Un abonnement à JoVE est nécessaire pour voir ce contenu. Connectez-vous ou commencez votre essai gratuit.
Method Article
In vivo par fluorescence dans le proche infrarouge (NIRF) intravasculaire d'imagerie moléculaire de la plaque inflammatoire, une approche multimodale d'imagerie de l'athérosclérose
Dans cet article
Résumé
Nous détaillons un nouveau proche infrarouge fluorescence (NIRF) cathéter pour deux dimensions d'imagerie moléculaire de la biologie de plaque intravasculaire In vivo. Le cathéter NIRF pouvez visualiser les principaux processus biologiques tels que l'inflammation par des rapports sur la présence de la plaque-avides fluorochromes NIR activable et ciblée. Le cathéter utilise l'ingénierie des exigences cliniques et de la puissance et est ciblé pour des applications dans les artères coronaires humaines. L'étude qui suit décrit une stratégie d'imagerie multimodale qui utilise un roman In vivo Intravasculaire NIRF cathéter à l'image et de quantifier la plaque inflammatoire dans athéromes lapin protéolytique actif enflammée.
Résumé
The vascular response to injury is a well-orchestrated inflammatory response triggered by the accumulation of macrophages within the vessel wall leading to an accumulation of lipid-laden intra-luminal plaque, smooth muscle cell proliferation and progressive narrowing of the vessel lumen. The formation of such vulnerable plaques prone to rupture underlies the majority of cases of acute myocardial infarction. The complex molecular and cellular inflammatory cascade is orchestrated by the recruitment of T lymphocytes and macrophages and their paracrine effects on endothelial and smooth muscle cells.1
Molecular imaging in atherosclerosis has evolved into an important clinical and research tool that allows in vivo visualization of inflammation and other biological processes. Several recent examples demonstrate the ability to detect high-risk plaques in patients, and assess the effects of pharmacotherapeutics in atherosclerosis.4 While a number of molecular imaging approaches (in particular MRI and PET) can image biological aspects of large vessels such as the carotid arteries, scant options exist for imaging of coronary arteries.2 The advent of high-resolution optical imaging strategies, in particular near-infrared fluorescence (NIRF), coupled with activatable fluorescent probes, have enhanced sensitivity and led to the development of new intravascular strategies to improve biological imaging of human coronary atherosclerosis.
Near infrared fluorescence (NIRF) molecular imaging utilizes excitation light with a defined band width (650-900 nm) as a source of photons that, when delivered to an optical contrast agent or fluorescent probe, emits fluorescence in the NIR window that can be detected using an appropriate emission filter and a high sensitivity charge-coupled camera. As opposed to visible light, NIR light penetrates deeply into tissue, is markedly less attenuated by endogenous photon absorbers such as hemoglobin, lipid and water, and enables high target-to-background ratios due to reduced autofluorescence in the NIR window. Imaging within the NIR 'window' can substantially improve the potential for in vivo imaging.2,5
Inflammatory cysteine proteases have been well studied using activatable NIRF probes10, and play important roles in atherogenesis. Via degradation of the extracellular matrix, cysteine proteases contribute importantly to the progression and complications of atherosclerosis8. In particular, the cysteine protease, cathepsin B, is highly expressed and colocalizes with macrophages in experimental murine, rabbit, and human atheromata.3,6,7 In addition, cathepsin B activity in plaques can be sensed in vivo utilizing a previously described 1-D intravascular near-infrared fluorescence technology6, in conjunction with an injectable nanosensor agent that consists of a poly-lysine polymer backbone derivatized with multiple NIR fluorochromes (VM110/Prosense750, ex/em 750/780nm, VisEn Medical, Woburn, MA) that results in strong intramolecular quenching at baseline.10 Following targeted enzymatic cleavage by cysteine proteases such as cathepsin B (known to colocalize with plaque macrophages), the fluorochromes separate, resulting in substantial amplification of the NIRF signal. Intravascular detection of NIR fluorescence signal by the utilized novel 2D intravascular NIRF catheter now enables high-resolution, geometrically accurate in vivo detection of cathepsin B activity in inflamed plaque.
In vivo molecular imaging of atherosclerosis using catheter-based 2D NIRF imaging, as opposed to a prior 1-D spectroscopic approach,6 is a novel and promising tool that utilizes augmented protease activity in macrophage-rich plaque to detect vascular inflammation.11,12 The following research protocol describes the use of an intravascular 2-dimensional NIRF catheter to image and characterize plaque structure utilizing key aspects of plaque biology. It is a translatable platform that when integrated with existing clinical imaging technologies including angiography and intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), offers a unique and novel integrated multimodal molecular imaging technique that distinguishes inflammatory atheromata, and allows detection of intravascular NIRF signals in human-sized coronary arteries.
Protocole
Modèle animal in vivo: Génération de l'athérosclérose aortique expérimentale
1) L'angiographie de base et la dénudation ballon
- Avant d'obtenir une angiographie de base et la dénudation ballon, un en Nouvelle-Zélande lapin blanc est alimenté un cholestérol élevé (1%) régime alimentaire pendant 1 semaine. Cet animal est utilisé pour la pertinence de translation que 1) les vaisseaux aorto-iliaques chez les lapins sont du même calibre que les artères coronaires humaines (2,5 à 3,5 mm) et 2) les hyperlipidémiques, ballon blessures modèle génère l'athérosclérose enflammées portant similaires cellules inflammatoires (macrophages ) et les molécules (cathepsines) comme dans l'athérosclérose humaine.
- Suite à l'alimentation de cholestérol, l'animal est anesthésié avec du propofol et de kétamine. Une incision d'un pouce ventrale ligne médiane du cou est faite en utilisant en utilisant une taille de 15 bistouri lame. En utilisant des techniques dissection, le muscle sous la aponévrose sur le côté droit de la trachée est exposée. Le muscle est séparé sternocephalicus gauche le long de sa jonction des tissus conjonctifs, et l'artère carotide commune droite est exposée. L'artère est séparé du nerf vague. Boucles de suture proximale et distale sont placés sur l'artère afin de permettre la rétraction et l'occlusion. A 1 à 2mm biseauté artériotomie est faite à travers lequel un 5 en français (diamètre extérieur 1.67mm) gaine vasculaire est inséré et l'héparine (1000μ/mL, ~ 150units/kg) est administré par voie intra-artérielle de la gaine.
- Colorant de contraste (Ultravist) est ensuite injecté (1 à 2 ml) sur une période de 2 secondes pour obtenir une angiographie de contrôle de l'aorte distale et les deux artères iliaques.
- Les artères ilio et l'aorte sont alors blessés par une dénudation endothéliale. En utilisant des méthodes standard de radioscopie, une sonde de Fogarty 3FR embolectomie est placé dans l'artère ilio-fémorale distale et gonflé avec 0,3 à 0,5 cc de produit de contraste (50% contrast/50% saline) ou de l'air. Le cathéter est ensuite retiré proximalement dans son état gonflé une distance le long de l'artère iliaque droite et l'aorte distale jusqu'à l'envol de l'artère rénale gauche. Suite à la dénudation ballon, l'angiographie est répété à documenter la perméabilité des vaisseaux. Suite à l'angiographie, tous les cathéters et les gaines sont retirés et la portion proximale artère carotide commune droite est ligaturé, le muscle et le fascia sont suturés par un surjet 4 / 0 résorbable, et l'incision cutanée fermée avec un 4 / 0 non résorbable.
- L'animal est alors autorisé à récupérer à l'administration d'une dose d'antibiotiques (céphazoline, 0,5 grammes de messagerie instantanée). Médicaments contre la douleur, y compris 0,01 IM mg / kg de buprénorphine (deux fois par jour selon les besoins). Les animaux sont ensuite poursuivi sur le cholestérol de 1% pour 4 semaines post-ballon dénudation. À la semaine 5, les animaux sont passés à régime riche en cholestérol de 0,3%.
Multimodal intégré d'imagerie du lapin athéromes
2) L'étiquetage des plaques enflammées protéolytique actif à l'aide nanocapteur injectables; angiographie, échographie intravasculaire (IVUS), et l'imagerie in vivo intravasculaire NIRF de Lapin Athérome
- Huit semaines après la blessure du ballon et 24 heures avant l'imagerie, le lapin est injecté par voie intraveineuse de 500 nmol / kg Prosense/VM110 (PerkinElmer) via veine de l'oreille.
- Vingt-quatre heures après l'injection, les animaux sont anesthésiés et l'accès artériel est obtenue via l'artère carotide commune gauche (voir étape 1.2). Intra-artérielle héparine est administrée (150 unités / kg). Base angiographie est obtenu comme ci-dessus.
- Un cathéter IVUS est chargé sur une artère coronarienne cliniques capables 0,014 pouces de fil et inséré dans la gaine. Utiliser guidage fluoroscopique, le bout du fil radio-opaque est positionné distalement dans l'artère iliaque droite. Le cathéter IVUS est alors avancé dans l'artère iliaque proximale en utilisant une norme technique clinique monorail.
- Un recul de 100 mm est lancé et les images sont enregistrées. La reconstruction longitudinale du navire est obtenue et la plaque luminale est identifié.
- Le cathéter NIRF 11,12 est chargé sur le fil 0,014 pouces (monorail), et le cathéter est soigneusement inséré dans la gaine et la tête d'imagerie est positionné distalement dans l'artère iliaque droite.
- Multiples retraits automatiques (1 mm / sec retrait longitudinal, 30 coups par minute) sont réalisées et les signaux de fluorescence dans les zones de l'athérosclérose sont notées. Les images sont enregistrées et le traitement ultérieur avec mise à l'échelle appropriée et de fenêtrage basé sur l'étendue du signal est réalisée.
3) L'euthanasie et l'isolement des ex vivo aorto-iliaque tissus
- L'euthanasie est accompli avec 1cc d'agent euthanasie (solution de sodium phénytoïne sodique 390mg pentobarbital et 50mg), intraveineuse, seule injection.
- L'arbre artériel est perfusé avec une solution saline normale à 0,9% jusqu'à la veine cave inférieure est clair de sang. Les artères iliaques athérosclérose aortique et sont identifiés et disséqués par les tissus environnants. En outre, les petits morceaux de 2 x 2 cm de liVer, du rein, la rate et le coeur sont également obtenus.
- Ex vivo NIRF imagerie avec le cathéter intravasculaire NIRF imagerie peut être fait à ce stade. Le navire est allongé et le cathéter est NIRF ré-inséré dans l'aorte proximale jusqu'à la tête d'imagerie est positionné à l'artère iliaque droite ou de bifurcation. Multiples retraits automatiques sont effectués comme ci-dessus (voir 2.6).
4) ex vivo par fluorescence Réflectance Imaging (FRI) de l'aorte et des artères iliaques disséqué
- Tissus disséqués est placé dans 10-20 cc de solution saline normale et transportés pour analyse VEN (Kodak Image Station 4000mm Pro, Carestream Health, Inc.)
- Aorte vaisseaux iliaques, sont allongés à rapprocher en temps réel les longueurs et les images sont obtenues à multiples longueurs d'onde [lumière blanche, vert fluo canaux (ex 495 nm, em 515 nm), Cy5 (ex 565 nm, em 670 nm) et Cy7 (ex 650 nm, em 760 nm)] canaux. Une série de temps d'exposition sont utilisés pour chaque longueur d'onde (0,1-30sec) et les images acquises sont exportés sous forme de DICOM ou 16-bit unscaled fichiers TIFF pour des analyses ultérieures. Comme les contrôles positifs et négatifs, les organes (foie, rate, des reins et du cœur) sont imagées à des canaux similaires et temps d'exposition.
- Domaines d'augmentation du signal dans le canal proche infrarouge (780nm +) sont notées dans les artères athérosclérotiques.
Enrobage des tissus 5) pour l'analyse de sectionnement et immunohistochimique
- Domaines de la normale (non blessés tissus, à savoir l'artère iliaque gauche) et les zones de la plaque sont identifiés et petits anneaux 5-10 mm de tissu sont intégrés dans de l'OCT (Température de coupe optimale) des médias. Les blocs sont stockés à -80 C jusqu'à la coupe.
- Les techniques standard pour les analyses de sectionnement et immunohistochimiques sont effectuées. Hématoxyline et éosine, Ram-11 et de la cathepsine B coloration sont effectuées.
Analyses et l'intégration des images multi-modales (angiographie, échographie intravasculaire, NIRF et ven.)
6) Le traitement des images et des NIRF ven.
- Fichiers contenant des données d'imagerie DICOM à partir NIRF et ven. (prise au proche infrarouge 780 nm de canal) pullbacks sont traitées en utilisant MATLAB et logiciels Osirix, respectivement. Fenêtrage approprié à afficher gamme complète de l'intensité du signal est réalisée. Images finales sont exportés sous forme de fichiers TIFF.
- Les fichiers sont importés dans le logiciel de traitement d'image standard (Keynote peut être utilisé). Les images sont alignées en fonction des points de référence (c'est à dire sur les vertèbres angiographie, bifurcation iliaque et l'artère rénale). Domaines d'vaisseau normal et la plaque sont identifiés.
- Régions d'intérêt (ROI) sont tracées manuellement (pour les tissus normaux et les zones de la plaque) et la moyenne des intensités du signal sont acquis à l'aide Osirix et MATLAB, respectivement pour les deux ven. et images NIRF. Pour guider le traçage appropriés, l'image IVUS longitudinale du navire est utilisé et l'identification des navires et la plaque normale sont facilement identifiés.
- Cible à fond (TBR) ratios sont calculés pour les zones de la plaque.
Les résultats représentatifs:
À la fin du protocole ci-dessus, nous pouvons identifier et caractériser les zones d'activité augmentée protéase cathepsine inflammatoires dans la plaque dans l'aorte et les vaisseaux iliaques. Injection d'une nanocapteur activable (Prosense/VM110) nous permet d'identifier la plaque protéolytique actif. Celles-ci apparaissent aussi lumineux ou un signal intense lorsque les zones imagées par MRF dans le canal proche infrarouge (750 nm). Les retraits NIRF en corrélation avec l'intensité du signal a augmenté de FRI et alignements avec IVUS qui permettent d'inscription anatomiques des signaux NIRF. TBR plaque Calculé obtenue à partir FRI et NIRF étaient similaires (voir Figure 3: moyenne NIRF TBR 4.2, signifie ven. TBR 2,9). L'analyse immunohistochimique de la plaque lumineuse confirme la présence intense de RAM-11 et de la cathepsine B dans les domaines d'activité de la plaque (données non présentées).
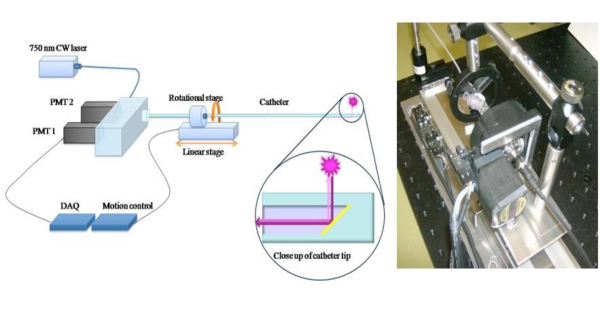
Figure 1. Schéma de la 2D NIRF cathéter pour élargir le potentiel clinique d'une approche 1D NIRF détection 6, nous avons construit un roman en 2-D NIRF-cathéter pour l'imagerie intravasculaire. 11,12 Le cathéter sur mesure se compose d'une fibre optique (125 microns de diamètre logé dans les tuyaux en polyéthylène: 2.9F) qui éclaire en utilisant une source laser à 750 nm d'excitation. La lumière laser est émis à un angle de 90 degrés par rapport à l'axe de la fibre. Le système utilise deux moteurs automatisés (rotation et de translation) pour permettre à l'imagerie simultanée de 360 degrés et pullback longitudinale pour obtenir vraie imagerie 2D. Les images utilisées avec la permission de la référence 11.
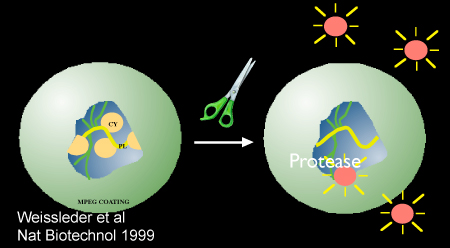
Figure 2. Schéma montrant la protéase médiée par l'activation de la nanocapteurs, Prosense/VM110. Image utilisée avec la permission de la référence 10.

Figure 3. In vivo et in vivo RBT ex plaque (la cible à des ratios de fond)
Discussion
Enflammé plaques à haut risque ou vulnérables sont probablement responsables de la majorité des infarctus du myocarde. L'identification de ces plaques avant l'apparition des symptômes a d'importantes implications cliniques à la fois dans la prédiction des résultats et de guider le traitement médical. Coronaire conventionnelle modalités d'imagerie artérielle tels que x-ray angiographie mettent généralement l'accent sur la caractérisation des rétrécissements luminale plutôt éclairant ...
Déclarations de divulgation
FAJ - Ancien consultant, VISEN médicale; honoraires, Boston Scientific
Remerciements
Prise en charge de ce travail a été fourni par National Institutes of Health octroi # 108229 R01 HL, l'American Heart Association Scientifique Development Grant # 0830352N, Howard Hughes Medical Institute Award de développement de carrière, Ventures Broadview, Programme de la Communauté européenne septième programme-cadre (FP7/2007-2013 titre de la subvention # 235689 accord), et l'HGM William Schreyer Bourse.
matériels
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Prosense 750 | Visen Medical | VM110 | 500 nmol/kg IV injection |
| Heparin Sodium | APP Pharmaceuticals | 401586D | |
| Cephazolin | NovaPlus | 46015683 | |
| Lidocaine HCL 2% | Hospira Inc. | NDC 0409-4277-01 | |
| Buprenorphine | Bedford Laboratories | NDC 55390-100-10 | |
| Ketamine | Hospira Inc. | NDC 0409-2051-05 | |
| High Cholesterol Diet 1% | Research Diets | C30293 | |
| HIgh Cholesterol Diet 0.3% | Research Diets | C30255 |
Références
- Andersson, J., Libby, P. Adaptive immunity and atherosclerosis. Clin Immunol. 134, 33-46 (2010).
- Calfon, M. A., Vinegoni, C. Intravascular near-infrared fluorescence molecular imaging of atherosclerosis: toward coronary arterial visualization of biologically high-risk plaques. Journal of Biomedical Optics. 15, 011107-011107 (2010).
- Chen, J., Tung, C. -. H. In Vivo Imaging of Proteolytic Activity in Atherosclerosis. Circulation. 105, 2766-2771 (2002).
- Jaffer, F. A., Libby, P. Molecular Imaging of Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation. 116, 1052-1061 (2007).
- Jaffer, F. A., Libby, P. Optical and Multimodality Molecular Imaging: Insights Into Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29, 1017-1024 (2009).
- Jaffer, F. A., Vinegoni, C. Real-Time Catheter Molecular Sensing of Inflammation in Proteolytically Active Atherosclerosis. Circulation. 118, 1802-1809 (2008).
- Kim, D. -. E., Kim, J. -. Y. Protease Imaging of Human Atheromata Captures Molecular Information of Atherosclerosis, Complementing Anatomic Imaging. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 30, 449-456 (2010).
- Libby, P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 420, 868-874 (2002).
- Naghavi, M., Libby, P. From Vulnerable Plaque to Vulnerable Patient: A Call for New Definitions and Risk Assessment Strategies: Part I. Circulation. 108, 1664-1672 (2003).
- Weissleder, R., Tung, C. -. H. In vivo imaging of tumors with protease-activated near-infrared fluorescent probes. Nat Biotech. 17, 375-375 (1999).
- Razansky, R. N., Rosenthal, A. Near-infrared fluorescence catheter system for two-dimensional intravascular imaging in vivo. Optics Express. 18, 11372-11381 (2010).
- Jaffer, F. A., Calfon, M. A. Two-Dimensional Intravascular Near-Infrared Fluorescence Molecular Imaging of Inflammation in Atherosclerosis and Stent-Induced Vascular Injury. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 57, 2516-2526 (2011).
Réimpressions et Autorisations
Demande d’autorisation pour utiliser le texte ou les figures de cet article JoVE
Demande d’autorisationThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon