Se requiere una suscripción a JoVE para ver este contenido. Inicie sesión o comience su prueba gratuita.
Amplified Luminescent Proximity Homogeneous Assay: A Bead-Based Proximity Assay to Screen Small Molecules Inhibiting Protein-Protein Interactions
En este artículo
Overview
In this video, we demonstrate the amplified luminescent proximity homogeneous assay—a bead-based proximity assay. It utilizes homogeneously-sized acceptor and donor beads, immobilized with two proteins that tend to interact to screen potential small molecules inhibiting protein interactions.
Protocolo
NOTE: An overview of this protocol is shown in Figure 1.
1. Expression and purification of GST-FKBP51 and GST-FKBP52 (Figure 1A)
- Plasmids
NOTE: Obtain cDNA clones for human FKBP51 (clone id: 5723416) and for human FKBP52 (clone id: 7474554) from IMAGE consortium.- Amplify the human FKBP51 DNA by PCR with primers (forward; 5`GGATCCATGACTACTGATGAAGGT-3`, reverse; 5`-CTCGAGCTATGCTTCTGTCTCCAC-3`) containing BamHI and XhoI overhangs and clone into pGEX6-1 vector at BamHI / XhoI restriction sites.
- Amplify the human FKBP52 DNA by PCR with primers (forward; 5`-GAATTCATGACAGCCGAGGAGATG-3`, reverse; 5`-CTCGAGCTATGCTTCTGTCTCCAC-3`) containing EcoRI and XhoI overhangs and clone into pGEX6-2 vector at EcoRI / XhoI restriction sites.
NOTE: PCR reaction set up and conditions are shown in Table 1 and Table 2. - Verify the inserted sequence and transform the plasmids into the chemically competent E. coli according to the manufacture protocol.
- Protein expression and purification
- Add 25 g of Luria broth (LB) base in 1 L of distilled water to make the LB solution. Autoclave it at 121 °C for 15 min. After cooling, add 50 µg/mL ampicillin.
- Take a colony of bacteria expressing GST-FKBP51 or GST-FKBP52 and mix with 500 µL of LB solution in a 1.5 mL tube. Vortex.
- Add the mixture of "1.2.2" into 1 L of LB solution in the Erlenmeyer flask covered with an aluminum foil. Incubate the Erlenmeyer flask in the shaker overnight at 37 °C.
- Induce protein expression by adding 1 mM isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG) to the Erlenmeyer flask and continue the incubation for a further 2 h.
- To get cell pellets, centrifuge at 5,000 x g for 15 min. Remove the supernatant.
NOTE: The cell pellets can be stored at -20 °C. - Resuspend the cell pellets in 40 mL of PBS and sonicate 3 x 20 s on ice. Add 1 mM PMSF, 1 mM EDTA, and protease inhibitor cocktail (1 tablet) to prevent proteolysis.
- Centrifuge the suspension for 30 min 50,000 x g to remove cell debris and apply the supernatant onto 5 mL GST-trap column.
- After washing the column with 30 mL PBS, elute GST-FKBP51 and GST-FKBP52 with 5 mL of 10 mM glutathione in PBS.
- Concentrate proteins on 15 mL 10.000 MWCO centrifugation unit. To remove free glutathione, pass concentrates through PD-10 column equilibrated with 0.5x PBS and again concentrate on the filter centrifuge device.
- Collect protein-containing fractions. Verify the proteins in SDS-PAGE and adjust protein concentrations to 1 mg/mL.
NOTE: Typical protein yield is 2-5 mg/L culture. The protein can be stored at -20 °C.
2. Coupling of Hsp90 C-terminal peptide to the acceptor beads (Figure 1B)
- Hsp90 peptide preparation
- Synthesize ten amino acid peptide NH2-EDASRMEEVD-COOH corresponding to amino acids 714-724 of human Hsp90 beta isoform (UniProt ID: P08238) by a peptide synthesis service.
- Dilute the Hsp90 peptide in PBS to 1 mg/mL concentration.
- Acceptor beads preparation
- Dilute the unconjugated acceptor beads in PBS to 1 mg/mL concentration and transfer to a 1.5 mL tube.
- Perform the washing by centrifugation at 16,000 x g for 15 min. Carefully remove the supernatant.
- Conjugation
- Set the ratio between beads and peptide as 10:1. In the 1.5 mL tube containing 1 mg of acceptor bead pellet (prepared as described above), add 1 mL of PBS (pH 7.4), 0.1 mg of diluted peptide, 1.25 µL of Tween-20, 10 µL of a 400 mM solution of sodium cyanoborohydride (NaBH3CN) in water.
CAUTION: NaBH3CN is toxic; use a fume hood and gloves. NaBH3CN solution should be freshly prepared. - Incubate for 24 h at 37 °C with end-over-end agitation (10-20 rpm) on a rotary shaker.
- Set the ratio between beads and peptide as 10:1. In the 1.5 mL tube containing 1 mg of acceptor bead pellet (prepared as described above), add 1 mL of PBS (pH 7.4), 0.1 mg of diluted peptide, 1.25 µL of Tween-20, 10 µL of a 400 mM solution of sodium cyanoborohydride (NaBH3CN) in water.
- Reaction quenching and beads washing
- Add 20 µL of 1 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) solution to the reaction to block unreacted sites. Incubate for 1 h at 37 °C.
- Centrifuge at 16,000 x g (or maximum speed) for 15 min at 4 °C. Remove the supernatant and resuspend the bead pellet in 1 mL of Tris-HCl solution (100 mM, pH 8.0).
- Repeat the washing step three times.
- After the last centrifugation, resuspend the beads at 1 mg/mL in storage buffer (1 mL of 0.5 × PBS with 0.01% sodium azide as a preservative). Store the conjugated acceptor bead solution at 4 °C light protected.
CAUTION: Sodium azide is toxic; use a fume hood and gloves.
3. The assay probing the interaction between GST-FKBP51 or GST-FKBP52 and Hsp90 C-terminal peptide, and inhibition with small molecular mass compounds (Figure 1C)
- GST-tagged proteins interacting with glutathione donor beads
- Set up the reactions in 384-well plates.
- Prepare the solution containing 10 µg/mL of the glutathione donor beads in 0.5x PBS, pH 7.4.
NOTE: After prolonged storage, beads settle down and need to be vortexed. - Add GST-FKBP51 or GST-FKBP52 to a final concentration of 10 µg/mL.
- Incubate in the dark at 25 °C for 10 min.
NOTE: At this step, GST-tagged proteins will interact with glutathione attached to the beads. For each well, 22.5 µL of this mixture will be used. The concentration of the binding partners must be determined empirically. Titrate GST-FKBP51 and GST-FKBP52 and choose the concentration that gives the best signal.
- Compound addition
- Make serial dilutions of test compounds in DMSO.
NOTE: The concentrations used are typically 10, 30, 100, 300, 1,000, and 3,000 µM. - Add 0.25 µL of DMSO (negative control) or Hsp90 C-terminal peptide (positive control, 30 µM) or compounds in DMSO to the corner of each well of the plate. Use triplicates for every compound concentration.
- Add 22.5 µL of the solution containing glutathione donor beads with GST-tagged proteins to each well.
- Shake the plate gently with hand but thoroughly. Incubate in the dark at 25 °C for 15 min.
NOTE: During this time, compounds will interact with the TPR domain at the Hsp90 C-terminal peptide binding site.
- Make serial dilutions of test compounds in DMSO.
- Acceptor beads addition
- Dilute the acceptor beads with attached Hsp90 C-terminal peptide to 100 µg/mL in 0.5x PBS.
- Add 2.25 µL of diluted acceptor beads to each well.
- Mix gently but thoroughly. Incubate in the dark at 25 °C for 15 min.
NOTE: At this step, donor and acceptor beads are brought into proximity by the protein-peptide interactions. The final volume of the reaction mixture is 25 µL. Therefore, the final concentrations of compounds are ranging from 0.1 to 30 µM.
- Plate reading
NOTE: Read the plate using a plate reader set in the relevant mode.- Turn on the instrument and open the software
- Choose the relevant protocol.
- Click Edit plate map and select the well being used in the plate for measurement.
- Click Next to continue and Run the selected protocol.
- After measurement, click Show Results to view results.
- Export the data.
Table 1: PCR reaction set up for human FKBP51 and FKBP52 DNA amplification.
| Reaction component | Volume (µL) |
| PCR buffer (5 x concentrate) | 4 |
| Forward primer | 1 |
| Reverse primer | 1 |
| Plasmid | 0.5 |
| dNTP mix (10 mM each) | 0.5 |
| Phusion DNA polymerase | 0.5 |
| Water (DNA grade) | 12.5 |
| Total | 20 |
Table 2: Thermocyler conditions for human FKBP51 and FKBP52 DNA amplification.
| Stage | Temperature (°C) | Time | Cycles |
| Initial denaturation | 94 | 3 min | 1 |
| Denaturation | 94 | 30 sec | 35 |
| Annealing | 56 | 30 sec | |
| Extension | 72 | 1 min | |
| Final extension | 72 | 5 min | 1 |
| Note: Lid temperature is 105 °C. | |||
Resultados
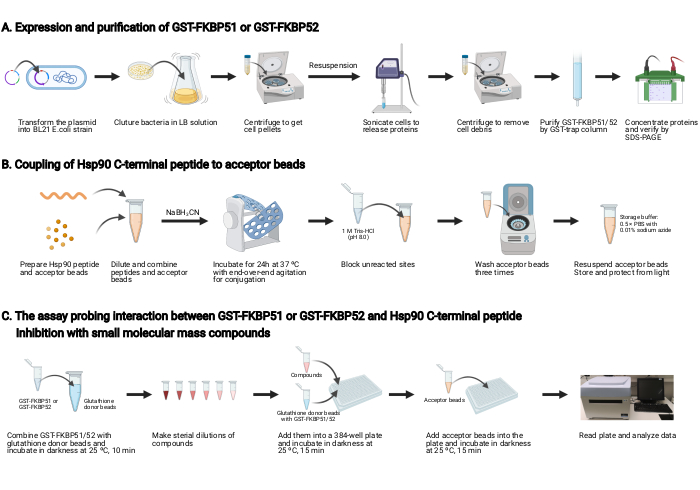
Figure 1: Schematic of this protocol. (A) Expression and purification of GST-FKBP51 and GST-FKBP52. (B) Coupling of Hsp90 C-terminal peptide to the acceptor beads. (C) The assay probing the interaction between GST-FKBP51 or GST-FKBP52 and Hsp90 C-terminal peptide. Inhibition with small molecular mass compounds.
Divulgaciones
Materiales
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 384-well plates | Perkin Elmer | 6008350 | Assay volume 25 ml |
| Amicon 10.000 MWCO centrifugation unit | Millipore | UFC901008 | Concentrate protein |
| Ampicillin | Sigma | A0166 | Antibiotics |
| Bacteria shaker Unimax 1010 | Heidolph | Culture bacteria | |
| cDNA clones for human FKBP51 | Source BioScience | clone id: 5723416 | pCMV-SPORT6 vector |
| cDNA clones for human FKBP52 | Source BioScience | clone id: 7474554 | pCMV-SPORT6 vector |
| Chemically Competent E. coli | Invitrogen | C602003 | One Shot BL21 Star (DE3) |
| DMSO | Supelco | 1.02952.1000 | Dilute compounds |
| DPBS | Gibco | 14190-144 | Prepare solution |
| EDTA | Calbiochem | 344504 | Prevent proteolysis during sonication |
| Glutathione | Sigma | G-4251 | Elute GST-tagged proteins |
| Glutathione donor beads | Perkin Elmer | 6765300 | Donor bead |
| GST-trap column | Cytiva (GE Healthcare) | 17528201 | Purify GST-tagged proteins |
| Isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside | Thermo Fisher Scientific | R0392 | Induce protein expression |
| LB Broth (Miller) | Sigma | L3522 | Microbial growth medium |
| PCR instrument | BIO-RAD | S1000 Thermal Cycler | Amplification/PCR |
| PD-10 column | Cytiva (GE Healthcare) | 17085101 | Solution exchange |
| pGEX-6P-1 vector | Cytiva (GE Healthcare) | 28954648 | Plasmid |
| pGEX-6P-2 vector | Cytiva (GE Healthcare) | 28954650 | Plasmid |
| Plate reader | Perkin Elmer | EnSpire 2300 Multilabel Reader | Read alpha plate |
| Plate reader software | Perkin Elmer | EnSpire Manager | Plate reader software |
| Plate reader software protocol | Perkin Elmer | Alpha 384-well Low volume | Use this protocol to read plate |
| PMSF | Sigma | P7626 | Prevent proteolysis during sonication |
| protease inhibitor cocktail | Sigma | S8830 | Prevent proteolysis during sonication |
| Sodium azide | Sigma | S2002 | As a preservative |
| Sodium cyanoborohydride (NaBH3CN) | Sigma | 156159 | Activates matrix for coupling |
| Ten amino acid peptide NH2-EDASRMEEVD-COOH corresponding to amino acids 714-724 of human Hsp90 beta isoform | Peptide 2.0 inc | Synthesize Hsp90 C-terminal peptide | |
| Test-Tube Rotator | LABINCO | Make end-over-end agitation | |
| Tris-HCl | Sigma | 10708976001 | Block unreacted sites of acceptor beads |
| Tween-20 | Sigma | P1379 | Prevent beads aggregation |
| Ultra centrifuge Avanti J-20 XP | Beckman Coulter | Centrifuge to get bacteria cell pellets | |
| Ultrasonic cell disruptor | Microson | Sonicate cells to release protein | |
| Unconjugated acceptor beads | Perkin Elmer | 6762003 | Acceptor beads |
| XCell SureLock Mini-Cell and XCell II Blot Module | Invitrogen | EI0002 | SDS-PAGE |
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Source: Wang, L. et al., Studies of Chaperone-Cochaperone Interactions using Homogenous Bead-Based Assay. J. Vis. Exp. (2021)
ACERCA DE JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos los derechos reservados