solutions for tissue engineering-based research and industry.
致谢
This work was funded by the National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research (NC3Rs) CRACK IT funding.
材料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Glass HFB Module | Soham Scientific | --- | Custom Item. (Section 2) |
| Sigmacote | Sigma-Aldrich | SL2 | (Section 2.1) |
| Silicoset 151 | Intertronics | ACCSS151 | Silicone Glue. (Section 2.3) |
| PTFE tape | Sigma-Aldrich | Z104388 | (Section 2.5) |
| Reservoir bottle | Fisher | 11972619 | PTFE the screw threads of the adapters and fitting nut. Attach to the Q-series cap. Attach an 8.5 cm section of the supplied PTFE tubing under the 1 mm adapter and a 4 cm section under the 3 mm adapter. (Section 3.2.1) |
| Q-series cap | Kinesis | 00932Q-3V | PTFE the screw threads of the adapters and fitting nut. Attach to the Q-series cap. Attach an 8.5 cm section of the supplied PTFE tubing under the 1 mm adapter and a 4 cm section under the 3 mm adapter. (Section 3.2.1) |
| Adapter, Male, 1.0 mm ID | Kinesis | 008NB10-KD5L | PTFE the screw threads of the adapters and fitting nut. Attach to the Q-series cap. Attach an 8.5 cm section of the supplied PTFE tubing under the 1 mm adapter and a 4 cm section under the 3 mm adapter. (Section 3.2.1) |
| Adapter, Male, 3.0 mm ID | Kinesis | 008NB30-KD5L | PTFE the screw threads of the adapters and fitting nut. Attach to the Q-series cap. Attach an 8.5 cm section of the supplied PTFE tubing under the 1 mm adapter and a 4 cm section under the 3 mm adapter. (Section 3.2.1) |
| Fitting Nut | Kinesis | U-350 | PTFE the screw threads of the adapters and fitting nut. Attach to the Q-series cap. Attach an 8.5 cm section of the supplied PTFE tubing under the 1 mm adapter and a 4 cm section under the 3 mm adapter. (Section 3.2.1) |
| Neoprene tubing | Fisher | 10366344 | Attach the Hepa filter to 6cm of neoprene tubing and attach this to the 'fitting nut'. Attach a 2x 30 mm sections of L/S14 tubing to the top two barbs of the Y-connector and a 3 cm section of L/S16 tubing to the bottom. Attach this to the barb of the 3 mm ID adapter. (Section 3.2.1) |
| HEPA-vent | Fisher | 11374634 | Attach the Hepa filter to 6cm of neoprene tubing and attach this to the 'fitting nut'. Attach a 2x 30 mm sections of L/S14 tubing to the top two barbs of the Y-connector and a 3 cm section of L/S16 tubing to the bottom. Attach this to the barb of the 3 mm ID adapter. (Section 3.2.1) |
| Y-connector, barbed | Cole Parmer | OU-06295-10 | Attach the Hepa filter to 6 cm of neoprene tubing and attach this to the 'fitting nut'. Attach a 2x 30 mm sections of L/S14 tubing to the top two barbs of the Y-connector and a 3 cm section of L/S16 tubing to the bottom. Attach this to the barb of the 3 mm ID adapter. (Section 3.2.1) |
| L/S16 Silicone tubing | Cole Parmer | OU-96410-16 | Attach the Hepa filter to 6cm of neoprene tubing and attach this to the 'fitting nut'. Attach a 2x 30 mm sections of L/S14 tubing to the top two barbs of the Y-connector and a 3 cm section of L/S16 tubing to the bottom. Attach this to the barb of the 3 mm ID adapter. (Section 3.2.1) |
| L/S14 Silicone tubing | Cole Parmer | WZ-96410-14 | Attach the Hepa filter to 6cm of neoprene tubing and attach this to the 'fitting nut'. Attach a 2x 30 mm sections of L/S14 tubing to the top two barbs of the Y-connector and a 3 cm section of L/S16 tubing to the bottom. Attach this to the barb of the 3 mm ID adapter. (Section 3.2.1) |
| L/S13 Silicone tubing | Cole Parmer | OU-96410-13 | 80 cm to connect the 1.0 mm barbed adapter on the Q-series cap to the pump tubing = Feed tube. (Section 3.2.1) |
| WM 205U/CA pump | Fisher | 1248-6300 | (Section 3.2.1) |
| WM pump tubing, PVC, blue-orange, 0.25 mm bore | Fisher | 12416310 | PTFE the screw thred of the male adapter and connect the female adapter. Work the pump tubing over one of the barbs. Repeat this set-up at the other end of the tubing. (Section 3.2.1) |
| Adapter, Male, 1.0 mm ID | Kinesis | 008NB10-KD5L | PTFE the screw thread of the male adapter and connect the female adapter. Work the pump tubing over one of the barbs. Repeat this set-up at the other end of the tubing. (Section 3.2.1) |
| Adapter, Female, 1.0 mm ID | Kinesis | 008NB10-KD2L | PTFE the screw thred of the male adapter and connect the female adapter. Work the pump tubing over one of the barbs. Repeat this set-up at the other end of the tubing. (Section 3.2.1) |
| Female Luer cap | Cole Parmer | WZ-45508-64 | Side port end caps. (Section 3.2.2) |
| L/S13 Silicone tubing | Cole Parmer | OU-96410-13 | 40 mm section to connect the pump tubing to a module connector. (Section 3.2.2) |
| L/S16 Silicone tubing | Cole Parmer | OU-96410-16 | 3x 30 mm of L/S16 fitted to 3x reducers = module connectors. (Section 3.2.2) |
| Barbed reducer 1/8"x1/16" | Cole Parmer | 30616-43 | 3x 30 mm of L/S16 fitted to 3x reducers = module connectors. (Section 3.2.2) |
| L/S13 Silicone tubing | Cole Parmer | OU-96410-13 | 55 cm section to connect the retentate to the L/S14 of the Y-connector on the Q-series cap. (Section 3.2.4) |
| L/S13 Silicone tubing | Cole Parmer | OU-96410-13 | 45 cm section to connect the permeate to the L/S14 of the Y-connector on the Q-series cap. (Section 3.2.4) |
| Straight barbed union | Cole Parmer | WZ-30612-43 | Attach to the end of the L/S13 that will connect with the L/S14 of the Y-connector. (Section 3.2.4) |
| Clamp | VWR | 229-0609 | (Section 3.4.2) |
| 4 mm Silicone tubing | Fisher | FB68858 | Fold over a 40 mm section of tubing and secure with a cable tie = Module end cap. (Section 4.3) |
| Cable tie | Fisher | 12326377 | Fold over a 40 mm section of tubing and secure with a cable tie = Module end cap. (Section 4.3) |
| MACSmix tube rotator | Miltenyi Biotech | 130-090-753 | An adaptation may be required to attach the modules. (Section 4.4) |
| Leur Injection port | Thistle Scientific | IB-10820 | Attach the end cap to the injection port. (Section 4.5) |
| Female Luer cap | Cole Parmer | WZ-45508-64 | Attach the end cap to the injection port. (Section 4.5) |
| L-lactic acid kit | Megazyme | K-LATE | (Section 5) |
| D-glucose kit | Megazyme | K-GLUC | (Section 5) |
| Scalpel / micro knife | InterFocus | 10315-12 | (Section 6.2) |
| Albumin ELISA | Bethyl Labs | E80-129 | (Section 7.4.3) |
参考文献
- Lewis, W. H. Experimental evidence in support of the theory of outgrowth of the axis cylinder. American J Anat. 6 (1), 461-471 (1906).
- Harrison, R. G. The development of peripheral nerve fibers in altered surroundings. Wilhelm Roux Arch Entwickl Mech Org. 30 (2), 15-33 (1910).
- Ding, L., et al. A genome-scale RNAi screen for Oct4 modulators defines a role of the Paf1 complex for Embryonic Stem Cell identity. Cell Stem Cell. 4 (5), 403-415 (2009).
- Groeber, F., Holeiter, M., Hampel, M., Hinderer, S., Schenke-Layland, K. Skin tissue engineering -In vivo and in vitro applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 63 (4), 352-366 (2011).
- Sinden, J. D., Vishnubhatla, I., Muir, K. W. Prospects for stem cell-derived therapy in stroke. Prog Brain Res. 201, 119-167 (2012).
- Ouyang, A., Yang, S. -. T. A two-stage perfusion fibrous bed bioreactor system for mass production of embryonic stem cells. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 8 (7), 895-909 (2008).
- Carnachan, R. J., Bokhari, M., Przyborski, S. A., Cameron, N. R. Taloring the morphology of emulsion-templated porous polymers. Soft Matter. 2 (7), 608-616 (2006).
- Deshpande, P., et al. Simplifying corneal surface regeneration using a biodegradable synthetic membrane and limbal tissue explants. Biomaterials. 34 (21), 5088-5106 (2013).
- Storm, M. P., Orchard, C. B., Bone, H. K., Chaudhuri, J. B., Welham, M. J. Three-dimensional culture systems for the expansion of pluripotent embryonic stem cells. Biotechnol Bioeng. 107 (4), 683-695 (2010).
- Wung, N., Acott, S. M., Tosh, D., Ellis, M. J. Hollow fibre membrane bioreactors for tissue engineering applications. Biotechnol Lett. 36 (12), 2357-2366 (2014).
- Ellis, M., Jarman-Smith, M., Chaudhuri, J. B., Chaudhuri, J., Al-Rubeai, Bioreactor systems for tissue engineering: A four-dimensional challenge. Bioreactors for tissue engineering; principles, design and operation. , 1-18 (2005).
- Silva, A. I., Mateus, M. Development of a polysulfone hollow fibre vascular bio-artificial pancreas device for in vitro studies. J Biotechnol. 139 (3), 236-249 (2009).
- De Bartolo, L., et al. Human hepatocyte functions in a crossed hollow fiber membrane bioreactor. Biomaterials. 30 (13), 2531-2543 (2009).
- Schmelzer, E., Finoli, A., Nettleship, I., Gerlach, J. C. Long-term three-dimensional perfusion culture of human adult bone marrow mononuclear cells in bioreactors. Biotechnol Bioeng. 112 (4), 801-810 (2015).
- Tapia, F., et al. Production of high-titer human influenza A virus with adherent and suspension MDKC cells cultured in a single-use hollow fiber bioreactor. Vaccine. 32 (8), 1003-1011 (2014).
- Deng, X., Zhang, G., Shen, C., Yin, J., Meng, Q. Hollow fiber culture accelerates differentiation of Caco-2 cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 97 (15), 6943-6955 (2013).
- Schutte, M., et al. Rat primary hepatocytes show enhanced performance and sensitivity to acetaminophen during three-dimensional culture on a polystyrene scaffold designed for routine use. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 9 (5), 475-486 (2011).
- Bokhari, M., Carnachan, R. J., Cameron, N. R., Przyborski, S. A. Novel cell culture device enabling three-dimensional cell growth and improved cell function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 354 (4), 1095-1100 (2007).
- Bokhari, M., Carnachan, R. J., Cameron, N. R., Przyborski, S. A. Culture of HepG2 liver cells on three dimensional polystyrene scaffolds enhances cell structure and function during toxicological challenge. J Anat. 211 (4), 567-576 (2007).
- Vivares, A., et al. Morphological behaviour and metabolic capacity of cryopreserved human primary hepatocytes cultivated in a perfused multiwell device. Xenobiotica. 45 (1), 29-44 (2015).
- Smith, I., et al. Human neural stem cell-derived cultures in three-dimensional substrates form spontaneously functional neuronal networks. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. , (2015).
- Davidson, A. J., Ellis, M. J., Chaudhuri, J. B. A theoretical approach to Zonation in a bioartificial liver. Biotechnol Bioeng. 109 (1), 234-243 (2012).
- Mulder, M. . The basic principles of membrane technology. 2nd ed. , (1996).
- Ellis, M. J., Chaudhuri, J. B. Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) hollow fibre membranes for use as a tissue engineering scaffold. Biotechnol Bioeng. 96 (1), 177-187 (2007).
- Shearer, H., Ellis, M. J., Perera, S. P., Chaudhuri, J. B. Effects of common sterilization methods on the structure and properties of poly(D,L lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffolds. Tissue Eng. 12 (10), 2717-2727 (2006).
- Forsey, R. W., Chaudhuri, J. B. Validity of DNA analysis to determine cell numbers in tissue engineering scaffolds. Biotechnol Lett. 31 (6), 819-823 (2009).
- Williamson, M. R., Coombes, A. G. A. Gravity spinning of polycaprolactone fibres for applications in tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 25 (3), 459-465 (2004).
- El-Salmawy, A., et al. Preparation and properties of pronectin F-coated biodegradable hollow fibres. J Artif Organs. 8 (4), 245-251 (2005).
- Meneghello, G., et al. Fabrication and characterization of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/polyvinyl alcohol blended hollow fibre membranes for tissue engineering applications. J Memb Sci. 344 (1-2), 55-61 (2009).
转载和许可
请求许可使用此 JoVE 文章的文本或图形
请求许可探索更多文章
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。