A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Ultrastructural Expansion Microscopy in Three In Vitro Life Cycle Stages of Trypanosoma cruzi
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
This study shows a detailed protocol to perform ultrastructure expansion microscopy in three in vitro life cycle stages of Trypanosoma cruzi, the pathogen responsible for Chagas disease. We include the optimized technique for cytoskeletal proteins and pan-proteome labeling.
Abstract
We describe here the application of ultrastructure expansion microscopy (U-ExM) in Trypanosoma cruzi, a technique that allows increasing the spatial resolution of a cell or tissue for microscopic imaging. This is performed by physically expanding a sample with off-the-shelf chemicals and common lab equipment.
Chagas disease is a widespread and pressing public health concern caused by T. cruzi. The disease is prevalent in Latin America and has become a significant problem in non-endemic regions due to increased migration. The transmission of T. cruzi occurs through hematophagous insect vectors belonging to the Reduviidae and Hemiptera families. Following infection, T. cruzi amastigotes multiply within the mammalian host and differentiate into trypomastigotes, the non-replicative bloodstream form. In the insect vector, trypomastigotes transform into epimastigotes and proliferate through binary fission.The differentiation between the life cycle stages requires an extensive rearrangement of the cytoskeleton and can be recreated in the lab completely using different cell culture techniques.
We describe here a detailed protocol for the application of U-ExM in three in vitro life cycle stages of Trypanosoma cruzi, focusing on optimization of the immunolocalization of cytoskeletal proteins. We also optimized the use of N-Hydroxysuccinimide ester (NHS), a pan-proteome label that has enabled us to mark different parasite structures.
Introduction
Expansion microscopy (ExM) was described for the first time in 2015 by Boyden et al.1. It is an imaging protocol with which a conventional microscope can achieve a spatial resolution below the diffraction limit. This higher resolution is obtained because of a physical enlargement of the sample. To accomplish this, fluorescently labeled molecules are crosslinked to a hydrogel, which is subsequently expanded isotropically with water. As a result of this expansion, the signals are separated nearly isotropically in all three dimensions. This method employs low-cost chemicals and enables a spatial resolution of approximately 65 nm using conventional....
Protocol
NOTE: Figure 1 illustrates the complete experimental design.
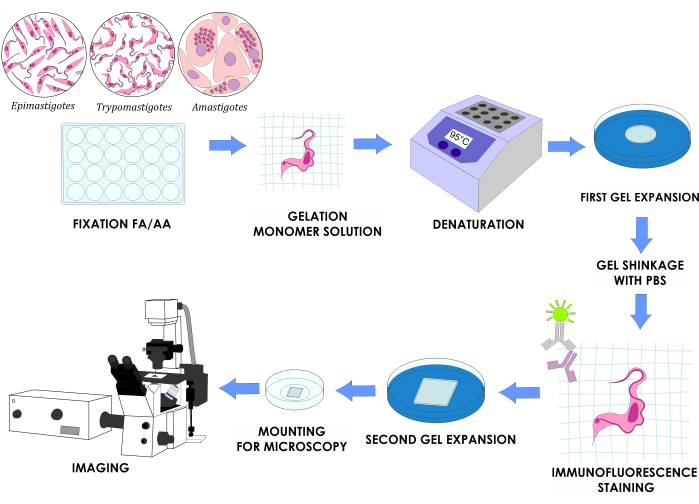
Figure 1: U-ExM workflow for three in vitro life cycle stages of T. cruzi. Please click here to view a larger version o.......
Representative Results
If the protocol has been properly executed (Figure 1), samples will be visible as a planar and translucent gel that can be expanded up to a factor of 4-4.5x in water (Figure 3A). This expansion provided an effective resolution of about 70 nm, which may vary depending on the final expansion factor and imaging system employed. After the second expansion process and image acquisition in a confocal microscope, we were able to observe expansion factors of around 4.5........
Discussion
Ultrastructural expansion microscopy is a technique that allows obtaining high-resolution images of biological samples by physically expanding them to several times their original size. The U-ExM protocol involves several critical steps that must be carefully executed to achieve optimal results4. First, the sample must be fixed with a CP agent and embedded in a swellable hydrogel matrix. The formaldehyde present in the CP solution interacts with the free covalent bonds of the acrylamide to prevent.......
Acknowledgements
We thank Dolores Campos for assisting with Vero cell culture and Romina Manarin for assisting with T. cruzi culture. This work was supported by Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica, Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación Productiva from Argentina (PICT2019-0526), Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (PIBAA 1242), and Research Council United Kingdom [MR/P027989/1].
....Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 0.22 micrometers sterile syringe filters PES | Membrane solutions | SFPES030022S | |
| 1 L beaker | Schott Duran | 10005227 | |
| 1.5-mL SPINWIN Micro Centrifuge Tube | Tarson | T38-500010 | |
| 10 mL disposable sterile serynge | NP | 66-32 | |
| 10 mL serological pipette sterile | Jet Biofil | GSP211010 | |
| 12-mm coverslips | Merienfeld GmbH | 01 115 20 | Round coverslips |
| 12-well plates | Jet Biofil | TCP011012 | |
| 22-mm coverslips | Corning | 2845-22 | Square coverslips |
| 24-well plates | Jet Biofil | TCP-011-024 | |
| 250 mL beaker | Schott Duran | C108.1 | |
| 3 mL Pasteur pipette | Deltalab | 200037 | |
| 35-mm glass bottom dishes | Matsunami glass ind | D11130H | |
| 4′,6-Diamidine-2′-phenylindole dihydrochloride | Sigma Aldrich | D9542 | DAPI |
| 5 ml serological pipette sterile | Jet Biofil | GSP010005 | |
| 6-well plates | Sarstedt | 83.3920 | |
| Acrilamide | BioRad | 1610101 | |
| Ammonium persulfate | Sigma Aldrich | A3678-25G | APS |
| ATTO 647 NHS ester | BOC Sciences | F10-0107 | For pan-proteome labelling |
| Biosafty Cabinet | Telstar | Bio II A/P | |
| Bovine Sodium Albumine | Sigma Aldrich | A7906 | BSA |
| CO2 Incubator | Sanyo | MCO-15A | |
| Confocal Microscope | Zeiss | LSM 880 | |
| Disposable Petridish | Tarsons | 460095 | 90 mm diameter |
| DMEM, High Glucose | Thermo Fisher Cientific | 12100046 | Powder |
| Electronic digital caliper | Radar | RADAR-SLIDE-CALIPER | |
| Ethanol Absolute | Supelco | 1,00,98,31,000 | |
| Fetal Calf Serum | Internegocios SA | FCS FRA 500 | Sterile and heat-inactivated |
| Fiji image processing package | ImageJ | doi:10.1038/nmeth.2019 | |
| Formaldehyde 37% | Sigma Aldrich | F8775 | FA |
| Glass Petridish | Marienfeld Superior | PM-3400300 | 60 mm diameter |
| Glucosa D(+) | Cicarelli | 716214 | |
| Glutaraldehyde 70% | Sigma Aldrich | G7776 | |
| Goat anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody Alexa Fluor 555 | Invitrogen | A-21422 | |
| Goat anti-Rabbit IgG Secondary Antibody FICT | Jackson Immunoresearch | 115-095-003 | |
| Graduated cylinder | Nalgene | 3663-1000 | |
| Graduated glass flask | Glassco | GL-274.202.01 | 100 mL |
| Heating Block | IBR | Made in house | |
| Hemin | Frontier Scientific | H651-9 | |
| Hydrochloric acid 36.8-38.0% | Ciccarelli | 918110 | |
| Ice bucket | Corning | 1167U68 | |
| Incubator | Tecno Dalvo | TOC130 | |
| Liver Infusion | Difco | 226920 | |
| Magnetic stirrer and heater | Lab companion | HP-3000 | |
| Metal spatula | SALTTECH | 200MM | |
| Metal tweezers | Marienfeld Superior | PM-6633002 | |
| Methanol absolut | Cicarelli | 897110 | |
| Microcentrifuge tube 1.5 mL | Tarson | 500010-N | |
| Microscopy grade paper KimWipes | Kimtech Science | B0013HT2QW | |
| Milli-Q water sistem | Merk Millipore | IQ-7003 | |
| mouse anti- alpha tubulin clone DM1A | Sigma Aldrich | T9026 | |
| mouse anti-PFR | Purified antibodies | Donated by Dr. Ariel Silber (USP) | |
| N,N´-methylenbisacrilamide | ICN | 193997 | BIS |
| Na2HPO4 | Cicarelli | 834214 | |
| Neubauer chamber | Boeco | BOE 01 | |
| p1000 pipette | Gilson | PIPETMAN P1000 | |
| p1000 pipette tips | Tarson | TAR-521020B | |
| p20 pipette | Gilson | PIPETMAN P20 | |
| p20 pipette tips | Tarson | TAR-527108 | |
| p200 pipette | Gilson | PIPETMAN P200 | |
| p200 pipette tips | Tarson | TAR-521010Y | |
| Paraformaldehyde | Sigma Aldrich | P6148 | PFA |
| pH / ORP / °C meter | HANNA Instruments | HI 2211 | |
| Poly-D-Lysine 0.1% | Sigma Aldrich | P8920 | |
| Potassium Chloride | Cicarelli | 867212 | KCl |
| Razor blade | Printex | BS 2982:1992 | |
| Sealing FIlm "Parafilm M" | Bemis | PM996 | |
| Sodium Acrilate | Sigma Aldrich | 408220-25G | SA |
| Sodium Bicarbonate | Cicarelli | 929211 | NaHCO3 |
| Sodium Chloride | Cicarelli | 750214 | NaCl |
| Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate | BioRad | 1610302 | SDS |
| Sodium Hidroxide | Merk | 1-06498 | NaOH |
| Sorvall ST 16 Centrifuge | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 75004380 | |
| T-25 flasks | Corning | 430639 | |
| TEMED | Invitrogen | 15524-010 | |
| Tissue paper | Elite | ||
| Triptose | Merck | 1106760500 | |
| Tris | BioRad | 1610719 | |
| Tween-20 | Biopack | 2003-07 | Polysorbate 20 |
| Vaccum pump | Silfab | N33-A | |
| Vero cells | ATCC | CRL-1587 | |
| Vortex MIxer | Dragon Lab | MX-S |
References
- Chen, F., Tillberg, P. W., Boyden, E. S. Expansion microscopy. Science. 347 (6221), 543-548 (2015).
- Chozinski, T. J., et al. Expansion microscopy with conventional antibodies and fluorescent proteins. Nature Methods. ....
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
ABOUT JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved