Passaging, or subculturing, of cells, is a common procedure wherein cells from a given culture are divided, or “split”, into new cultures and fed with fresh media to facilitate further expansion. While the concept itself is relatively simple, in this video we will discuss some of the more important steps for the successful maintenance and expansion of cell lines.
Toxic metabolites accumulate in cell culture media over time. When expanding cells, it is particularly important to change the media regularly to maintain cell health and to monitor the cell expansion to avoid cell overgrowth.
Generally, two main types of cells are subcultured: immortalized cell lines and stem cell lines
Immortalized cell lines are cells that are derived from multicellular organisms that have experienced some type of mutation affecting their cell cycle regulation, allowing them to proliferate indefinitely. Perhaps the most famous immortalized cell line is the HeLa cell line, which was derived from a cervical cancer lesion found on a biopsy taken from Ms. Henrietta Lacks in 1951.
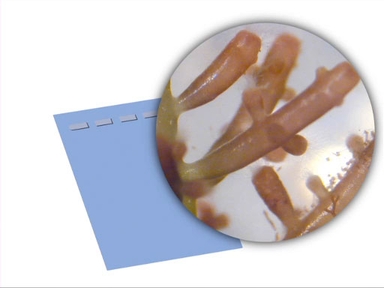
In contrast to cell lines immortalized by cancer, stem cell lines are generated by isolating self-renewing and multipotent cells from a variety of tissues both from adult and embryonic tissues. Under the right conditions these cells, like the human embryonic stem cells you see here, can be maintained in culture indefinitely.
Cells are either optimally cultured in suspension, like immortalized cells isolated from blood, or they grow best when adhered to a surface, as is the case for many tissue-derived cells.
The growth of these adherent cells must be closely monitored to ensure cell health. Depending on the cell type, most adherent cells need to be passaged when they are 70-90% confluent, that is, when they cover 70-90% of the culture container surface.
Bear in mind that cell lines retain many characteristics of the original cell culture, but with each successive passage they can also begin to acquire characteristics unique to the expanded culture. Therefore, consider limiting the number of times you continue to passage an individual cell culture.
When passaging cells, it is important to use sterile technique and the appropriate reagents and equipment.
It is essential to use the appropriate media for the optimal growth and expansion of your cell line. Each cell line will require a specific growth supplement cocktail, however, most cell lines at minimum require supplementation with the following: Serum, such as Fetal Bovine Serum, which must be heat-treated to inactivate the bovine complement and which provides vital growth factors for the cells, antibiotics, like penicillin and streptomycin, which help limit contaminating growth in the culture, and other growth factors, like fibroblast growth factor, to help prolong the growth and expansion of the cell lines. Store the supplemented, or “complete”, cell culture media at 4 C when you’re not using it.
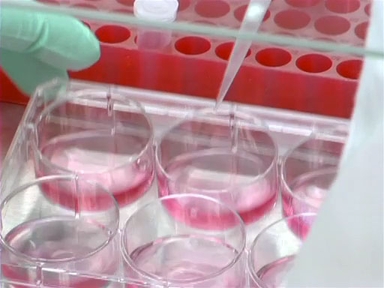
First, take note of the color of the tissue culture media. Fresh, cell culture media is rich in nutrients and appears a clear, orange color, partly due to the addition of the pH indicator, phenol red.
As cells begin to use up nutrients in the media, waste and acid begin to build up in the cell culture, lowering the pH. For this reason, many tissue culture medias contain phenol red, which turns the media from orange to yellow when cells turn the culture acidic. Change the media before it turns this color!
When the phenol red turns the media a pinkish color, indicating that the pH has become too basic for healthy cell growth, it may be time to change your CO2 tank as well as your media.
Most adherent cell lines attach naturally to uncoated plastic. Therefore plastic cell culture plates, like petri dishes or 6 well plates, are frequently used for subculturing cells.
Plastic cell culture flasks are also used. The T25 cell culture flask, for example, is often used to expand small cell line populations or to start the growth of a slowly expanding cell line. T75 culture flasks are commonly used for cell lines that proliferate more quickly or to generate larger numbers of cells than can fit in a T25 flask.
When removing adherent cells, the proteins that bind the cells to the plastic must first be cleaved. For this purpose, the digestive enzyme trypsin is frequently used. It is important to carefully time the trypsin exposure, as treatment for too long can result in damage to other cell surface proteins.
Cell culture media can contain trypsin neutralizers. Therefore, phosphate buffered saline, or PBS, is often used to wash the cells before trypsinization.
EDTA, a calcium chelator, is sometimes also used to enhance the proteolytic function of trypsin.
For expansion of the cell colony, the freshly-passaged cells are then grown in a cell culture incubator under the conditions appropriate to that cell line, typically at about 37 C, 5% CO2, and 95% humidity.
Before you begin, it is important to understand how frequently your cells should be monitored, which will depend on how fast your cells proliferate.
Now that your media is a happy orange color, observe the other culture conditions, such as whether or not the culture is cloudy – possibly indicating contamination -- the size and density of the cell colonies, and the overall quality of the cells.
If the cells have reached about 90% confluency, remove the tissue culture media and wash the cells with calcium- and magnesium-free PBS.
Now add trypsin to the cells and then incubate them at 37 C. After about 5 minutes, confirm that the cells have detached, and then stop the proteolysis by adding fresh tissue culture media.
Transfer the cell suspension into a conical tube for centrifugation. Then, after spinning down the cells, carefully remove the supernatant without disturbing the pellet and resuspend the cells in fresh media. Count how many cells you’ve collected and then seed the cells according to the density appropriate for immediate or later expansion.
Now that you know how to passage cells, let’s look at some different applications of the method.
As mentioned earlier, human embryonic stem cells are a type of cell that must be passaged. They are typically cocultured with mouse embryonic fibroblasts, or MEFs, which provide factors that help stem cells retain their pluripotent state.
Stem cell colonies grown on feeder cells need to be “picked” once they’ve reached the proper stage of development. They can be selected by micropipette or by gentle scraping with a glass picking tool and then plated in a new culture for expansion.
Some cell lines are sensitive to enzymatic digest or they are so tightly adherent they can’t be resuspended with trypsin treatment alone. A cell scraper can be used to gently remove the cells from the bottom of the culture plate. If the cells are particularly adherent, try moving a serological pipette in a firm scraping motion while rinsing the bottom of the cell container with media or another appropriate solution. Take care with this method, as delicate cells can be damaged by this mechanical method of dissociation.
To more quickly and reproducibly scale up the expansion of your cells than can be achieved in single layer flasks, multilayer flasks, which can expand cell cultures 3-5 fold compared to single layer flasks, can be used.
You’ve just watched JoVE’s introduction to passaging cells. In this video we reviewed what a cell line is, how to subculture one, and some different applications of passaging cells. Thanks for watching and remember to keep your media fresh!