29.4 : Magnetic Field Due To A Thin Straight Wire
Consider an infinitely long straight wire carrying a current I. The magnetic field at point P at a distance a from the origin can be calculated using the Biot-Savart law.
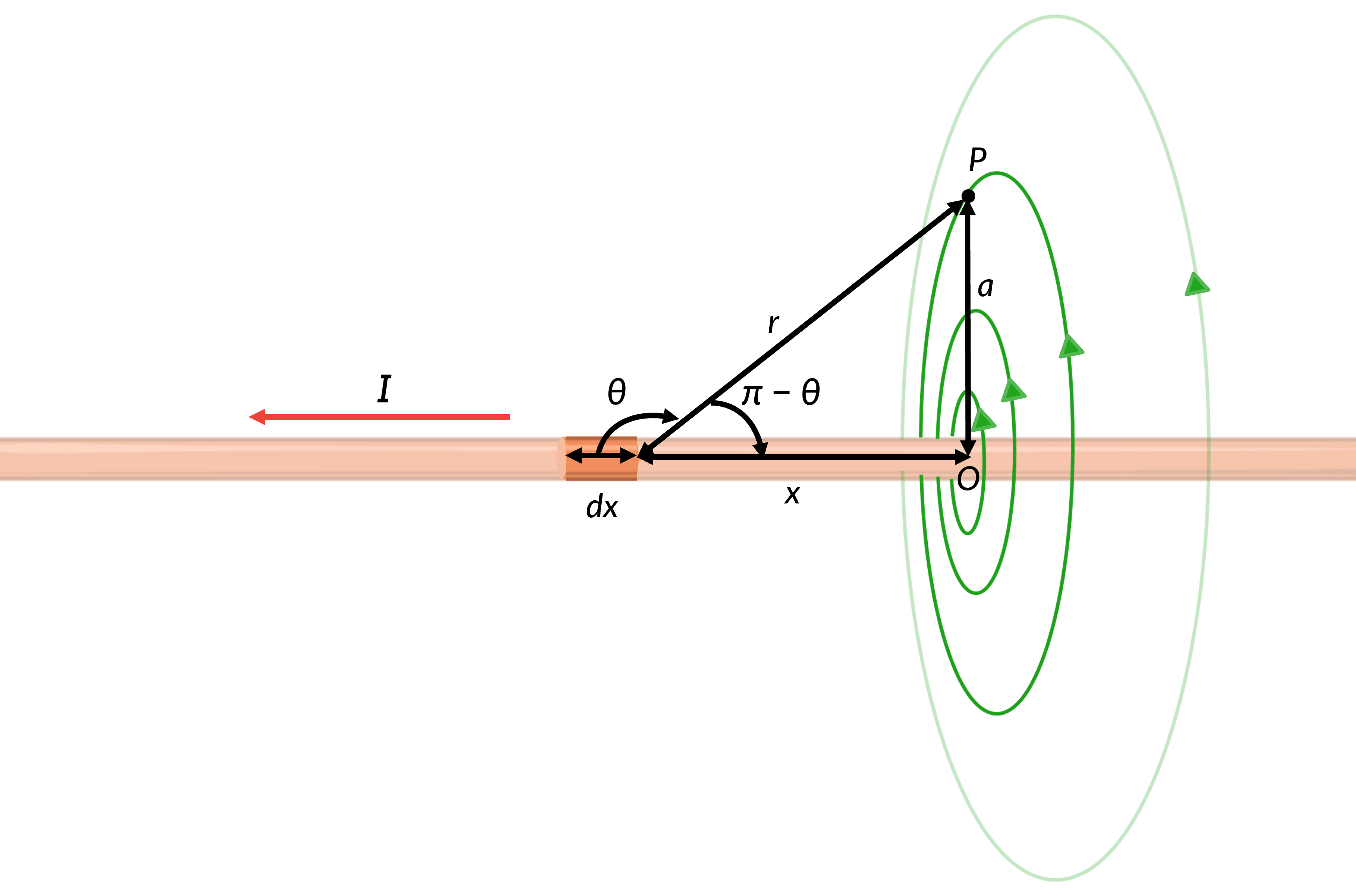
Consider a current element dx at a distance x from the origin. The current element makes an angle ÃÂø with the line joining dx and P. Using the Pythagorus theorum to express the distance between the current element and the point, the magnetic field due to the current element at point P can be estimated using Equation 1.
The wire is symmetrical about the origin. Hence, integrating Equation 1 within the limits of zero to infinity gives the equation for the magnetic field in terms of the current and the distance of point P from the wire.
The magnetic field lines of the infinite wire are circular and centered at the wire, and they are identical at every plane perpendicular to the wire. Since the intensity of the field decreases with the distance from the wire, the spacing of the field lines also increases correspondingly with distance.
The right-hand rule gives the direction of magnetic field lines. If the thumb points along the current, the fingers wrap around the wire in the same way as the magnetic field. Therefore, the field points into the page at point P. The magnetic fields due to all the current elements have the same direction.
Du chapitre 29:

Now Playing
29.4 : Magnetic Field Due To A Thin Straight Wire
Sources of Magnetic Fields
4.7K Vues

29.1 : Champ magnétique dû à des charges mobiles
Sources of Magnetic Fields
8.3K Vues

29.2 : Loi Biot-Savart
Sources of Magnetic Fields
5.8K Vues

29.3 : Loi Biot-Savart : résolution de problèmes
Sources of Magnetic Fields
2.4K Vues

29.5 : Champ magnétique dû à deux fils droits
Sources of Magnetic Fields
2.3K Vues

29.6 : Force magnétique entre deux courants parallèles
Sources of Magnetic Fields
3.4K Vues

29.7 : Champ magnétique d’une boucle de courant
Sources of Magnetic Fields
4.3K Vues

29.8 : Divergence et courbure du champ magnétique
Sources of Magnetic Fields
2.7K Vues

29.9 : Loi d’Ampère
Sources of Magnetic Fields
3.6K Vues

29.10 : Loi d’Ampère : résolution de problèmes
Sources of Magnetic Fields
3.5K Vues

29.11 : Solénoïdes
Sources of Magnetic Fields
2.4K Vues

29.12 : Champ magnétique d’un solénoïde
Sources of Magnetic Fields
3.7K Vues

29.13 : Tores
Sources of Magnetic Fields
2.8K Vues

29.14 : Potentiel vectoriel magnétique
Sources of Magnetic Fields
522 Vues

29.15 : Potentiel dû à un objet magnétisé
Sources of Magnetic Fields
252 Vues
See More