3.4 : Velocidad instantánea - II
Instantaneous velocity is the quantity that measures how fast an object is moving along its path. In other words, the instantaneous velocity of an object is the limit of the average velocity as the elapsed time approaches zero, or the derivative of displacement with respect to time. Like average velocity, the instantaneous velocity is a vector with the dimensions of length per unit time. Instantaneous velocity can have both positive and negative values. The instantaneous velocity can be calculated from the position-time graph. The instantaneous velocity at a specific time point is the rate of change of the position function, which is the slope of the position function at that point. The slope of the tangent at any point on the position-time graph equals the velocity at that point. A zero slope indicates that the instantaneous velocity is zero. A positive slope indicates positive instantaneous velocity, while a negative slope indicates a negative instantaneous velocity. The steeper the slope (positive or negative), the greater the particle’s speed in the positive or negative direction.
Consider the motion of a particle in which the position is given by

What is the instantaneous velocity at t = 0.25 s?
The known quantities are the expression for the position as a function of time. To determine the instantaneous velocity, first, consider the equation
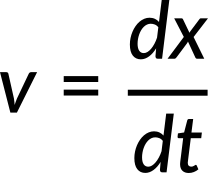
Using the expression of x(t), the expression for velocity is

Substituting the value for time, in the above equation, the instantaneous velocity at 0.25 s is 1.5 m/s.
This text is adapted from Openstax, University Physics Volume 1, Section 3.2: Instantaneous Velocity and Speed.
Del capítulo 3:

Now Playing
3.4 : Velocidad instantánea - II
Movimiento rectilíneo
9.1K Vistas

3.1 : Posición y desplazamiento
Movimiento rectilíneo
17.4K Vistas

3.2 : Velocidad media
Movimiento rectilíneo
18.1K Vistas

3.3 : Velocidad instantánea - I
Movimiento rectilíneo
12.3K Vistas

3.5 : Aceleración media
Movimiento rectilíneo
9.4K Vistas

3.6 : Aceleración instantánea
Movimiento rectilíneo
7.6K Vistas

3.7 : Ecuaciones de cinemática - I
Movimiento rectilíneo
10.3K Vistas

3.8 : Ecuaciones de cinemática - II
Movimiento rectilíneo
9.3K Vistas

3.9 : Ecuaciones de cinemática - III
Movimiento rectilíneo
7.5K Vistas

3.10 : Ecuaciones de cinemática: resolución de problemas
Movimiento rectilíneo
11.9K Vistas

3.11 : Cuerpos en caída libre: introducción
Movimiento rectilíneo
8.1K Vistas

3.12 : Cuerpos en caída libre: ejemplo
Movimiento rectilíneo
15.8K Vistas

3.13 : Velocidad y posición mediante el método gráfico
Movimiento rectilíneo
7.3K Vistas

3.14 : Velocidad y posición mediante el método de integración
Movimiento rectilíneo
5.9K Vistas
ACERCA DE JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos los derechos reservados